b1 and 2 cell structure and support
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Students should be able to demonstrate an understanding of the scale and size of cells and be able to make order of magnitude calculations, including the use of standard form. Students should be able to, when provided with appropriate information,explain how the structure of different types of cell relate to their functionin a tissue, an organ or organ system, or the whole organism. Students should be able to explain the importance of cell differentiation Students should be able to: • understand how microscopy techniques have developed over time • explain how electron microscopy has increased understanding of sub-cellular structures. Students should be able to calculate cross-sectional areas of colonies or clear areas around colonies using πr². MS 5c Students should be able to calculate the number of bacteria in a population after a certain time if given the mean division time. MS 1a, 2a, 2h (HT only) Students should be able to express the answer in standard form. Students need to understand the three overall stages of the cell cycle but do not need to know the different phases of the mitosis stage. Cell division by mitosis is important in the growth and development of multicellular organisms. Students should be able to recognise and describe situations in given contexts where mitosis is occurring. Students should be able to describe the function of stem cells in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants. Students should be able to explain how different factors affect the rate of diffusion. Students should be able to calculate and compare surface area to volume ratios. Students should be able to explain the need for exchange surfaces and a transport system in multicellular organisms in terms of surface area to volume ratio. Students should be able to explain how the small intestine and lungs in mammals, gills in fish, and the roots and leaves in plants, are adapted for exchanging materials. Students should be able to, when provided with appropriate information, explain how the structure of different types of cell relate to their function in a tissue, an organ or organ system, or the whole organism.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus. eukaryotic cellular complex multicellular organisms
Bacterial cells (prokaryotic cells) are much smaller in comparison and unicellular. They have cytoplasm and a cell membrane surrounded by a cell wall. The genetic material is not enclosed in a nucleus. It is a single DNA loop and there may be one or more small rings of DNA called plasmids.
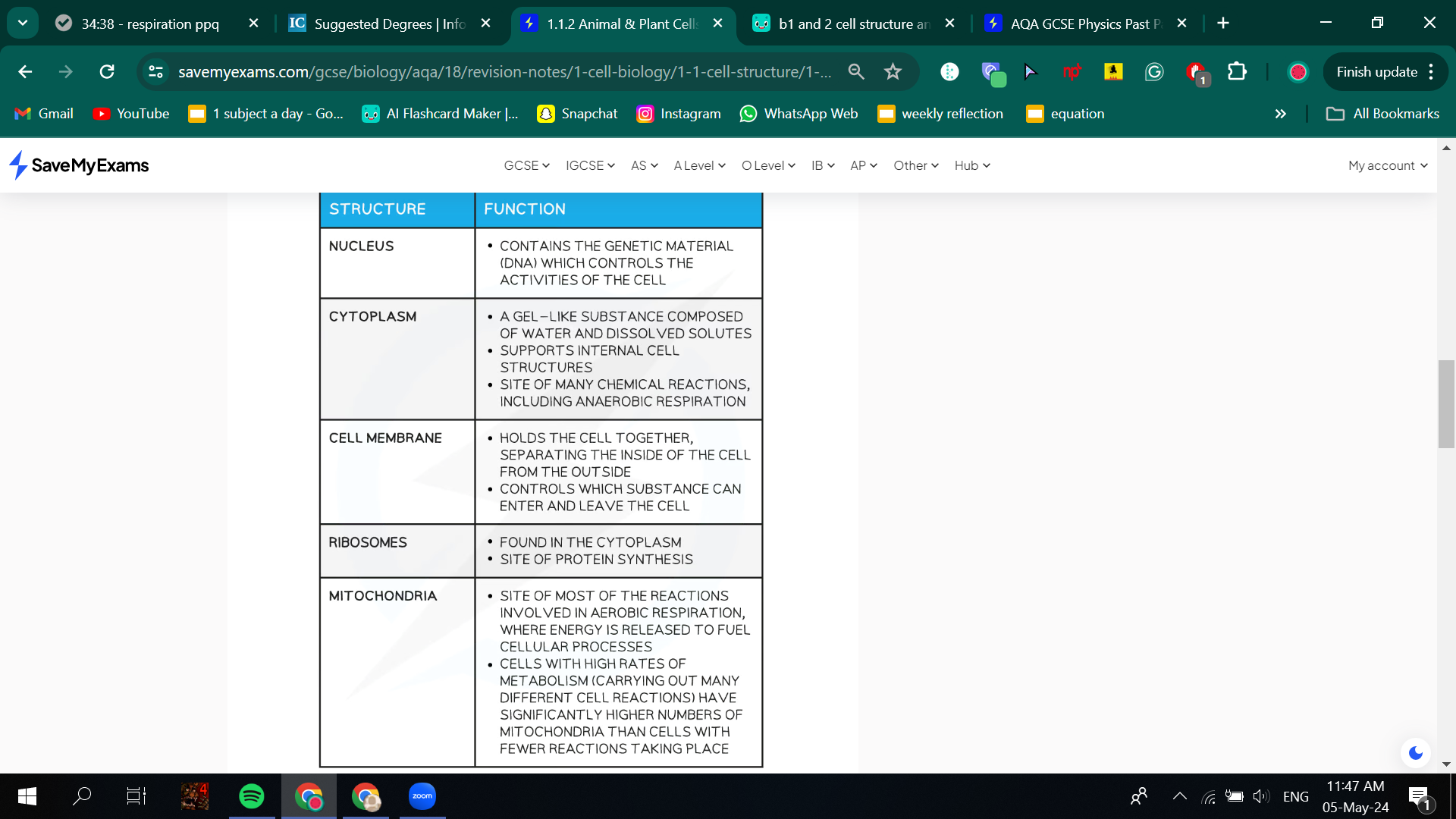
Animal and plant cells features
Most animal cells have the following parts:
• a nucleus controls the activities of the cells
• cytoplasm mainly water that holds the ribosomes
