Inflammation (Cram)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the latin word meaning "to set on fire"?
Inflammare
What are the five cardinal signs of inflammation?
Heat
Redness
Swelling
Pain
Loss of function
What are the latin names for the five cardinal signs of inflammation?
Calor – Heat
Rubor – Redness
Tumor – Swelling
Dolor – Pain
Functio laesa – Loss of function
Suffix that means inflammation of a particular tissue or organ
Itis (ex. dermatitis, orchitis, meningitis, etc)
What are the three ways that inflammation minimizes the effect of an irritant?
Attack
Inactivate
Destroy
Accumulation of fluid and cells in the tissue effected by inflammation
Exudate
Where are the two places that exudate may collect?
On the serosal surface (outer surface)
Within tissues
What are the five functions of inflammatory exudate? Remember: Don't Let Dads Ride Rollarcoasters (mine always threw up)
Dilute
Localize
Destroy
Remove
Replace
What are the three componants of the inflammatory response?
Vascular response
Cellular response
Chemotaxis
What is present in tissues in an inactive form, and is activated by injury?
Chemical mediators (ex. histamins, prostagladin, kinins)
What are the two effects of chemical mediators?
Vasodilation
Increased permeability
Migration of blood cells through the unruptured wall of capillary vessles
Diapedesis
What are the movements that leukocytes do during diapedesis?
Amoeboid movements
What WBC is usually the first to respond to injury?
Neutrophils
What are the three things that neutrophils respond well to?
Bacteria
Necrotic tissue
Antigen–antibody reactions
What are the two functions of neutrophils?
Phagocytosis
Lysosome release
Because phagocytosis and lysosome release stimulate the inflammatory response by damaging tissue, inflammation is said to be ___________
self–perpetuating
On a leukogram, the hallmark of inflammation is what?
Left shift
Neutrophilia with an increased number of immature neutrophils (mature neutrophils still out number immature)
Regenerative left shift
Normal neutrophil count or neutropenia with increased immature neutrophils, or the number of bands approaches of exceeds the number of mature neutrophils
Degenerative left shift
What are the two situations where more eosinophils are seen?
Allergic reactions
Parasites
Eosinophils can produce pus, especially in what species?
Cats
True or false: Basophils are primarily found in circulation, not tissues
True
What type of cell has similar properties to basophils?
Mast cells (but these can be found in tissue)
Basophils are part of the phagocytic system, is it phagocytic?
No. Despite being part of this system, basophils do not phagocytize
What are the two things that basophils release?
Histamines
Heparin
Anticoagulant released by basophils that prevents clotting so other WBC's can move freely
Heparin
Vasodilator released by basophils which promotes blood flow to the tissues
Histamine
What kind of symptoms are basophils associated with?
Allergic symptoms
What kind of response are lymphocytes primarily associated with?
Immune responses
What two areas do lymphocytes rove back and forth between?
Circulation
Lymph tissue
Monocytes are associated with ________ inflammation
chronic
True or false: Monocytes respond later than other WBC's to tissue insult/injury
True
What do monocytes become in tissue?
Macrophages
What is the primary function of monocytes?
Phagocytosis
What type of cell is formed by the activation and differentiation of macrophages?
Epithelioid cell
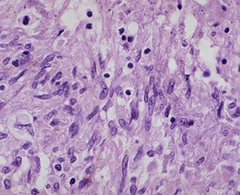
What gives epithelioid cells their name?
Large and flattened like epithelium
Epithelioid cells are common in what type of lesion?
Granulomatous lesions
What are some examples of diseases featuring epithelioid cells?
Tuberculosis, johnes disease, syphilis
What type of cells develop from the further differentiation and fusion of epithelioid cells?
Giant cells
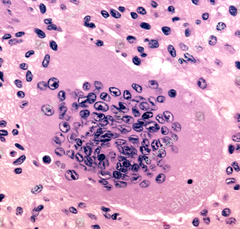
Giant cells are common in what type of reaction?
Foreign body reaction
What are the two ways to classify exudates?
Chronological (time)
Morphological (appearence)
What are the four chronological catagories?
Per acute <24hrs
Acute >24hrs
Subchronic 1–3 weeks
Chronic weeks, months, year
What are the six morphological catagories? Remember: Seniors F*cking Hate Cats Peeing in Gardens
Serous
Fibrinous
Hemorrhagic
Catarrhal
Purulent
Granulomatous
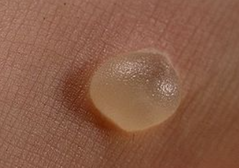
Which morphological catagory is this exudate?
Serous. It's watery and clear. May be cloudy as neutrophils begin to appear (picture is of a blister)

Which morphological catagory is this exudate?
Catarrhal. The primary component is mucus (ex. respiratory infection)

Which morphological catagory is this exudate?
Hemorrhagic (picture is of a dog with parvovirus)
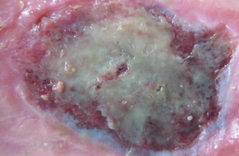
Which morphological catagory is this exudate?
Fibrinous. Is a gelatinous yellow fluid or solid rubber mat
What bacterial disease features fibrinous exudate?
Bovine shipping fever
What two surfaces can fibrinous exudate form on?
Serosal surface
Mucosal surface
True or false: Fibrinous exudate indicates severe vascular injury, allowing leakage of large plasma proteins such as fibrinogen
True
What does fibrinogen polymerize into?
Fibrin
Organization of fibrinous exudates into fibrinous tissue can cause _____ tissue
scar
What is fibrinous exudate called when it entirely fills the lumen of an organ?
Fibrin cast
What is fibrinous exudate called when it is embedded in tissue and not easily removed?
Diptheretic membrane

Which morphological catagory is this exudate?
Purulent. It is primarily composed of pus
Term for the process of pus formation?
Suppuration
Term for something causing pus to be formed
Pyogenic (ex. Strep. equi, Staph. aureus)
Term for a circumscribed (partially walled off) collection of pus
Abscess
Term for when an abscess drains to the skin
Fistula
Term for a localized collection of pus under the epidermis
Pustule
Term for a collection of pus within a body cavity or hollow organ
Empyema (ex. pyothorax)
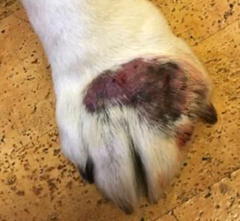
Which morphological catagory is this exudate?
Granulomatous exudate (picture is a lick granuloma)
What are the two predominant components of granulomatous exudate?
Marcophages
Lymphocytes