ICT || 1st Midterms
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Alexander Graham Bell
revolutionized the communications field by inventing telephone
PRE MECHANICAL PERIOD (3000BCE - 14th Century)
- Words and pictograms curved in rocks
- Discovery of Papyrus and Paper
MECHANICAL PERIOD (16th Century)
mechanical calculators, modern computers
Abacus
Mesopotamia 2500 BCE
Pascaline (1642)
First mechanical calculator for addition and subtraction.
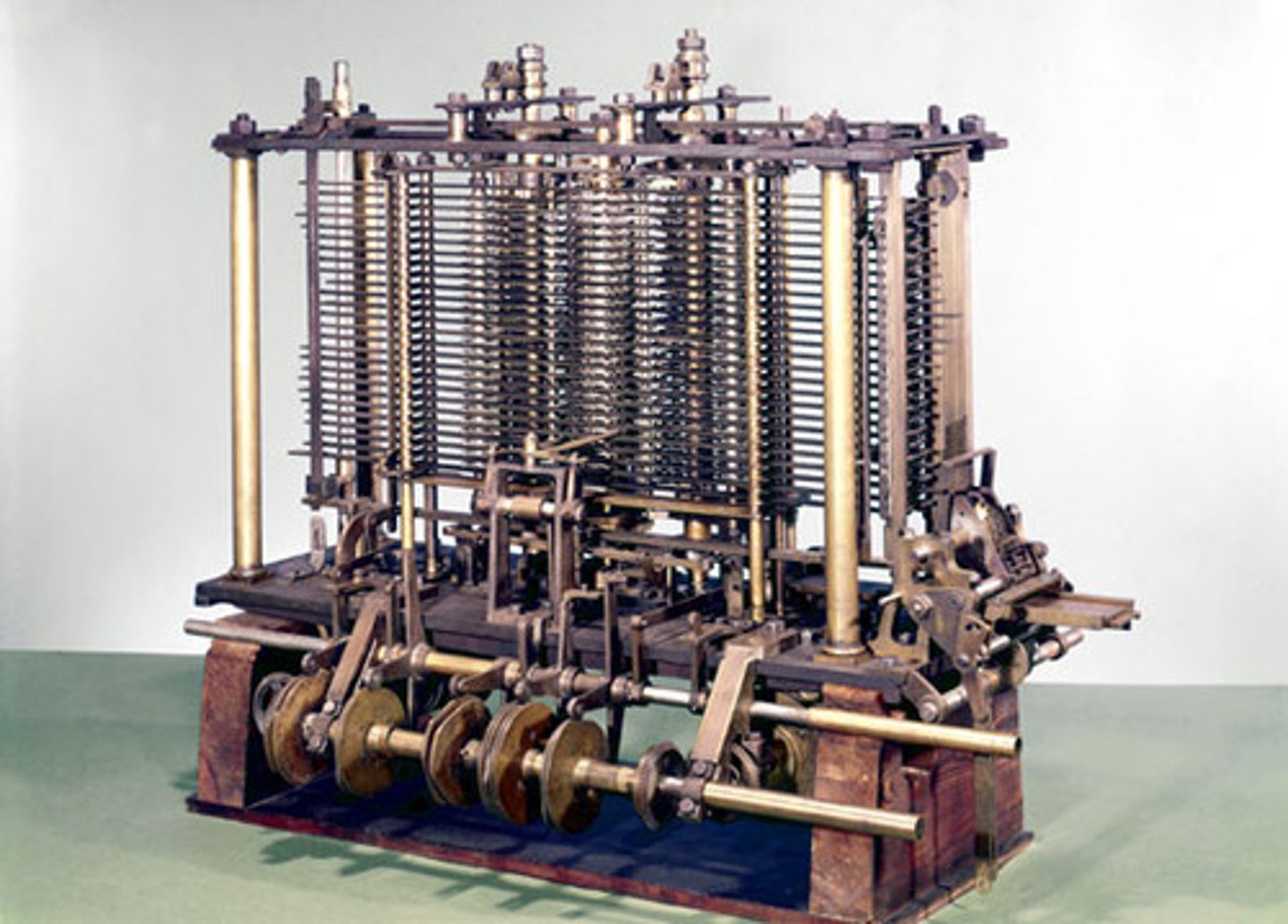
Difference Engine (1821)
was invented by Charles Babbage as the first calculator
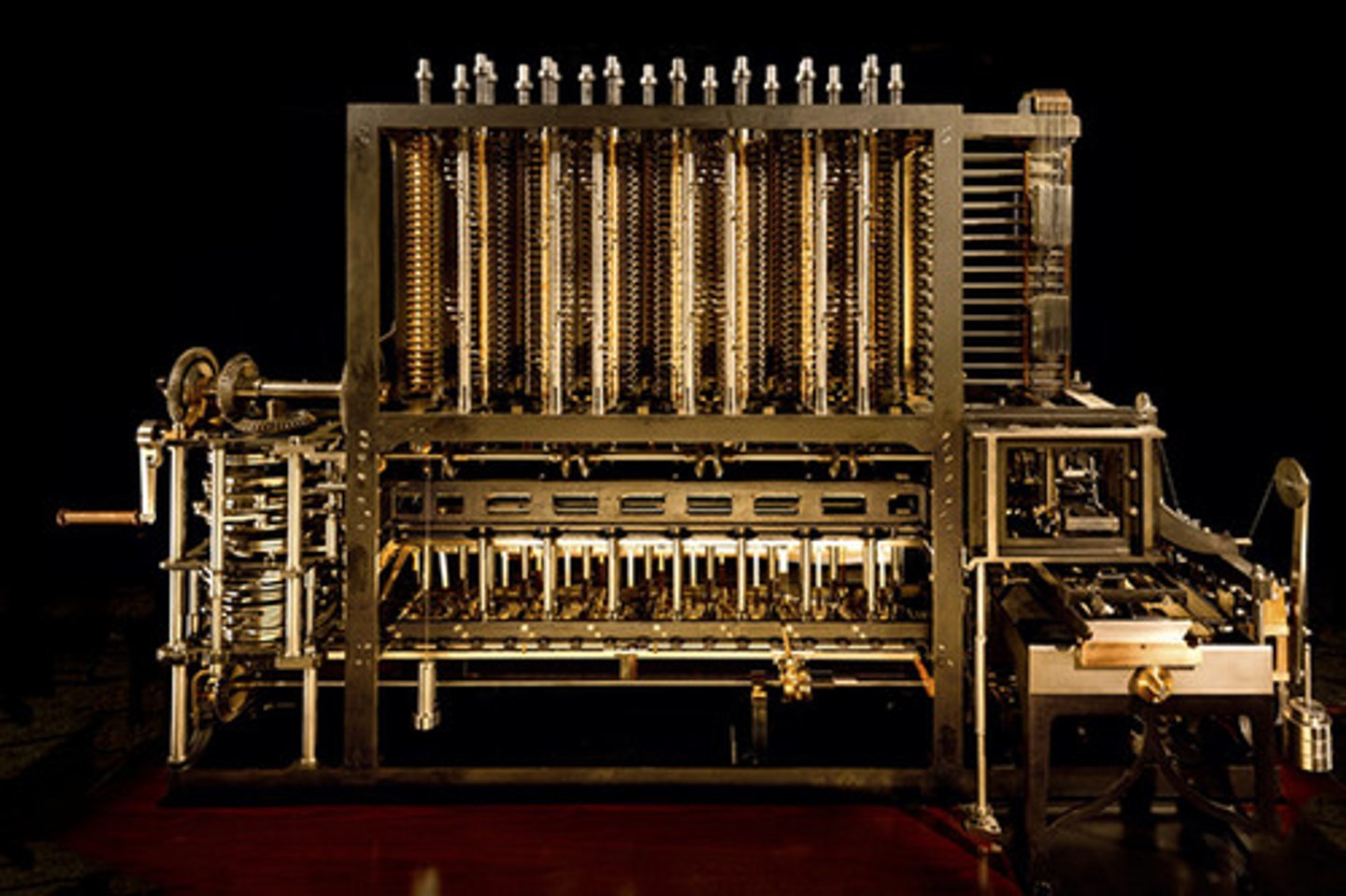
Analytical Engine (1832)
1st mechanical computer. Ran off of punched cards. Created by Charles Babbage, but never completed by him.