• a cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out. glucose and oxygen in carbon dioxide out via diffusion
• mitochondria small organelle which are the site of respiration. they have folds that increase the surface area to volume ratio making them more efficient
• ribosomes site of protein synthesis
In addition to the parts found in animal cells, plant cells often have: • chloroplasts needed for photosynthesis and produce chlorophyll
• a permanent vacuole filled with cell sap keeping the cell turgid and strong
Plant and algal cells also have a cell wall made of cellulose, which strengthens the cell.
cell specialisation
Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function:
• nerve cells they have a long fibre (axon) so they can carry messages up and down the body over long distances
in a stimulated neuron, an electrical nerve impulse passes along the axon
the axon is insulated by a fatty (myelin) sheath - the fatty sheath increases the speed of the nerve impulses along the neuron
at each end of the neuron are tiny branches (dendrons), which branch even further into dendrites - the dendrites receive incoming nerve impulses from other neurons
muscle cells have lots of mitochondria for contraction and relaxation. contain filaments of protein that slide over each other to cause muscle contraction.
• root hair cells large surface area to volume ratio to absorb as much water and minerals as possible.they also have lots of mitochondria for the active transport of minerals
xylem dead There are no top and bottom walls between xylem vessels, so there is a continuous column of water running through them. Their walls become thickened and woody. They therefore support the plant.
phloem live cells in plants that have sieve plates Dissolved sugars and amino acids can be transported both up and down the stem. Companion cells, adjacent to the sieve tubes provide energy required to transport substances in the phloem.
adaptations of sperm
Its role is to deliver genetic material to an egg cell to fertilise it
It has half as much genetic material as a normal cell, so that the sperm and egg together will have the normal amount
It has lots of mitochondria to provide the energy for movement
It has a flagellum to allow it to swim to reach the egg
It is streamlined to make swimming easier
It has digestive enzymes in its head to break through the wall of the egg
Give two drawbacks of using embryonic stems cells in stem cell therapy.
model answer:The embryonic stem cells must come from embryos. These are in limited supply, and some people have ethical objections to it, as they think the embryos could have developed into a person.The cells could be rejected by the person's immune system as it would identify them as foreign.
Stem cells have a limited supply
The risk of rejection
Ethical issues associated with stem cells
List three factors that affect the rate of diffusion.
