Comps - dysphagia
1/406
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
407 Terms
Which muscle is responsible for the elevation of the hyoid bone?
Geniohyoid
The geniohyoid acts to elevate the hyoid bone.
Which cranial nerve primarily controls the larynx during swallowing?
CN X
CN X is the vagus nerve, and it is the source of innervation for the primary muscles acting on the larynx.
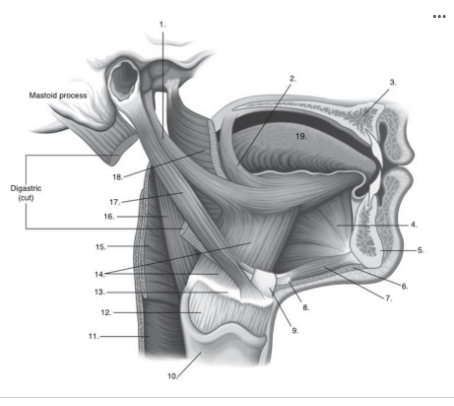
Identify number 6 in the image below:
Mylohyoid
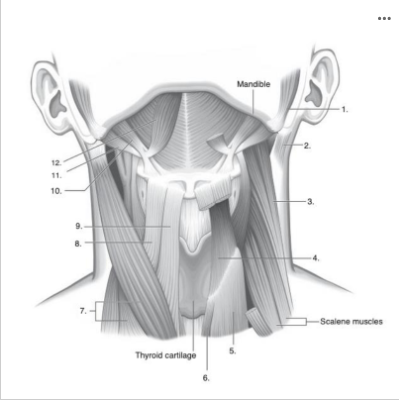
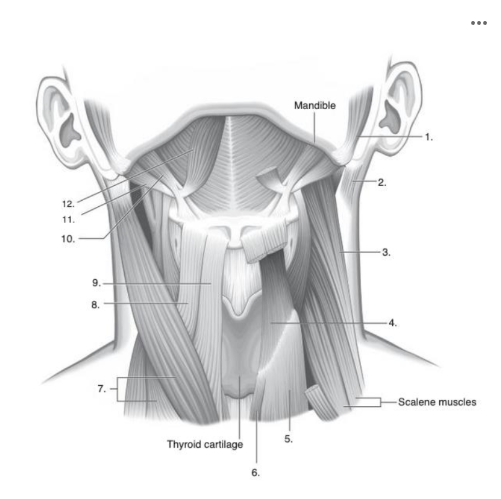
What muscle is indicated by the number 10 in the image below
Stylohyoid
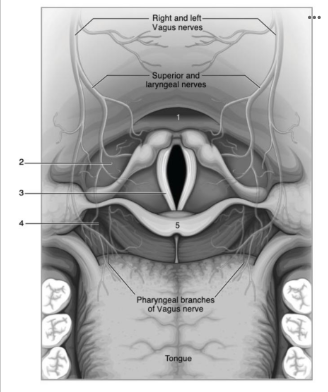
Use the image below to identify the structure labeled with a number 2:
