BIO 210 lab Tissues
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
fibrocartilage connective tissue
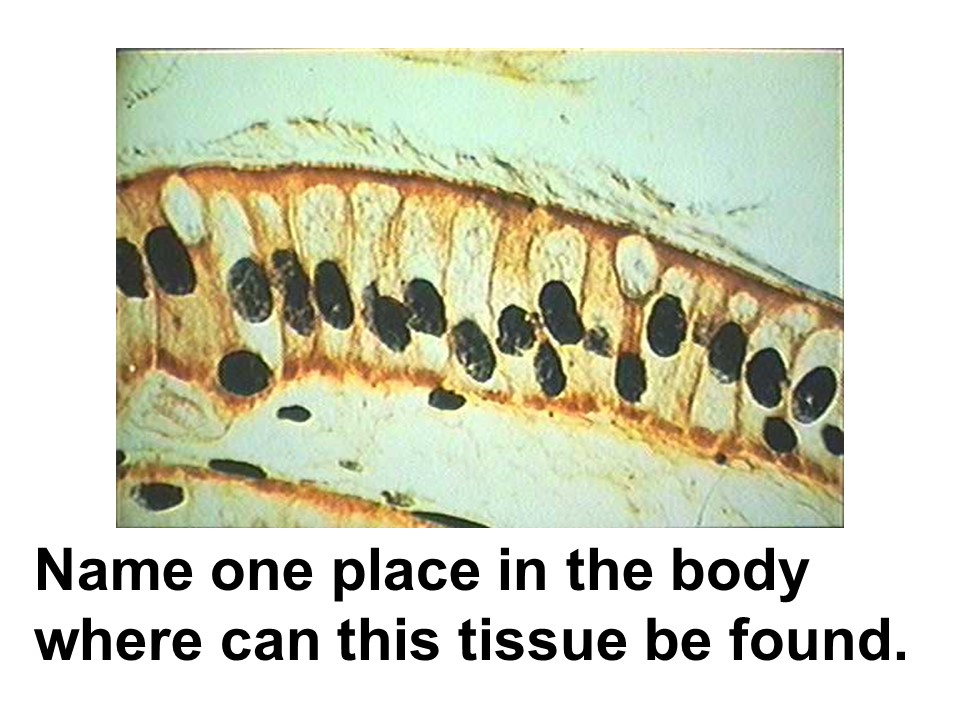
Intestines
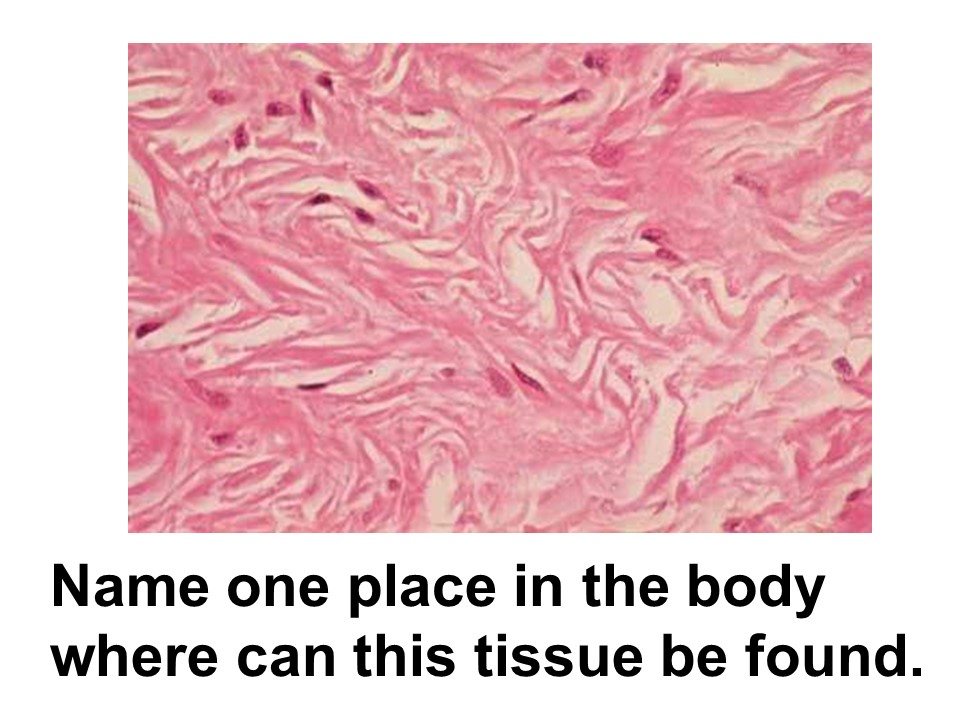
reticular layer of dermis
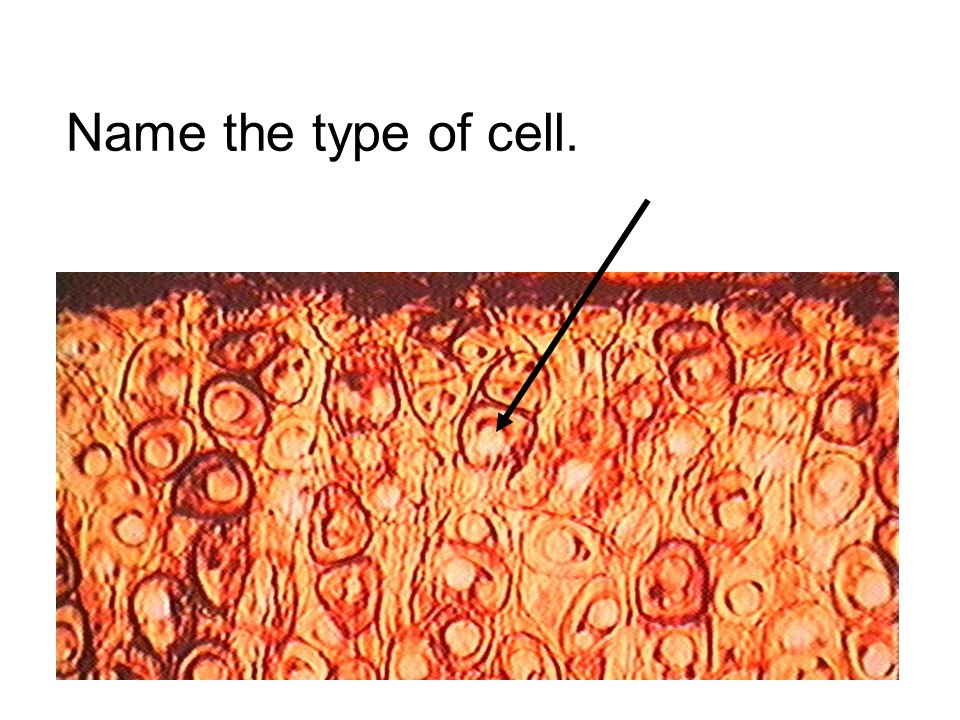
chondrocyte
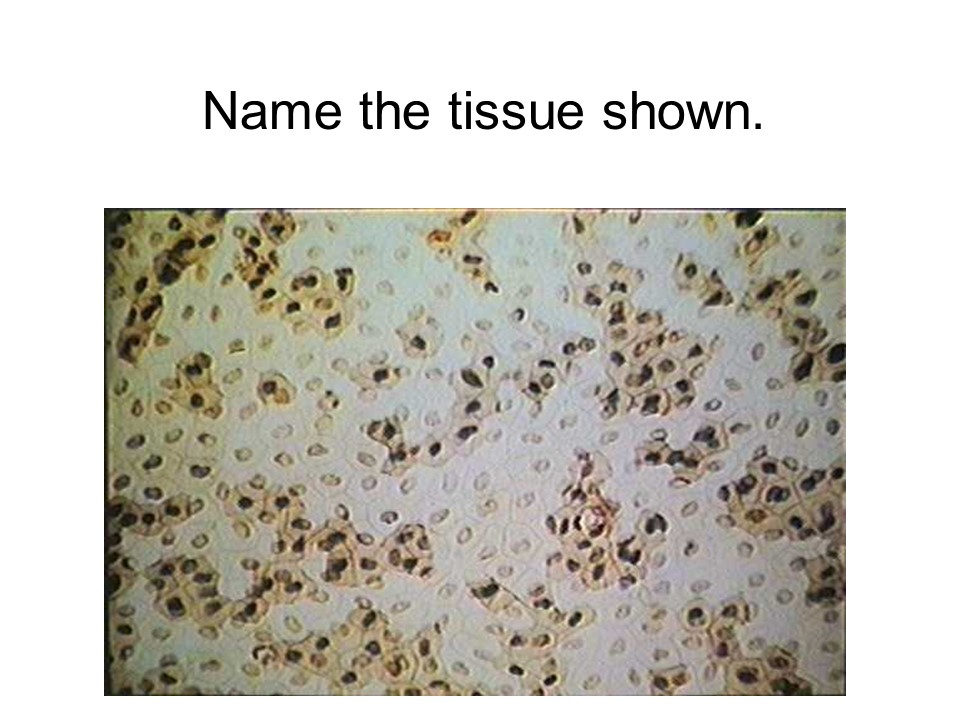
glandular epithelium
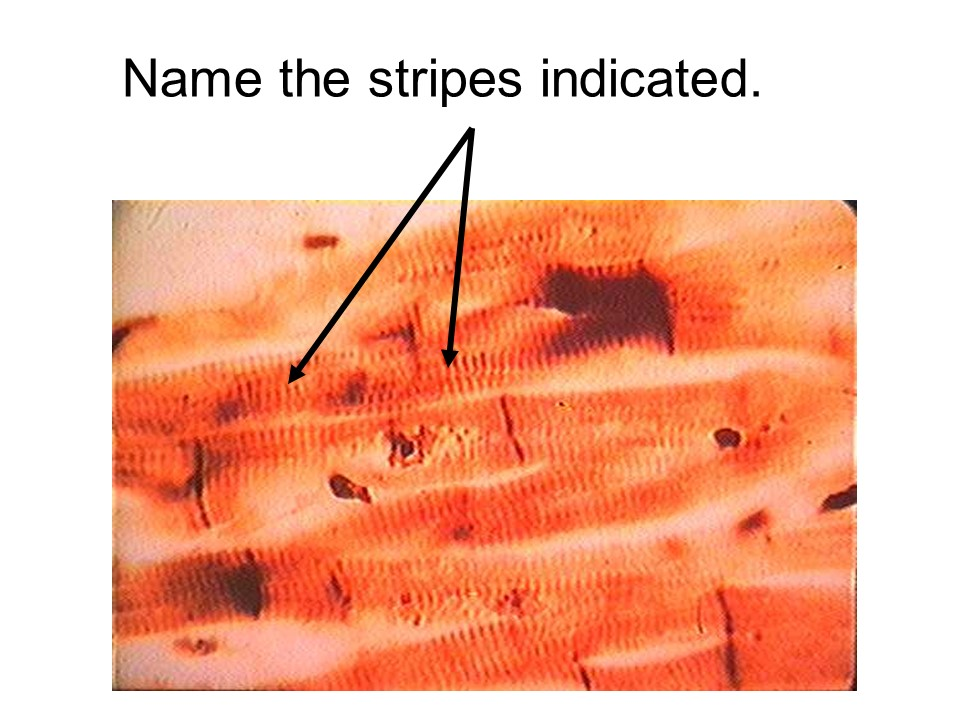
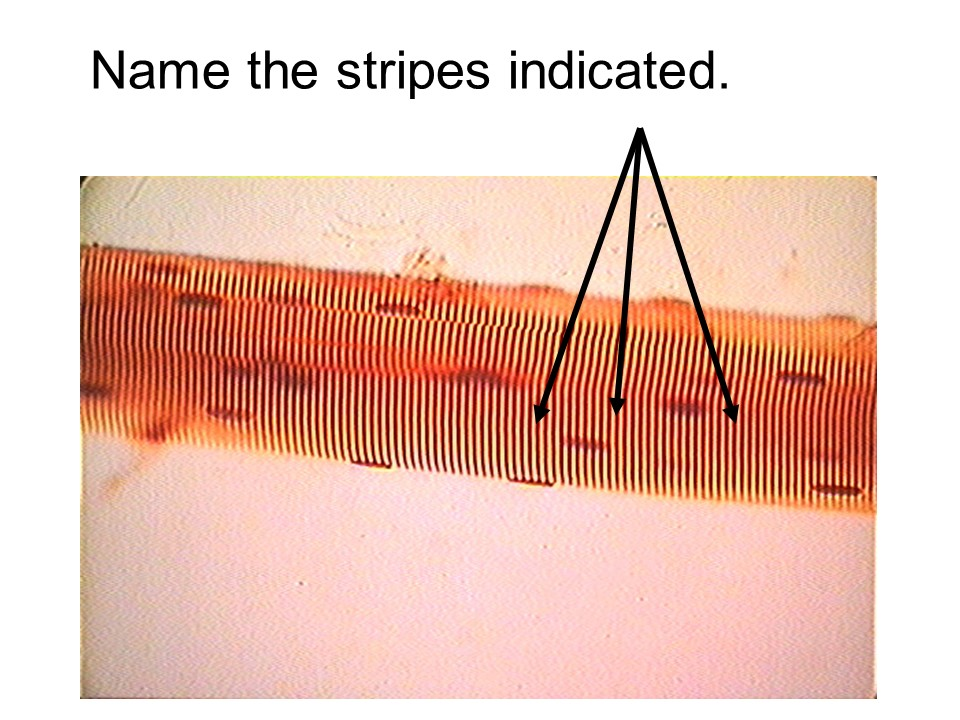
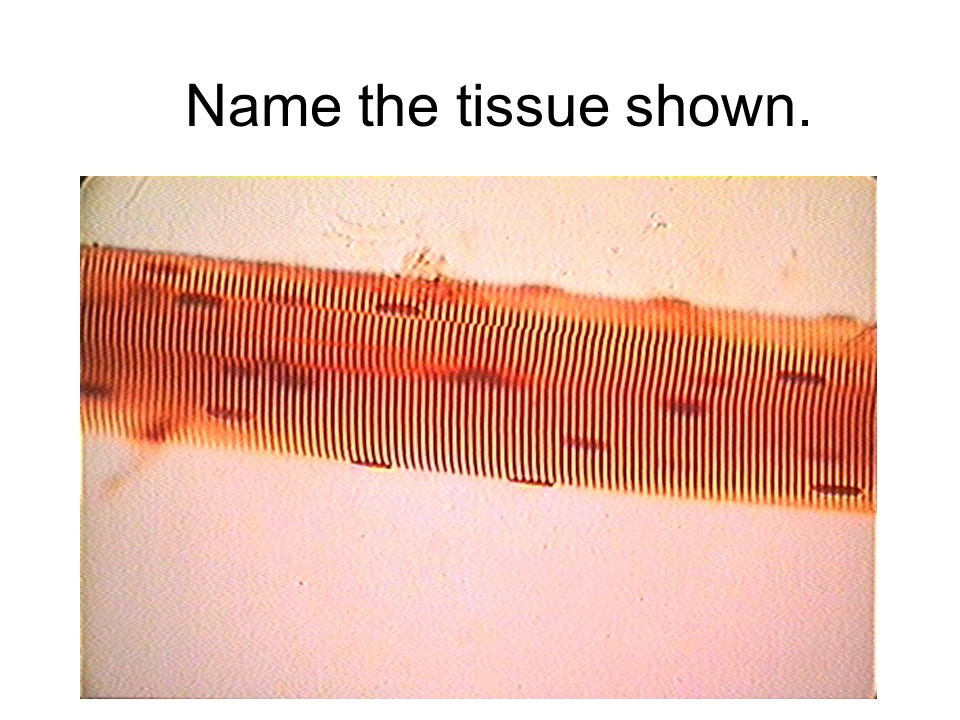
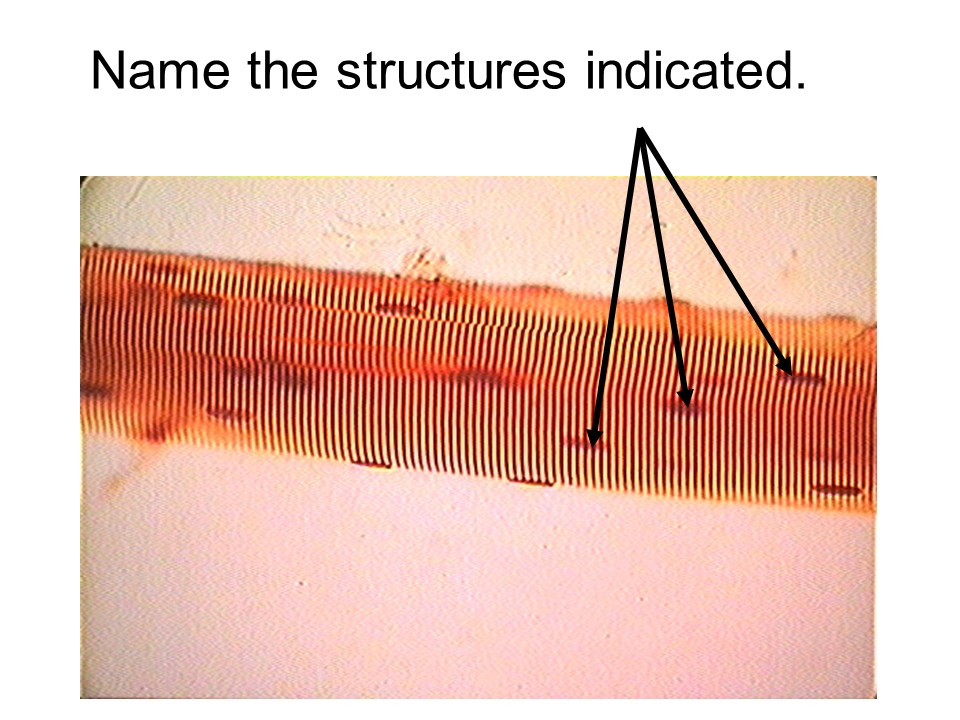
striations
tip of nose
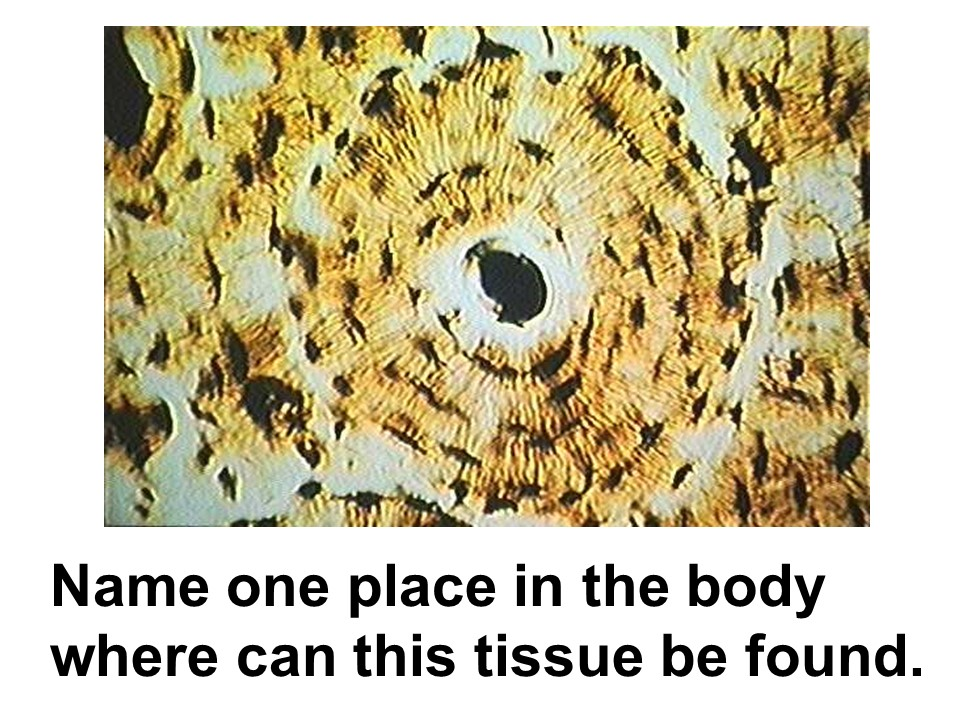
compact bone
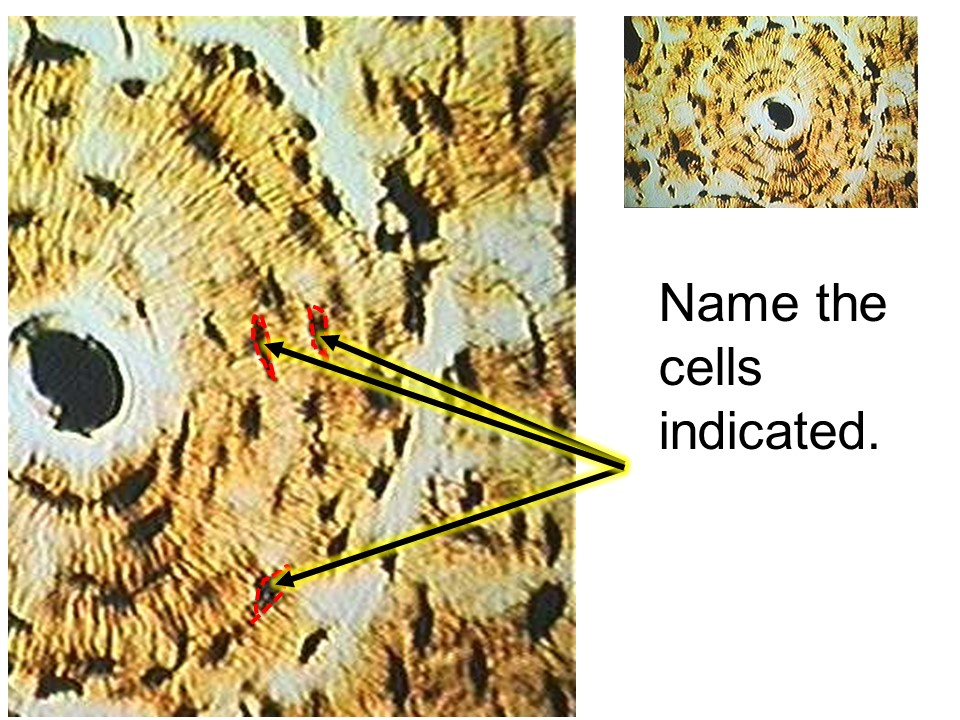
osteocyte
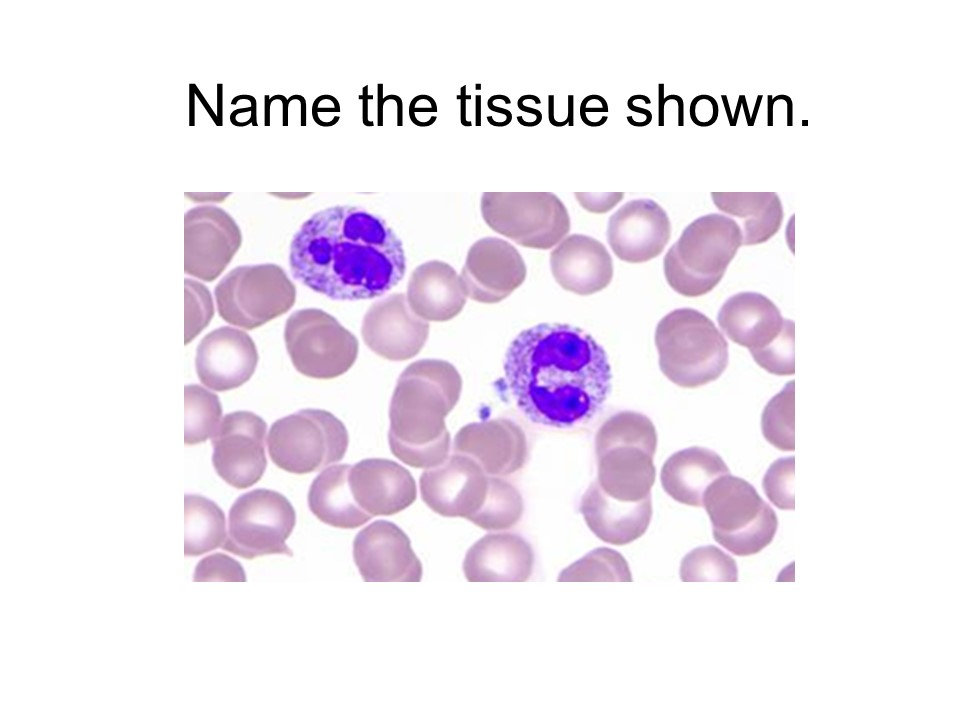
blood
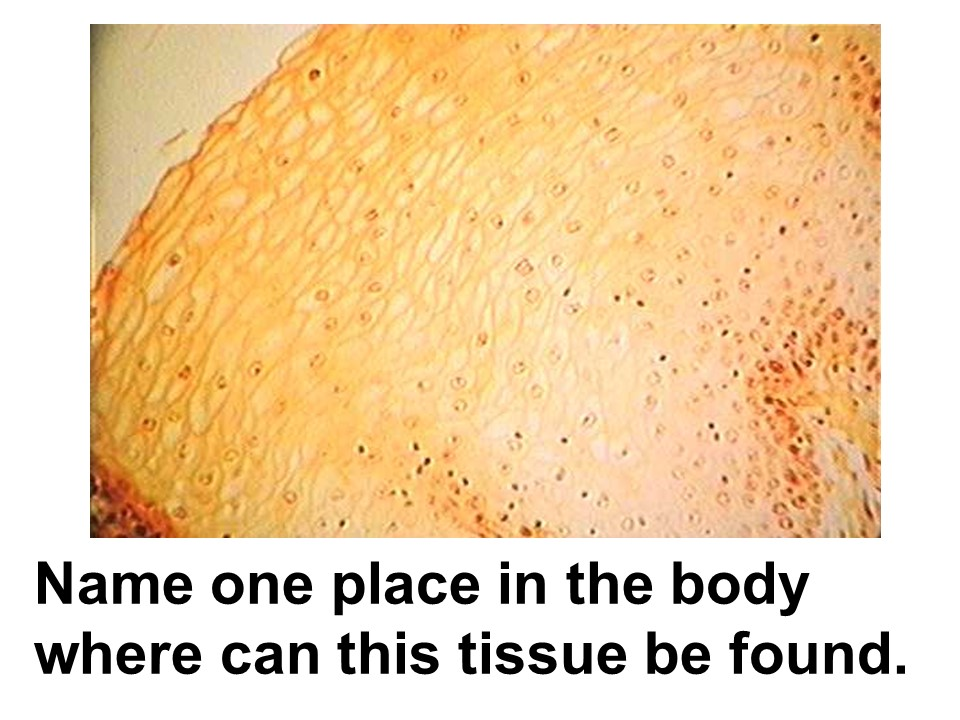
oral cavity
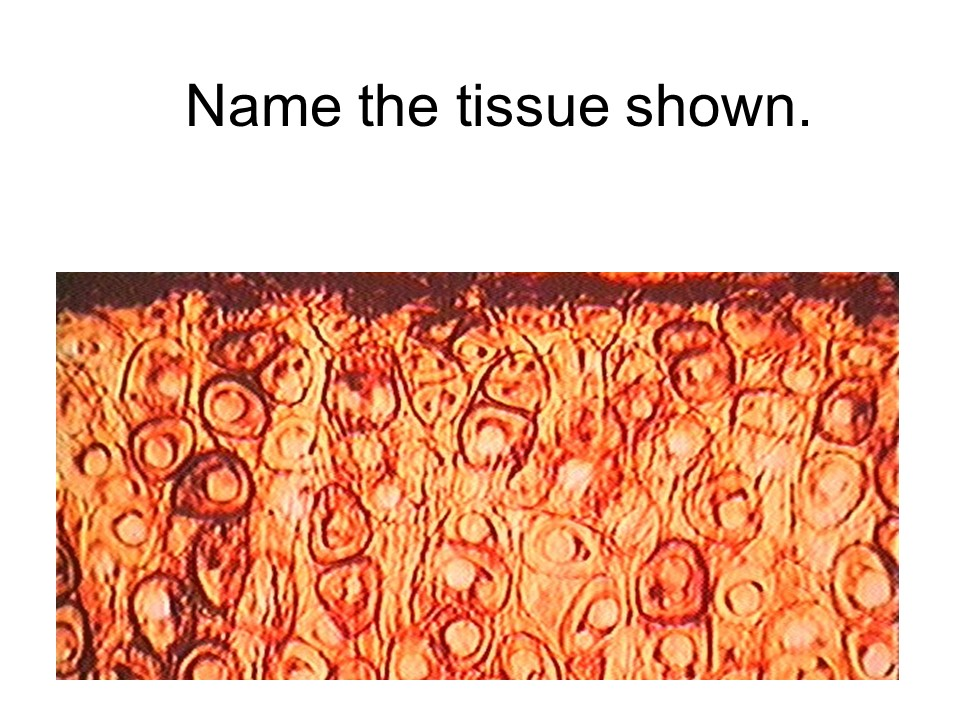
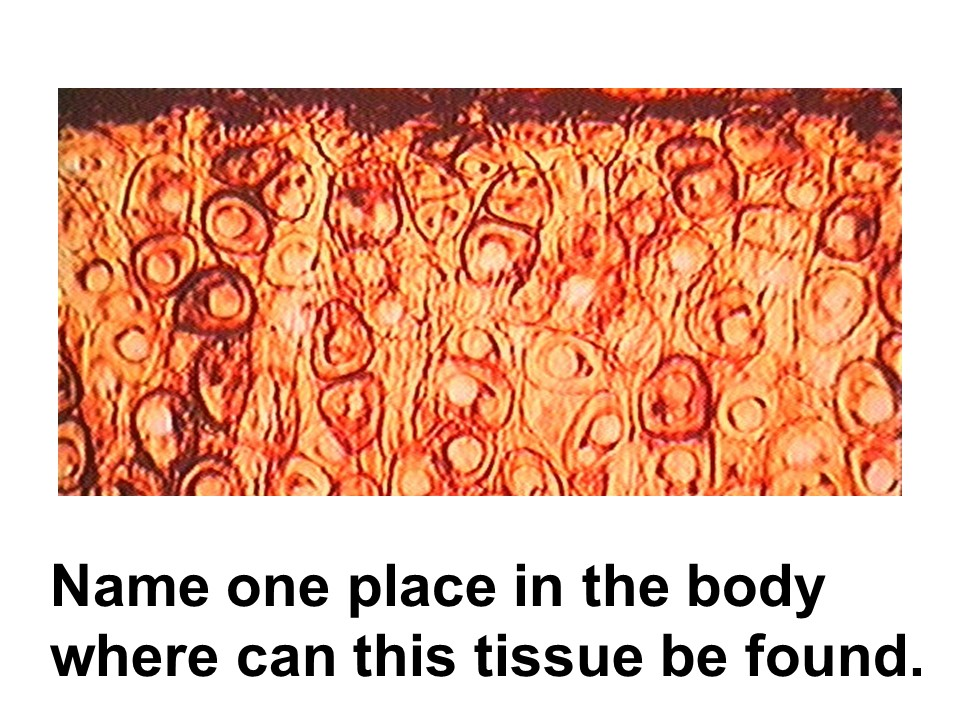
elastic cartilage
reticular connective tissue
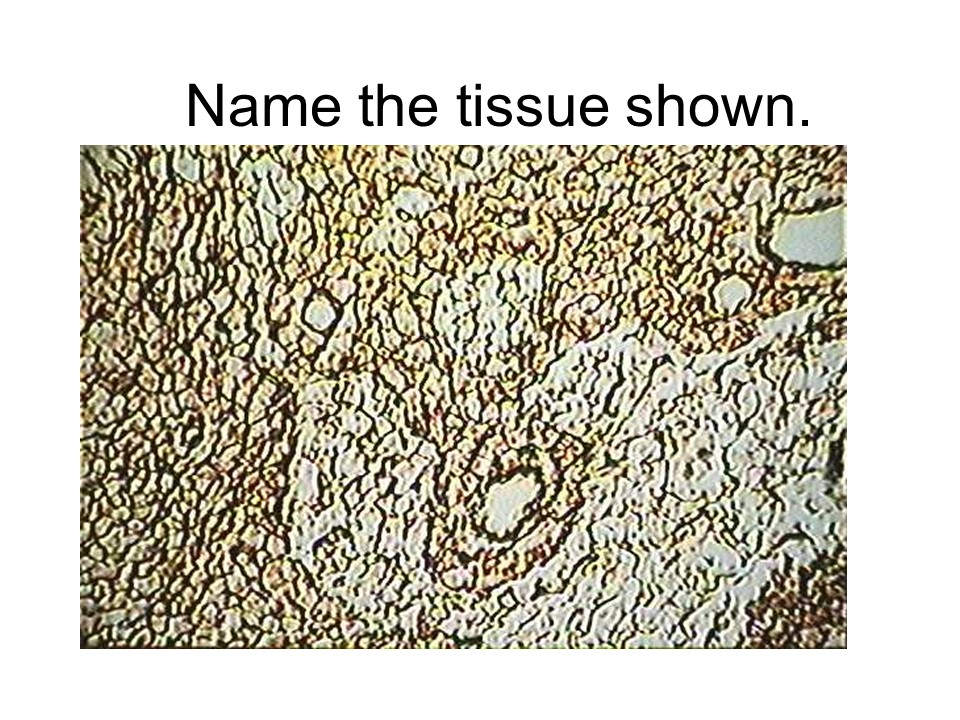
transitional epithelium
striations
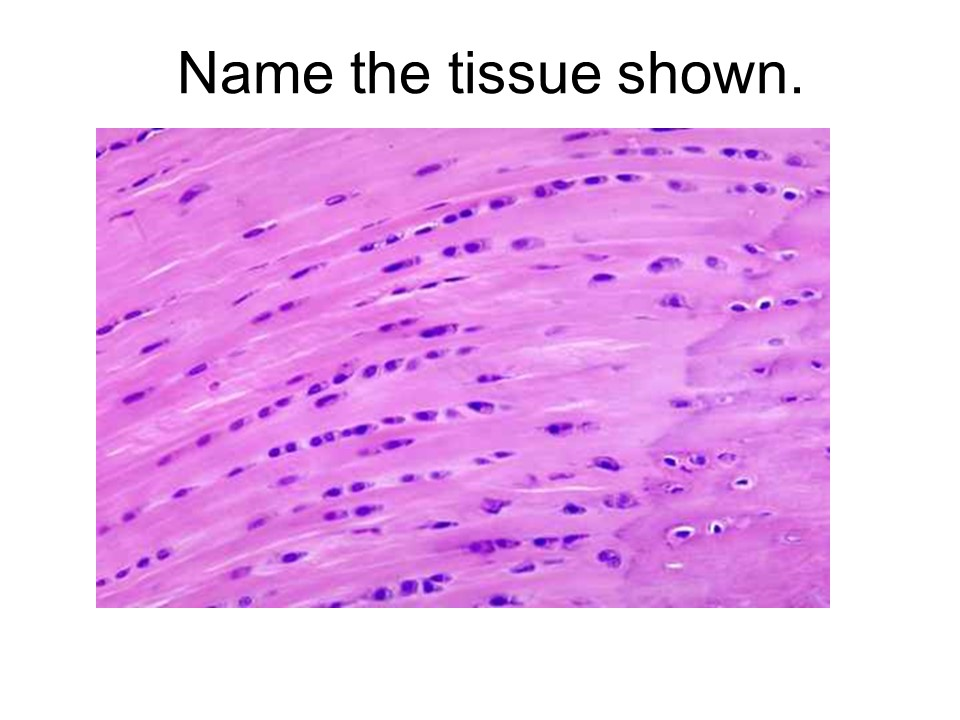
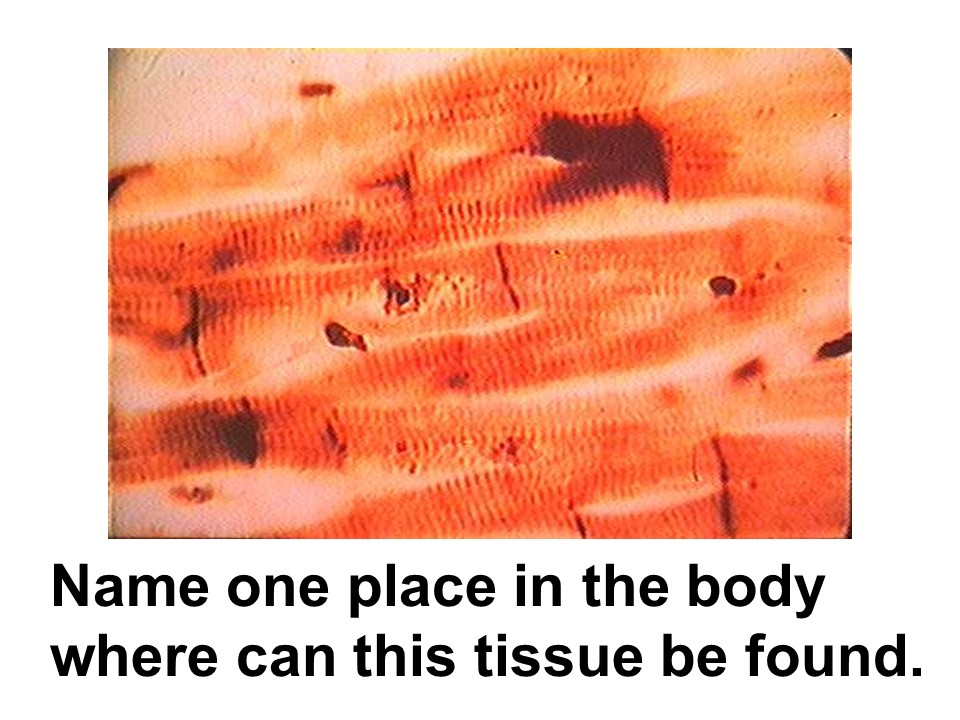
heart
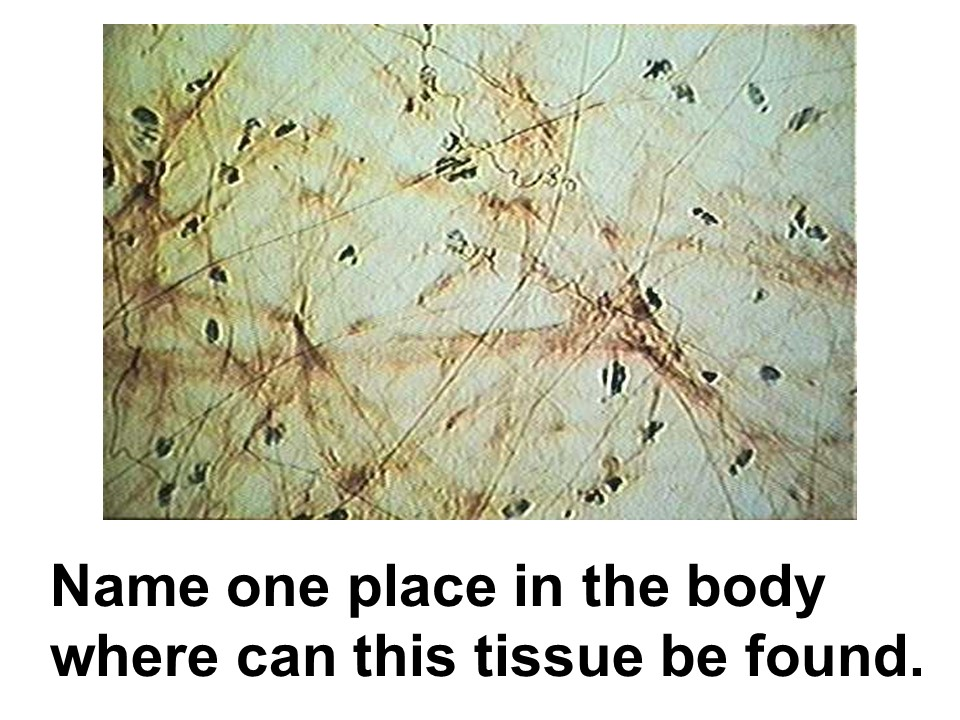
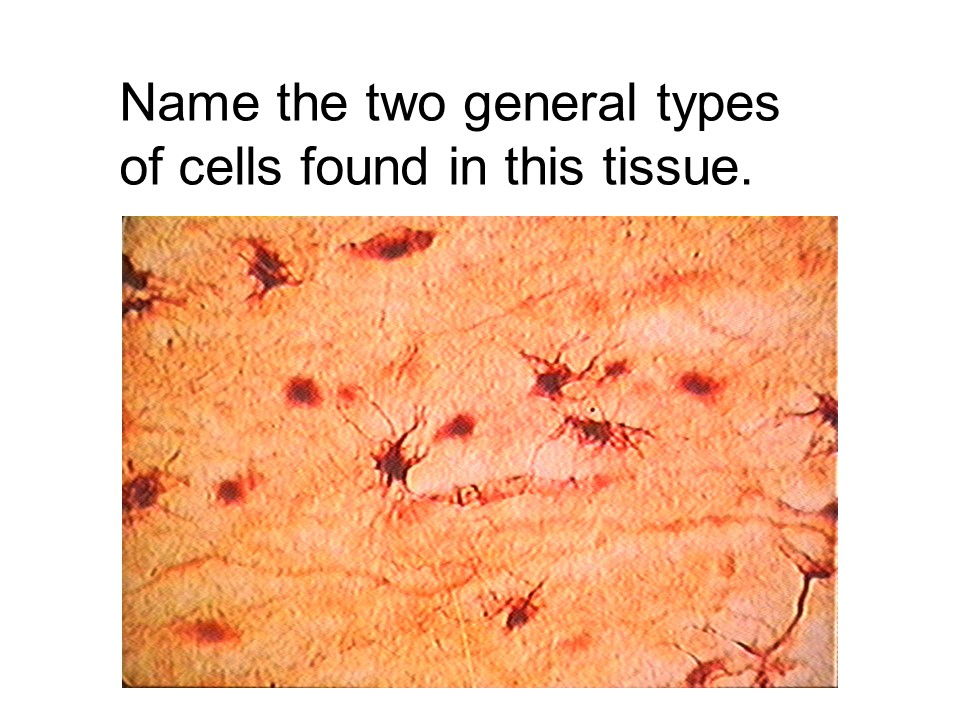
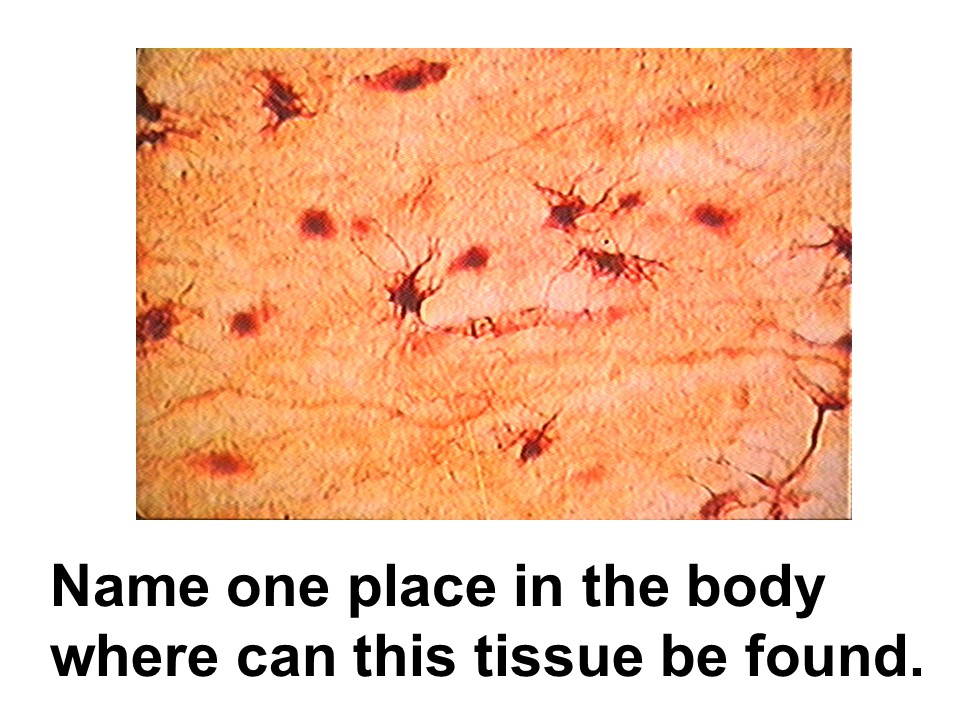
nervous tissue