ELECTROMECHANICAL PERIOD (18th Century)
telegraph, telephone, radio
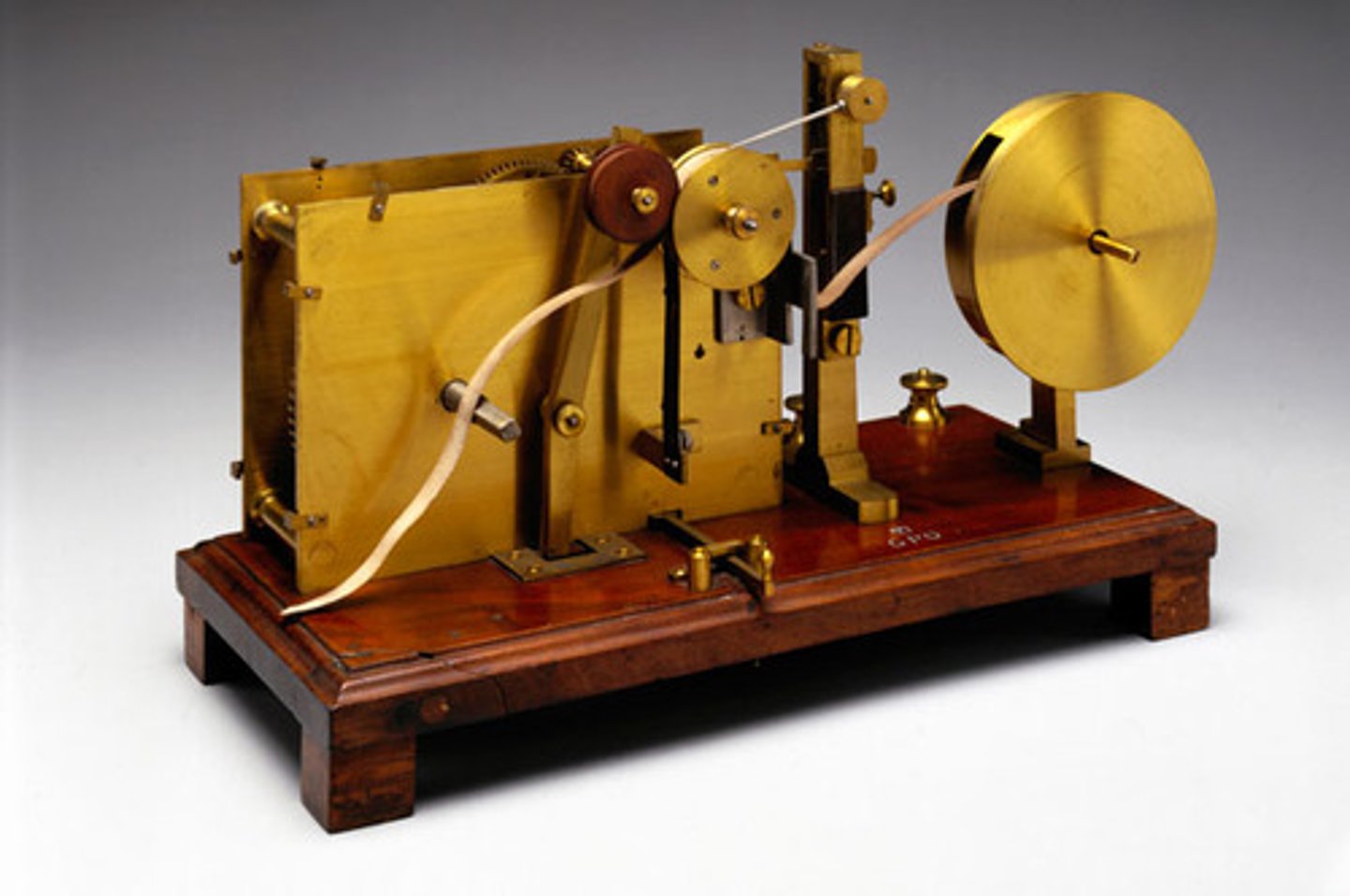
Telegraph (1837)
- William Cooke & Sir Wheatstone
- 1st device to use electricity to transmit information over an electrical media
First Single-Circuit Telegraph (1844)
- Samuel Morse
- gave rise to Morse Code
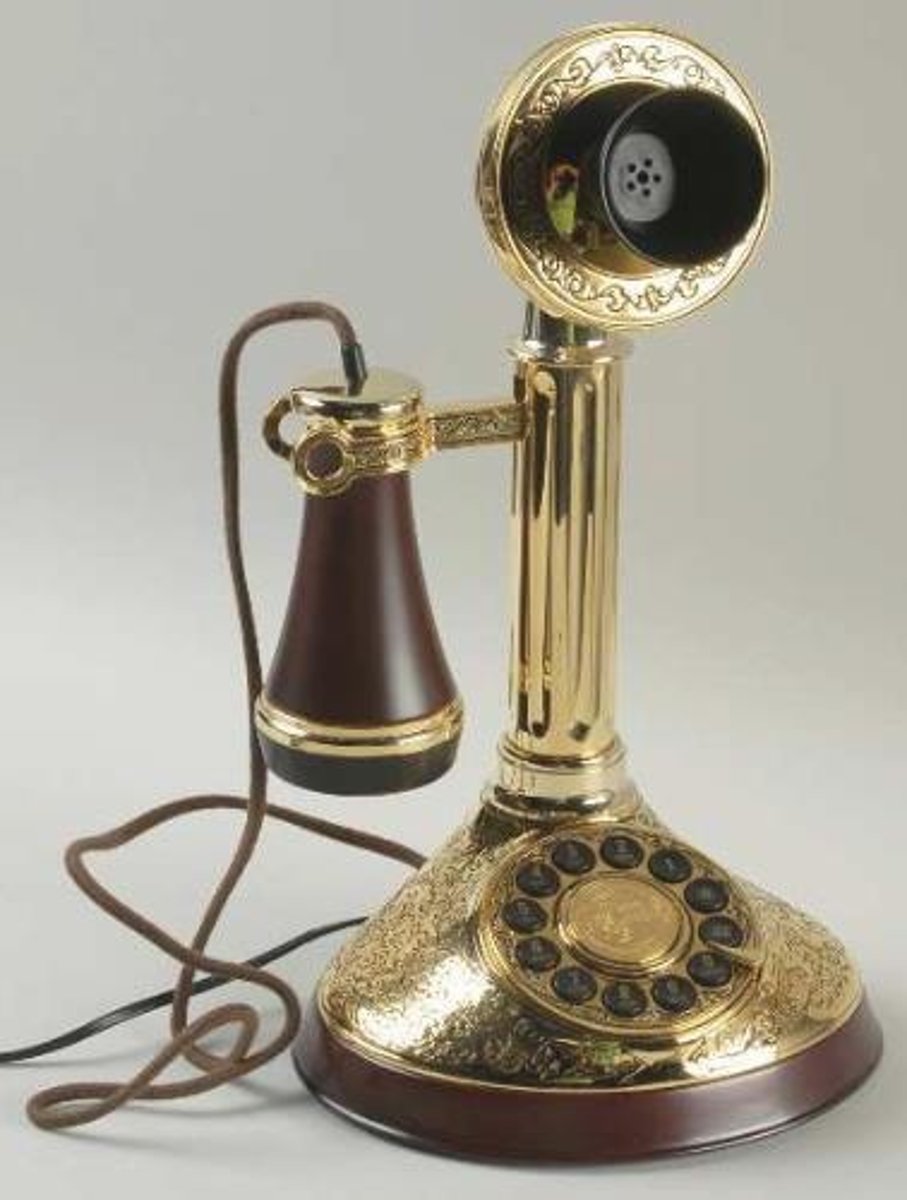
Telephone (1876)
- Alexander Graham Bell
- converts sounds into electricity and enables the telephone network to transmit it through copper wire

Radio (1894)
- Macaroni
- electrical waves travel through space and can produce an effect far from where it originated
ELECTRONIC PERIOD (1940 up to the present)
1. Vacuum Tube
2. Transistor
3. Integrated Circuit
4. Computer Microprocessors