Concentration gradient
Temperature
Surface area
Distance to diffuse across (if diffusing across a membrane
Why does a higher temperature increase the rate of diffusion?
Higher temperature means particles have more (kinetic) energy
So they move around faster
And can diffuse more quickly
Give two examples of exchange surfaces in humans and describe their function.
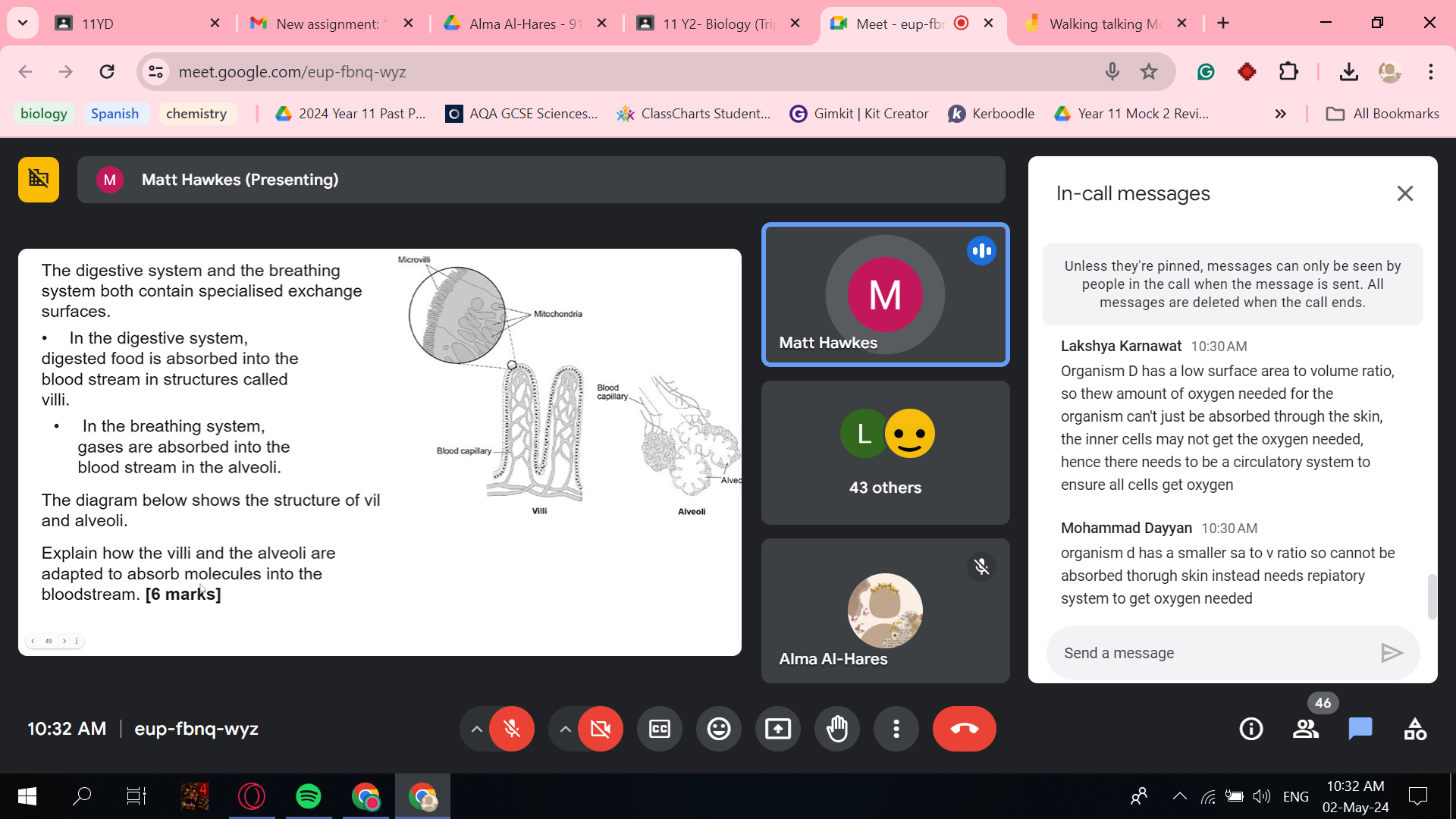
Example 1 - Alveoli (or lungs)
Example 1 - Alveoli allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse in and out of the body/bloodstream
Example 2 - Villi (or small intestines)
Example 2 - Villi allow nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, mineral ions etc to be absorbed from the small intestines into the bloodstream
State and explain three features that most exchange surfaces have in common.
