Lab Notes + Appendix A
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
1
New cards
What do we do in science?
- develop ideas, design experiments, conduct observations to test ideas, uses statistical methods to interpret our results, and communicate our findings to larger community
2
New cards
what is the study of science?
- study of natural phenomena
3
New cards
what is the scientific method?
- tool we used to achieve high standards of research
- overcome biases and conduct logically reliable research
- overcome biases and conduct logically reliable research
4
New cards
what are the steps of the scientific method?
1. observing outside world through our senses
2. asking a question about natural phenomena
3. hypothesizing an explanation for the phenomenon
4. testing the hypothesis through a correlational/experimental study
5. collecting and analyzing data from the experiment
6. creating a conclusion from the experimental data
2. asking a question about natural phenomena
3. hypothesizing an explanation for the phenomenon
4. testing the hypothesis through a correlational/experimental study
5. collecting and analyzing data from the experiment
6. creating a conclusion from the experimental data
5
New cards
Observations
- receiving knowledge of the outside world
- observations of phenomenon
- preliminary observations allows use to formulate questions about our surroundings, which we can investigate
- observations of phenomenon
- preliminary observations allows use to formulate questions about our surroundings, which we can investigate
6
New cards
Questions
- how's and why's of nature
- relevant questions that have capacity to be testes
- form of question can influence the type of study
- relevant questions that have capacity to be testes
- form of question can influence the type of study
7
New cards
Hypothesis
- tentative answer to your question
- clearly stated, proposed explanation for observations
- states factors that influence observed phenomena
- we can only disprove hypotheses
- clearly stated, proposed explanation for observations
- states factors that influence observed phenomena
- we can only disprove hypotheses
8
New cards
Null Hypothesis
- when hypothesis is rejected, provides support for our hypothesis
- proposes no relationship between factor being studied and observed phenomenon
- proposes no relationship between factor being studied and observed phenomenon
9
New cards
What is the difference between hypothesis and null hypothesis?
- null states that the factor has no effect on the observed results
- hypothesis states it has an effect on the results
- hypothesis states it has an effect on the results
10
New cards
What makes a good hypothesis?
- testable predictions
- ability to generate specific predictions of scenarios that will reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis
- ability to generate specific predictions of scenarios that will reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis
11
New cards
What is experimental manipulation?
- used artificial manipulation to investigate the relationship between one factor and another
- actively altering the study system and measures the effects of manipulation
- actively altering the study system and measures the effects of manipulation
12
New cards
what are correlational studies?
- use natural variation to investigate the relationship between one factor and another
- observing nature
- observing nature
13
New cards
what is the independent variable?
- factor that is being manipulated in the study
- was is altered in the system is controlled by the researcher
- was is altered in the system is controlled by the researcher
14
New cards
what is the dependant variable?
- factor that is expected to be affected by the manipulation
15
New cards
What does an experimental manipulation test?
it tests whether the independent variable has an effect on the dependant variable
16
New cards
What is a control group? or a control?
- reference to which the results of an experiment manipulation can be compared
- act as a reference to measure the effect of the experimental manipulation on the dependant variable
- ensure that conclusions drawn from an experimental manipulation are biologically valid
- act as a reference to measure the effect of the experimental manipulation on the dependant variable
- ensure that conclusions drawn from an experimental manipulation are biologically valid
17
New cards
Advantages of Correlational Study
- less handling of organisms
- systems under study are more likely to be observed in their natural state
- represent biologically relevant variation
- experimental manipulation is not practical or ethical
- systems under study are more likely to be observed in their natural state
- represent biologically relevant variation
- experimental manipulation is not practical or ethical
18
New cards
Advantages of Experimental Manipulation
- more likely to control for confounding variable
- know direction of causation
- know direction of causation
19
New cards
What are confounding variables?
- factors that the researcher failed to control or eliminate which can damage the validity of an experiment
20
New cards
What are controlled variables?
- variables that are held constant
- EM allows for more control for confounding variables
- EM allows for more control for confounding variables
21
New cards
Analyzing and Interpreting Data
- what does your data tell you?
- tests of significance
- tests of significance
22
New cards
What are the two tests of significance?
x^2-square test and t-test
23
New cards
Theory
- explaining and predicting natural phenomena
- if proven, hypothesis may be accepted as part of general theory
- if proven, hypothesis may be accepted as part of general theory
24
New cards
What makes a good theory?