Pyriform recess or sinus
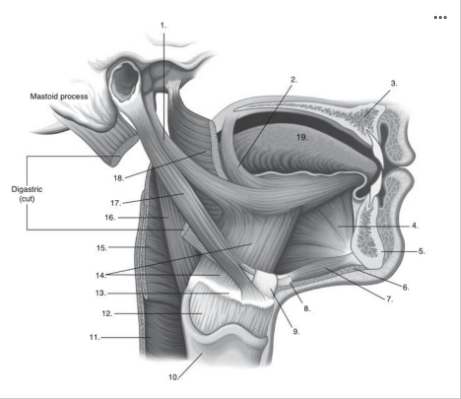
Identify number 5 in the image below:
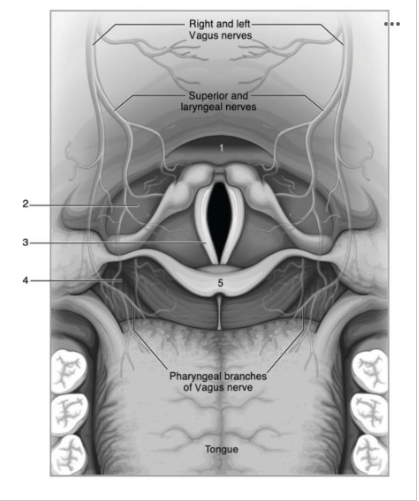
Use the image below to identify the structure labeled with a number 4:
Vallecula (epiglottis vallecula)
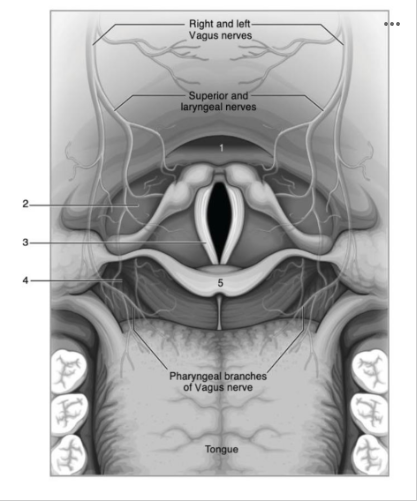
Use the image below to identify the structure labeled with a number 5:
Epiglottis
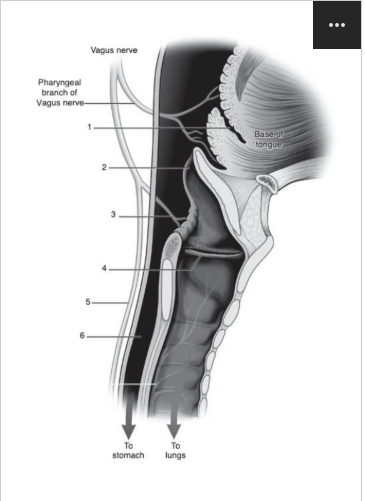
Identify number 2 in the image below:
epiglottis
Identify number 4 in the image below:
vocal folds
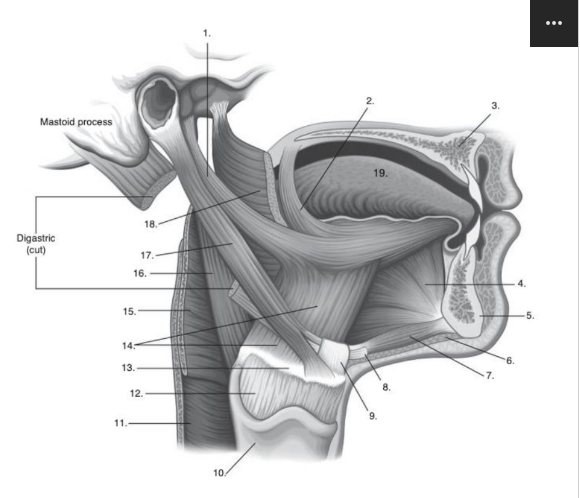
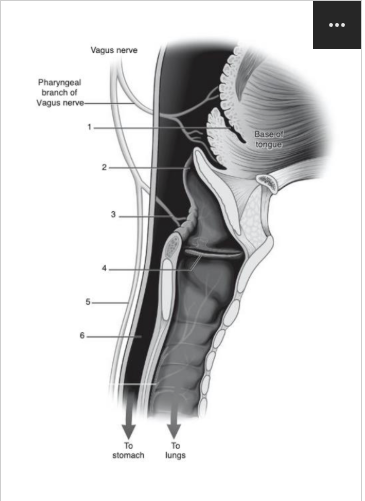
Identify number 7 in the image below:
geniohyoid
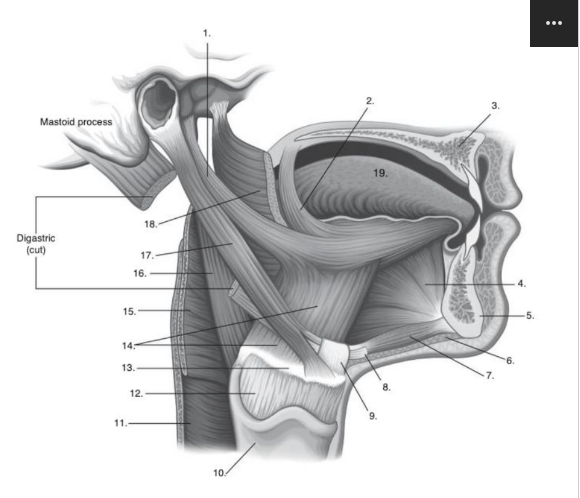
Identify number 3 in the image below:
hard palate
