Plant Phys exam 1 material
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
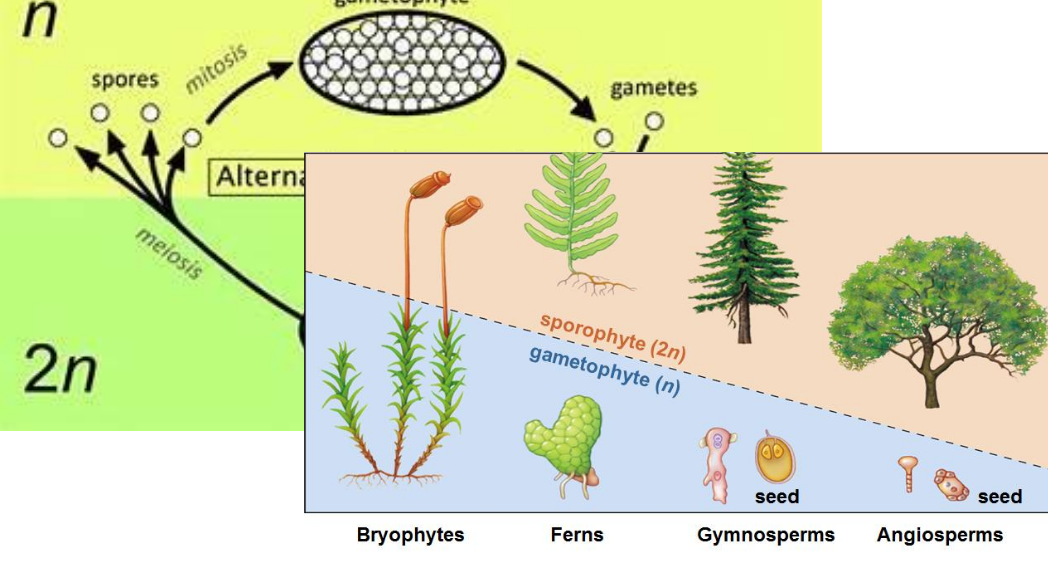
Plant Life: Commonalities in design elements
• Primary producers
• Non-motile
• Terrestrial plants are structurally reinforced
• Terrestrial plants have mechanisms for moving water, minerals, & photosynthates
• Terrestrial plants lose water continuously via evaporation
• Meristematic growth is indeterminate
• Alternation of generations
alternation of generations
Plant structure
rigid cell wall
middle lamella
primary cell wall
secondary cell wall
simple pits
pit pairs
cytoplasm
cytosol
middle lamella
made of Ca and Mg
pectins that act as a glue between plant cell walls.
primary cell wall
thin (<1um) characteristic of young, growing cells
that provides support and flexibility.
Secondary cell wall
thicker and stronger. Lignin makes cell walls tough.
It is formed after the primary cell wall and provides additional support and protection to the plant cell, often found in mature cells.
simple pits
circular gaps in secondary wall with thin primary cell wall.
Facilitates water movement between cells
pit pairs
adjoining simple pits
cytoplasm
everything except for the nucleus (ions, molecules, organelles, cytoskeleton, NOT nucleus)
cytosol
liquid portion, separate from organelles, vesicles, ribosomes
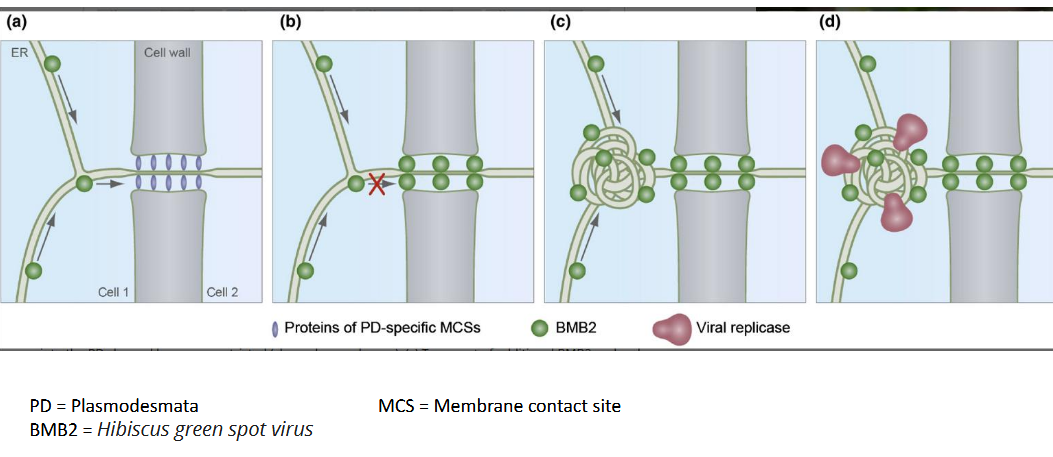
plasmodesmata
channel connecting adjacent cells through cell wall. Filled with cytoplasm, derived from the endoplasmic reticulum. Allows movement of molecules from cell to cell through the symplast
symplasm/symplast
Continuous system of cell interconnected by
plasmodesmata.
