Vaginal Secretions
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Benefit of wet mount vaginal secretions and KOH examinations of vaginal secretions
tests allow health provider to immediately diagnose and determine cause of vaginitis/vaginosis
Most common gynecological complaints
- vaginal discharge
- vaginal discomfort
- vaginal odor
Major causes of most common gynecological complaints
- bacterial vaginosis
- candidiasis
- trichomoniasis
- atrophic vaginitis
True or false: treatment of sexual partner may be indicated to avoid infection?
TRUE
What is required for optimal recovery and detection of micro-orgaisms in vaginal secretion?
Appropriate specimen collection and handling
How/when are vaginal secretions collected? Who collects them?
- health care provider collects vaginal secretion sample during pelvic examination
Procedure for vaginal secretion specimen collection
obtain vaginal sample using a:
- non-lubricated speculum (moistened with warm only)
Why can't the speculum be lubricated with lubricant when collecting vaginal secretions
- lubricants may contain antimicrobial agents
Type of swab used for vaginal secretion collection
- Sterile, polyester-tipped swab on a plastic shaft
- exampled: dacron
- Sterile wire loops can also be used
Why can cotton-tipped swabs not be used for vaginal secretion collection?
Cotton tipped swabs are toxic to Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Why can't swabs with wooden shafts be used for vaginal secretion collection?
toxic to Chlamydia trachomatis
Where are vaginal secretions collected from?
- posterior vaginal fornix and vaginal pool
What other information should be on vaginal secretion collection for transportation
- menstrual status
- exposure to sexually transmitted diseases
Patients should be instructed to avoid what 3 things prior to vaginal secretion collection
- lubricants
- creams
- douches
When should vaginal secretion testing be performed?
testing should be performed immediately
If testing of vaginal secretions cannot be performed immediately after collection, how should it be stored for later viewing
- room temperature storage
Vaginal secretions should not be stored in the refrigerator if you are looking for what 2 organisms?
N. gonorrhorae and T. vaginalis are adversely affected by refrigeration
Vaginal secretion evaluation involves what 3 tests
- pH
- wet mount examination (microscopic exam)
- KOH preparation and examination
Refrigeration should be used for vaginal secretions when looking for what 2 organisms? Purpose of refrigeration?
- Chlamydia trachoma's
- Viruses
- putting in fridge prevents overgrowth of normal bacteria flora
pH range for healthy vagina
pH of 3.8 - 4.5
When should the vaginal pH be determined and how is its tested?
- pH should be determined before placing swab into saline
- generally use commercial pH paper
- pH testing is performed at the time of the pelvic examination
If the vagina has a pH of above 4.5...
pH above 4.5 is associated with:
- bacterial vaginosis
- trichomoniasis
- atrophic vaginitis
What is the predominant bacteria of the vagina?
Lactobacilli
Lactobacilli produce:
- Lactobacilli produce lactic acid (metabolite byproduct)
- some lactobacilli also produce hydrogen peroxide
Function of lactobacilli product
Lactobacilli produce lactic acid (and some times hydrogen peroxide)
- Lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide maintain the acidic vaginal environment needed for health
Appearance of lactobacilli
(won't need to identify pictures of them)
- very large (long) thin nonmotile rods
- may show central selling as a result of cell wall damage (form antibiotic therapy)
Presence of lactobacilli will cause a positive for what dipstick value?
Causes nitrite dipstick positive
What are you looking for when performed a wet mount direct examination of vaginal secretions?
- RBC
- WBC
- epithelial cells
- clue cells
- bacteria
- yeast
- mycelial elements
- trichomonads
What are you looking for when doing KOH prep and examination for vaginal secretions?
- Amine test: whiff test
- Yeast
- mycelial elements
What specific types of cells are not present when doing KOH prep and why?
- KOH destroys blood cells and epithelial cells
- Thus, you cannot see blood cells or epithelial cells
Wet mount examination- instructions
- collect swab of vaginal secretions
- place swab into about 0.5-1ml of sterile physiological saline (0.9% NaCl)
- twirl swab in saline to elute secretions from swab
- place a drop of saline-suspended specimen onto a properly labeled clean glass slide (patients name on slide_
- apply clean coverslip and evaluate using bright field and phase microscope
What vaginal secretion components can be evaluated why using low power?