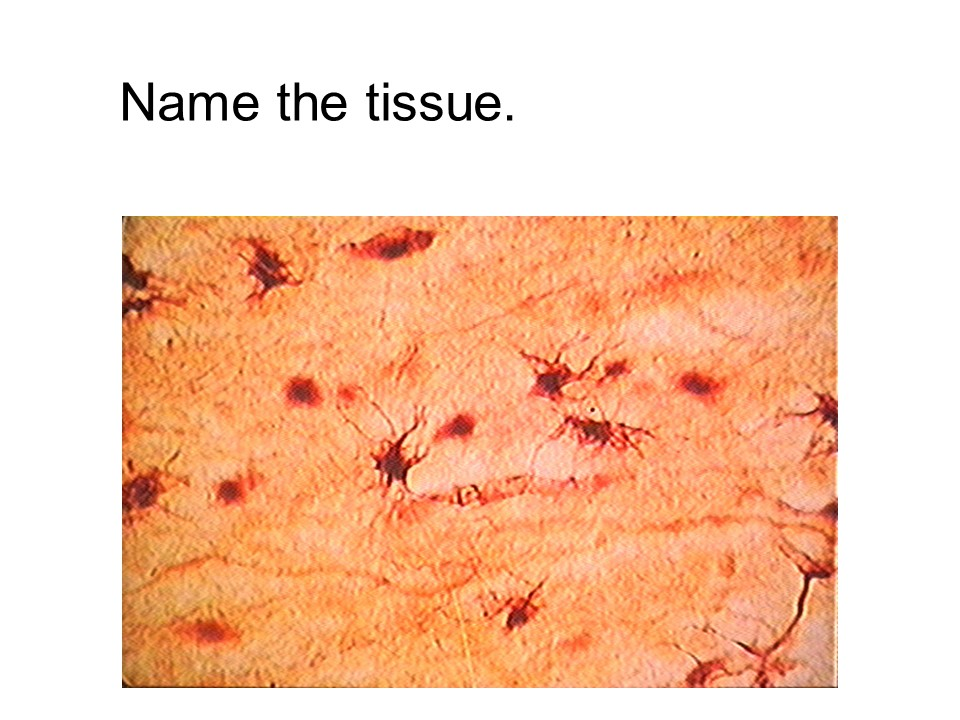
areolar connective tissue
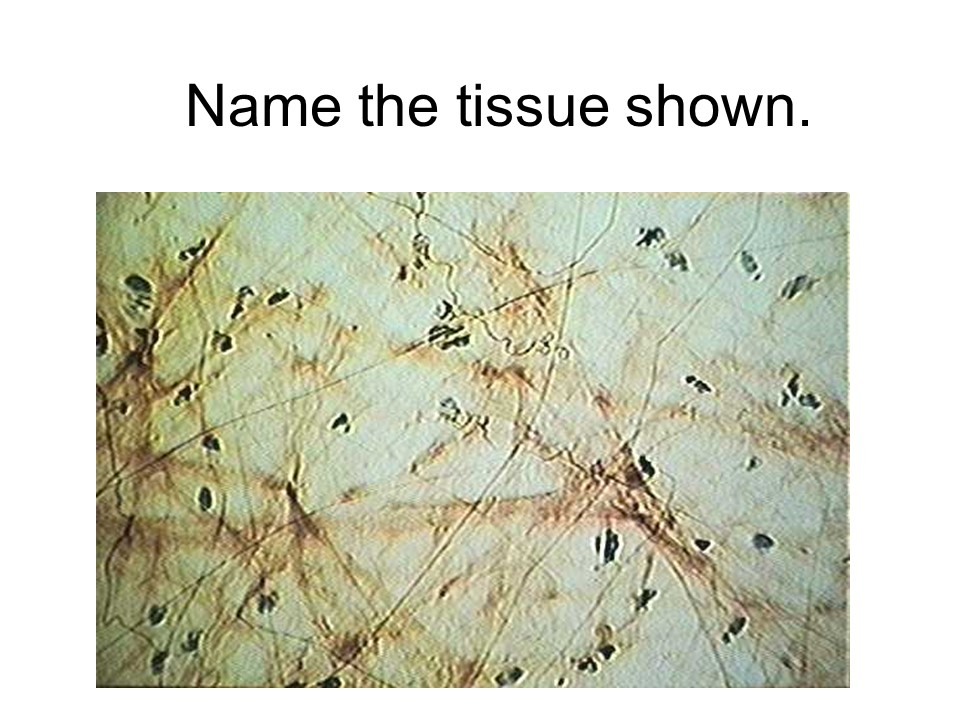
alveoli of the lungs
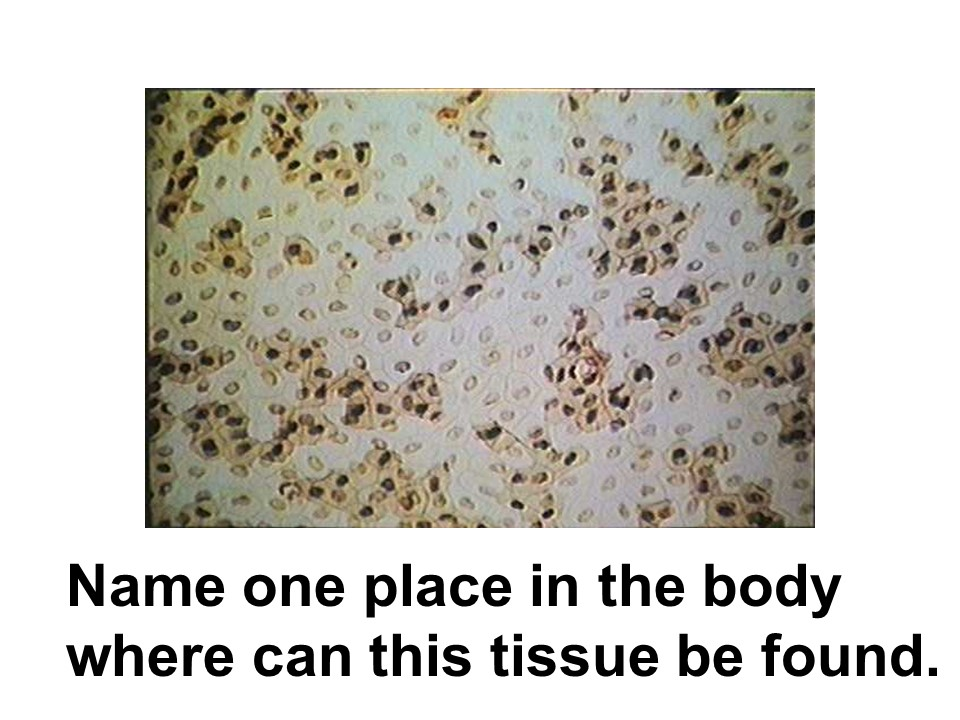
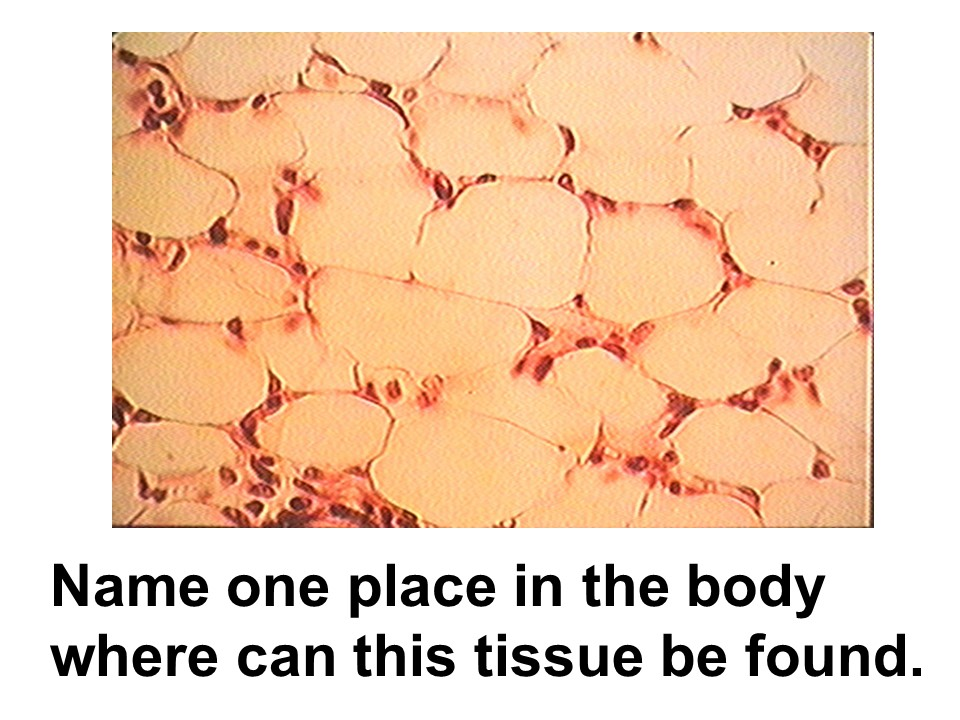
subcutaneous layer
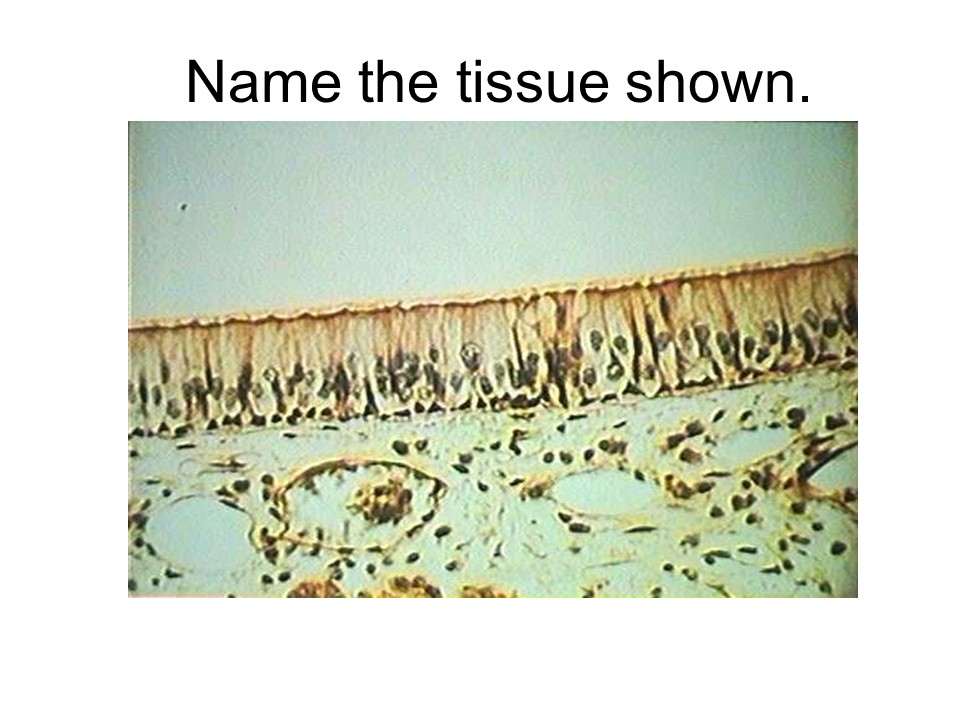
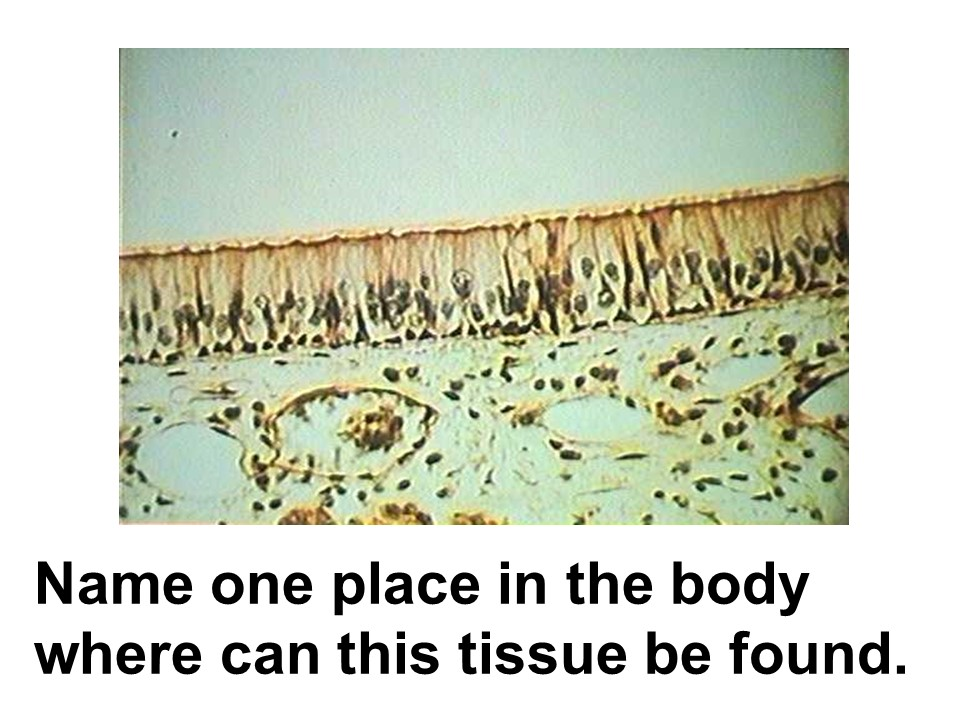
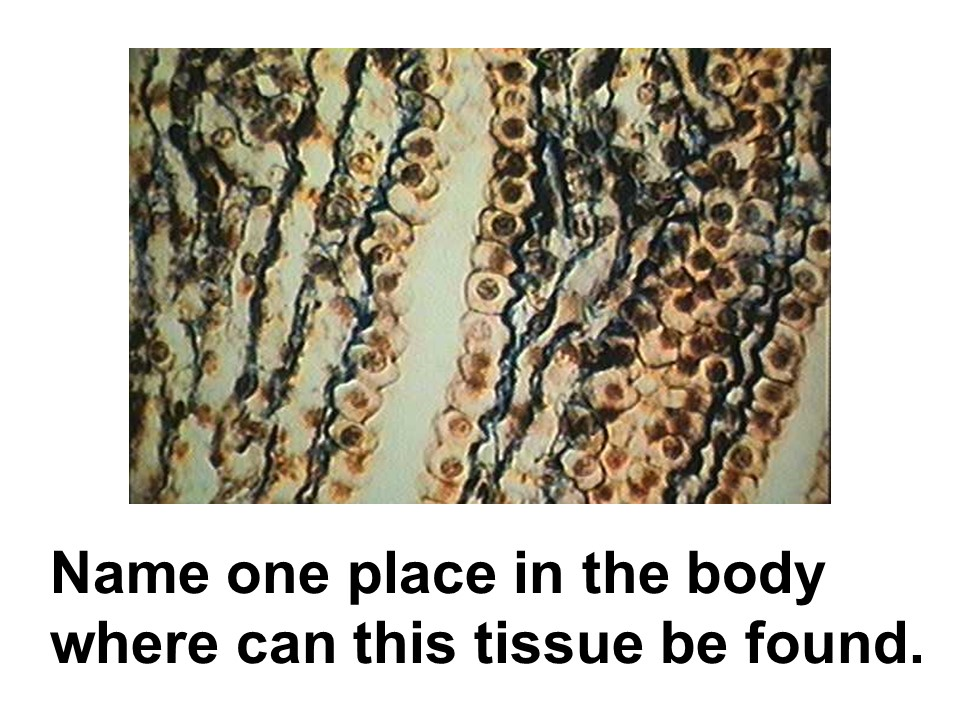
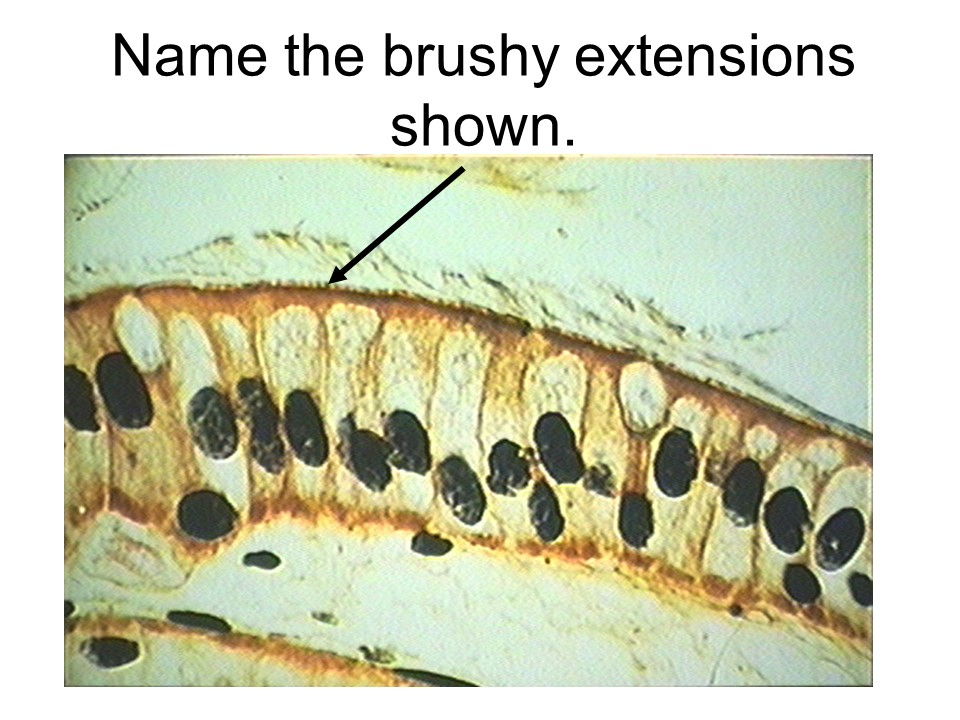
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
simple squamous epithelium
tendons
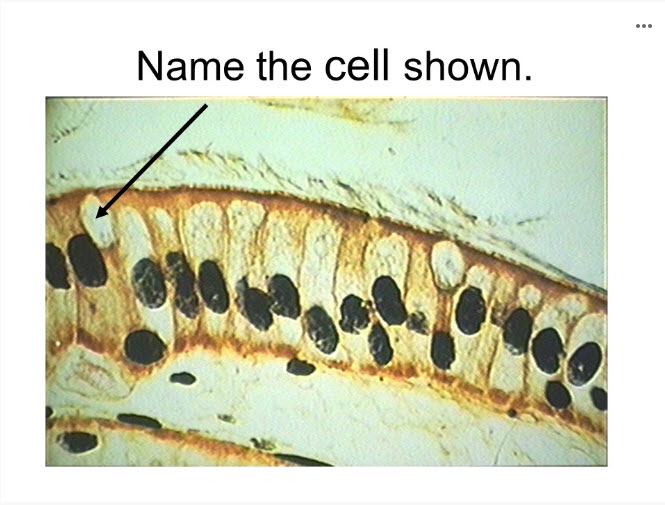
goblet cell
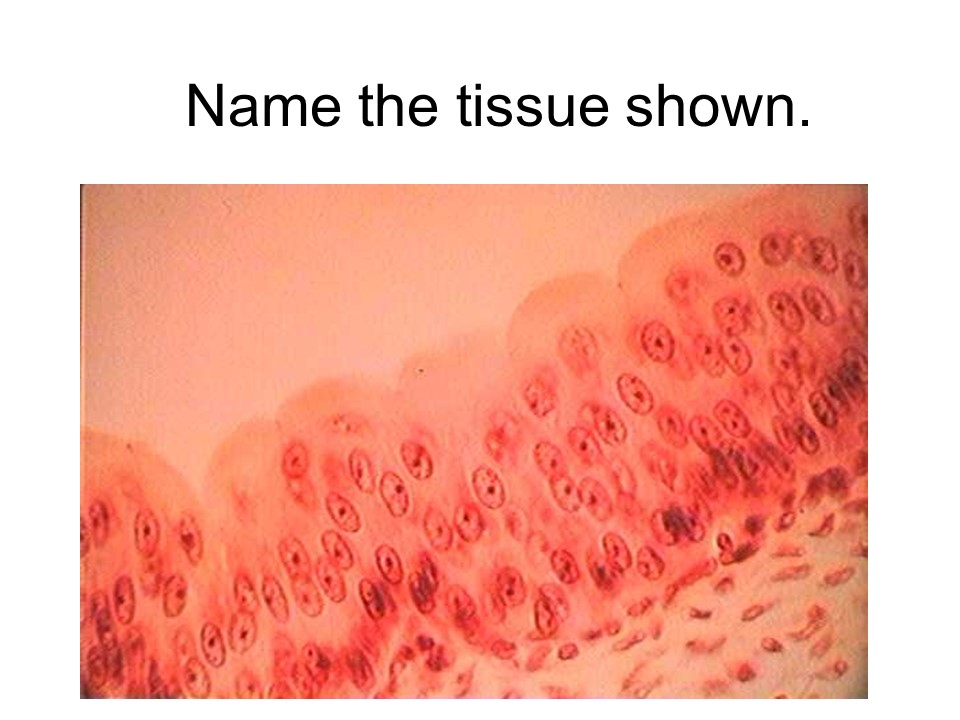
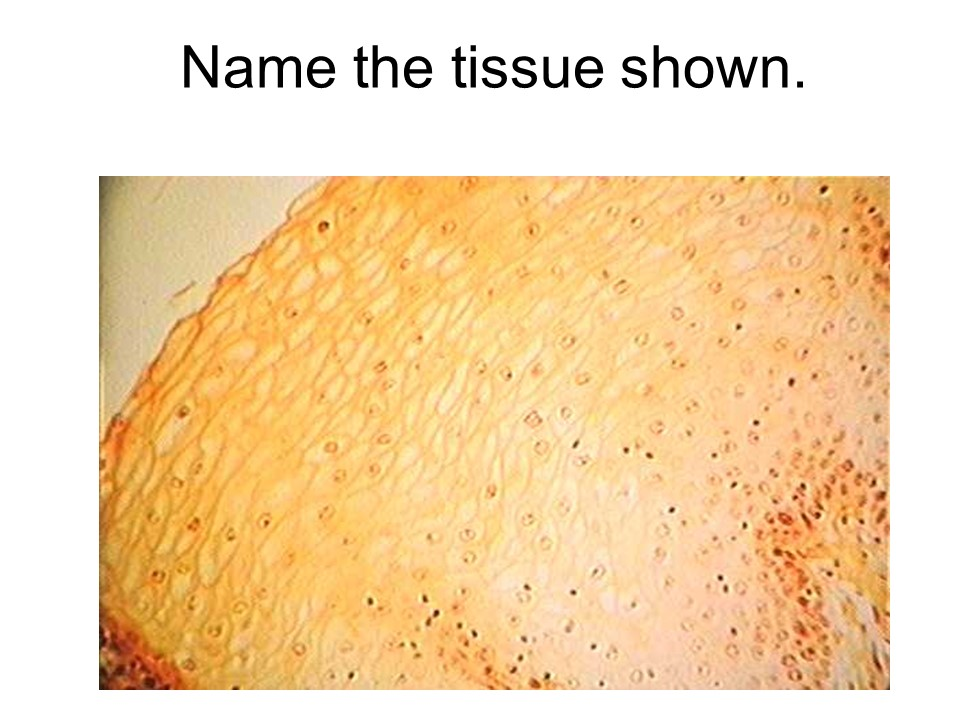
stratified squamous epithelium
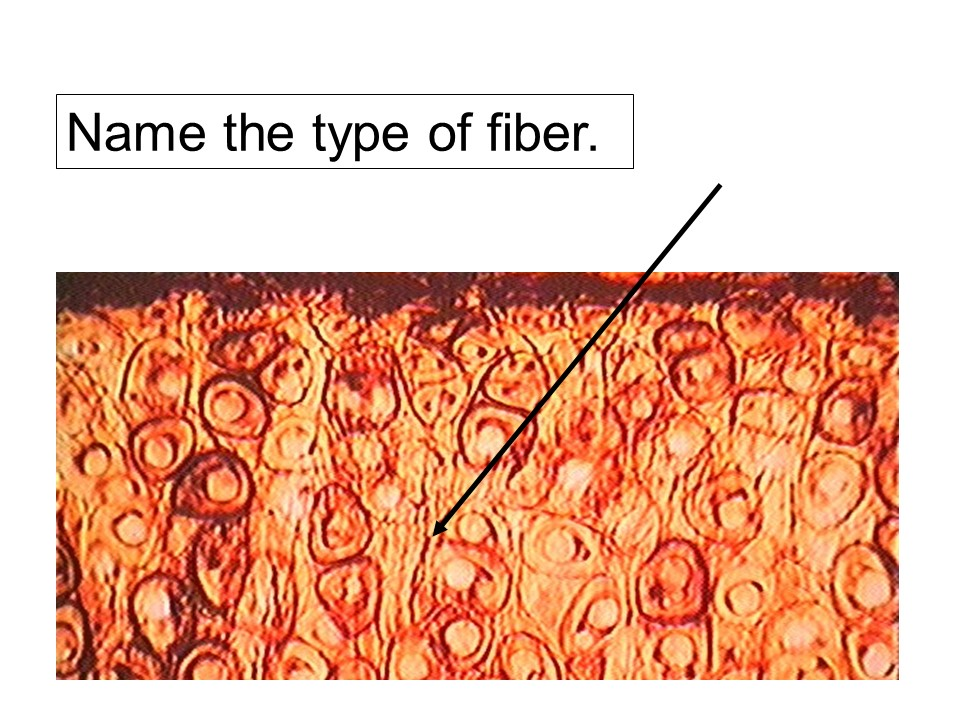
elastic fiber
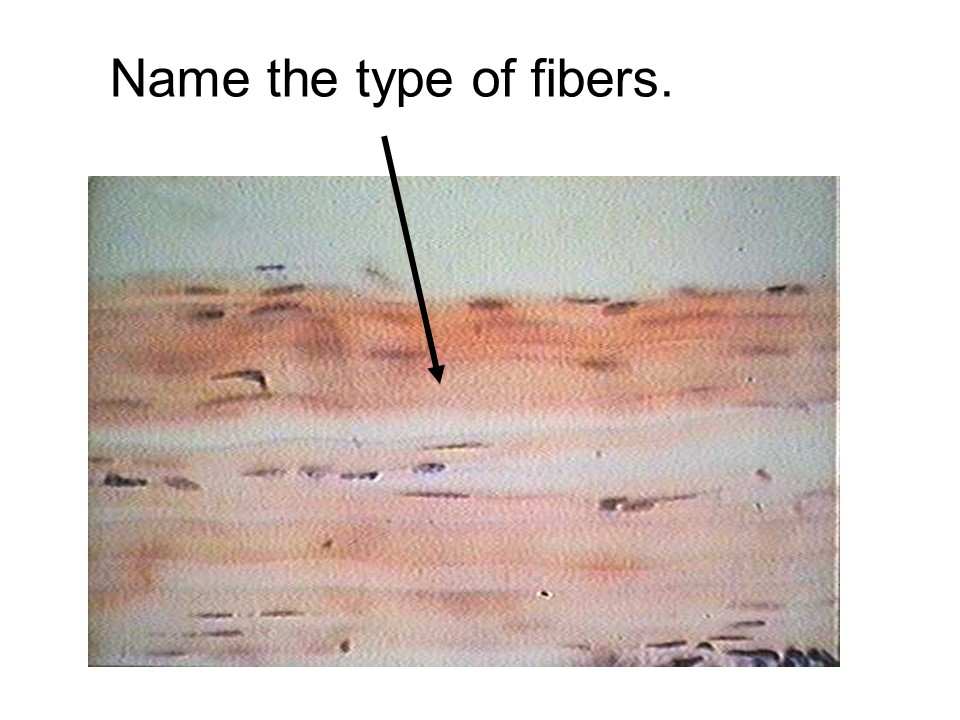
collagen fibers
wall of arteries
papillary layer
central canal

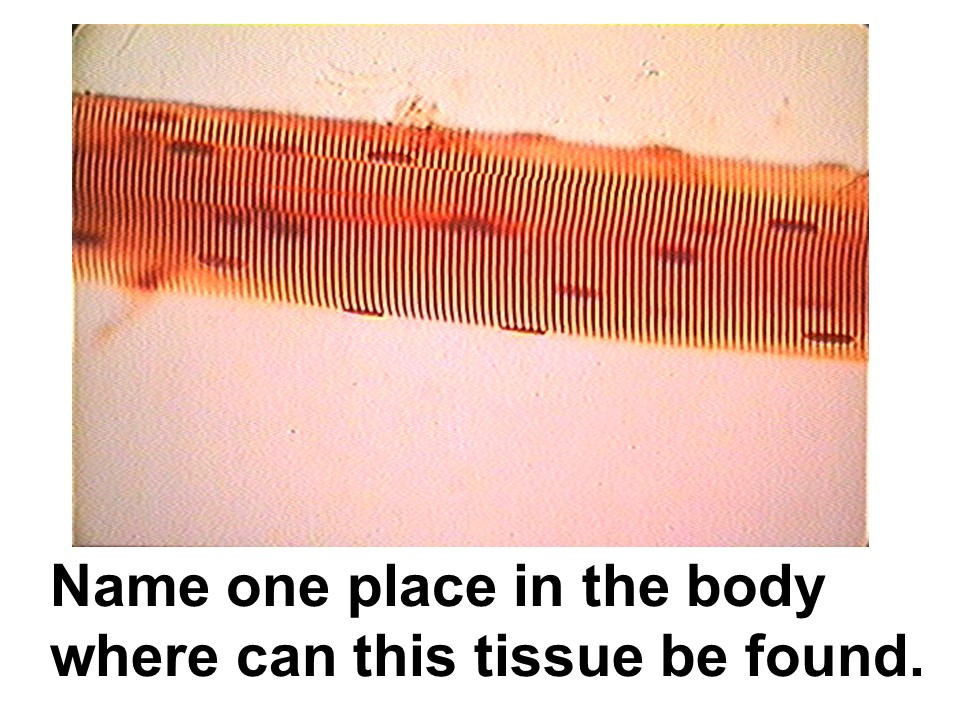
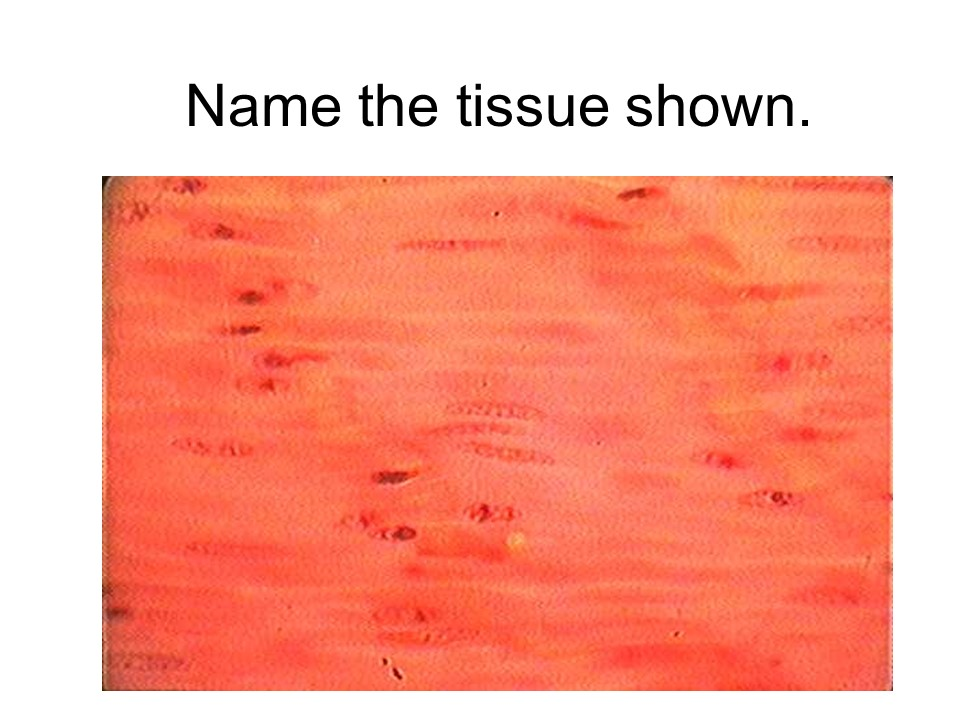
skeletal muscle
osteon

neuron and neuroglia
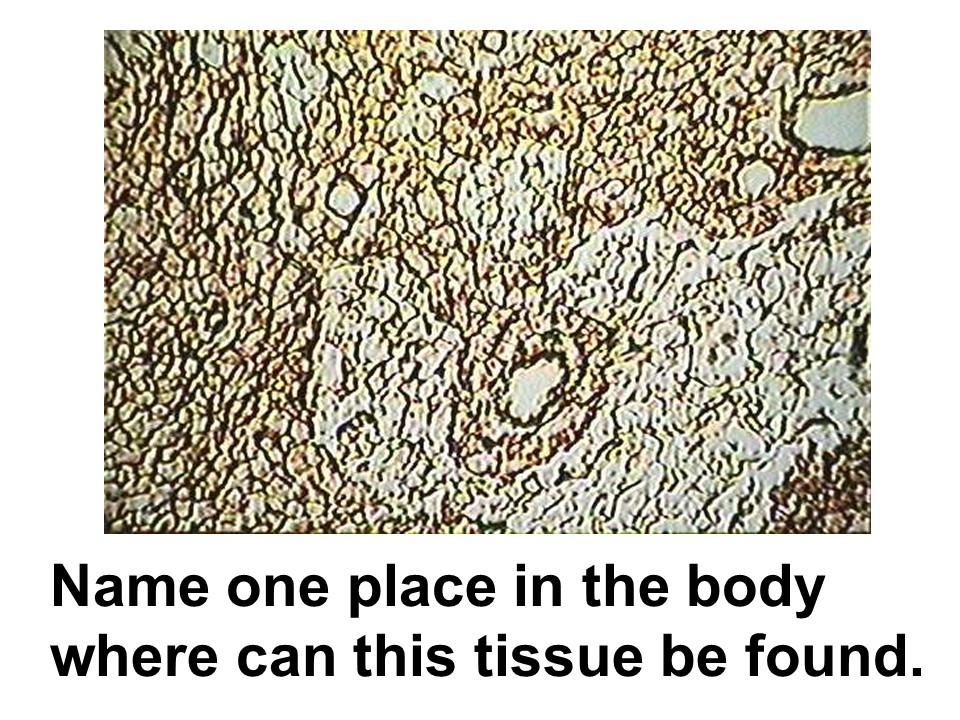
spleen
nasal cavity
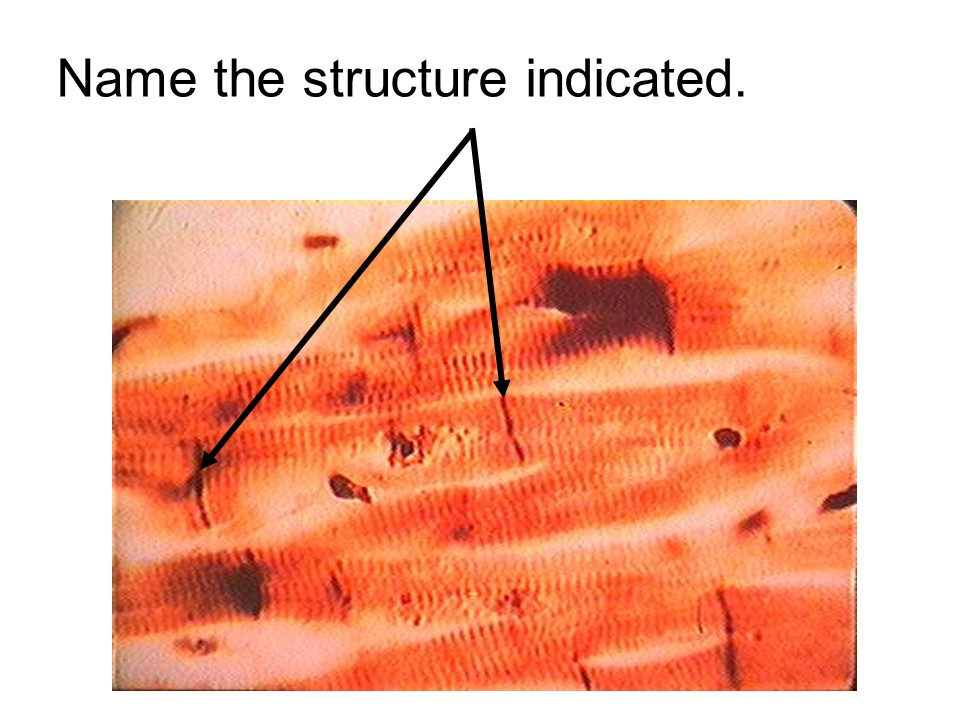
muscle
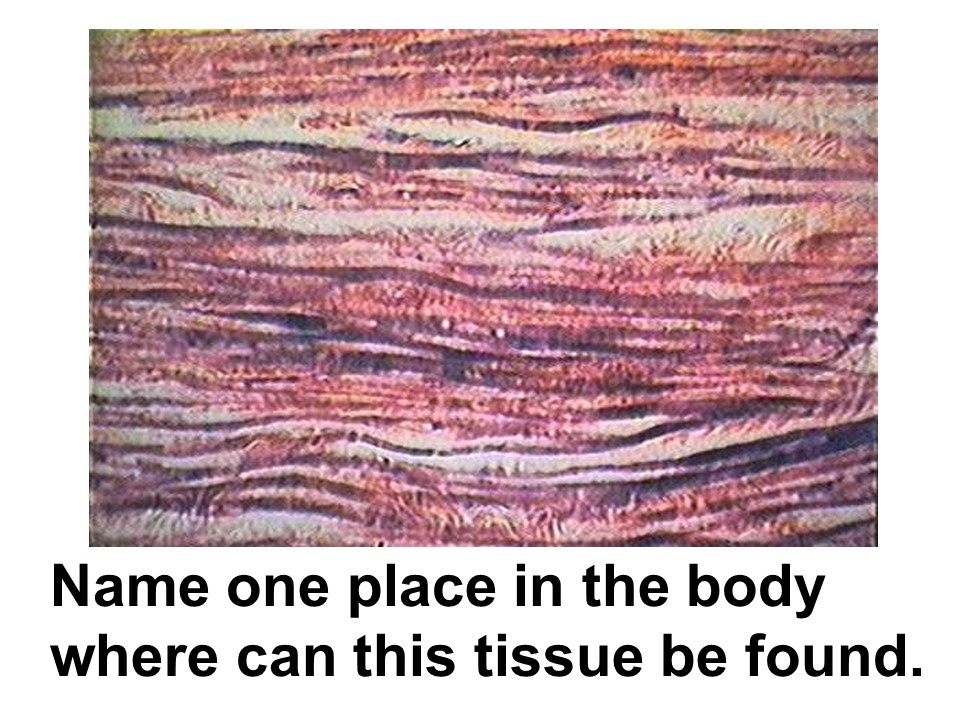
intercalated discs
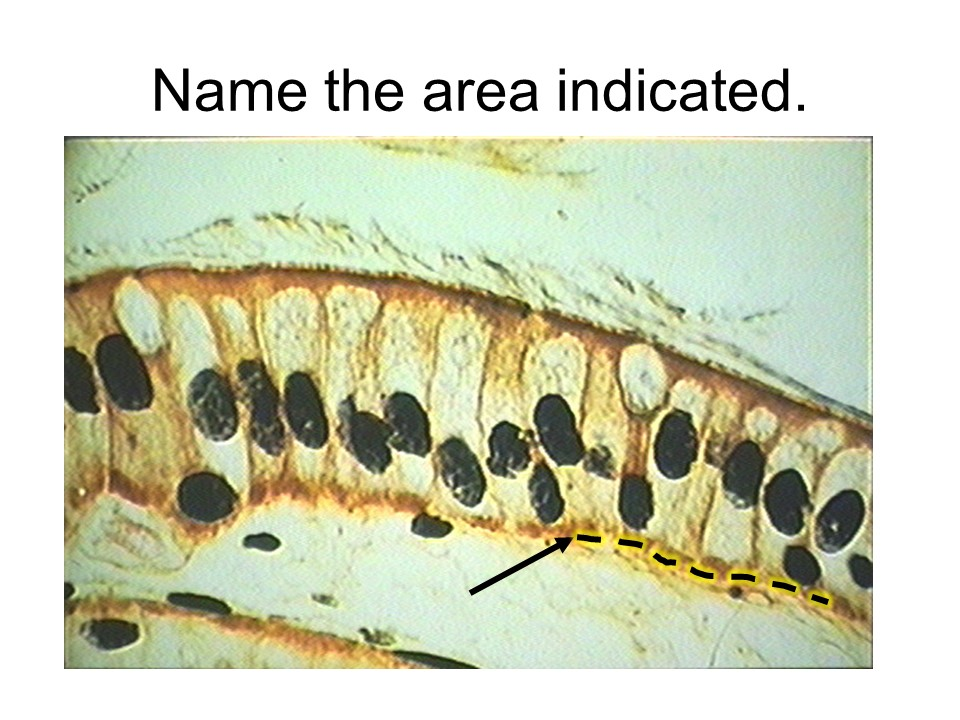
basement membrane
