Computer Systems
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
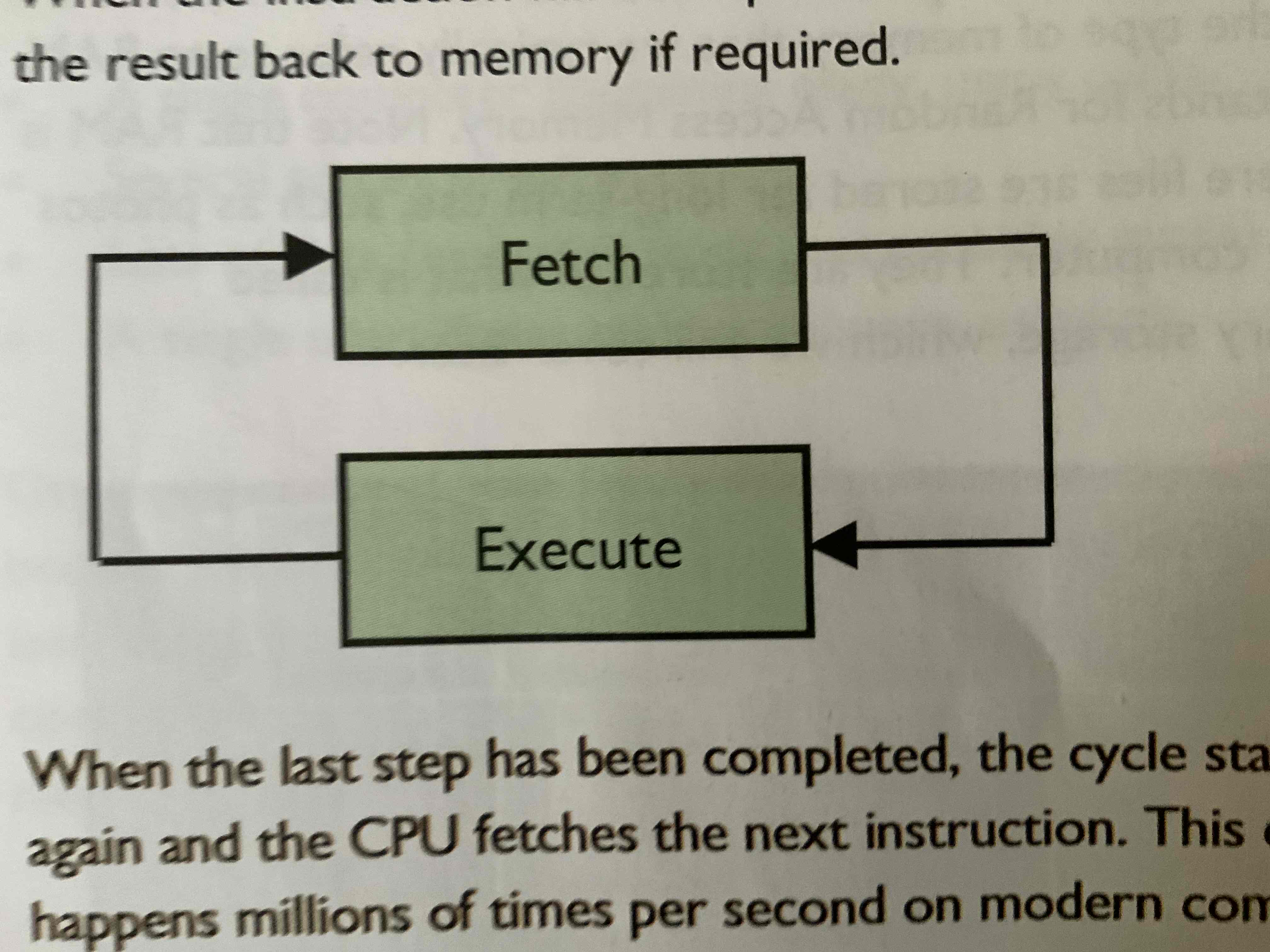
Fetch(Decode) - Execute Cycle
the fundamental process by which a CPU processes instruction:
Fetch – The computer gets (fetches) the next instruction from its memory.
Decode – It figures out (decodes) what the instruction means.
Execute – It carries out (executes) the instruction, like doing a calculation or moving data.
This cycle repeats to run programs.
Logic gates
Basic electronic components that perform logical operations on one or more binary inputs to produce a binary output.