EVALUATE
- epithelial cells
- assess overall distribution of specimen
Difference in objective lenses between low and high power?
Low power: 10x objective
High power: 40x objective
What components of vaginal secretions can evaluated using high power lens
QUANTIFY ELEMENTS
- RBC
- WBC
- bacteria morphotypes
- yeast
- mycelial elements
- trichomonads
- clue cells
- parabasal cells
- basal cells
- squamous epithelial cells
Do you evaluate KOH prep or Wet mount first?
Evaluate KOH prep last
How to prepare KOH prep for vaginal secretion
- Place a drop of saline-suspended specimen onto a properly labeled clean glass slide
- add one drop of 10% KOH directly onto the drop of specimen on the slide
How do you perform amine test on vaginal secretion?
Whiff test
- wave hand over the slide and observe/smell for a fishy odor
- report as a positive or negative
What are you looking for when examining vaginal secretion via KOH prep?
Looking for fungal elements
- yeast and/or mycelial elements
KOH does what to cellular elements in vaginal secretion sample?
- KOH dissolves cellular elements (RBC, WBC, epithelial cells) so that fungal elements are enhanced
How can you speed up the process of dissolving cellular elements when using KOH?
heat up the slide
Effect of KOH on pH
- KOH changes the pH to alkaline
the distinct foul-smelling odor produced is due to trimethylamine, caused by the volatilization product of polyamides at alkaline pH
Significance of KOH testing
- when microbial flora of vagina changes significantly, proliferation of microbes that produce polyamides increase
- this leads to the development of discharge and increased foliation of epithelial cells
Are RBC cells usually present in vaginal secretions?
NO
what could cause RBC cells to be present in vaginal secretions but is not pathologic...
contamination due to menstruation
Are WBC normal to be present in vaginal secretions?
- a few to several are seen in health women
- number is increased during ovulation and menses
What accounts for 50-90% of microbes present in healthy vagina?
Lactobacilli
are Lactobacilli normally present in healthy vagina?
YES
Description of lactobacilli shape
- large
- non-motile
- rods (gram positive)
Function of lactobacilli in the vagina?
- production of lactic acid as a waste product
- some species also produce hydrogen peroxide
= acid pH maintains bacterial flora in balance by preventing proliferation of "other bacteria"
Other types of bacteria that can be found in the vagina other than lactobacilli
- Garderella vaginalis
- Mobiluncus
Are yeast, hyphae, or pseudohyphae normally found in healthy vagina?
Normal: none or occasional
What indicates candidiasis in vaginal secretions?
- increased numbers of yeast, hyphae, and pseudohypahe
- Abnormal: more than one seen per high-field power
Hyphae, yeast, and pseudohyphae can be confused with _________. How do you decrease the chance of confusion?
-Can be confused with RBC
- KOH destroys RBC, WBC, and epithelial cells to decrease confusion
What is the predominant cell found in vaginal mucosa?
- squamous epithelial cells
Description of squamous epithelial cells
- large
- thin
- flagstone-shaped appearance
- small central nucleus that is about the size of RBC
How can squamous epithelial cells be confused with clue cells?