chondrocyte
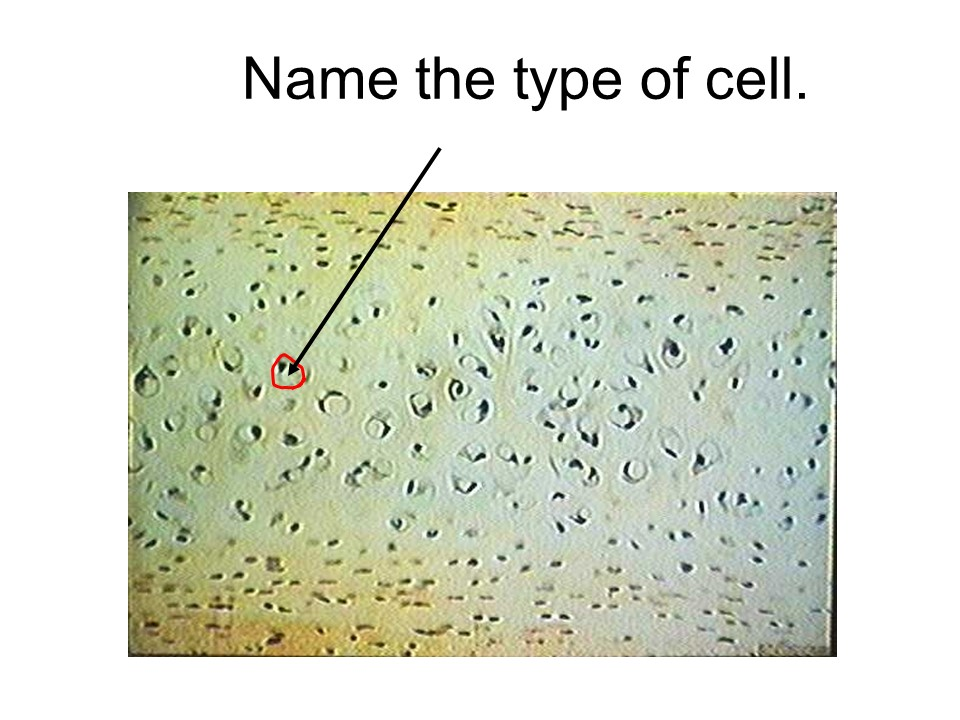
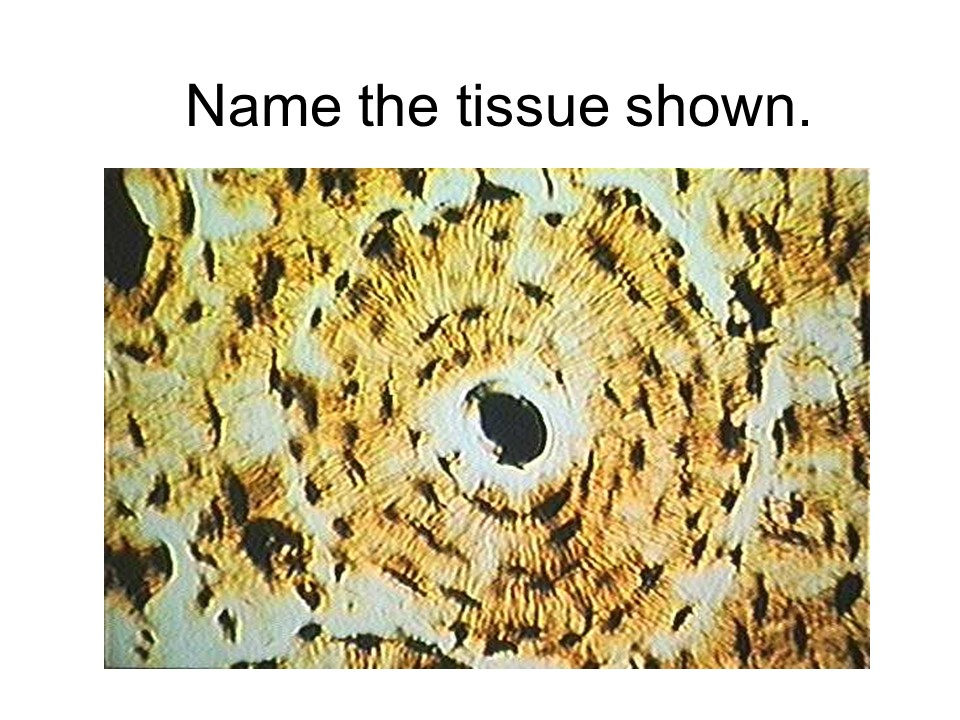
thyroid follicle
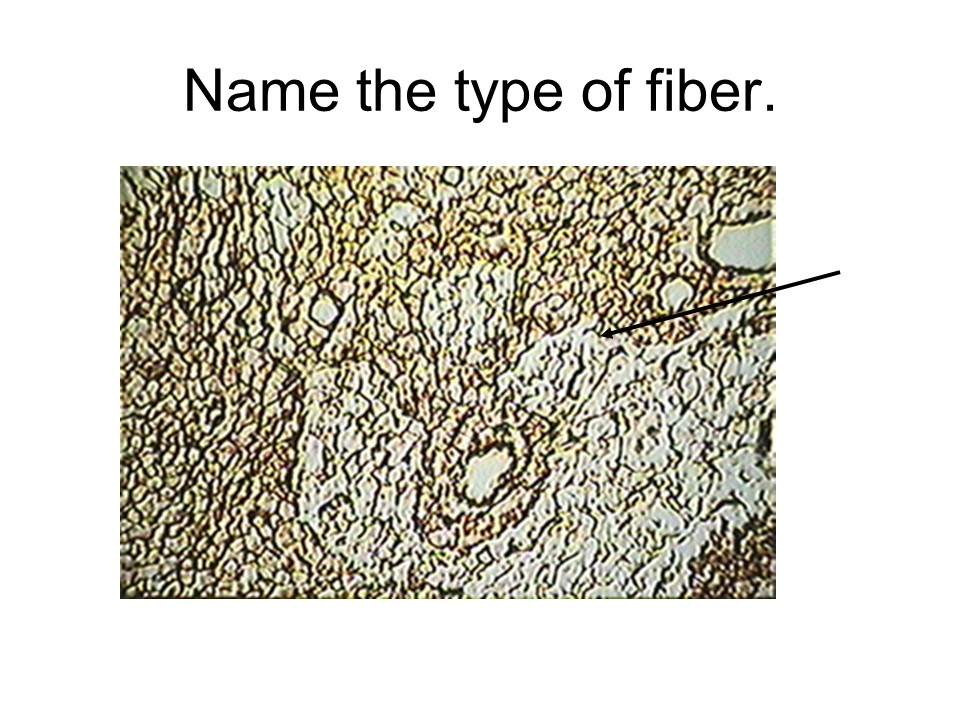
reticular fiber
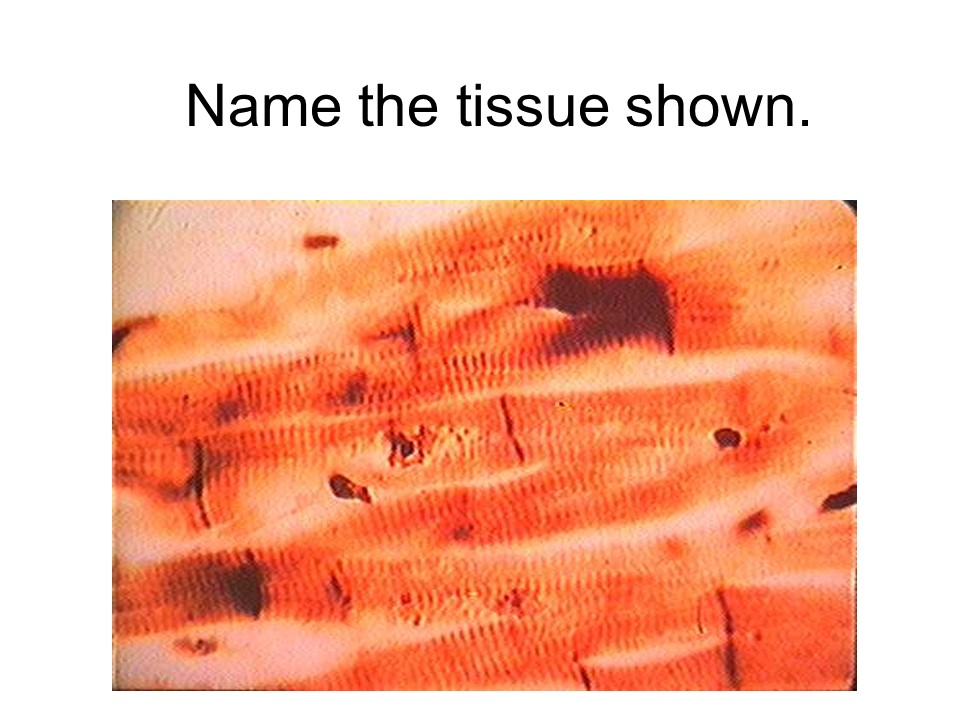
cardiac muscle
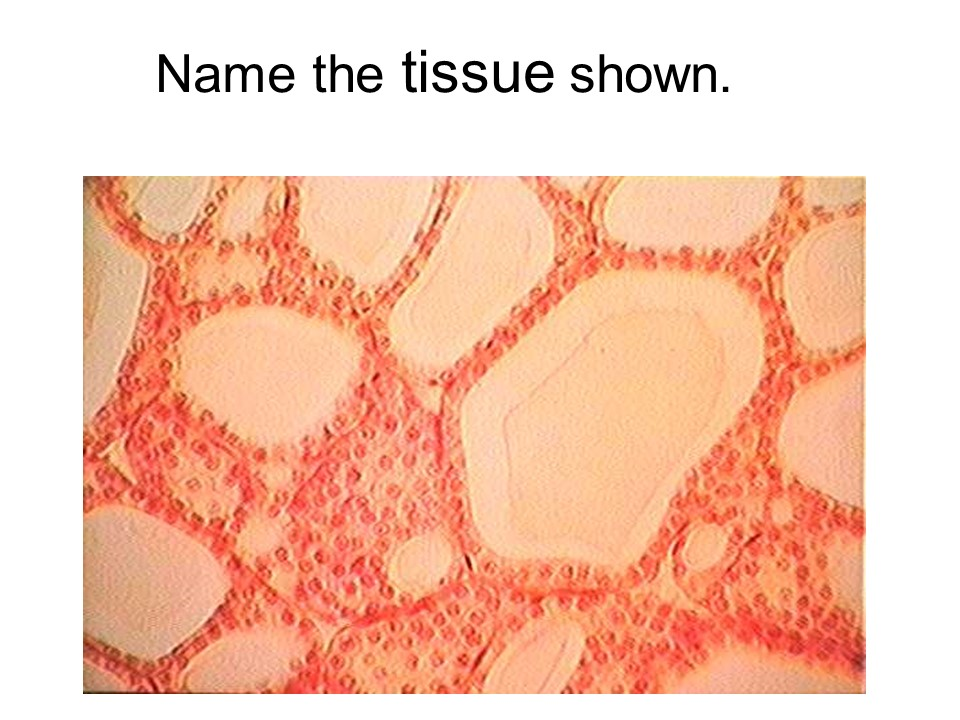
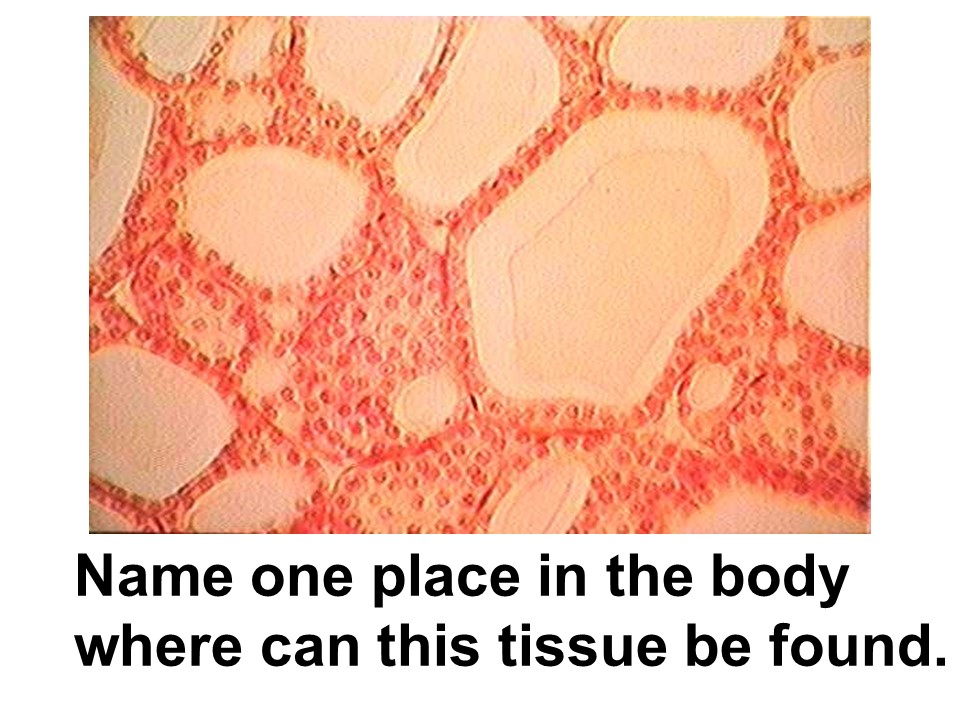
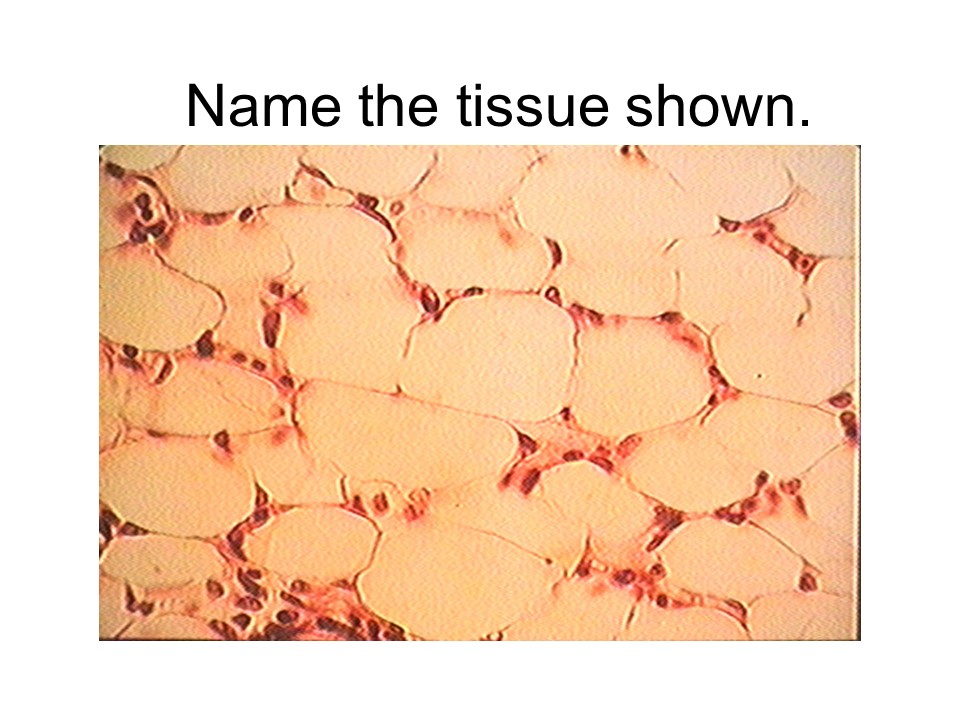
adipose connective tissue
bones
external ear
pancreas
microvilli
brain
nuclei
smooth muscle tissue
stomach
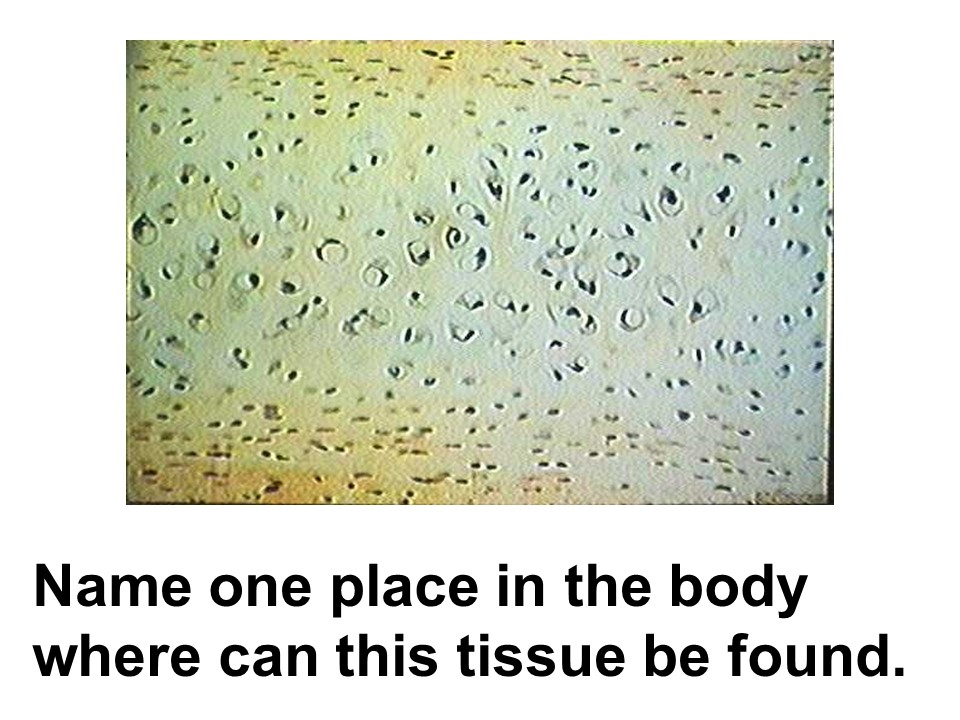
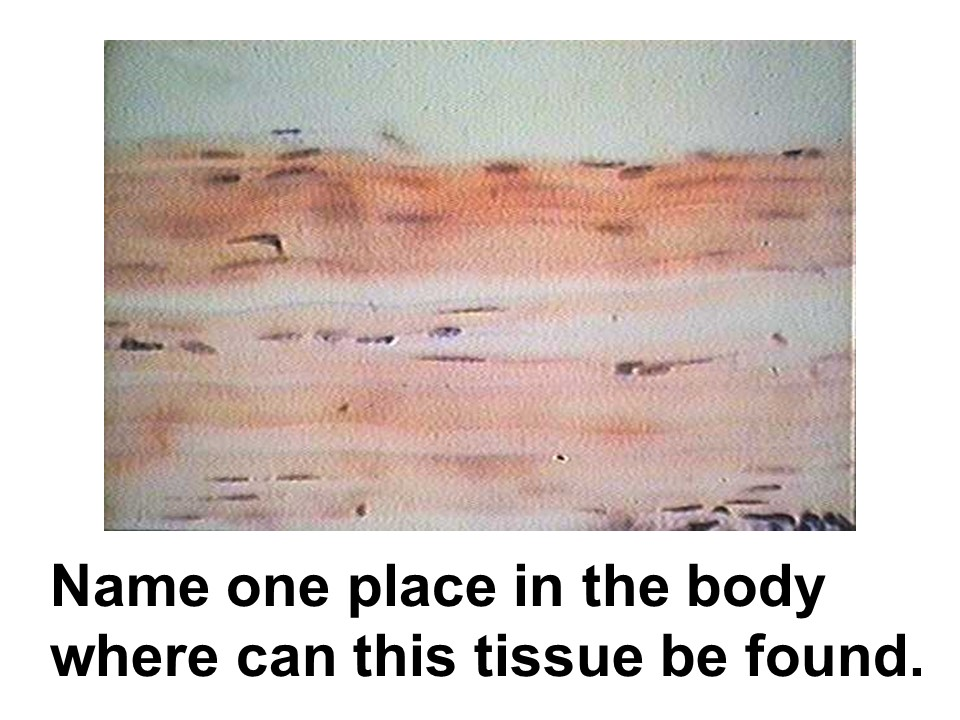
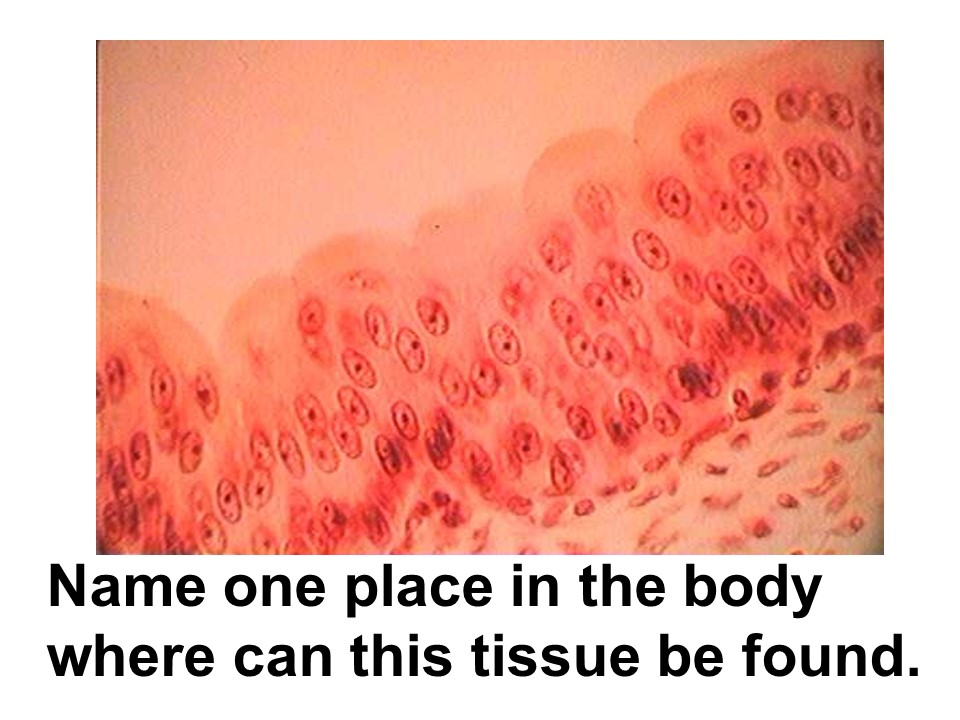
Where in the body is this tissue found?
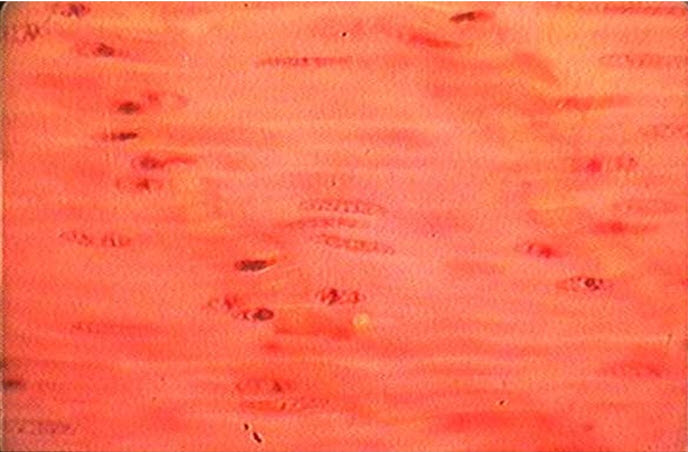
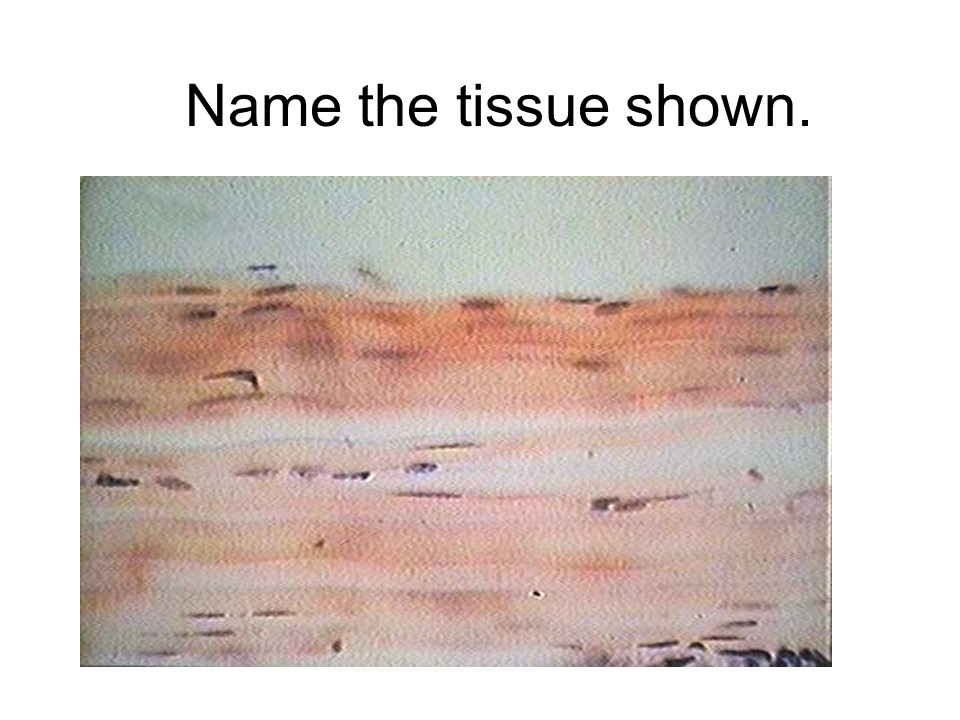
elastic connective tissue
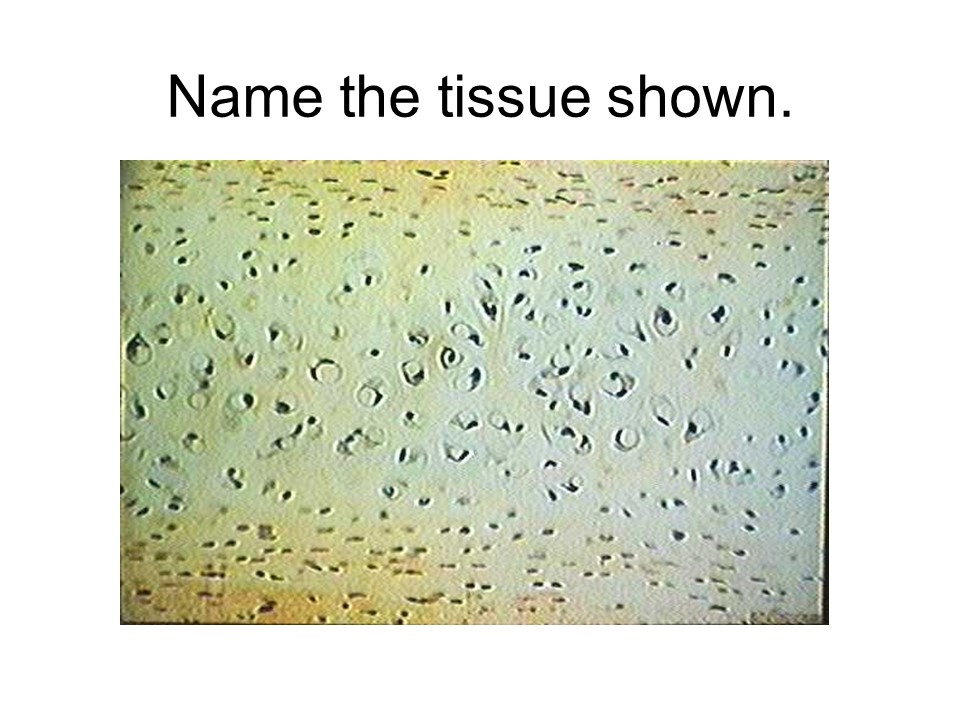
hyaline cartilage
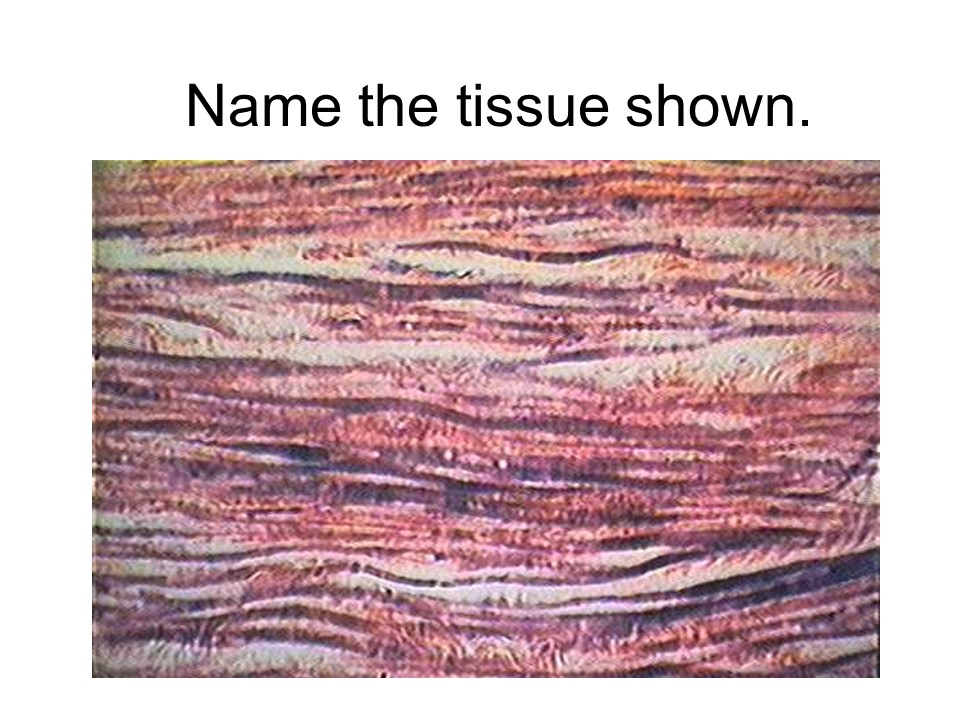
dense regular connective tissue
simple columnar epithelium
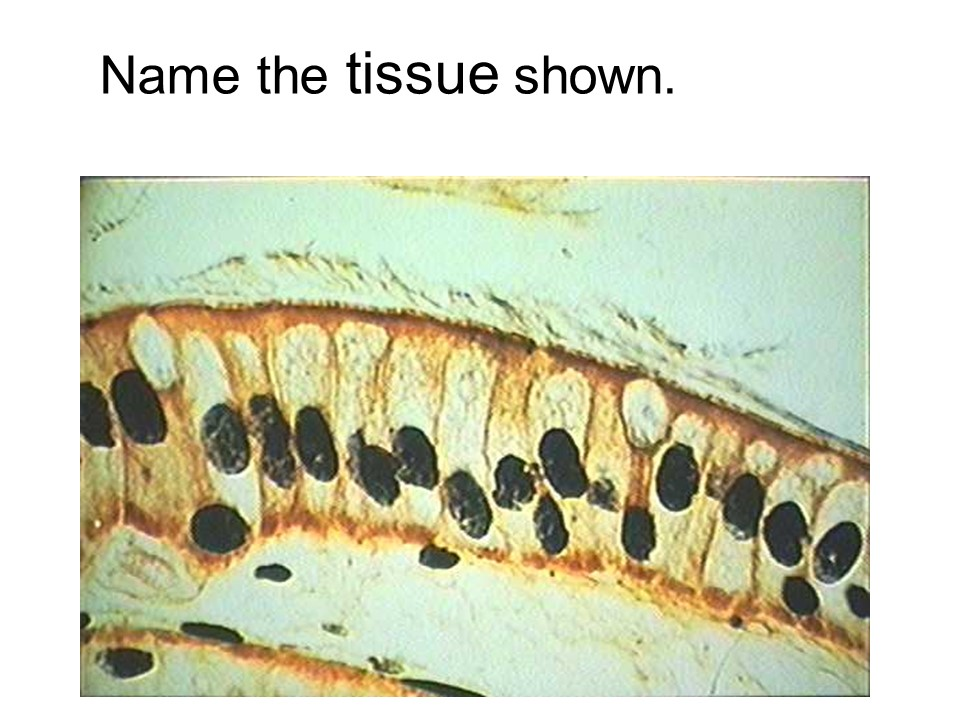
simple cuboidal epithelium
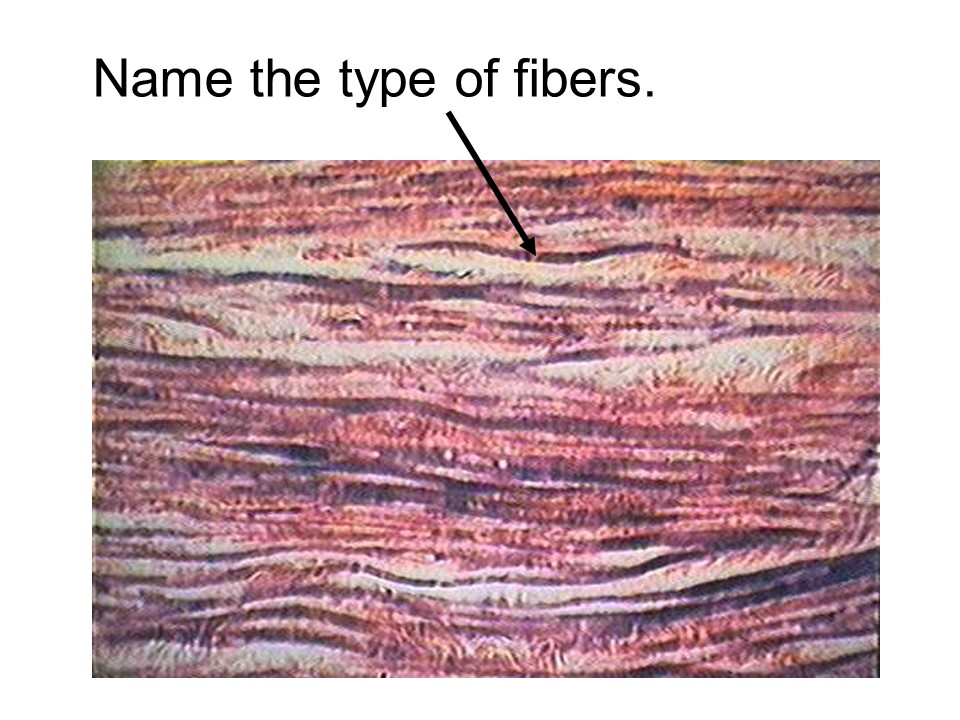
elastic fibers
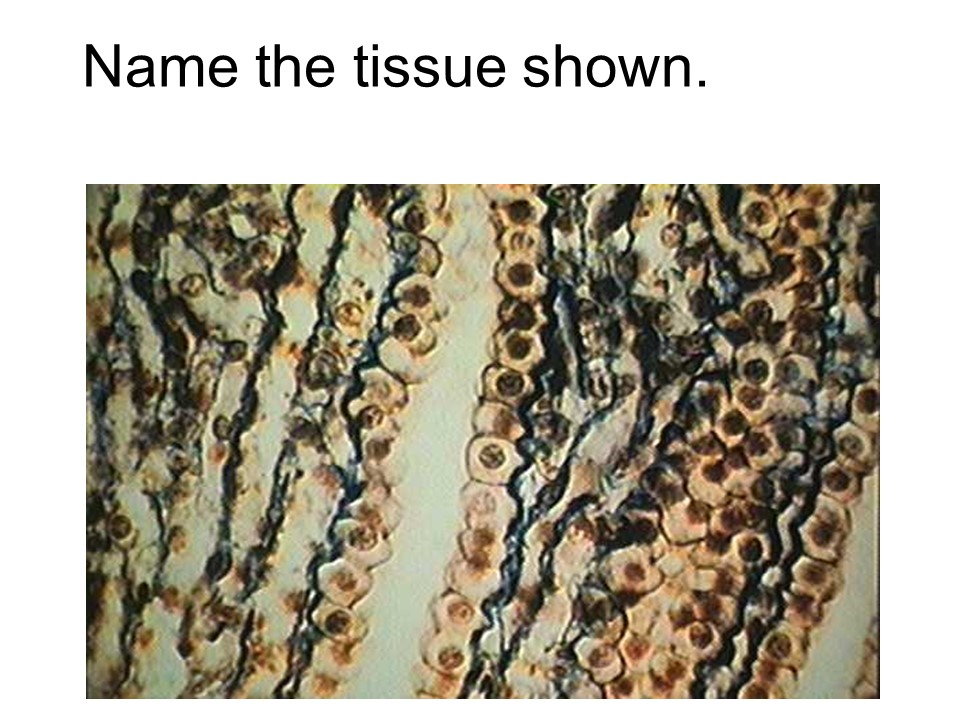
urinary bladder
lacunae
dense irregular connective tissue
transitional
Which cell is described as a rounded cell that changes shape with degree of stretching?