- it accurately describes a large class of observations
- makes definite predicts about the results of future observations
- makes definite predicts about the results of future observations
25
New cards
What do reduviid bugs do?
- they cover their thorax with a layer of dust, sand, and soil particles to form dust coat
- attack dead ants to thorax using elastic threads that are produced by glands on their back to from backpack
- attack dead ants to thorax using elastic threads that are produced by glands on their back to from backpack
26
New cards
What are adaptations?
- traits that contribute to fitness by increasing organisms chance of surviving and reproducing
- physical feature or a behaviour
- physical feature or a behaviour
27
New cards
What are arthropods?
- insects, animals with jointed legs
28
New cards
What are the three main sections in arthropods?
- head, thorax, abdomen
29
New cards
What is Natural Selection? according to Darwin
- process of adaptation
30
New cards
How are new traits and combinations of traits created?
- through mutations and recombination
31
New cards
how is fitness measured?
- as the number of offspring an individual produces relative to another in the population
32
New cards
what is evolution?
- the change over generations in the proportion of individuals with a certain trait
33
New cards
What are the 3 criteria for a trait to evolve?
1) is heritable
2) variation btw individuals
3) variation in trait leads to individuals leaving more offspring in next generation than others
2) variation btw individuals
3) variation in trait leads to individuals leaving more offspring in next generation than others
34
New cards
How else can populations change and evolve?
genetic drift and gene flow
35
New cards
What id the difference btw viability and competition?
- viability is the success in survival and acquisition
- competition is for mating; reproduction
- competition is for mating; reproduction
36
New cards
What is viability selection? Examples?
- natural selection arising from variation in viability
- camouflage in grasshoppers; avoid predation
- feeding; ants have strong jaw (mandibles), butterflies have long tongue (proboscis)
- camouflage in grasshoppers; avoid predation
- feeding; ants have strong jaw (mandibles), butterflies have long tongue (proboscis)
37
New cards
What is sexual selection?
- natural selection arising from variable mating success
- results in secondary sexual characteristics
- results in secondary sexual characteristics
38
New cards
What is sexual dimorphism?
- difference in shape or size of male and female
39
New cards
What are two principles of sexual selection?
- intersexual competition
- mate choice
- mate choice
40
New cards
What is intersexual competition?
- males fight with other males for access to females
- male who wins usually has more offspring
- examples: horns, tusks, "weapons"
- females usually have smaller version
- male who wins usually has more offspring
- examples: horns, tusks, "weapons"
- females usually have smaller version
41
New cards
What is mate choice?
- females and males that choose their mates
- attractive individuals produce more mates
- examples: structure, colouration, courtship
- attractive individuals produce more mates
- examples: structure, colouration, courtship
42
New cards
What is a complete metamorphism?
- undergoing a series of profound changes in body form, behaviour, and lifestyle
- eggs hatch into larvae (caterpillars), feed on vegetation
- becomes pupa; in cocoon caterpillar develops into adult
- butterfly feeds on nectar and flowers can reproduce
- eggs hatch into larvae (caterpillars), feed on vegetation
- becomes pupa; in cocoon caterpillar develops into adult
- butterfly feeds on nectar and flowers can reproduce
43
New cards
What is warning colouration?
- colours warn predators and makes them seem dangerous
44
New cards
How are water striders able to stay still on water?
- fine hairs that are water repellent
- females engage males in pre-mating struggles
- capture insects entrapped by water's surface tension
- light weight
- thin legs
- good eyesight
- females engage males in pre-mating struggles
- capture insects entrapped by water's surface tension
- light weight
- thin legs
- good eyesight
45
New cards
What are the uses of the water striders legs?
- front allow them to grab predators
- middle act as paddles
- back provide power, steer and brake
- middle act as paddles
- back provide power, steer and brake
46
New cards
How do water striders grab prey?
- grab prey quickly
- use moth parts to pierce and suck juice
- use moth parts to pierce and suck juice
47
New cards
Why do male leaf insects prefer longer females?
- because longer females produce more and larger eggs
48
New cards
Why do male Madagascar hissing cockroaches have bumps on their dorsal prothorax?
- plate that protects their head
- fend off rivals
- fend off rivals
49
New cards
Why do waterfleas grow long heads and tails?
- they grow them as a response to the presence of predators
- spines interfere w the predator's ability to consume the flea
- spines interfere w the predator's ability to consume the flea
50
New cards
What is phenotypic plasticity?