- as cells degenerate, keratohyalin granulation (KHG) occurs that can cause misidentification as clue cells
Picture of squamous epithelial cell
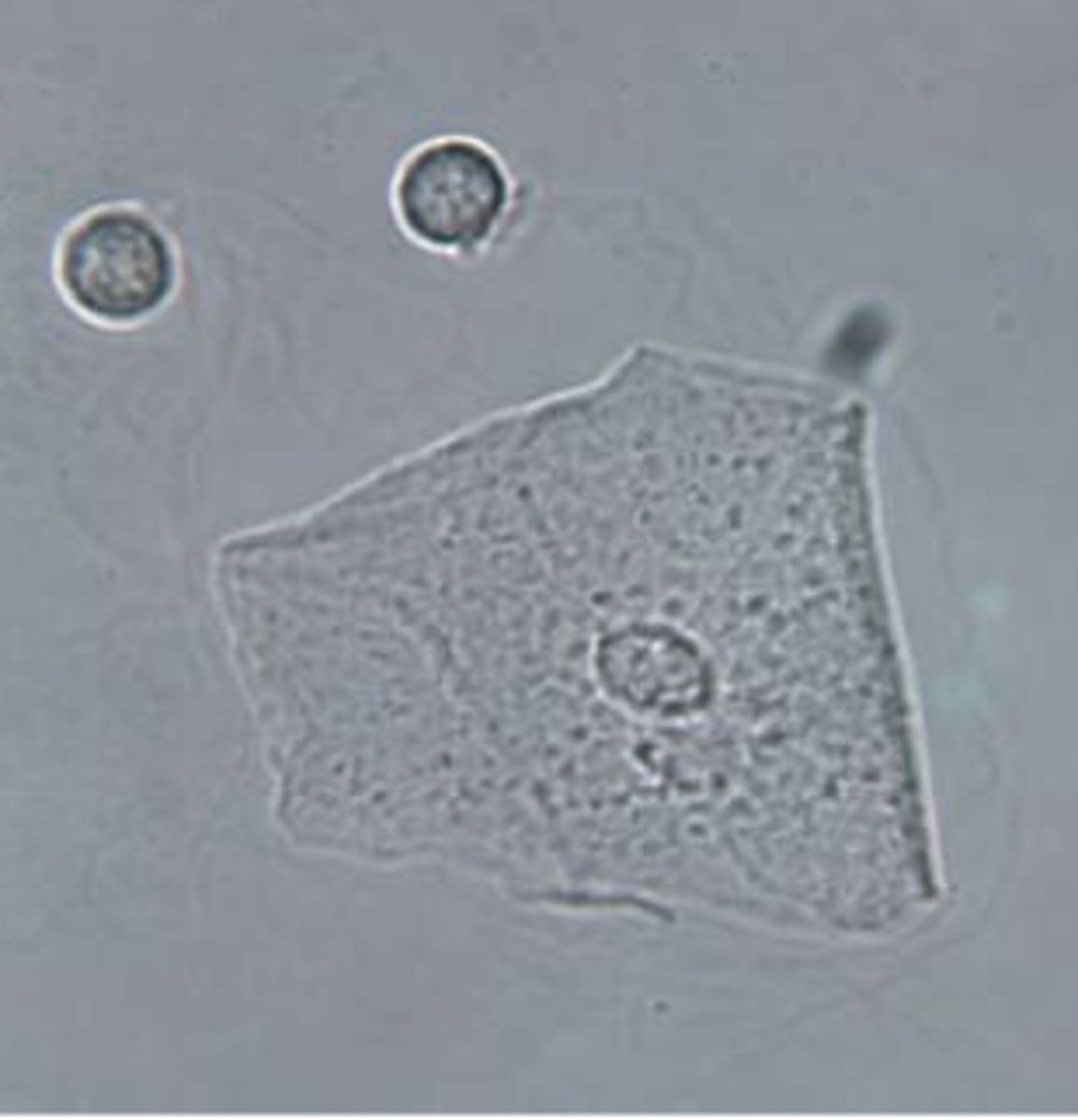
Clue cells
- Squamous epithelial cells with numerous bacteria adhering to the outside of the cell membrane
Adhesion of numerous bacteria to the clue cel causes...
