Unit 5: States of Conciousness
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Consciousness
Our awareness of ourselves & our environment
Circadian Rhythm
Physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24 hour cycle
- Our biological clock
Circadian rhythm is controlled by the
hypothalamus
What factors can affect circadian rhythm?
Jet lag, shift work(night shift), or travelling in between time zones
Desynchronization
The term for a shifted circadian rhythm
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
A pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm
- Suprachiasmatic nucleus can be affected by light which in return modifies melatonin production (the sleep hormone)
What produces the sleep-inducing hormone melatonin?
The pineal gland
Adenosine
Is responsible for making us sleepy
- Adenosine binds to receptors on certain CNS neurons that initiate a cellular response to increase drowsiness
Caffeine
Antagonist for adenosine, blinds to adenosine receptors therefore blocking the receptor and temporarily blocking drowsiness and maintaining or restoring alertness
Ultradian rhythms
Those that occur more than once a day
ex. Appetite or hormonal release
Infradian rhythm
Those that occur monthly or yearly
ex. Menstrual cycle
The 4 stages of sleep
NREM Stage 1
NREM Stage 2
NREM Stage 3
REM Sleep
Sleep
Periodic, natural loss of consciousness
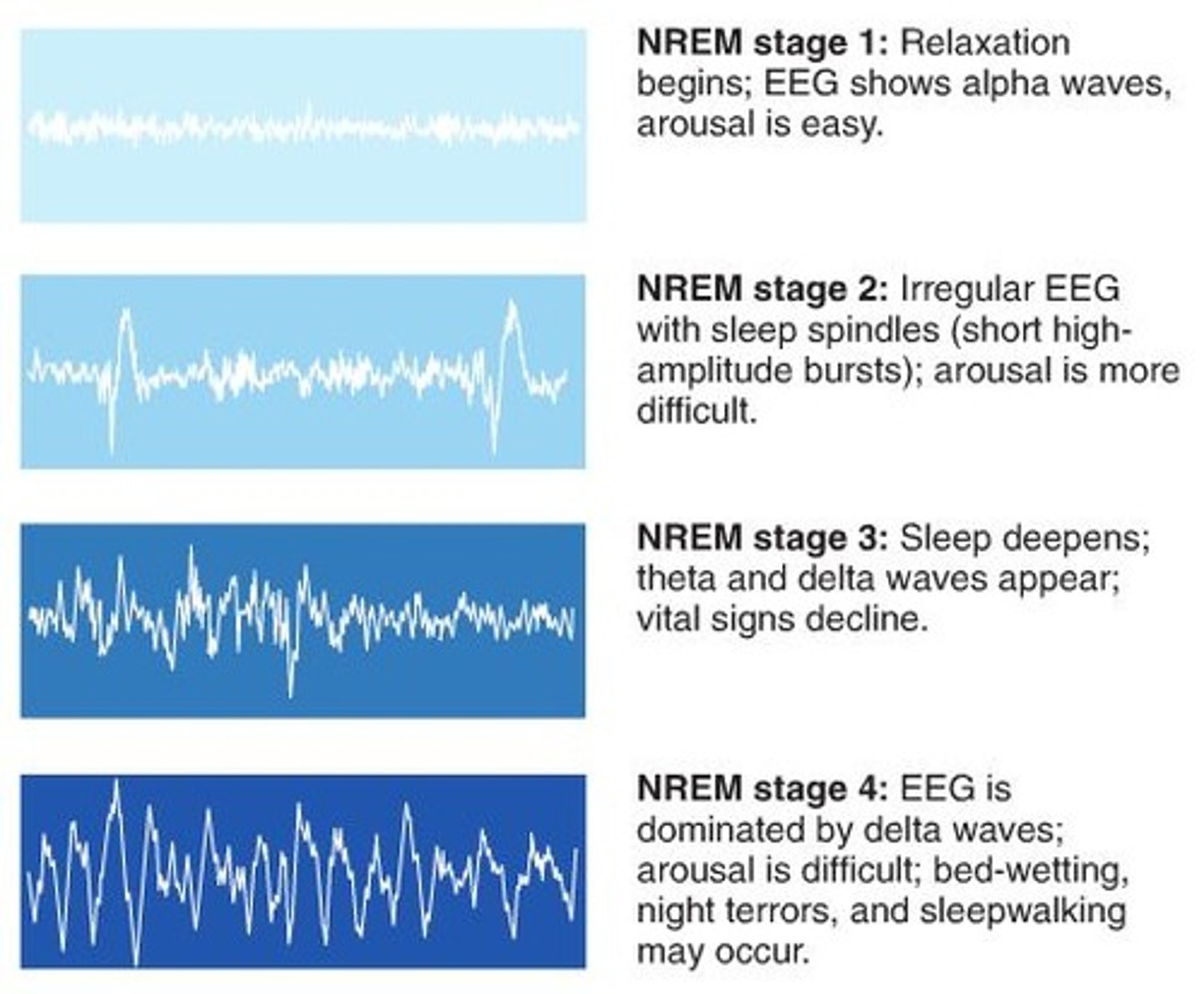
NREM Stage 1 Sleep
The transition period between wakefulness and sleep
- Lighest stage of sleep, theta waves present
- Lasts about 1-7 mins
-4-5% of time spent here each night
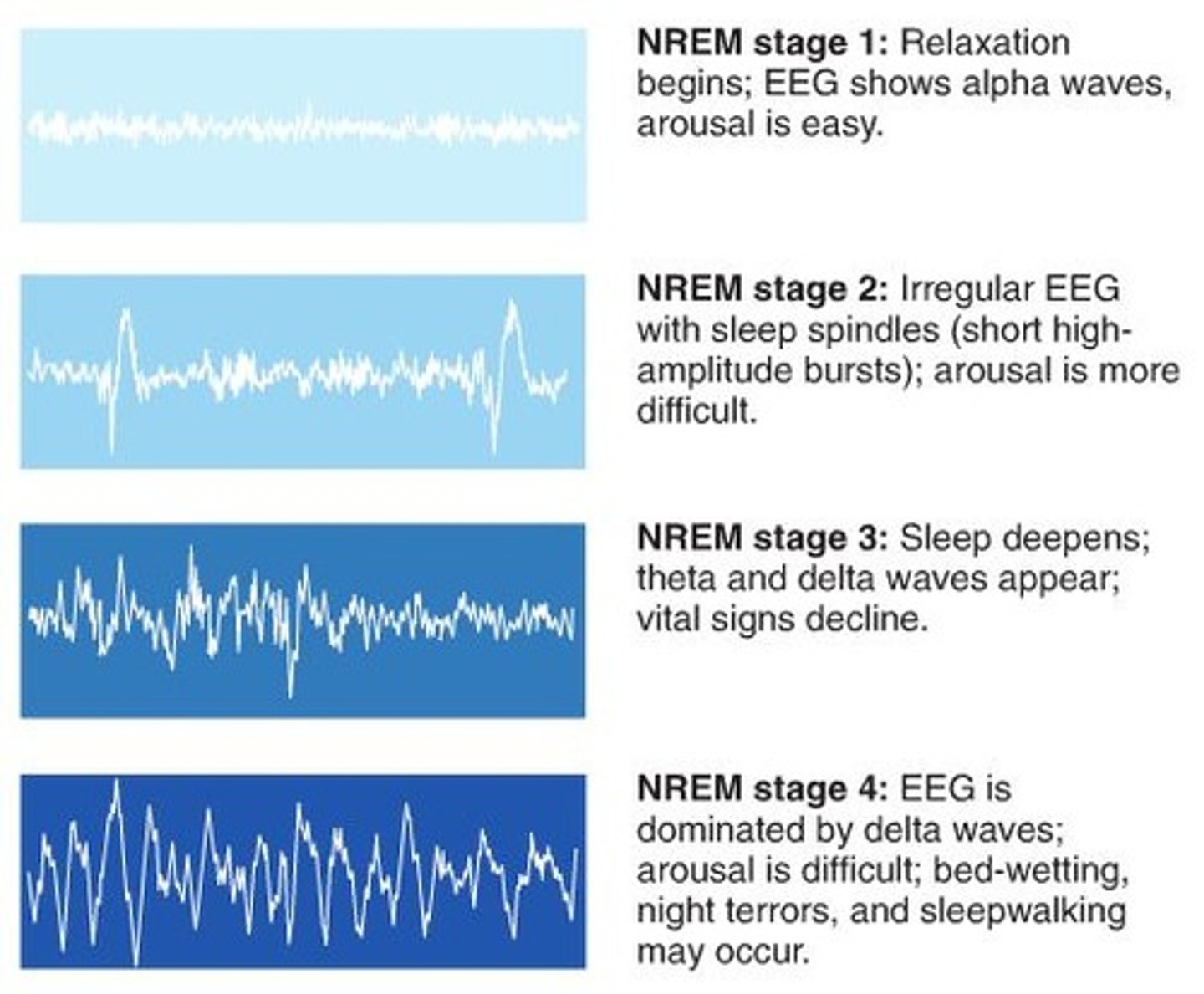
NREM Stage 2 Sleep
- Body temp drops and heart rate begins to slow
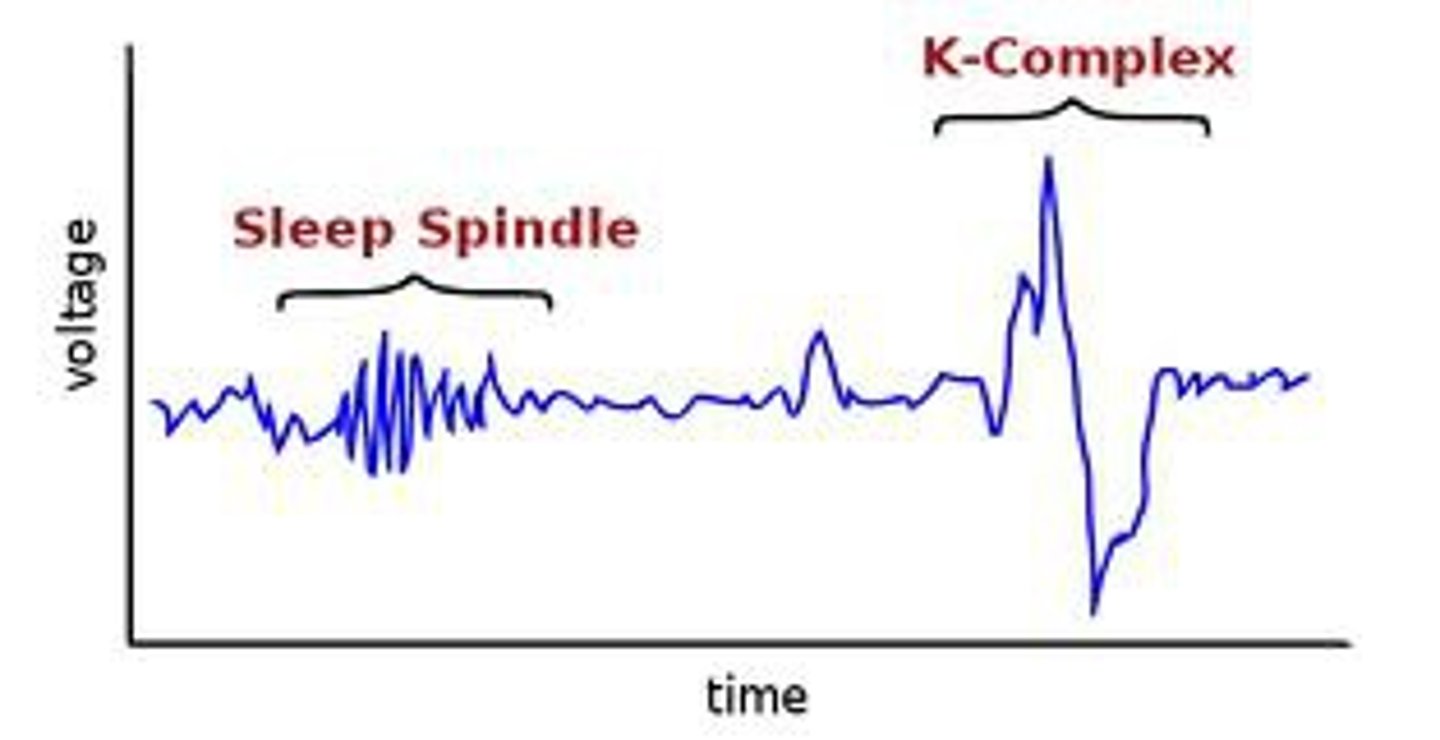
- Brain starts to produce sleep spindles
- Lasts approx. 20 minutes
- Becomes more difficult to be awakened from
Sleep Spindles (K Complexes)
Periodic bursts of brain activity that occur during NREM 2 Sleep
NREM Stage 3 Sleep
- Muscles relax, blood pressure and breathing rate drops
- Deepest sleep occurs here
- Brain emits large slow delta waves
- Lasts for about 30 minutes
- Growth hormone secreted here
- Helps clear out excess short term memories in the hippocampus & chose the ones we want to store in LTM (long term memory)