- single genotype can produce different phenotypes in response to its environment
51
New cards
what is a phenotype?
- observable appearance of a specific genotype
52
New cards
what is an organism's phenotype composed of?
morphology, behaviour, and physiology
53
New cards
What can variation in a phenotype be a result of?
- genetic variation
- the environment
- interactions of both components
- the environment
- interactions of both components
54
New cards
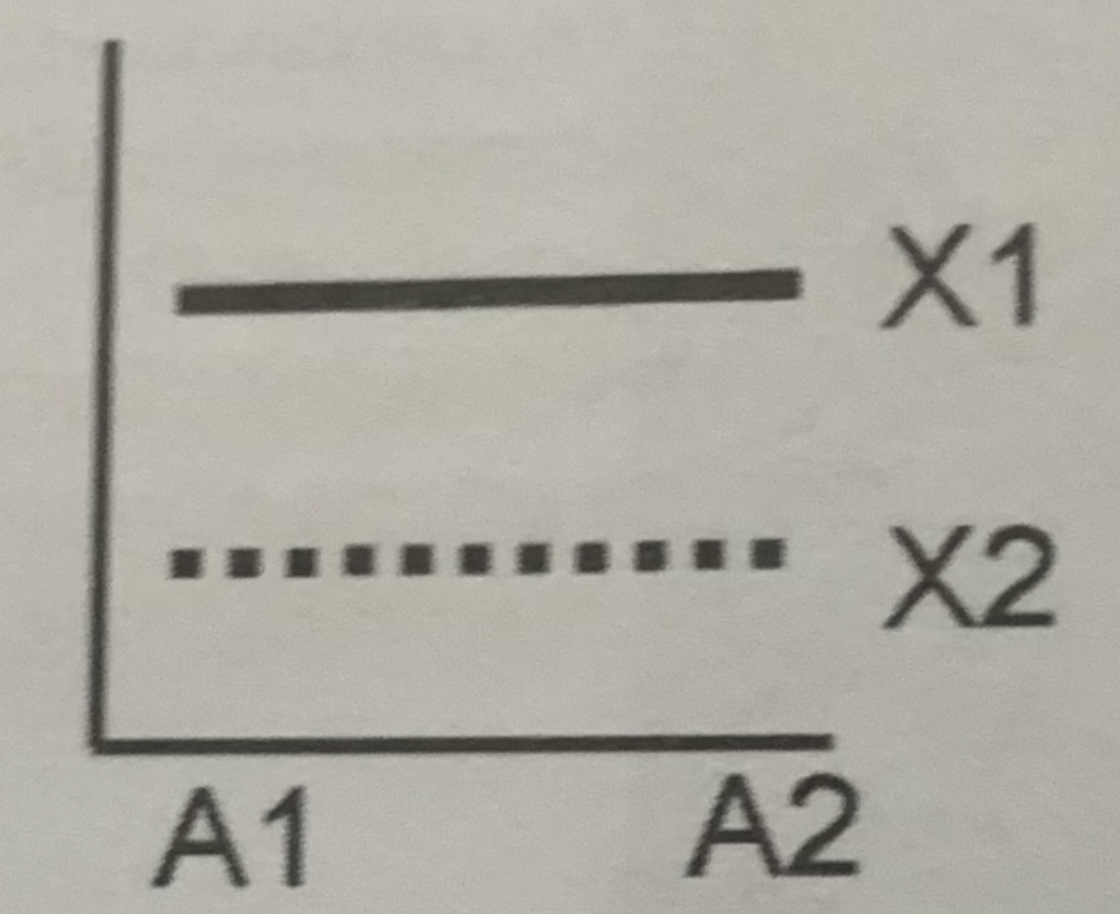
What does this graph tell us?