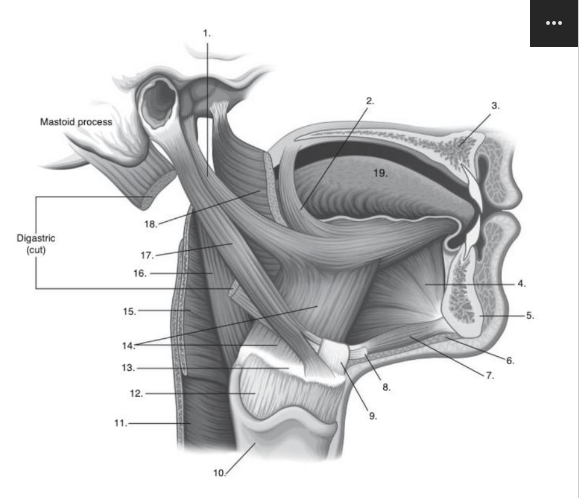
Identify number 19 in the image below:
tongue
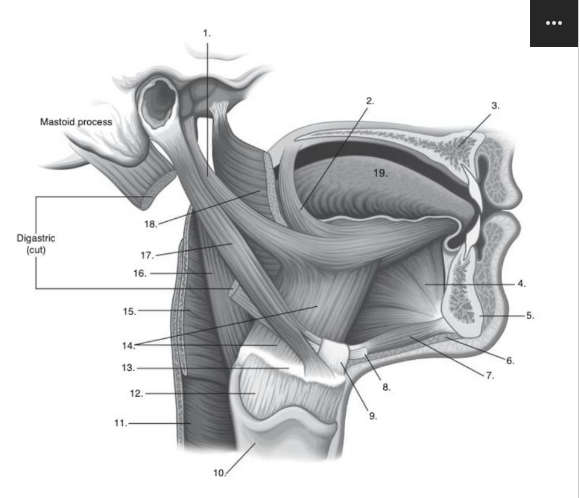
Identify number 10 in the image below:
thyroid cartilage
What muscle is indicated by the number 4 in the image below?
thyrohyoid
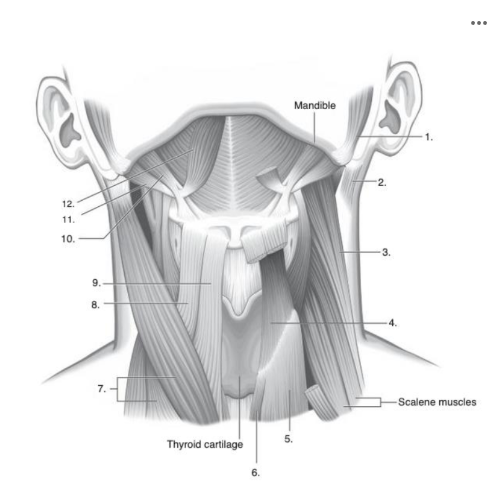
What muscle is indicated by the number 8 in the image below?
omohyoid
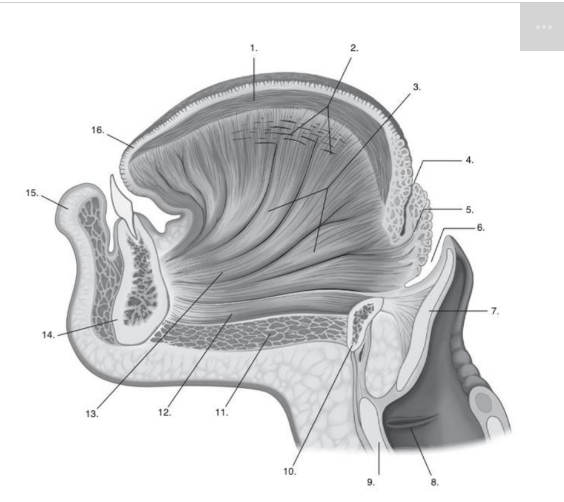
Identify number 13 in the image below:
genioglossus muscle
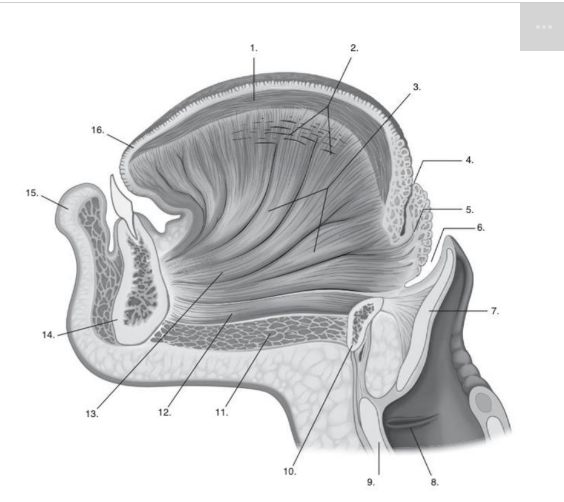
Identify number 6 in the image below:
vallecula of the epiglottis
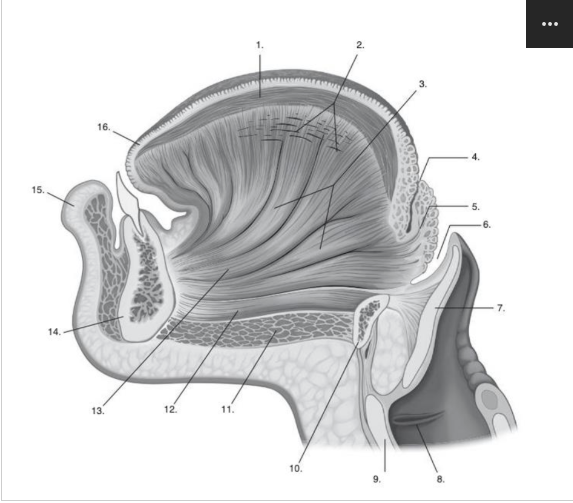
Identify number 1 in the image below:
superior longitudinal muscle of tongue
Which nerve provides motor innervation to the tongue?