REM Sleep
The brain becomes more active, body becomes relaxed and paralyzed
- Dreams occur
- Eyes move rapidly
- Occurs about an hour after falling asleep
- Visuospatial regions, amygdala, hippocampus, and motor cortex become active but frontal lobes logic and reasoning are turned off during this time which explains weird dreams
- REM sleep helps form connections & develop the brain, important for creativity and problem solving, helps develop implicit memory and helps process emotional memories
- Also helps maintain emotional awareness
Definition of REM (rapid eye movement sleep)
A recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active. Only occurs in mammals.
BATS DRINK BLOOD Sleep Wave Mneumonic
B eta (Awake)
A lpha (Sleepy)
T heta (NREM 1)
S leep spindles (NREM 2)
Drink (Delta) NREM3
Blood (Beta) REM
Hypnagogic sleep
The very relaxed drowsy state that you pass through before entering sleep
Insomnia
Consistent difficulties in going to sleep or staying asleep at night
Side effects: Fatigue, lack of concentration, memory problems
Causes: Stress, death of a loved one, mental health problems, drug or alcohol use, change in sleep pattern, and too much or too little exercise
Treatment: Lifestyle changes, sleeping pills (extremely addictive)
Hallucinations
False sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
Narcolepsy
A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks and muscle paralysis (cataplexy). The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times
Causes: Lack of the brain chemical hypocretin (orexin)
Treatment: Amphetamines, to keep patients awake
Sleep apnea
A sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep followed by repeated momentary awakenings
Causes: obesity, sleeping pill use, alcohol use
Treatments: breathing machine, weight loss
Night terror
A sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during Stage 4 sleep, within two or three hours of falling asleep, are not remembered
- Common in children aged 4-12
REM Behavior Disorder
Voluntary muscles are not paralyzed and sleeps can (and do) act out their dreams
Nightmares
Occur during REM sleep. Person has frightening images and thoughts which can make it hard for them to fall back asleep. When awake, they can usually visually describe them.