- genotype affects height
55
New cards
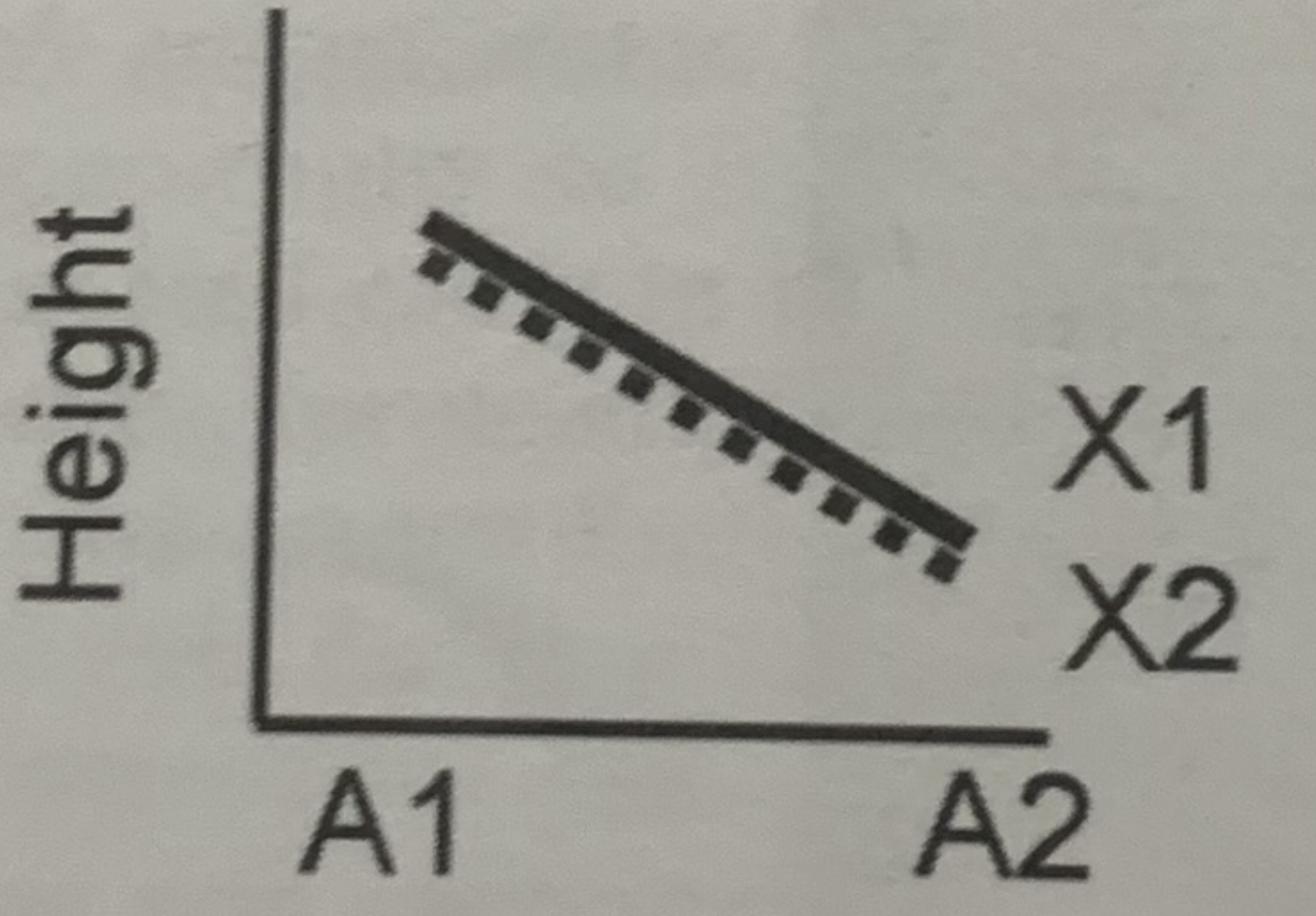
What does this graph tell us?