Allows for intercellular transport of water
and solutes
apoplast
Mostly continuous system of cell walls, intercellular
air spaces and xylem vessels
symplasm
transports water, solutes, macromolecules between cells without crossing the plasma membrane. However, there is a restriction on the size of molecules
how do plant viruses spread
systemically through the symplast if viral movement proteins expand the size exclusion limit
pericycle
lateral roots
vascular cambium
between xylem & phloem, increases girth, produces wood
cork cambium
produces periderm (water-resistant protectant layer)
three major tissue system
dermal tissue
vascular tissue
ground tissue
parenchyma tissue
very little intercellular space
and is involved in storage, photosynthesis, and tissue repair.
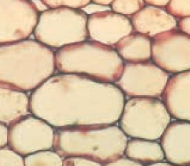
collenchyma tissue
provides support and flexibility to young plants.
more intercellular space
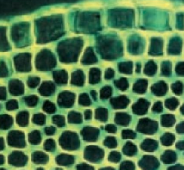
sclerenchyma tissue
provides structural support with thickened secondary cell walls.
typically contains dead cells at maturity.
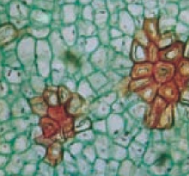
dicot stem vs monocot stem
dicot = vascular tissue in ring
monocot = vascular tissue throughout
Endomembrane system & peroxisomes
ER, nuclear envelope, Golgi apparatus,
vacuole, endosomes, plasma
membrane, oil bodies, peroxisomes,
glyoxysomes.
organelle functions,
secretory processes, cell signaling,
metabolits and hormone production,
membrane recycle, cell cycle, cell
expansion.
Independently dividing semiautonomous organelles of
endosymbiotic origin
Plastids, mitochondria
Function: energy metabolism and
energy storage
fluid mosaic model
double layer (bilayer) of either phospholipids or
glycosylglycerides in which proteins are
embedded
phosolipids
Hydrophilic head containing a
phosphate group with a variable
component (such as serine, choline, or
inositol).
• Hydrophobic tail derived from fatty
acids
• Tail and head joined by a glycerol
molecule
GLYCOSYLGLYCERIDES
• Head group: galactose, digalactose, sulfated galactose
• Primarily found in chloroplast membranes
• Consist of glycerol, attached to one or two sugar molecules and two fatty acids.
• The sugars attached to the glycerol are either glucose,
galactose, or a digalactose unit
protein functions
enzymes
transport molecules
storage
electron carriers
integral proteins
embedded in the lipid bilayers. Usually span the entire
width of the phospholipid bilayer.
Transporters (ion channels, carriers, pumps), signal transduction
peripheral proteins
bound to membrane by noncovalent bonds (ionic or hydrogen bonds) and hydrophobic interactions, and can be dissociated from membrane with high-salt solutions or agents that break ionic and hydrogen bonds.
Receptors, Microtubules, and Actin microfilaments
• (Anchored): bound to membrane surface by lipid molecules to which they are covalently attached. Usually reversible
endoplasmic reticulum
RER: secretory protein synthesis
(carried to destination by vesicle)
SER: membrane phospholipids and
carbohydrate synthesis
golgi aparatus
• Golgi body: polarized stack of
cisternae (i.e., sided – cis/trans).
• Accepts tubules and vesicles from ER
• Transport, modify & package proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to target destination
• Plant cells can contain 100s of G.A.
COP II proteins
ER to Golgi
COP I proteins
Golgi to ER
Clathrin
endocytosis (envagination)
oil bodies
• organelles that accumulate oil during seed development
• store triglycerides
• oil bodies break down during seed germination
peroxisomes
• Peroxisomes and glyoxisomes
• Peroxisomes – detoxify ROS
• Glyoxysomes – associated with
mitochondria and oil bodies
mitochondria
• Cellular site of respiration
• Synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi)
• Contains proton-pumping ATP synthase
• Proton gradient
• Electron transport chain
Leucoplasts
non –pigmented, store starch & oils
Amyloplasts
produce & store starches
microtubules
a microscopic tubular structure present in numbers in the cytoplasm of cells, sometimes aggregating to form more complex structures.
tublin dimers
can “treadmill” through the cell
orientation determines the shape (sphere vs cube)
microfilaments
actin subunits
the plant cytoskeleton
• Monomers contain bound nucleotide
• Actin – ATP/ADP
• Tubulin – GTP/GDP
• Both polarized
• Proteins prevent depolymerization
myosins
move along microfilaments (toward the + end)
kinesins
move along microtubules
cell cycle
• G1: newly formed daughter cell has not yet replicated its DNA
• S: DNA is replicated.
• G2: a cell with replicated DNA has not yet proceeded to mitosis
• G1, S, G2 = Interphase
• M-phase = mitosis