Feature 1 - Large surface area
Explanation 1 - Lots of molecules can diffuse across at the same time
Feature 2 - Surfaces are very thin
Explanation 2 - Substances only have to diffuse a short distance
Feature 3 - Surfaces are permeable
Explanation 3 - Substances are able to pass through the surface
Feature 4 - Good blood supply (good supply of 'internal medium')
Explanation 4 - Maintains a strong concentration gradient as blood is constantly replaced
Feature 5 - Good supply of 'external medium'
Explanation 5 - Maintains a strong concentration gradient as the air or food etc is constantly replaced
State and explain three features of alveoli that make them good exchange surfaces.
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
Cell differentiation
As an organism develops, cells differentiate to form different types of cells.
• Most types of animal cell differentiate at an early stage.
• Many types of plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughout life. In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacement. As a cell differentiates it acquires different sub-cellular structures to enable it to carry out a certain function. It has become a specialised cell.
Microscopy
Limited to the differences in magnification and resolution. An electron microscope has much higher magnification and resolving power than a light microscope. This means that it can be used to study cells in much finer detail. This has enabled biologists to see and understand many more sub-cellular structures. formula: magnification = size of image /size of real object
Culturing microorganisms (biology only)
Bacteria multiply by simple cell division (binary fission) as often as once every 20 minutes if they have enough nutrients and a suitable temperature. Bacteria can be grown in a nutrient broth solution or as colonies on an agar gel plate. Uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms are required for investigating the action of disinfectants and antibiotics.
method of culturing microorganisms
Petri dishes and culture media must be sterilised before use
• inoculating loops used to transfer microorganisms to the media must be sterilised by passing them through a flame
• the lid of the Petri dish should be secured with adhesive tape and stored upside down
• in school laboratories, cultures should generally be incubated at 25°C.
chromosomes
The nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules. Each chromosome carries a large number of genes. In body cells the chromosomes are normally found in pairs.
cell division
Cells divide in a series of stages called the cell cycle. Students should be able to describe the stages of the cell cycle, including mitosis. During the cell cycle the genetic material is doubled and then divided into two identical cells. Before a cell can divide it needs to grow and increase the number of sub-cellular structures such as ribosomes and mitochondria. The DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome. In mitosis one set of chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides. Finally the cytoplasm and cell membranes divide to form two identical cells.
stem cells
A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which is capable of giving rise to many more cells of the same type, and from which certain other cells can arise from differentiation. Stem cells from human embryos can be cloned and made to differentiate into most different types of human cells. Stem cells from adult bone marrow can form many types of cells including blood cells. Meristem tissue in plants can differentiate into any type of plant cell, throughout the life of the plant.
Knowledge and understanding of stem cell techniques are not required. Treatment with stem cells may be able to help conditions such as diabetes and paralysis. In therapeutic cloning an embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient. Stem cells from the embryo are not rejected by the patient’s body so they may be used for medical treatment. The use of stem cells has potential risks such as transfer of viral infection, and some people have ethical or religious objections.
Stem cells from meristems in plants can be used to produce clones of plants quickly and economically.
• Rare species can be cloned to protect from extinction.
• Crop plants with special features such as disease resistance can be cloned to produce large numbers of identical plants for farmers.
diffusion
Substances may move into and out of cells across the cell membranes via diffusion. Diffusion is the spreading out of the particles of any substance in solution, or particles of a gas, resulting in a net movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Some of the substances transported in and out of cells by diffusion are oxygen and carbon dioxide in gas exchange, and of the waste product urea from cells into the blood plasma for excretion in the kidney.
