Biological approach
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is the biological approach
it combines psychology and biology to provide physiological explanations for human behavior.. Biological psychology tries to explain how we think, feel and behave in terms of physical factors within the body.
Key assumptions?
•Everything psychological is at first biological
•Much of human behaviour has a physiological cause which may be genetically or environmentally altered.
•Genes affect behaviour and influence individual psychological differences between people. Evolutionary psychology considers genetic influences in common behaviours
•The central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord is the main focus when explaining behaviour.
•The biochemistry of the body (neurotransmitters and hormones) influences behaviour and account for psychological disorders when out of balance.
What are the psychologists trying to determine?
the extent to which behaviours, or a characteristic such as intelligence, are the product of inheritance (genes), or environmental influences
What book did Charles Darwin write?
On the Origin of Species (1859)
Outline the theory of evolution
Charles Darwin proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection. In simple terms, the theory states that organisms that are better suited for their environment will survive and reproduce, while those that are poorly suited for their environment will die off.
What did Francis Galton say and then change?
1869 'all natural abilities are inherited' This is a simplistic viewpoint- Galton had to later agree that any resemblance between family relatives could be a result of both genes and shared environment.
Adoption studies
These studies involve comparing a trait or characteristic between adopted children and their biological or adoptive parents.
Selective breeding
artificially selecting male and female animals for a particular trait. These animals are then put together in order to breed and produce offspring.
What does selective breeding demonstrate
How a number of behavioural characteristics may have a genetic basis.e.g.maze bright rats
What do these studies show about the influence of genes on behaviour
-there is evidence from twin, family and adoption studies to suggest that certain behaviours for example, intelligence are genetically determined.
-research has shown that the environment can also play a role in determining behaviour
-selective breeding studies have demonstrated how a number of behavioural characteristics, for example, agression, can have a genetic basis.
What is physiology
the study of the body and its parts and how they function.
What impact did this theory have on psychology?
It inspired the development of evolutionary psychology.
Methods of investigating the genetic basis of behavior?
-twin studies
-family studies
-adoption studies
-selective breeding
What are Monozygotic twins
These twins are formed from one zygote that when fertilized, splits into two and forms two seperate embryos. Identical
What are Dizygotic twins
Two zygotes- these twins are formed when two seperate eggs both become fertilized by different sperm cells. Fraternal
Concordance rates
the proportion of pairs of individuals(within a population) that share a particular attribute, given that one of the individuals has that characteristic
Explain concordance rates in MZ twins
There should be 100% concordance rates between them if a particular characteristic is a purely genetic one.
Explain concordance rates in DZ twins
They will show lower concordance rates
What could you investigate
comparing twins raised together and twins raised apart
How are family studies used
uses genetic inheritance to explain how behaviors and traits are passed down through generations.
Lagerspetz(1979)- Selective breeding of agression in mice PROCESS
-mice were raised in isolation. he separated the mice into two groups depending on the level of aggression displayed when they were mixed with other mice.
-the mice that were most aggressive were classifies as aggressive(TA) and the others as non aggressive(TNA)
-These mice were interbred.
RESULTS
By the 19th generation aggressive biting behaviour in TA mice was 52%
In TNA it was only 5%
There were also structural differences. TA mice had heavier testes, and increased serotonin
Was the environment still envolved?
yes it had an influence as both types of mouse could be tamed
What are genes
the basic units of heredity. They function in pairs and the recombination of genes from parents to offspring provides the basis for genetic variability. Genes can only determine the potential for characteristics (genotype)
What is a genotype
The actual set of genes an individual has, or is made up of. The genetic material is made up of DNA which are given by the sperm and egg of the parents.
What does the genotype dictate
characteristics such as hair and eye colour. sets genetic potenitals for behaviour. each person apart from MZ twins has a genotype that is unique to them.
What is a phenotype
result of the interaction between that persons genotype and the environment. the individuals anatomical features or observed traits, such as behavioural and physical characteristics (shape, metabolic activities, size, colour)
What does it determine
these behavioural characteristics and physical attributes determine an individuals ability to reproduce and survive in the environment.
Give an example that shows the phenotype is influenced by the environment
Height.
The persons genotype will dictate the maximum height the person can reach.
environmental factors such as nutrition will affect the likelihood of the person reaching that height.