- genotype does not affect height
- environment affects height
- environment affects height
56
New cards
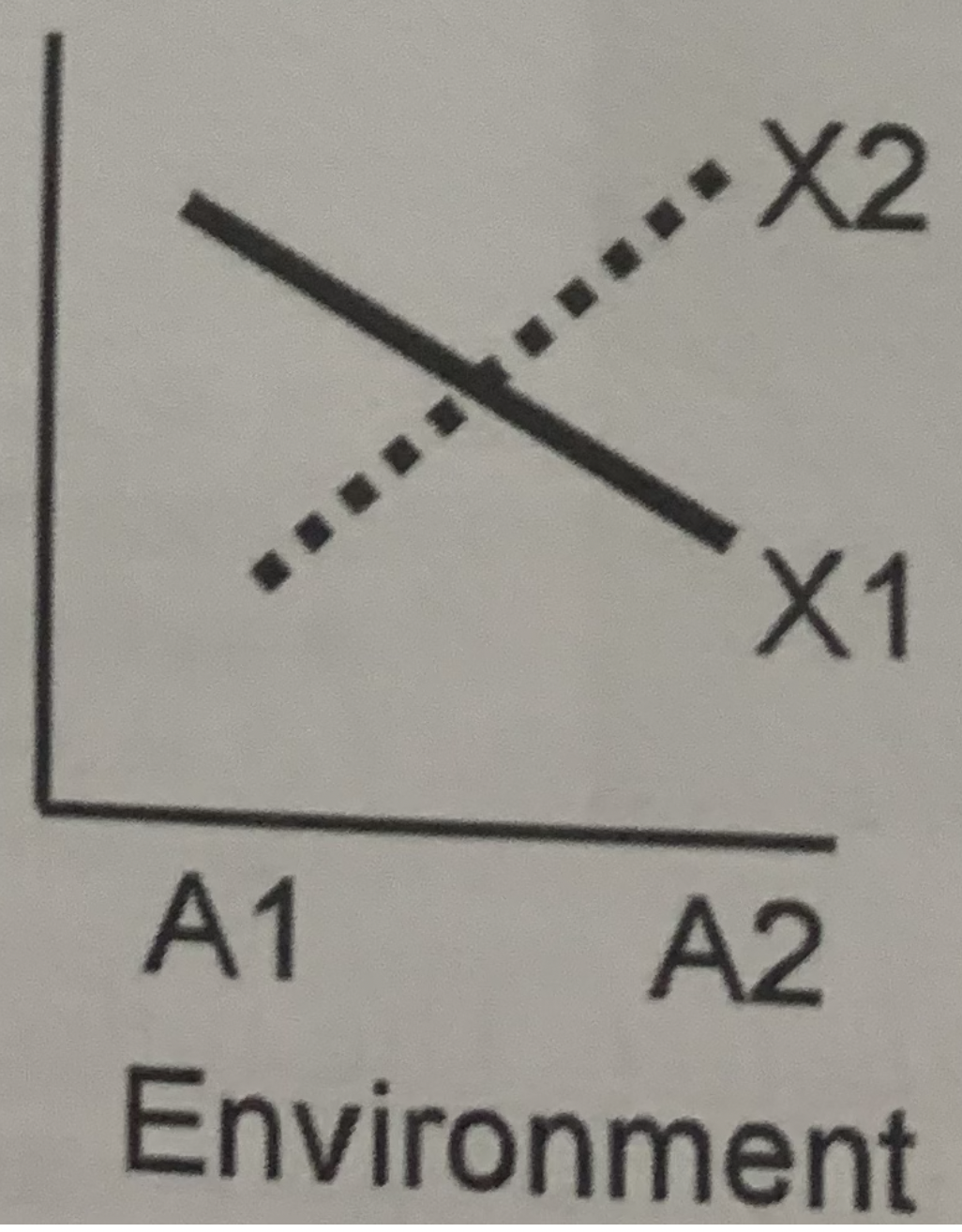
What does this graph tell us?
- both genotype and environment affect phenotypic variation
57
New cards
What is a genotype?
- organism's allele
- complete genetic constitution of an organism
- complete genetic constitution of an organism
58
New cards
What are quantitative or polygenic traits?
- continuous traits such as hair, skin colour
- result of genes and environment
- large or small effect on phenotypic expression
- result of genes and environment
- large or small effect on phenotypic expression
59
New cards
What is acclimation?
- altering the phenotype
- individuals acclimate to their environment
- individuals acclimate to their environment
60
New cards
What is phenotypic plasticity?
- individual can alter the expression of a phenotypic trait in response to the environment
- ability of one genotype to produce different phenotypes in different environments
- ability of one genotype to produce different phenotypes in different environments
61
New cards
What are the two types of phenotypic plasticity?
- discrete and continuum
62
New cards
Why are not all traits phenotypical plastic?
- insufficient genetic variation
- inherent costs and limitations to the benefits of PP
- inherent costs and limitations to the benefits of PP
63
New cards
What is a limitation w producing phenotypes?
- accuracy w which an organism can process environmental cues to acclimate
- time difference btw environmental change and alteration of phenotype
- time difference btw environmental change and alteration of phenotype
64
New cards
What is a maladapted phenotype?
- organism senses environment incorrectly or rapidly
65
New cards
what sort of individual is able to acclimate to changing conditions in terms of number of genotypes?