True
Exocrine glands produce chemicals that are released through ducts onto epithelial surfaces.
False
Exocrine glands produce hormones and release them into the bloodstream.
False
Glial cells have a cell body, dendrites (like antennae), and a long axon that sends the electrical impulses to another cell.
elastic connective tissue
This tissue that is dominated by elastic fibers instead of collagen fibers. This tissue is found in the walls of arteries, in the walls of the lungs, and in the elastic ligaments of the vertebrae.
reticular connective tissue
This tissue is found in organs where the cells are very organized and the reticular tissue helps to hold the cells, blood vessels, and other organ structures in place.
hyaline cartilage
This tissue is found covering bone surfaces located at synovial joints, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and between the tips of ribs and sternum.
Bone
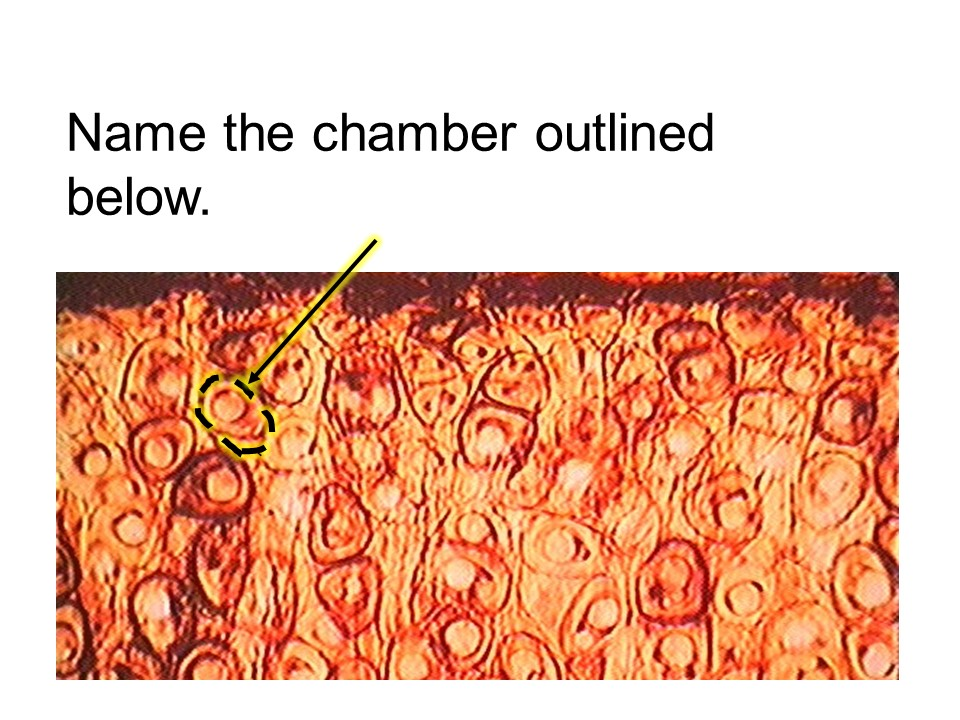
This tissue has cells called osteocytes. They are enclosed by tiny chambers, called lacunae.
simple squamous epithelium