- obscures visualization of the distinct cytoplasmic border causing shaggy-appearing edges
What type of cell is described as large cell with shaggy-appearing borders, and nuclei may not be visible
- Clue cell
Cells that appear soft and "finely stippled" with indistinct cellular borders
Clue cells
What is a diagnostic indicator of bacterial vaginosis
- Clue cells
- because they are covered in bacterial
Clue cell picture
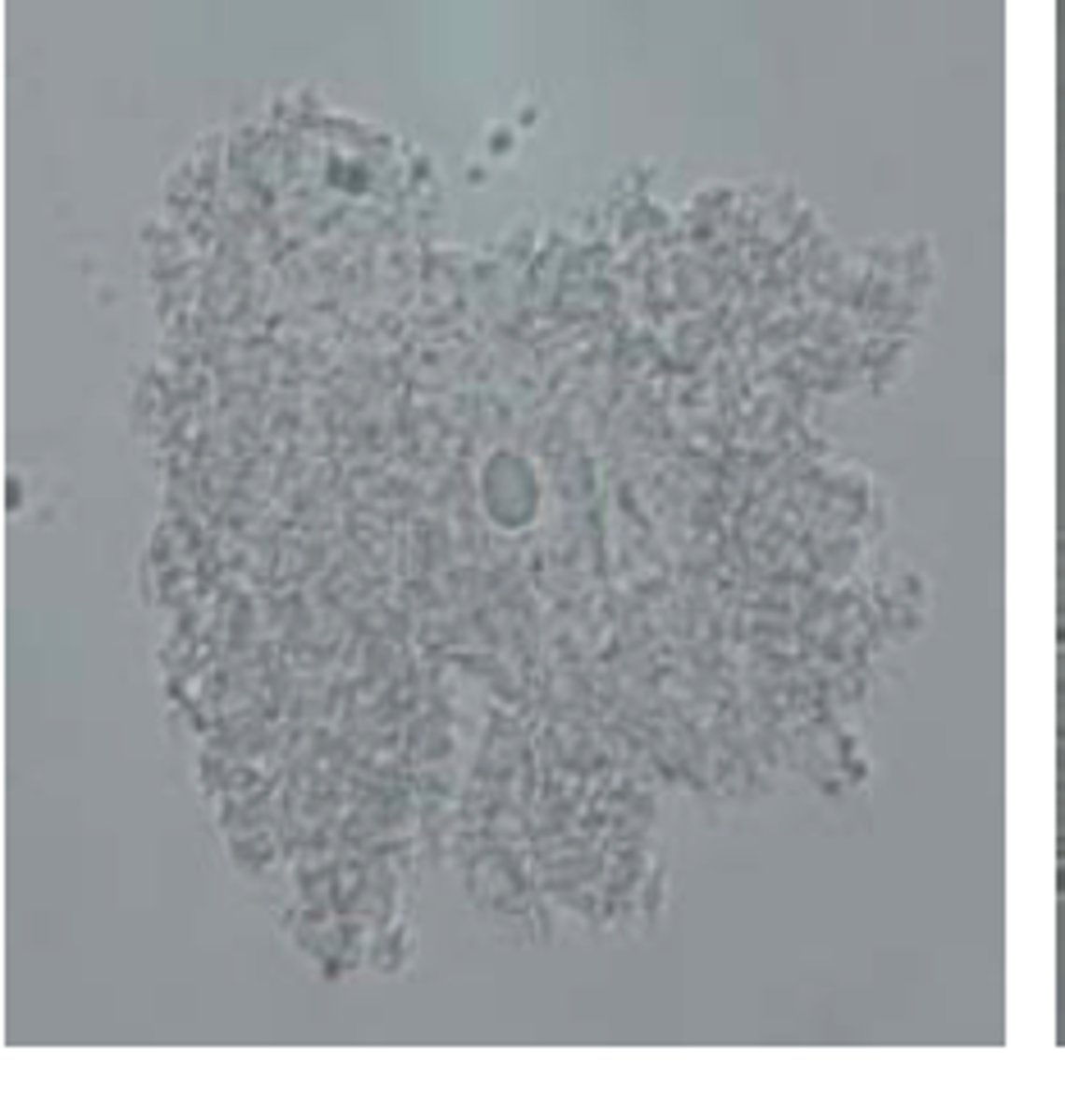
Criteria for cell to be a Clue Cell
- significant number of bacterial must extend beyond and obscure visualization of the cytoplasmic borders of the epithelial cells
Parabasal cells
- reside below the surface or lumina of vaginal mucosa
What cells reside below the surface or lumina of vaginal mucosa?
Parabasal cells
Are parabasal cells found i normal vaginal secretions?
NO
When are elevated levels of parabasal cells in vaginal secretions expected?
- increased numbers are found during menstration and in postmenopausal women
Paranasal cells resemble what other cell type?