So a persons genotype give them the potential to be tall but if the environment does not provide the optimum conditions the person will not fulfil their potential.
Another example with twins
any differences between them e.g. personality are due to differences in their experience or environment as they are genetically identical.
Evolution
the changes in inherited characteristics in a biological population over successive generations.
Charles Darwins two main concepts
-natural selection
-sexual selection
What are adaptive traits?
Particular traits that an animal has which provides them with an advantage meaning these traits are passed on to their offspring
What do the behaviours need to adapt to?
the environment that the animal is living in which is dependent on three principles
What are the three principles that the environment the animal is living in depend on?
-the principle of diversity - the variety within a species
-the principle of interaction - which is how this variety of species adapt and fit in with the environment e.g. animals that breathe air wouldn't be able to permanently live under water
-the principle of differential amplification - those who adapt to their environment will reproduce and those that do not will die out.
In the context of sexual selection, what leads females to be more particular on who fathers their children
Males have an abundance of sperm and can reproduce with as many females as they want.
Females, however, are limited by the number of eggs she produces and the fact that she must carry the baby for 9 months and then raise it till the age of 18.
Therefore they are more particular due to the investment they have to make.
Describe the human body
the human body is a collection of biological systems, which all work together to keep us alive.
What are the key structures used to explain the behaviour and psychology of a person?
-The nervous system
-The endocrine system
What does the nervous system consist of?
-central nervous system (CNS)
-peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What does the CNS consist of and what does it do?
-brain and spinal chord
-where all the complex processing of info is done and where decisions are made
What does the PNS do?
brings information from the senses to the CNS and transmit information from the CNS to the muscles and glands
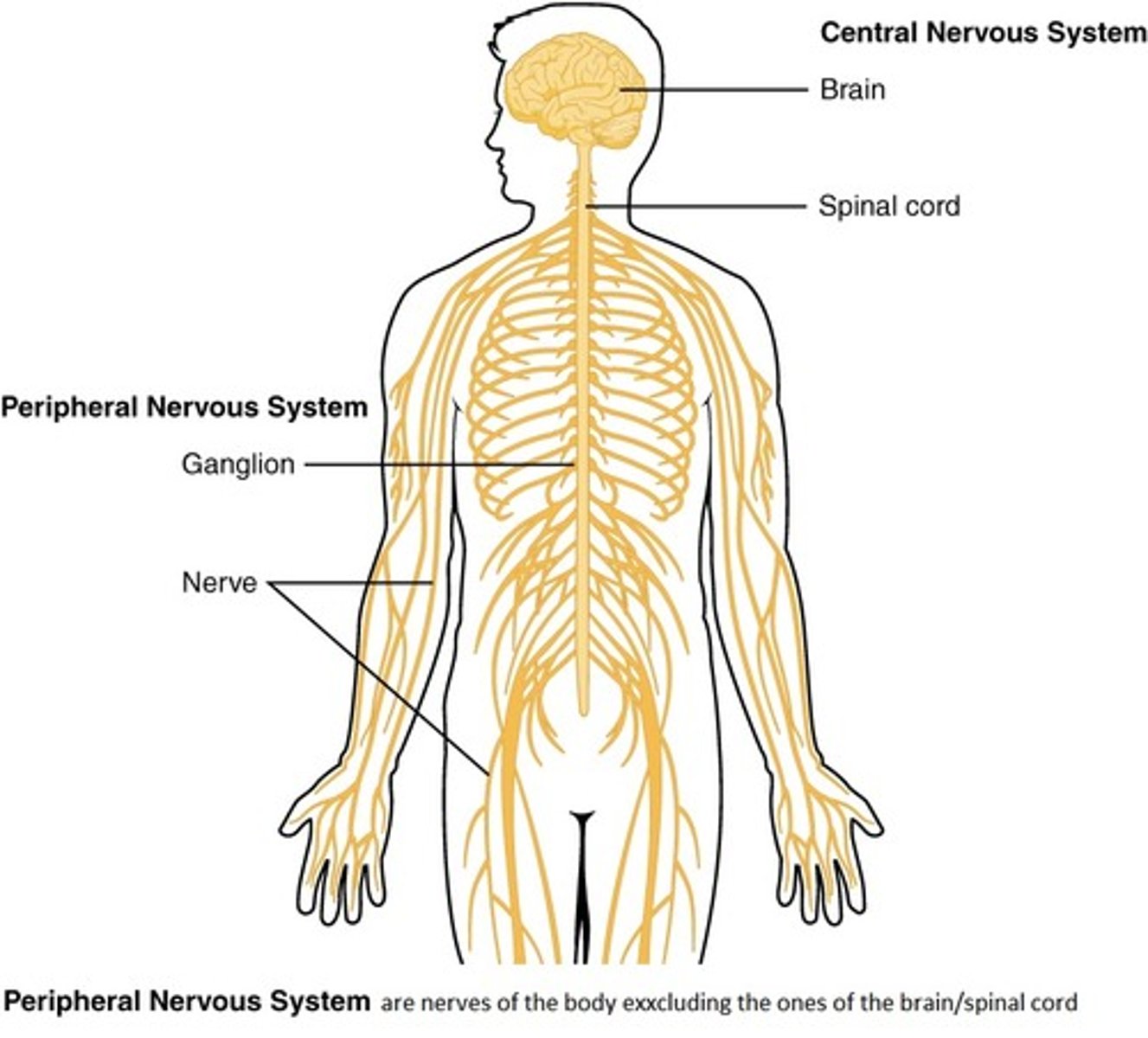
List the major sub-divisions of the human nervous system
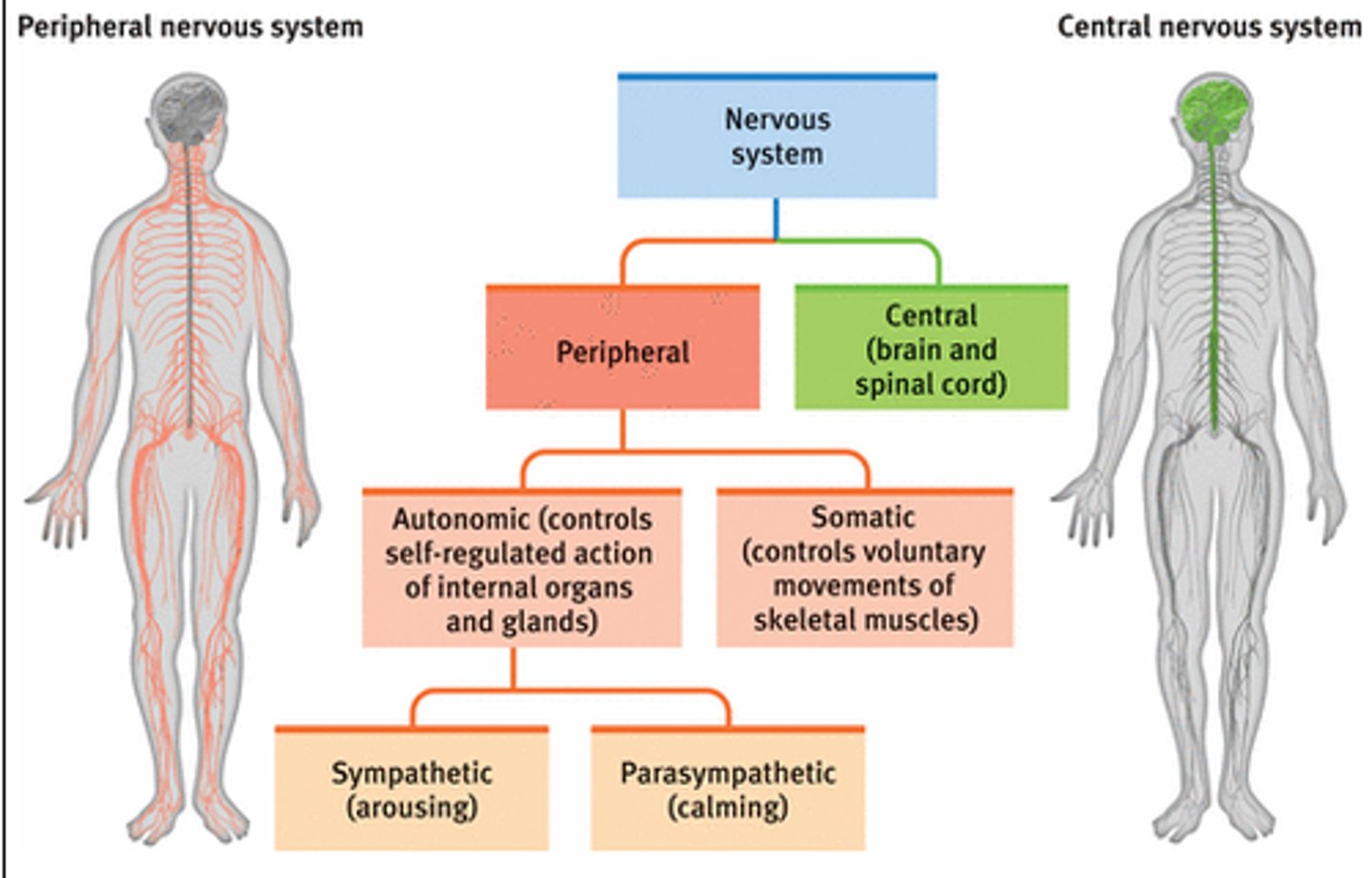
Human nervous system-PNS,CNS
-CNS-brain,spinal chord
-PNS-autonomic nervous system,somatic nervous system
-autonomic nervous system-sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system.