Factors which affect the rate of diffusion are: • the difference in concentrations (concentration gradient) • the temperature • the surface area of the membrane. A single-celled organism has a relatively large surface area to volume ratio. This allows sufficient transport of molecules into and out of the cell to meet the needs of the organism.
exchange surfaces
In multicellular organisms, surfaces and organ systems are specialised for exchanging materials. This is to allow sufficient molecules to be transported into and out of cells for the organism’s needs. The effectiveness of an exchange surface is increased by: • having a large surface area • a membrane that is thin, to provide a short diffusion path • (in animals) having an efficient blood supply • (in animals, for gaseous exchange) being ventilated.
osmosis
Water may move across cell membranes via osmosis. Osmosis is the diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane.
active transport
Active transport moves substances from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution (against a concentration gradient). This requires energy from respiration. Active transport allows mineral ions to be absorbed into plant root hairs from very dilute solutions in the soil. Plants require ions for healthy growth. It also allows sugar molecules to be absorbed from lower concentrations in the gut into the blood which has a higher sugar concentration. Sugar molecules are used for cell respiration. Students should be able to: • describe how substances are transported into and out of cells by diffusion, osmosis and active transport • explain the differences between the three processes.
electron microscopes
use electrons in rays of light to creat an image since electrons are very smaller than visible light higher magnifications can be used .
metod of preparing onion cell to see thorugh microscope
Use tweezers to peel back a layer of epidermal tissue
Add a drop of water to a clean slide
Spread the epidermal tissue out on the slide
Ensure the tissue is one cell thick
Add a drop of dye / iodine / stain so structures are visible / clear
Place a cover slip over the top
Tap gently to remove air bubbles
Dab away any excess dye from the slide
why is an under developed root hair cell detrimental to a plant
The purpose / function of the root hair is to increase surface area; [1 mark]
For absorption of water (by osmosis); [1 mark]
(And) for absorption of mineral ions / named example (e.g. magnesium ions, nitrate ions); [1 mark]
Less root hairs would reduce absorption; [1 mark]
Water is essential for photosynthesis / maintaining pressure / as a solvent; [1 mark]
(Reduced absorption) could lead to mineral deficiencies, causing stunted growth / named example of mineral deficiency described; [
an four of
Differentiation plays the following role in producing root hair cells which allow them to carry out their function:
Differentiation determines cell shape / development of specific organelles (to allow them to carry out a particular function); [1 mark]
Root cells grow extensions / root hairs to give a large surface area to volume ratio this allows maximum uptake of water by osmosis; [1 mark]
They also develop many mitochondria to provide energy for active transport of mineral ions; [1 mark]
A large vacuole for storage of water and minerals to maintain a concentration gradient (for continuous uptake of water by osmosis); [1 mark]
Root hair cells have no chloroplasts, as they do not photosynthesize; [1 mark]
Starch found in the roots of grass supports growth in the following way:
Glucose is stored as starch in plants; [1 mark]
Energy is released from glucose in respiration; [1 mark]
Energy is required for growth / building of new molecules OR energy is required for active transport of mineral ions / nitrates into the root; [1
mitosis
2 daughter cells are produced
used to help cells reproduce naturally
tutorial:
chromosome multiply and line up as the membrane and nucleus dissapear
then the copies and original chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell
cell membrane divides(cytokinesis)
cells are formed
simalarities between mitosis and meiosis
mitosis produces two (daughter) cells but meiosis produces four (daughter) cells
one cell division in mitosis but two cell divisions in meiosis
mitosis produces cells with two of each chromosome, but meiosis produces cells with one of each chromosome
mitosis produces genetically identical cells, but meiosis produced genetically different cells
simalarities between mitosis and meiosis
DNA doubles / copies / replicates (once)
increase in the number of mitochondria / ribosomes / sub-cellular structures
advantages of asexual reproduction
many offspring produced • takes less time
• (more) energy efficient
• genetically identical offspring allow offspring are clones
• successful traits propagated / maintained / passed on (due to offspring being genetically identical)
• no transfer of gametes or seed dispersal allow no vulnerable embryo stage allow no need for animals
• not wasteful of flowers / pollen / seeds