CN XII
CN XII provides motor (efferent) innervation to the tongue.
Which cranial nerve controls sensation (tactile and pain) to the tongue?
CN V
Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal) is responsible for sensation (not taste) to the tongue.
The hyoid bone plays a role in swallowing.
True
The Vagus nerve (CN X) plays a crucial role in swallowing.
True
The intrinsic muscles of the tongue are controlled by
CN XII
CN XII (Hypoglossal) innervates the intrinsic tongue muscles.
Which type of pneumonia is commonly associated with dysphagia?
aspiration
Pneumonia associated with dysphagia is referred to as aspiration pneumonia. However, it's important to know that dysphagia is not the only cause of aspiration pneumonia, and not everyone with dysphagia ends up with aspiration pneumonia.
Which of the following is voluntary?
aspirating
reflexive coughing
chewing
moving food through the esophagus to the stomach
Chewing
Aspiration can be reliably detected by the presence of a cough or throat clear when an individual is eating or drinking.
False
Aspiration is silent up to 35% of the time, meaning there isn't a reliable way of accurately detecting aspiration without instrumentation.
Dysphagia only affects the elderly population.
False
Aspiration refers to
liquid or food passing into the airway below the vocal folds
Aspiration is the term for liquid or food entering the airway, past the vocal folds. The term for food or liquid feeling caught in the throat is globus sensation. The inability to cough when choking is simply the description of choking. Coughing after swallowing food or liquid can be related to aspiration, but is not always. Sometimes aspiration happens without any cough at all, referred to as silent aspiration.
What percentage of hospitalized older adults are estimated to have dysphagia?
70%
A large percentage of the elderly hospitalized population experiences dysphagia as a result of the deconditioning effects of their hospitalization or related to the reasons for hospitalization.
Aspiration pneumonia is unrelated to dysphagia.
False
What is a common consequence of untreated dysphagia?
weight loss
Weight loss is commonly associated with dysphagia.
What is the typical response to aspiration of foods or liquids for a healthy individual?
cough response
Typically, a healthy individual coughs in response to food or liquid entering the airway (aspiration).
What is the term for difficulty in swallowing?
dysphagia
Aspiration pneumonia is a pulmonary infection.
True
(Choose all that apply) Dysphagia is associated with
depression
social instability
loss of muscle bulk
general decline of health
All of them
A stroke can result in dysphagia.
True
Strokes affecting the ______ are more likely to result in dysphagia when compared to other areas of the brain.
brainstem
Brainstem strokes directly affect the central pattern generator for swallowing (in the medulla oblongata) and typically result in dysphagia.
Which population is most at risk for dysphagia?
elderly adults
Elderly adults have the highest risk for dysphagia.
Dysphagia can lead to dehydration or malnutrition.
True
Dysphagia is typically a symptom of a larger problem or diagnosis.
True
Normal aging can cause dysphagia.
True
Which method is commonly used to diagnose dysphagia?
Modified Barium Swallow Study
While the Modified Barium Swallow Study does use x-ray technology in the form of videofluoroscopy, it is not referred to as an x-ray. The other choices are not used for diagnosing dysphagia at present.
A normal swallow is possible even if not all structures involved in swallowing are normal.