- an individual which can produce more genotypes is more likely to acclimate to changing conditions then individual who can only produce one
66
New cards
Stereo Microscope
- three-dimensional
- less magnification power
- less magnification power
67
New cards
What are the parts of a Stereo Microscope?
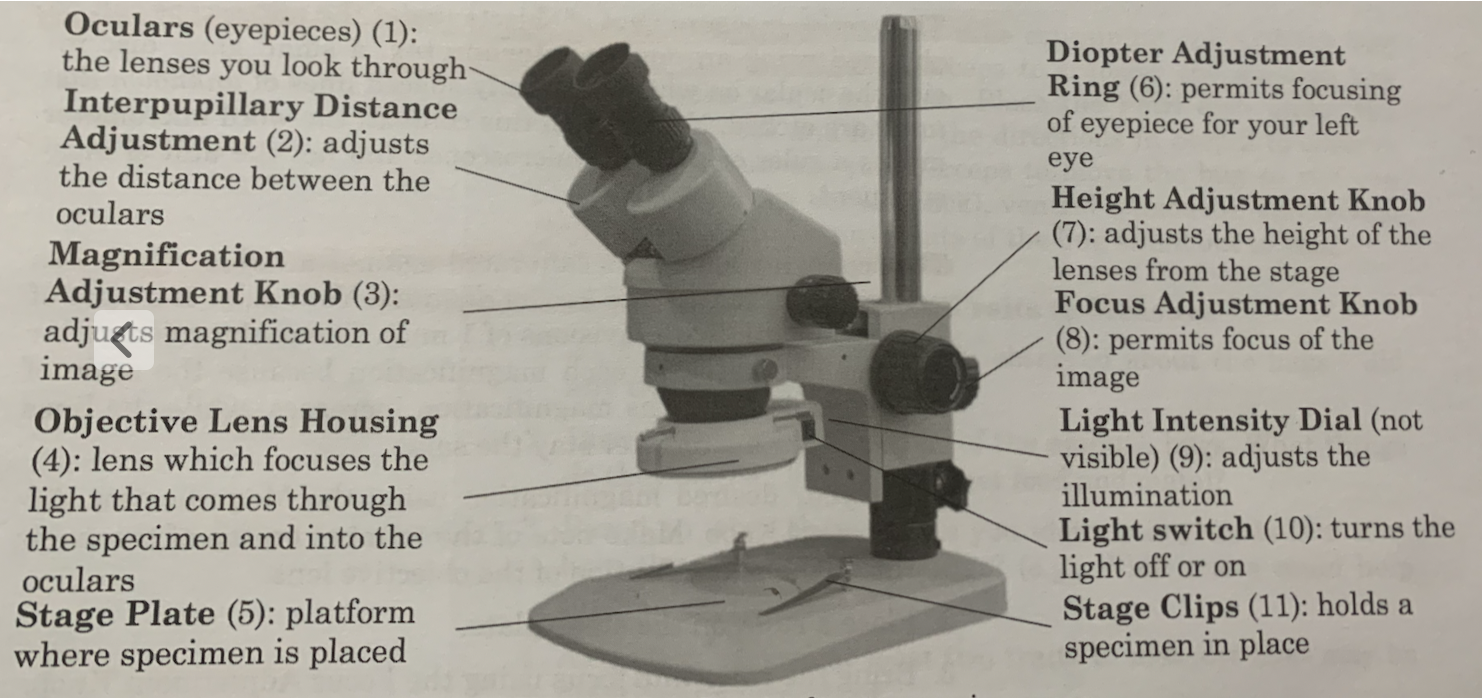
68
New cards
What is a ocular micrometer?
- precise measurement of objects under the microscope
69
New cards
What is a phytochrome?
- a photoreceptor that detects shading by other plants
- detects like quality
- regulates gene expression
- genes alter morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics in plants
- detects like quality
- regulates gene expression
- genes alter morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics in plants
70
New cards
what are the parts of a compound microscope?