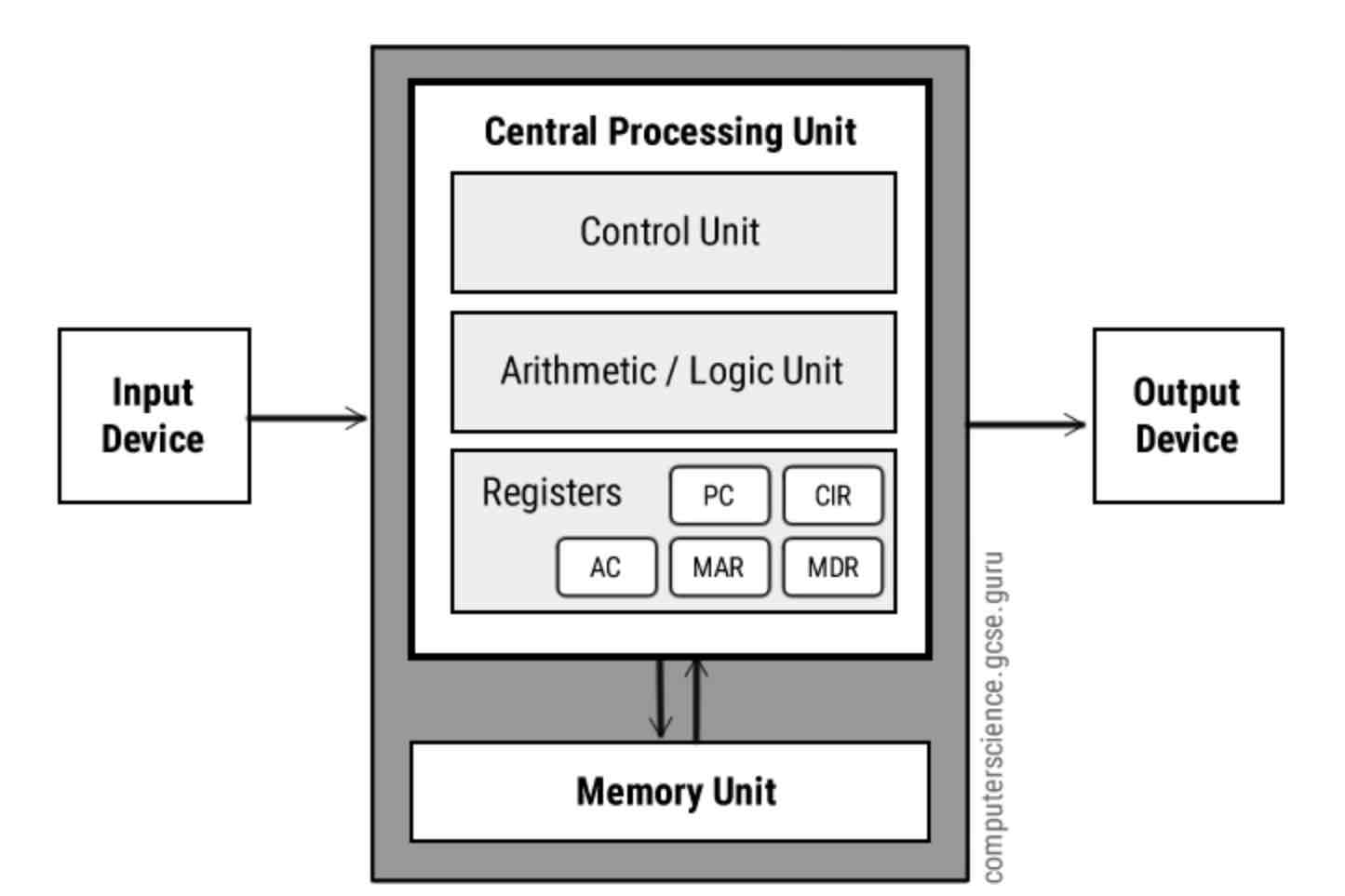
Von Neumann Architecture
Clock Speed
Refers to the rate at which a computers central processing unit (CPU) executes instructions. It is measured in Hertz (Hz).
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of increasing a CPU’s clock speed beyond its factory-set maximum to improve performance.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
• Type: Volatile memory (data is lost when power is off).
• Purpose: RAM temporarily stores data that is actively being used or processed by the CPU.
Read Only Memory (ROM)
• Type: Non-volatile memory (data remains even when the power is off).
• Purpose: ROM permanently stores essential instructions for the computer, such as the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) firmware that helps start the system when it is powered on.
Volatile Memory
A type of computer memory that requires power to maintain the stored data.
Non-Volatile Memory
A type of computer memory that retains data even when the power is turned off.
Operating System
A system that consists of a collection of programs that control the operation of the computer, application programs and any attached devices.
Functions of Operating Systems
Managing how data is received from input devices and sent to output devices.
Managing how the computer interacts with other computers.
Controlling where programs and data are located in the computers memory.
Providing the interface between the user and the computer, referred to as the “user interface”. This allows the user to interact with the computer.
Managing the file system on the computer.
Controlling access and security.
Transistors
A switch in a circuit that converts a mechanical charge to a change in electric current.
Resistors
A device that reduces current flow.
Capacitators
A component that stores electrical energy (in the form of electric charge.)
Function of general registers
General registers temporarily store data and instructions to help the CPU process tasks quickly and efficiently.
MAR (Memory Address Register)
Holds the address of the memory location that is to be read from or written to.
MDR (Memory Data Register)
Holds the data being transferred to or from memory. This could be the instruction being fetched.
Accumulator
During the execute stage, the Accumulator stores the result of calculations or operations performed by the ALU.
What are registers?
Small memory locations inside the CPU that hold temporary data or instructions during processing.
Function of the control unit
The Control Unit directs the CPU by fetching, decoding, and managing instructions, making sure all parts of the computer work together properly.
In computing terms, what is meant by software?
The part of a computer made up of programs and applications which tells the computer what to do and how to use its hardware.
Function of the ALU component of the CPU
The ALU performs all the arithmetic (like addition and subtraction) and logic (like comparisons) operations in the CPU.
Integrated Circuits
A tiny chip made of silicon that contains many electronic parts, like transistors and resistors, all working together to help devices like computers run.
Voltage of a Circuit
pressure(work done) from an electrical circuit's power source to push current through an electronic circuit
Current of a circuit
Rate of flow of charge at a point on an electronic circuit.
Hardware of a computer system
Hardware is the physical parts of a computer system, like the keyboard, mouse, screen, and the internal parts such as the CPU and memory that help the computer run and do tasks.
USB (Universal Serial Bus)
A standard way to connect devices to a computer. It’s used to transfer data, power, or both between devices.
Program Counter
A register in the CPU that holds the address of the next instruction to be fetched from memory. It’s role is to keep track of where the next instruction is in a program.
What are Buses in a CPU?
Physical connections that carry data/ instructions from the CPU to the memory unit and vice versa.
Differentiate between Primary and Secondary storage.
Primary: directly accessible by the CPU I.e. RAM, ROM and Registers.
Secondary: Not directly accessible by the CPU I.e. HDD and SSD.