Brains outer layer
cerebral cortex- highly developed in humans
What is the spinal chord responsible for?
reflex actions
How does the PNS transmit messages?
via millions of neurons, to and from the central nervous system
What is the somatic nervous system responsible for?
carrying out sensory and motor information to and from the spinal chord
What does the autonomic nervous system do?
Governs vital functions in the body such as breathing, heart rate, digestion, sexual arousal and stress responses.
What is the autonomic nervous system's main role?
to maintain homeostasis
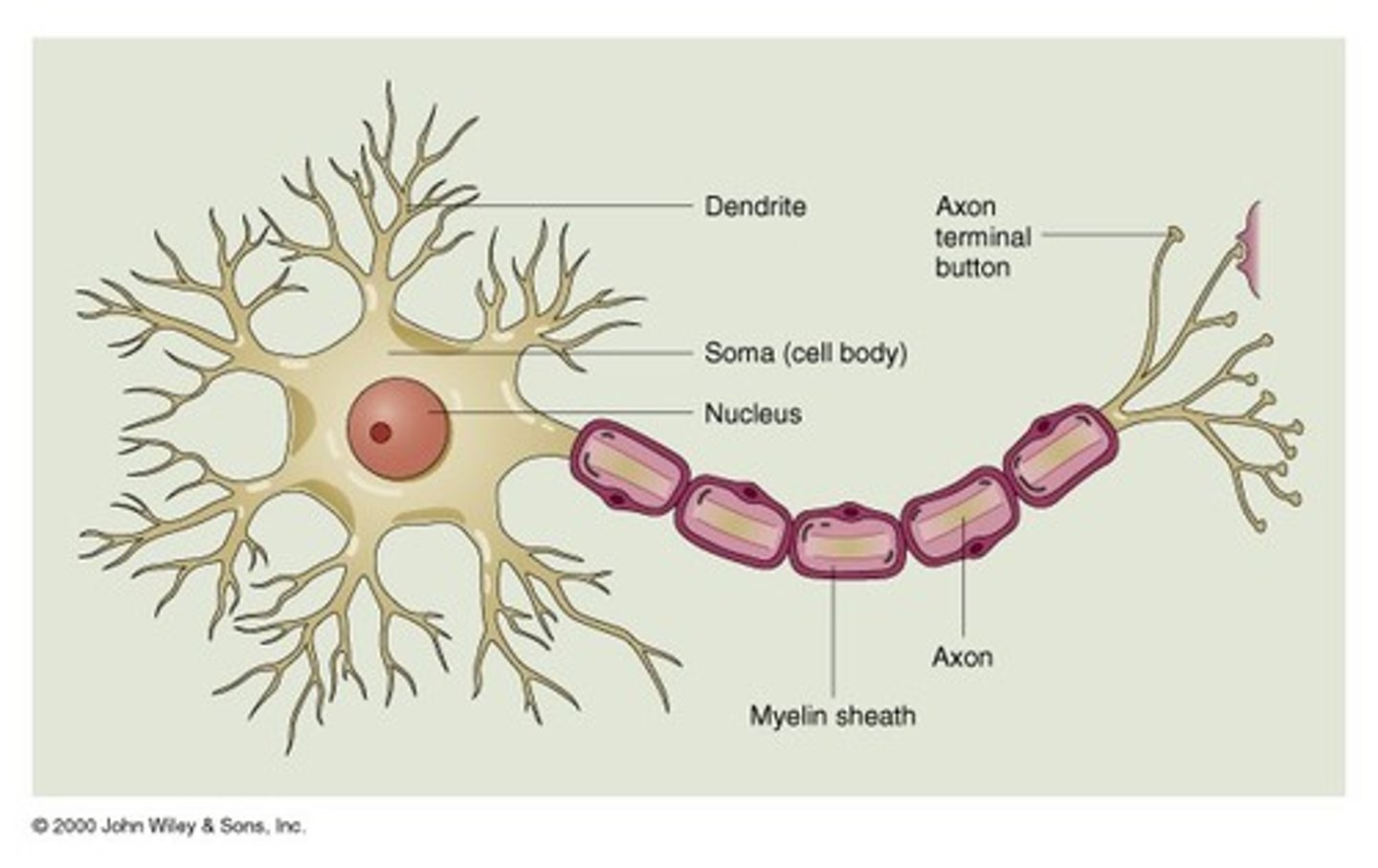
What are neurons
nerve cells that transfer information throughout the nervous system
Main role of the endocrine system?
to maintain levels of hormones in the blood and other bodily fluids. This is done by using the various glands in the body.
Which is the master gland that controls all of the other glands?
Pituitary
What types of body processes is the endocrine system in charge of?
ones that happen slowly, such as cell growth
What are the faster processes like breathing and body movement controlled by?
The nervous system
How do these systems help the body function properly?
By working together
What does neurochemistry refer to?
the chemicals that travel in the cerebral fluid (the fluid of the brain) between neurons.
What are the chemicals called?
These chemicals are called neurotransmitters and are extremely important in the normal functioning of the brain.
Reason why a neurotransmitter could be out of balance?
If a neurotransmitter is out of balance that can be the cause of a psychological abnormality. For example, high levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine are associated with schizophrenia.
Why don't neurons make direct contact?
There is a small gap between the neurons- synapse
How does the signal cross the gap to continue its journey to or from the CNS?
This is done using chemicals which diffuse across the gap between the two neurons. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters.
One strength
It is a scientific approach. This suggests that we can find cause and effect relationships of both physiology and behaviour.