- closely resemble urinary transitional epithelial cells
- oval to round with distinct borders
What type of cells are most often found in atrophic vaginitis?
Parabasal cells
Increased levels of parabasal cells (not during menstruation or postmenopausal) are indicative of.....
Atrophic vaginitis
Basal cells
- form the basal layer of the vaginal epithelium
Basal cells of vaginal secretions are similar in size to what other cell type?
WBC
Are basal cells found in healthy vaginal secretions?
NO
Presence of basal cells in vaginal secretions indicate....
presence of desquamative inflammatory vaginitis
Trichomonas vaginalis
- flagellated protozoan that infects and causes inflammation of the vaginal epithelium
Appearance of trichomonas vaginalis
- pear or turnip-shaped with unicellular body about the size of WBC
- 4 anterior flagella and undulated membrane
How do trichomonas vaginalis move?
flagella and undulating membrane
- 4 anterior flagella and undulating membrane produce propulsion and wave-like motion
If you see something flitting or jerky motion in vaginal secretion.... likely identification?
Trichomonas vaginalis
Do trichomonas vaginalis survive well away from vaginal mucosa?
NO
- not a hardy organism
- once removed from vaginal mucosa, they die quickly
Tichomonas vaginalis picture
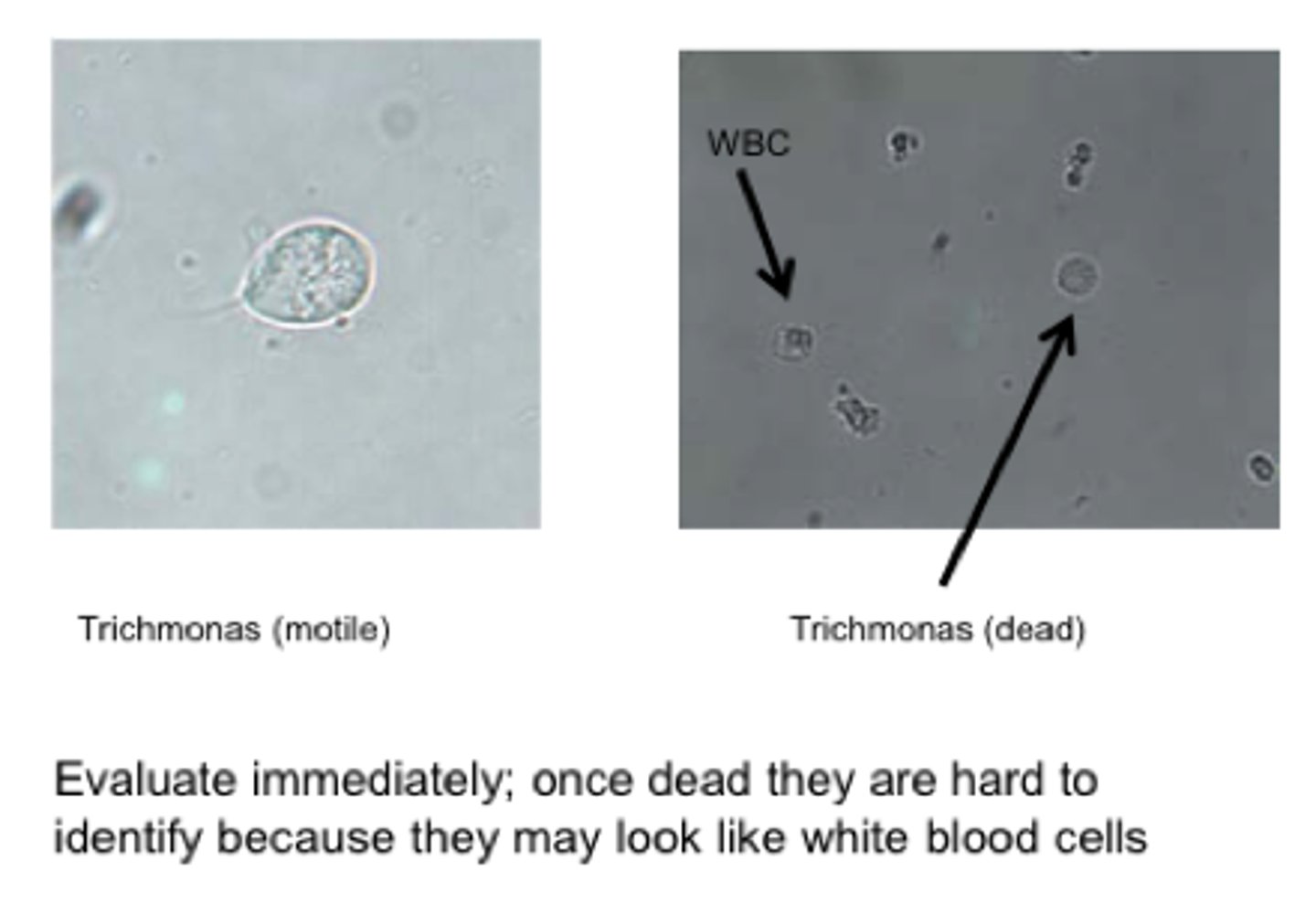
Significance of trichomonas vaginalis dying quickly once removed form vaginal mucosa...