• colonisation of local area
why is sexual reproduction an advantage
genetic variation (in offspring) 1 (so) better adapted survive allow reference to natural selection or survival of the fittest 1 (and) colonise new areas by seed dispersal
or
can escape adverse event in original area (by living in new area) must imply new area 1 many offspring so higher probability some will survive
stem cells in mammels
stem cells:embryonic and adult stem cells
can differentiate into other types of cells
embryonic stem cells
can differentiate in ANY type of cell and are found in the embryo aka totipotent after this it can change anymore
advantages and disadvantages of embryonic cells
can create many embryos in a lab
• painless technique
• can treat many diseases / stem cells are pluripotent / can become any type of cell (whereas bone marrow can treat a limited number) embryos disadvantages
• harm / death to embryo
• embryo rights / embryo cannot consent
• unreliable technique / may not work
advanatages nd disadvantage from stem cells collected from bone marrow
bone marrow advantages
• no ethical issues / patient can give permission
• can treat some diseases
• procedure is (relatively) safe / doesn’t kill donor
• tried and tested / reliable technique
• patients recover quickly from procedure
bone marrow disadvantages
• risk of infection from procedure
• can only treat a few diseases
• procedure can be painful both procedures advantage can treat the disease / problem both procedures disadvantages
• risk of transfer of viral infection
• some stem cells can grow out of control / become cancerous
adult stem cells
found in bones
use to repair the body when damaged
they can only differentiate into the type of cells that they are near
they cannot differentiate into any type of stem cell
aka multipotent
example animals with embryonic stem cells throughout their lives
starfish can regrow itself if all its legs are ripped off
lizards can regrow their tail and parts of their body
stem cells in plants
stem cells can differentiate throughout their whole lives
found in the meristem
found at the roots and shoots of plants
hence cutting can be taken and grow well
rare plants are grown this way
e.g roses and orchids
stem cell research
is an ethical issues
people disagreee for religous and moral reasons
religous-jehovas witness
moral- some thing its bad because the research comes from aborted babies
medical uses of stem cells
treatment for paralysed patients creating new nerve cells in spinal chord or brain
treat conditions such as diabetes
replaces choroid in eye so patient can see
replace defective organ
how gases/minerals are transferred through the vili and alveoli
asceptic techniques
Aseptic technique is a set of practices that protects patients from healthcare-associated infections and protects healthcare workers from contact with blood, body fluid and body tissue.
in regards to culturing microorganisms they help obtain and pure culture of bacteria
aseptic techniques to use when investigatingculturing microorganisms
Aseptic technique is a set of practices that protects patients from healthcare-associated infections and protects healthcare workers from contact with blood, body fluid and body tissue.
features of nerve cells
long
has branches
has insulation
simalarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
both have
• cytoplasm
• (cell) membrane
• DNA / genetic material
ribosomes
substances in growth medium
glucose / sugars / starch
amino acids / protein
hormones allow named hormones e.g. auxin
ions / minerals allow magnesium / nitrate
vitamins
water allow H2O / H2O ignore oxyg
how is mycoprotein produced
fungus / Fusarium
with glucose (syrup
aerobic conditions or in presence of oxygen ignore air
mycoprotein is harvested / purified allow ammonia added (as source of nitrog
adaptations of lungs
(many) alveoli • provide a large(r) surface area (: volume)
• capillaries are thin or alveoli / capillary walls are thin or one cell thick or capillaries are close to the alveoli
• which provides short diffusion path (for oxygen / carbon dioxide)
• breathing (mechanism) moves air in and out or lungs are ventilated
• to bring in (fresh) oxygen
• to remove carbon dioxide • to maintain a concentration / diffusion gradient
• large capillary network (around alveoli) or good blood supply • to remove oxygen(ated blood) quickly
• to bring carbon dioxide to the lungs quickly • to maintain a concentration / diffusion gradient
how ion, water and sugar are transported through a plant
Water: (P) taken up by osmosis • from an area of low to high concentration allow high concentration of water to low concentration of water allow from high water potential to low water potential ignore along a concentration gradient (V) travels in the xylem (M) to the leaves or from the roots / soil (P) transpiration stream • movement replaces water as it evaporates from leaves (V) in the xylem Sugar: (P) made during photosynthesis travels in the phloem (M) to other parts of the plant or to storage organs or travels up and down