unit 1 human factors and ergonomics
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
define human factors
a term used for the combination of ergonomics and anthropometrics
what are the aims of human factors
reduce stress and fatigue to do things faster with less mistakes
increase safety
increase ease of use
enhance operational comfort
improve system performance, reliability, and maintenance
what are ergonomics
the application of scientific information regarding the relationship of human beings to the design of objects, systems, and environments
what do we mean by physical ergonomics? give an example
it most often deals with work related to the subjects of posture, worksite development, operating layout, repetitive stress and movement, etc. It is the aspect of ergonomics that deals with body measurements such as strength, size. strength and
what do we mean by cognitive ergonomics?
it is concerned with mental processes such as perception, memory, reasoning, and motor responses as they affect interactions among humans and other elements of a system.
What do we mean by the term organizational ergonomics? give an example
it includes communication, work design, shift (work hours) management, teamwork, quality management, etc.
what is anthropometric data?
it is sub-classified as static and dynamic data
what is structural anthropometric data?
aka static data refers to measurements taken while the subject is in a fixed position ex. height. it is easier to gather.
what is functional / dynamic data?
the measurement taken during physical activities, ex. overhead reach.
what tools can be used to collect anthropometric data?
sliding callipers, cloth tape, sitting height meters, and stadiometer
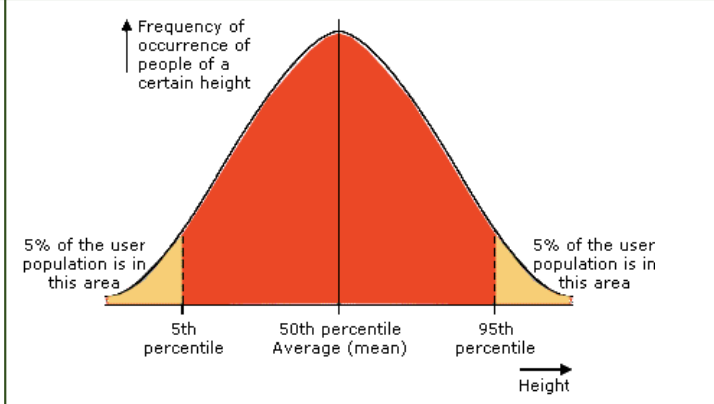
percentiles and percentile ranges
percentiles are shown in anthropometry tables and they tell you whether the measurement given in tables relates to the average person or if someone is below or above average in certain dimensions
what do we mean when we discuss clearance in human factors?
Clearance can be seen as the minimum distance required to enable the user group into or through an area. This is especially important when designing emergency exits and safety hatches.
what is reach
aka workspace envelope, it is the 3D space within which you carry out physical work activities when you are at a fixed position. usually designed for the 5th percentile of the user population, which means 95% of users will be able to reach everything within the envelope.
why does a designer need to consider adjustability when designing seating
certain products tend to be available in diff. sizes / adjustability, therefore this needs to be considered as it has an effect on the design of the legs.
what is meant by the range of sizes VS. adjustability
clothing comes in various sizes as one size cannot be adjusted to fit all but car seats are adjustable to allow for different range of sizes to fit.
what is an argonome and when are they used + advantages and disadvantages
A 2D scaled physical anthropometric model based on a specific percentile of human forms is called an ergonome. They are used with drawings of the same scale as the model to consider the relationships between the size of an object and the people. mainly used for orthographic drawings and modeling.
what is a manikin, and what are the advantages and disadvantages?
It is an anatomical 3D model of the human body. It is used by the artists. It is useful to assess the relationship of body parts to spatial arrangements. They are generally more expensive than ergometers, but they give a better representation of the overall ergonomics.
what is human error
it comes in serval different forms but two important ones are slips and mistakes. slips result from automatic behavior that is intended to satisfy our goals while mistakes results from conscious deliberations.
what are ways of optimizing environmental factors to maximize workplace performance?
lighting
thermal comfort
workspace
noise
vibration
what are some perception effects in products?
The principle that explains that the human mind considers objects in their entirety before the perception of their individual parts. This that suggests the whole is seen rather than the sum of parts.
what are physiological factors concerned with
they have to do with bodily tolerances such as comfort and fatugue. when users interact with a product, they may put stress on their bodies.
what is physical ergonomics concerned with
the human anatomy and some of the anthropometric, psychological, and biomechanical characteristics as they relate to physical activity.
what are some human values with types of physiological factors
it considers which activities can be carried out and how human values (ex. quality of life) are enhanced.
what is fatigue
the temporary diminishment of performance. it can be physical or mental fatigue.
what is comfort
the qualitative consideration that informs design decisions and can affect users.
what are biomechanics and what are they concerned with
it includes the research and analysis of muscle, joints, and tendons in the human body. it is used to measure the amount of force put on the muscles and joints of people when working in different positions. it deals with 4 criteria:
force
repetition
duration
posture
what are some factors affecting muscle strength and human factors
gender
age
pain / physical training
what is cognitive psychology / cognitive ergonomics
it is concerned with mental processes such as perception, memory, reasoning, etc. These affect interactions among humans and others
what are methods of collecting psychological factor data
observation
surveys and interviews
standardized testing
case studies
what is a nominal data scale
the classification / division of objects into discrete groups where each are identified with a name.
what is an ordinal data scale
the order or position of items where the letters / number / scales are in hierarchal order.
what is an interval data scale
organized into even divisions or interval of equal size without a zero
what is a ratio data scale
organized into even divisions of equal size however there is a true zero.
what are some psychological factor data
smell
light
sound
taste
texture
temperature
value
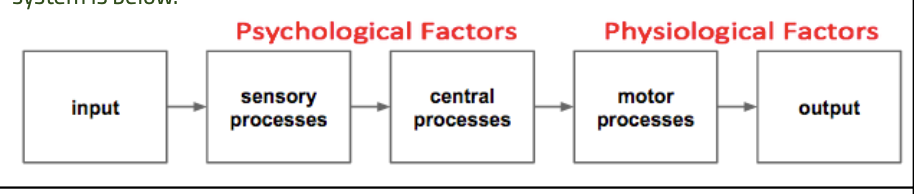
what is the human information processing system
it considers the input processes (sensory, central, and motor) and the outputs.
input: generated or received
sensory process: human senses take in info
central process: brain processes info and makes decision
motor process: a physical response
output: action carried out
what are examples of environmental factors
noise
temperature
lighting
humidity
hearing
etc
what is alertness
being aware of what is happening in the vicinity in order to understand how information and one’s own actions affect goals and objectives immediately and in near future. It depends on environmental factors.