- Since they i.e. quickly, you need to evaluate the vaginal secretion sample ASAP
- once they are dead they are difficult to identify because they may look like WBC
What is the most common cause of vaginal infections?
Bacterial vaginosis
What causes bacterial vaginosis?
- caused by alteration of the normal bacterial flora of the vagina
- NOT an exogenous pathogen
Bacterial vaginosis involved replacing lactobacilli with....
Lactobacili= present in healthy vaginal secretions
- Lactobacilli are replaced by overgrowth/proliferation of:
Gardnerella vaginalis, Mobiluncus species, and others
Malodorous vaginal discharge, especially following intercourse, indicates....
Bacterial vaginosis
In patient with bacterial vaginosis, why does the malodorous discharge occur following sex?
- Alkaline seminal fluid (7.2-7.8) alters vaginal pH which volatilizes the polyamides present to trimethylamine
Symptoms associated with bacterial vaginosis
- often asymptomatic with only complaint of a malodorous vaginal discharge
- alteration of vaginal pH causes trimethylamine = foul, fishy smell
- gray to off-white, thin, homogenous vaginal discharge
An alkaline fluid alters the vaginal pH which volatilizes the polyamides present to.....
Trimethylamine
= gives the foul, fishy odor of the vaginal discharge
What symptoms are noticeably absent in bacterial vaginosis?
- vulvovaginal pruritus, soreness, and dyspareunia
Dysparenunia defintion
- painful sexual intercourse
Diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis involves...
ruling out candidiasis and trichomoniasis
Complications of bacterial vaginosis...
If bacterial vaginosis goes undiagnosed or untreated...
- progression to endometritis and pelvic inflammatory disease if not treated
- pregnant women have increased risk of premature amor and delivery of low-birth-weight infants
Diagnosis of Bacterial vaginosis
3 of the following 4 features is diagnostic
- Presence of clue cells
- positive amine test (whiff test)
- Vaginal pH >4.5
- Homogenous vaginal discharge
Additional consistent findings:
- lack if increase in WBC
- lack of decreased lactobacilli
- KOH examination is negative
When trying to diagnose bacterial vaginosis, if the wet mount and amine test are inconclusive... next step?
DNA probe analysis for Gardnerella vagialis is useful
Are cultures used to diagnosis bacterial vaginosis?
Culture is NOT useful
- 50-60% of healthy, asymptomatic women have a positive culture
Vaginosis vs Vaginitis
- Vaginitis: Increased WBCs are consistent with Vaginitis
- Vaginosis: Lack of increase in WBC suggest no invasion of the sub epithelial tissue
Treatment for Bacterial vaginosis
- Methronidazole (oral) is recommended treatment
How common is recurrence of bacterial vaginosis, and reason for recurrence?
- Recurrence in 30% of cases
- failure to re-establish microbial balance dominated by lactobacilli
New treatment for bacterial vaginosis that is not an oral antibiotic
- suppositories containing lactobacillus to recolonize once the invading bacteria has been killed