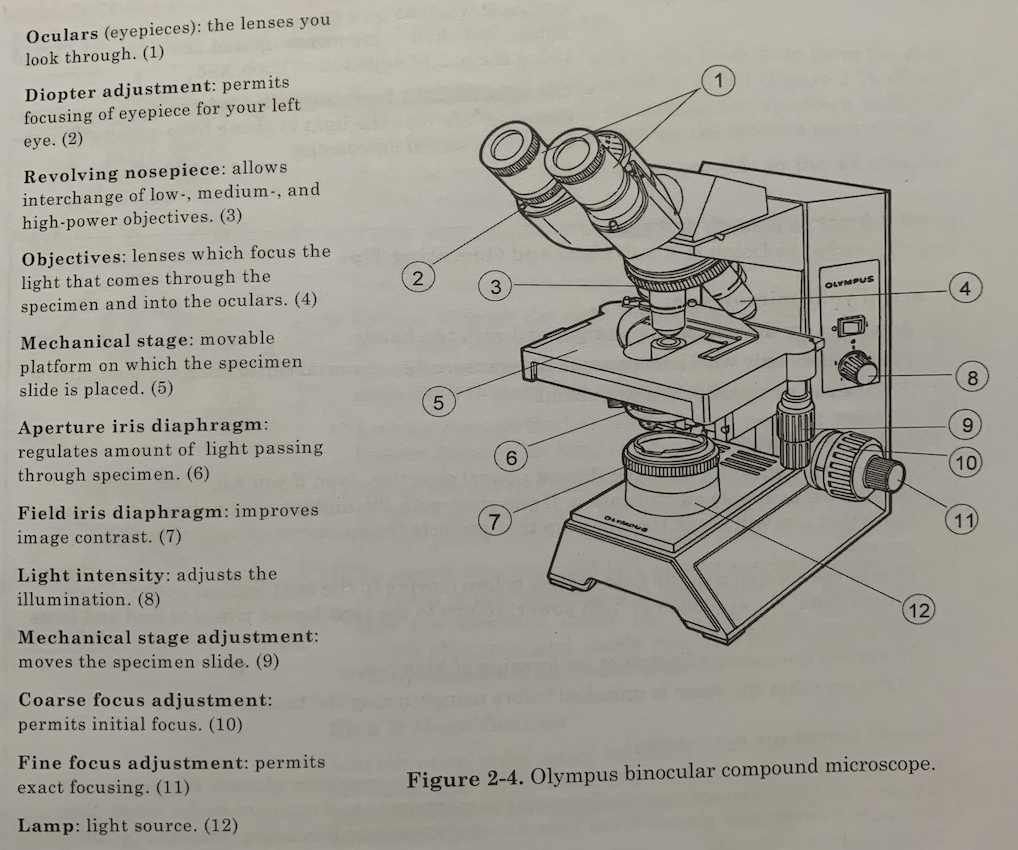
71
New cards
what are the major differences btw a compound microscope and stereo microscope?
- compound microscope does not have adjustment knob
- two focus adjustment knobs on compound microscope
- move stage up and down on a compound microscope
- light is shone from below the stage on a compound
- two focus adjustment knobs on compound microscope
- move stage up and down on a compound microscope
- light is shone from below the stage on a compound
72
New cards
What is magnification?
- factor by which the image of a specimen is enlarged
- magnification of objective lens times the magnification of the ocular lens
- magnification of objective lens times the magnification of the ocular lens
73
New cards
How is an ocular micrometer is calibrated?
- against the stage micrometer
74
New cards
What are the parts of a leaf cross-section?
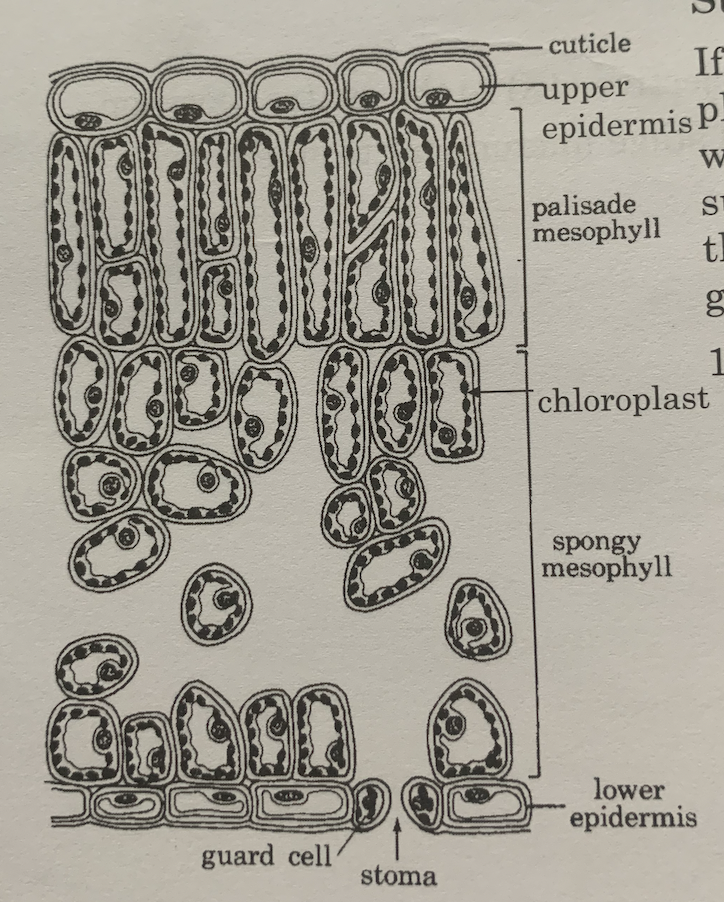
75
New cards
What is an upper epidermis?