This tissue is found in areas that are more protected and not subject to a great deal of friction, examples of which are the mesothelium and endothelium.
cardiac muscle
This tissue is considered involuntary, striated, and one or two nuclei.
supportive connective tissue
This category of connective tissue consists of distinct cells and tightly-packed fibers in a gel-like or calcified matrix.
nervous tissue
This tissue forms the central and peripheral nervous system structures.
transitional epithelium
This tissue allows for considerable stretching and is found in organs, such as the urinary bladder.
smooth muscle
This tissue is considered involuntary, non-striated, and single nucleated.
elastic cartilage
This tissue is dominated by elastic fibers. It is found in the external ear, the auditory tube, and some cartilages of the larynx.
epithelial tissue
The tissue that always has a free surface exposed to the internal or external environment is
connective tissue
Which tissue will establish a structural framework for the body as well as transport fluids and substances throughout the body?
simple columnar epithelium
This tissue is responsible for secretion, absorption, and protection. It is located in digestive organs, such as the stomach and intestines.
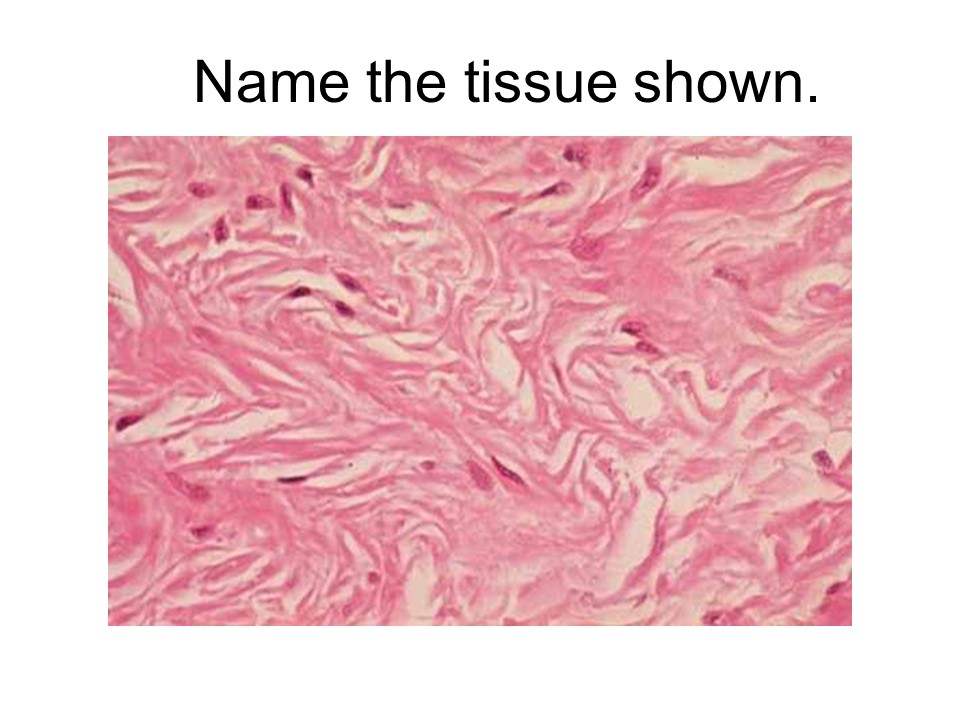
dense irregular connective tissue
This tissue is made of collagen fibers, but the fibers run in all different directions. This makes the tissue very strong. The dermis of the skin contains this tissue. It is also located around cartilages (the perichondrium) and around bone (the periosteum). It also forms a tough capsule around many organs.
adipose connective tissue
This tissue adds padding or support, stores fat, and acts as insulation.
cartilage
This tissue has cells called chondrocytes.
connective tissue
This tissue supports structures within the body, transports materials, and stores nutrients that can be broken down for energy.
adipose tissue
This tissue has cells called adipocytes.
skeletal muscle
This tissue is considered voluntary, striated, and multinucleated.
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
This tissue is found lining the respiratory tract. This epithelium contains cilia, hair-like projections that sweep material over the surface of the cell. Goblet cells are also found in this epithelium.
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