Another strength
Scientific approach lends credence to study of psychology - establishes psychology as a respectable science
AAnother strength
Impact of biology on behaviour can lead to treatment and intervention to those suffering
AAAnother strength
Understanding how an abnormal brain works can shed light on normal brain functioning
AAAAnother strength
Measurements can be objective as it can be performed by machines which have no vested interest in the outcome e.g. PET scans, EEGs etc. Use of complex machinery allows accurate and precise measurements
One limitation
It is a deterministic approach as it believes that we are determined by our physiological, genetic or evolutionary make-up. Thus stating that there is no free will.
Another limitation
This approach is reductionist by stating that all human behaviour can be explained through biological processes and we are therefore not unique as individuals. It is also dehumanising to present humans as 'biological machines'
AAnother limitation
Biological approach ignores the role of the environment etc. it should be used in combination which is known as the biosocial approach.
AAAnother limitation
Research may focus on rare conditions that have little impact on the everyday lives of most people
AAAAnother limitation
Complex machinery operated by humans and therefore measurements could be subject to human error
AAAAAnother limitation
Correlations frequently employed - cannot determine cause and effect
AAAAAAnother limitation
Small or restricted samples make findings difficult to generalise
AAAAAAAnother limitation
Laboratory experiments lack ecological validity
Exam questions
Explain what is meant by genotype and phenotype (2 marks each)
Outline the influence of genes on behaviour (3 marks)
Using an example, explain how neurochemistry can influence behaviour (3 marks)
Outline the relationship between evolution and behaviour (4 marks)
Outline two weaknesses of the biological approach in psychology (4 marks)
What is the function of a neuron
It is a nerve cell which transfers information between the nervous systems.