- layer of transparent cells; light is absorbed through this layer
76
New cards
what is a cuticle?
- waxy layer which retards water loos from leaf surface
77
New cards
what is palisade mesophyll?
- layer beneath upper epidermis, cells that do photosynthesis
78
New cards
What are spongey mesophyll?
- cells that carry out photosynthesis
79
New cards
What are chloroplasts?
- in mesophyll cells
- moves up into direct light, moves down to shaded part
- moves up into direct light, moves down to shaded part
80
New cards
What are vascular bundles or veins?
- xylem: carries water to mesophyll cells
- phloem: carbohydrates by photosynthesis into mesophyll, transports to rest of plant
- phloem: carbohydrates by photosynthesis into mesophyll, transports to rest of plant
81
New cards
What are lower epidermis & stomata?
- where gas exchange and water evaporation occur
82
New cards
Why do devil's garden only have one species of tree?
because ants are responsible for keeping out other species
83
New cards
What are plant-animal interactions important?
- animals that feed on plants retain energy from plants
- organisms help plants to reproduce and survive
- lead to array od adaptations, which spur diversity
- organisms help plants to reproduce and survive
- lead to array od adaptations, which spur diversity
84
New cards
What are the different types of Interactions?
- mutualism
- competition
- consumer-resource interaction
- competition
- consumer-resource interaction
85
New cards
What is a positive effect?
- species benefit from interaction
86
New cards
What is negative effect?
- species do not benefit from reaction
87
New cards
What is no effect?
- species have no cost or benefit of interaction
88
New cards
What is effect does completion have?
- negative effect
- same resources between species
- same resources between species
89
New cards
What is the effect of mutualism?
- both species benefit
- example: animal pollination
- example: animal pollination
90
New cards
What is the effect of consumer-resource interactions?
- positive effect on one species
- negative on another
- example: predator and prey
- negative on another
- example: predator and prey
91
New cards
What are plant-herbivore interactions? negative or positive effect?
- herbivores that feed on plants
- reductions in seed set decrease plant fitness
- herbivores that consume and kill seeds have - effect
- transmit bacteria and viruses through mouth
- reductions in seed set decrease plant fitness
- herbivores that consume and kill seeds have - effect
- transmit bacteria and viruses through mouth
92
New cards
What is plant resistance?
- traits that increase a plants' resistance to herbivory
- resist attacks through tolerance and defence
- resist attacks through tolerance and defence
93
New cards
what is tolerance?
- plant's ability to reduce effects of herbivory on fitness
- physiological responses
- physiological responses
94
New cards
what is defence?
- trait that reduces damage to a plant by herbivores
95
New cards
What are the three different defences?
- timing of flowering or leaf production
- structural defences
- chemical defences
- structural defences
- chemical defences
96
New cards
What is phenology the study of?
- life cycles of plant and animals in relation to seasonal changes
- producing flowers when herbivores are least abundant
- producing flowers when herbivores are least abundant
97
New cards
What are some structural defences?
- roses have thorns
- poppies have trichomes hats that trap herbivores, preventing them from laying eggs or feeding
- poppies have trichomes hats that trap herbivores, preventing them from laying eggs or feeding
98
New cards
what are some chemical defences?
- protease inhibitors
- PSMs
- PSMs
99
New cards
What are constitutive defences?
- does not significantly fluctuate over time
100
New cards
What are induce defences?
- chemical is produced in response to damage