This tissue is found in the epidermis of the skin.
collagen fibers
Straight and unbranched fibers that are strong and numerous in connective tissue proper. These fibers make up tendons and ligaments.
reticular fibers
These fibers branch and interconnect, forming a supportive framework of fibers. These fibers are found where stability is needed, such as around functional cell (or parenchyma) of organs, like the liver or kidneys.
elastic fibers
These fibers are built from the protein elastin. They can stretch and recoil back to their original length. Some ligaments in our body, like those connecting the vertebrae, are made of elastic fibers so that they can recoil after stretching.
cuboidal
Which cell is described as cube-shaped or hexagonal?
nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
This tissue is found lining the mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, and vagina.
epithelial tissue
This tissue covers the outside of the body, lines the body surfaces and internal passageways, and forms glands.
fibrocartilage
This tissue contains many interwoven collagen fibers. It is extremely strong and makes up the intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis (the joint between the two pubic bones). It can also be found in and around joints, such as the knee.
areolar connective tissue
This tissue has an open framework and is found in the subcutaneous layer, which lies under the skin. It is commonly found supporting epithelial tissue.
nervous
Tissue that is specialized for the conduction of electrical impulses is ______ tissue.
dense regular connective tissue
The collagen fibers of this tissue run parallel to each other and are tightly packed. Tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses (broad, flat tendons) are examples of this tissue.
dense regular connective tissue
This tissue has a mostly cells called fibroblasts.
areolar connective tissue
This category of connective tissue is characterized by a loosely arranged network of fibers (collagen, elastin, and reticular) embedded in a gel-like ground substance, providing support, cushioning, and flexibility to various organs and tissues by connecting them together.
squamous
Which cell is described as thin, flat, scale-like?
columnar
Which cell is described as a tall, column-like cell?