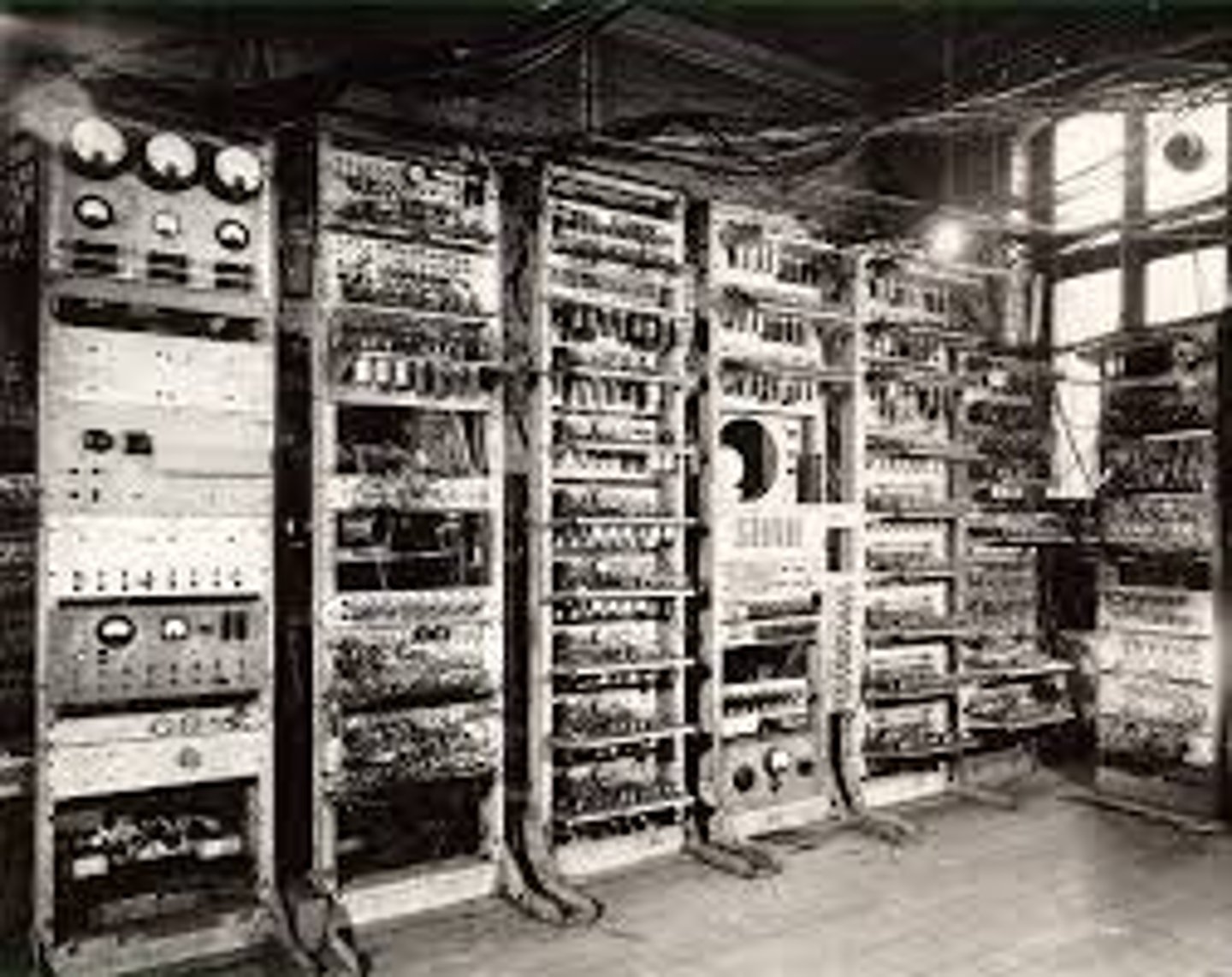
Vacuum Tube (1946)
- John W. Mauchly
- ENIAC - Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer
- First General Purpose Electronic Digital Computer
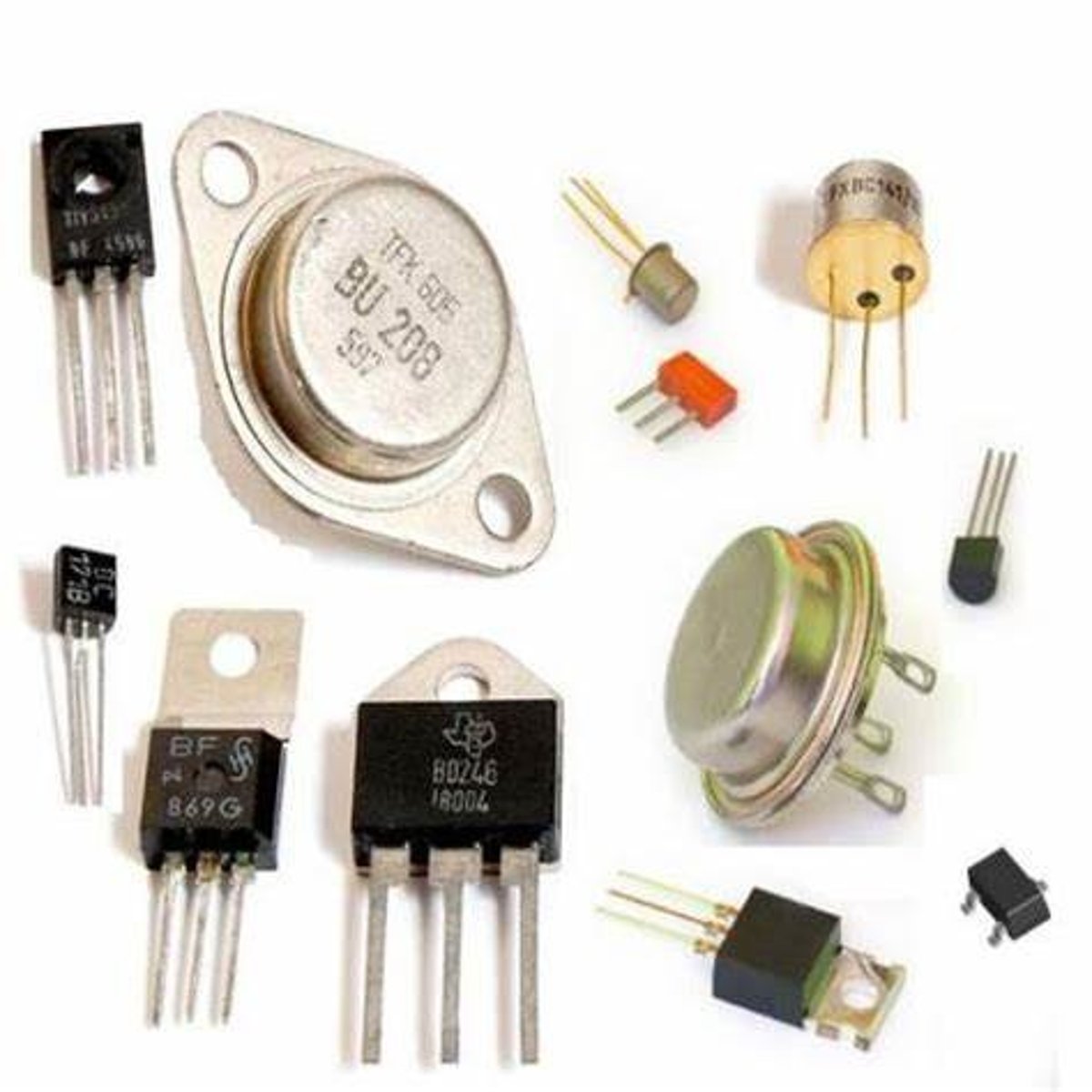
Transistor (1947)
- John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, William Shockley at Bell Labs
- small electronic switch that can turn current on or off, or amplify signals

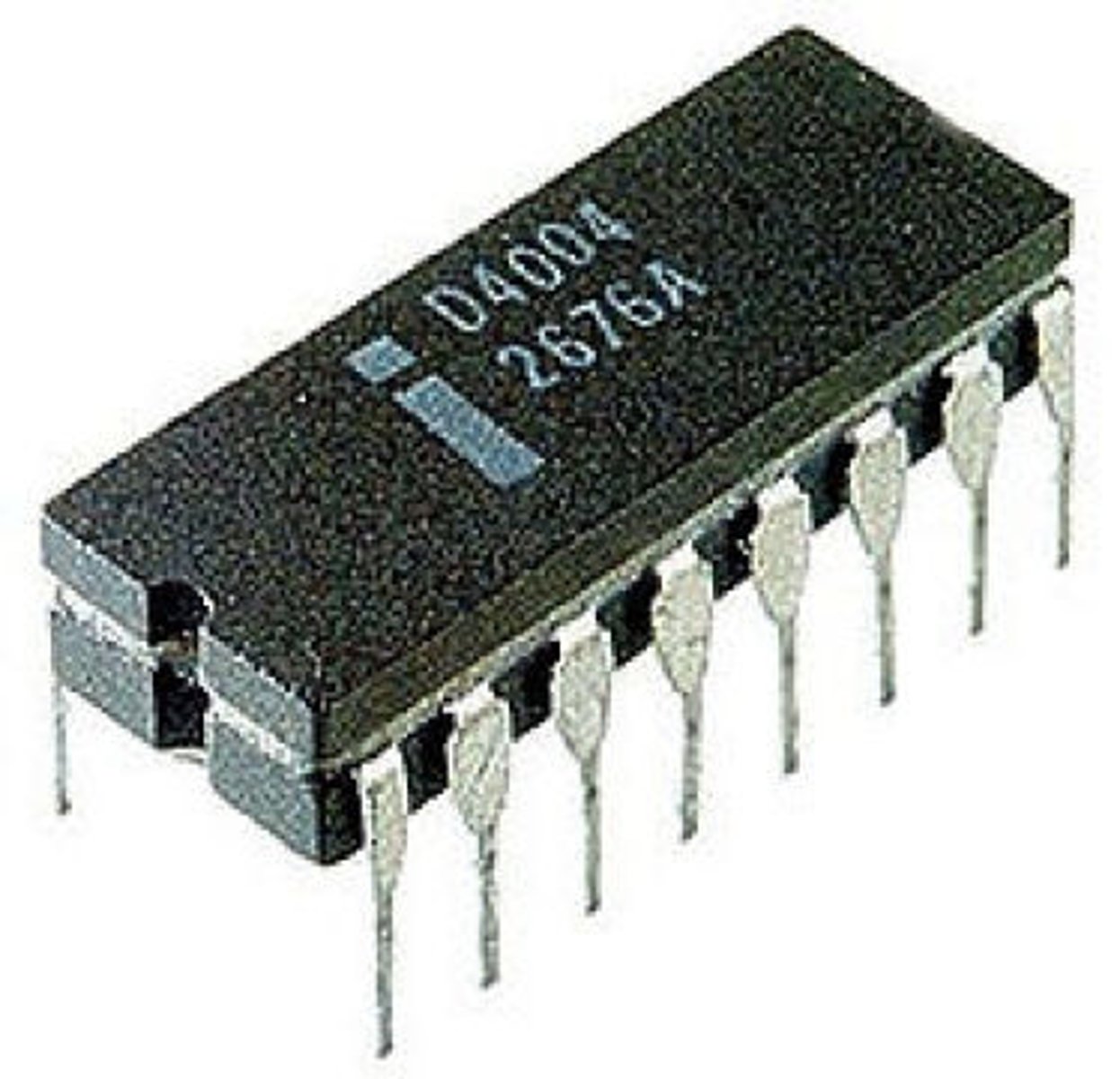
Integrated Circuit (1958)
- Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce
- tiny chip made of semiconductor material that holds multiple transistors, resistors, and other components in one package

Information and Communications Technology