True
Up to 20% of individuals die of aspiration pneumonia in the year following a stroke.
True
Weight loss is a potential sign of dysphagia.
True
Most people will occasionally aspiration some food and liquid.
True
Studies of rates of aspiration pneumonia suggest that early intervention programs for dysphagia can reduce the overall cost of treating pneumonia.
True
Which phase of the swallow is most fully under voluntary control?
oral
The oral phase of the swallow includes biting, sipping, chewing, and moving the food around in the mouth. Those actions can be easily controlled by a healthy individual. Some parts of the pharyngeal phase of swallowing may be under voluntary control, but others are reflexive in nature. The esophageal phase is entirely reflexive. There is no laryngeal phase of swallowing, because having food or liquid pass through the larynx is aspiration.
Some researchers have described swallowing as including 4 distinct phases: the oral preparatory phase, the oral phase, the pharyngeal phase, and the esophageal phase. These four phases can best be used to describe deglutition of a solid food and not liquids, because liquids don't require the same level of oral preparation. Therefore, scholars currently view swallowing in 3 phases and not 4 to universally describe swallowing.
True or False
True
The oral phase involves mastication and bolus formation.
True or False
True
While some scholars may describe mastication (chewing) and bolus formation as belonging to an oral preparatory phase, the current thinking is that there is 1 oral phase that includes both the oral preparation of a bolus and the oral propulsion of a bolus.
The pharyngeal phase of the swallow is under complete voluntary control.
True or False
False.
All swallowing phases are controlled by the peripheral nervous system.
True or False
False
The central pattern generator for coordinating swallowing is located in the brainstem.
True or False
True
The esophagus extends from the
area just below the cricopharyngeus muscle to the entrance to the stomach
Current dysphagia scholars emphasize the interconnectedness/interdependence of the actions of swallowing and de-emphasize swallowing as occurring in the distinct phases (oral, pharyngeal, esophageal). In other words, while we study swallowing in phases to aid our understanding, we acknowledge that the phases overlap in their timing and sequence.
True
Which structure helps prevent food from entering the trachea?
epiglottis
The epiglottis inverts to cover the airway during the pharyngeal phase of the swallow.
Injury to the motor branch of the Vagus nerve results in
possible nasal regurgitation
pooling of bolus residue in the hypopharynx
inadequate velopharyngeal closure
all of these are possible results of injury to the motor branch of CN X
Failure of the velopharyngeal sphincter to close during a swallow is most likely to result in air or bolus leakage into the airway.
True or False
True
Which of the following is NOT part of the pharyngeal phase of swallowing?
gastroesophageal reflux
laryngeal elevation
epiglottic inversion
opening of the Upper Esophageal Sphincter or Pharyngoesophageal Segment
gastroesophageal reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux, if it occurs, is after the pharyngeal swallow. It may occur during the esophageal phase of the swallow or later when there is no swallowing at all.
Chewing is part of the pharyngeal phase of swallowing.
True or False
False
Which structures in the oral cavity are responsible for bolus containment? (Select all)
epiglottis
tongue
lips
cheeks
tongue
lips
cheeks
The lips contain the bolus anteriorly, the cheeks hold tension to keep the bolus from falling into the lateral sulci, the tongue manipulates the bolus for chewing and transit, and the soft palate works to keep the bolus from falling posteriorly into the pharynx too soon. The epiglottis serves to protect the airway.
Normal bolus movement through the oral cavity is a combination of pressure and tongue placement/posture.
True or False
True
The velopharyngeal sphincter is important for:
prevention of nasal regurgitation
The velum makes a tight seal to build positive pressure on the bolus and to prevent food/liquid from leaking into the nasal cavity (nasal regurgitation).
The most important sphincter for preventing the entrance of food or liquid into the subglottic airway is the vocal folds.
True or False
False
The velopharyngeal sphincter is the most important for preventing food or liquid into the subglottic airway before or during the swallow.
The soft palate elevates during which phase of swallowing?
pharyngeal
During the oral phase of the swallow, the soft palate is lowered to prevent early leakage of food/liquid into the pharynx. At the beginning of and throughout the pharyngeal phase of the swallow, the soft palate is raised to form a seal with the pharyngeal wall to prevent nasal regurgitation and to provide a significant amount of positive pressure on the bolus for safe and efficient transport through the pharynx.