Sleepwalking
Getting up and walking while still asleep
Causes: increased stress, anxiety, mental problems
Dream
A sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping person's mind. Dreams are notable for their hallucinatory imagery, discontinuities, and incongruities, and for the dreamer's delusional acceptance of the content and later difficulties remembering it
Manifest content
According to Freud, the remembered storyline of a dream
- What actually happens in the dream
Latent content
According to Freud, the underlying meaning of a dream
Freud's wish-fulfillment (Dream Theory)
According to Freud, Dreams provide a "psychic safety valve" expressing otherwise unacceptable feelings; contain manifest content and a deeper layer of latent content
Limits: Does not have any scientific support; dreams may be interpreted in many different ways
Information-processing (Dream Theory)
Dreams help us sort out the day's events and consolidate our memories
- Scientific evidence that REM sleeps helps with info processing of memories during REM
Limits: Does not explain why we often dream about things we have not personally experienced
Physiological Function (Dream Theory)
Regular brain stimulation from REM sleep may help develop and preserve neural pathways
Limits: Does not explain why we experience meaningful dreams
Activation-synthesis (Neural Activation) [Dream Theory]
REM sleep triggers neural activity that evokes random visual memories, which our sleep brain weaves into stories
Limits: The individual's brain is weaving the stories, which still tells us something about the individual
Cognitive development (Dream theory)
Dream content reflects dreamers' cognitive development, their knowledge and understanding
REM Rebound
The tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation (created by awakenings during REM)
Hypnosis
A social interaction in which one person suggests to another that certain perceptions, feelings, thoughts, or behaviors will spontaneously occur
Posthypnotic suggestion
A suggestion, made during hypnosis session, to be carried out after the subject is no longer hypnotized; used by some clinicians to help control undesired symptoms and behaviors
Dissociation
A split in consciousness, which allows some thoughts and behaviors to occur simultaneously with others
Psychoactive Drug
A chemical substance that alters perceptions & moods
Tolerance
The diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of a drug, requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug's effect
WIthdrawal
The discomfort and distress that follows discontinuing the use of an addictive drug
Physical dependence
A physiological need for a drug, marked by unpleasant withdrawal symptoms when the drug is discontinued
- You need the drug or your body will go through withdrawal
Psychological dependence
A psychological need to use a drug, such as to relieve negative emotions
- You want the drug really really bad and you think you need it but your body doesn't actually need it
Addiction
Compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences
Depressants
Drugs (such as alcohol, barbiturates, & opiates) that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
- Increases the availability of GABA
Barbiturates
Drugs that depress the activity of the CNS reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgement
- Can be lethal when mixed with alcohol due to the total depressive state of the body (ex. sleeping pills w/ alcohol)
Opiates
Opium and its derivatives, such as morphine and heroin; they depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety.
- Work as agonists for endorphins, stimulate glutamate receptors, physically changes the neurons structure and rewires the neuron to need the opiate to work properly
Stimulants
Drugs (such as caffeine, nicotine, and the more powerful amphetamines, cocaine, and Ecstasy) that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
- Increase heart and breathing rates, cause pupils to dilate, appetite to diminish (due to blood sugar increase), along with a rise in self confidence and energy
Amphetamines
Drugs that stimulate neural activity, causing sped-up body functions and associated energy and mood changes
- Increases the release and decreases the removal of norepinephrine (controls alertness and arousal) and dopamine (movement, attention) at synapses
- Reduces activity of GABA
Methamphetamine
A powerfully addictive drug that stimulates the central nervous system, with sped up body functions and associated energy and mood changes; over time, appears to reduce baseline dopamine levels
MDMA (Ecstasy)
A synthetic stimulant and mild hallucinogen. Produces euphoria and social-intimacy, but with short-term health risks and longer-term harm to serotonin-producing neurons and to mood and cognition
Hallucinogens
Psychedelic drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
LSD
A powerful hallucinogenic drug; also known as acid
- Simulates serotonin and dopamine
-Creates hallucinations
THC
The major active ingredient in marijuana; triggers a variety of effects, including mild hallucinations
Near-death experience
An altered state of consciousness reported after a close brush with death (such as through cardiac arrest); often similar to drug induced hallucinations