processing of data that includes sending, editing, receiving, locating, and saving using different hardware and software components
ICT Components
- datafication
- internet access
- cloud computing
- software/hardware
- transactions
- communication technology
Goals of ICT
- Unified way to communicate
- Economic Development "4th Industrial Revolution"
ICT Hub of Asia
ICT in the Philippines
World Wide Web (WWW)
information system on the internet that allows document to be connected to other documents by hypertext links
Web Page
hypertext document connected to the WWW
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
the transfer method used by WWW to transmit and receive Web pages
Websites
connections between single web page to multiple web pages
Timothy John Berners-Lee
- English engineer and computer scientist
- June 8, 1955, London, UK
- invented www
Web 1.0
- the page is "as is" and cannot be manipulated by the user
- website contents and layouts are inseparable
- website contents are stored in files
- uses HTML tags
- do not embed guestbook in the content page
- website forms are usually sent by email
Darcy DiNucci (1999)
Coined the term Web 2.0
Tim O'Reilly and Dale Dougherty (2004)
they popularized Web 2.0
Web 2.0
- user-generated contacts
- emphasis on user experience
- improved interoperability (incorporates API)
- e.g. blogs, wikis, web apps, video sharing sites
Folksonomy
- categorize through hashtags
- ex. #ayokona
Rich User Experience
- content is dynamic and responsive to the user's input
- website that look nice, interactive, and easy to use
User Participation
- owner of the website is not the only one who is able to put content
- users create and share contents
- ex. facebook, users post pics, stories, videos
Long Tail
- services that are offered on demand rather than on a one-time purchase
- offers niche content for small audience
- ex. spotify
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- users subscribe to a software only when needed rather than purchasing them
- online software you don't need to install
- ex. gdocs, gslides, gsheets
Mass participation
- diverse information sharing through universal web access
- lots of people joining in
- wikipedia is written and edited by millions of people