What phase of swallowing includes keeping the food/liquid within the oral cavity, forming a cohesive bolus, and propelling the bolus toward the pharynx?
oral phase
The oral phase includes bolus formation, holding the bolus within the oral cavity, and propelling it posteriorly into the pharynx for the pharyngeal swallow.
Difficulty chewing or the inability to chew various textures of food is a problem in the pharyngeal phase of swallowing.
True or False
True
Which phase of swallowing involves bolus transfer to the stomach?
esophageal
The esophageal phase involves transporting the bolus from the pharynx to the stomach.
The internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve is responsible for glottic closure during the passage of the bolus to the esophagus.
True or False
True
The esophageal sphincter is crucial for:
preventing reflux
The esophageal sphincter (also referred to as UES or PES) prevents air from entering the esophagus and reflux from entering the upper airway.
The soft palate prevents food from entering the nasal cavity.
True or False
True
Despite modification of food textures or bolus size, a pharyngeal phase swallowing problem is unlikely to improve.
True or False
False
The esophageal phase is the final phase of swallowing.
True or False
True
All of the phases of swallowing are amenable to treatment in a proper dysphagia management program.
True or False
True
The larynx elevates during the swallow to prevent aspiration.
True or False
True
The internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve is responsible for sensory input to the higher levels of swallowing from the
false vocal folds, true vocal folds, and cricopharyngeus muscle
The vocal folds do not have to close for the swallow to occur without aspiration or penetration.
True or False
True
None of the major sphincters in the swallowing mechanism are likely to lead to a swallowing problem.
True or False
False
Which condition is most commonly associated with pediatric dysphagia?
Cerebral palsy
While ASD can be associated with dysphagia (especially behavioral feeding challenges), approximately 50% of children with cerebral palsy experience some level of dysphagia.
What is a hallmark symptom of pediatric dysphagia?
feeding refusal
As a result of young children's limited communication skills and perhaps reduced conscious awareness of body functions, they respond to threats to their airway through refusal. The primary need for airway protection takes over and causes children to refuse.
If an infant is swallowing air during a bottle feeding, that is considered abnormal and a cause for further evaluation for dysphagia.
True or False
False
Infants typically swallow air while being fed, leading to the need for burping.
What happens when infants experience apnea during feeding?
It protects the airway by closing it temporarily.
Which reflex is typically suppressed before an infant can begin spoon feeding?
tongue protrusion
The tongue protrusion reflex triggers and pushes all food out of the mouth. This reflex must be suppressed before the infant is able to propel a bolus back in the mouth for a swallow.
What is the primary role of the nasal cavity?
To warm and clean the air before it enters the lungs.
What do sucking pads in infants help with?
Support oral and pharyngeal function during feeding.
In a typical pharyngeal phase of swallowing, the epiglottis closes first, then the larynx lifts and moves forward, followed by true vocal fold closure.
True or False
False
What changes occur in the anatomy of the tongue and larynx during the first four years of life?
The base of the tongue and larynx descend, altering swallowing mechanics.
An infant initially uses suckling to feed from a nipple but develops a true suck between the ages of 6-9 months. Sucking can be distinguished from suckling in that the tongue moves more up and down without as much jaw movement and the lips seal around the nipple with greater force in sucking.
True or False
True
What reflex helps infants find the nipple during feeding?
The rooting reflex.
What is a major developmental milestone related to feeding that occurs around six months of age?
Introduction of spoon feeding.
How do infants' feeding patterns change as they grow?
They develop more complex sucking and swallowing patterns as their anatomy matures.
A 6 week-old infant would be expected to have a 1:1:1 suckle-swallow-breathe pattern, meaning for every suckle, there is a swallow, followed by a breath.
True or False
True
Pressure generation (positive and negative) can depend on several factors. Which is NOT a factor that may affect pressure generation during suckling.
the level of noise in the environment
Solid foods can be introduced at any point in a child's life after 4-6 months. The most important factor is that a child feels ready for solids.
True or False
False
There is a critical period for introducing solid foods around 4-7 months and no later than 12 months (Harris & Mason, 2017).
At what age does an infant typically begin to transition from suckling to sucking?
Around six to nine months of age.
Infants can breathe while swallowing.
True or False
False
What is the main reason infants prefer nasal breathing?
The anatomical arrangement of their airway structures.
Which infant reflex persists throughout an individual's life, but may not be found in around 30% of adults?
gag
The gag and swallowing reflex persist throughout the lifespan. Gagging may not be found in 30% of the population of adults, but a swallowing reflex is found in most if not all adults.
GERD does not commonly cause aspiration pneumonia.
False