Abnormal Psychobiology Exam 2 Part 4
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
The prevalence of ASD in white children was highest in 2017, but is now somewhat lower compared to Black, Hispanic, and Asian children
Which statement is TRUE regarding the prevalence of ASD diagnoses in Black, Hispanic, and Asian children relative to White children in the United States?
Since 2017 the prevalence of ASD in white children has been the highest
The prevalence of ASD in white children was highest in 2017, but is now somewhat lower compared to Black, Hispanic, and Asian children
The prevalence of ASD in white children used to be the lowest, but is now much higher compare to Black, Hispanic, and Asian children
In 2021, the prevalence of ASD was highest in White children, followed by Black, then Asian, then Hispanic children, respectively
fire action potentials both when observing an action performed by another organism and when an organism itself acts
Mirror neurons
are located within the primary visual cortex
are located within the fusiform face area in the temporal lobe
fire action potentials only when observing an action performed by another organism of the same species
fire action potentials both when observing an action performed by another organism and when an organism itself acts
There is no credible evidence linking MMR vaccination to an increased chance of ASD
Which of the following is TRUE?
In the current version of the DSM, ASD is considered a subcategory of Intellectual Disability
Rosa’s Law established mental retardation as the official term to refer to learning difficulties under federal law
Symptoms of ASD are similar to those of mercury poisoning
There is no credible evidence linking MMR vaccination to an increased chance of ASD
low APGAR score
According to the readings from this week, the largest risk factor in developing ASD would be
genetic female (XX) sex
having a younger-than-average age mother
low APGAR score
MMR vaccination
Concordance rate of ASD is higher for dizygotic than for monozygotic twins
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
The disrupted connectivity hypothesis of ASD proposes cortical underconnectivity of long-distance connections coupled with local overconnectivity
The letter P in APGAR score stands for pulse
Concordance rate of ASD is higher for dizygotic than for monozygotic twins
The letter G in APGAR score stands for grimace
involves a different chromosome
Compared to Down Syndrome, Williams Syndrome
is more common
involves a different chromosome
is a DSM diagnostic category, whereas Down Syndrome is a genetic condition
is now the preferred term for Down Syndrome in the latest version of the DSM
the amygdala is more activated when viewing threatening scenes
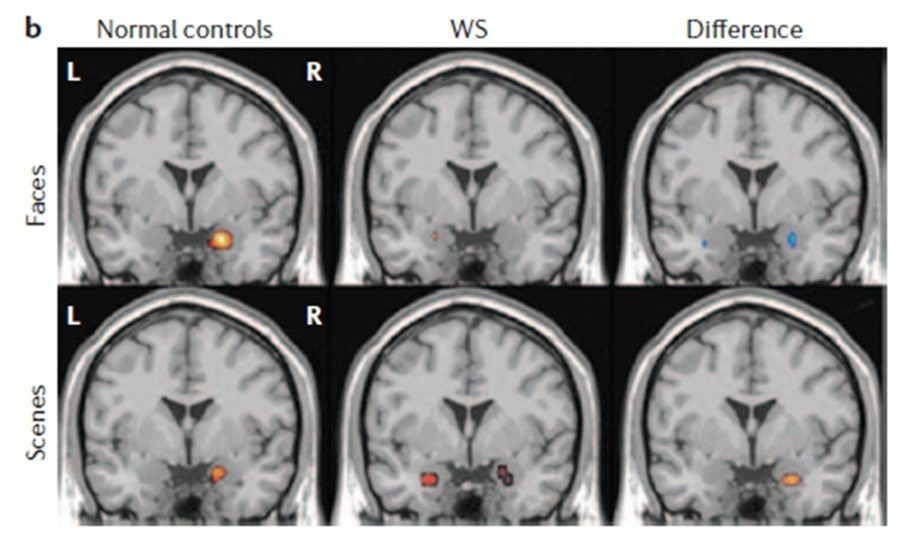
The images above show that in Williams Syndrome (WS), compared to controls,
the dorsal visual stream is more activated when viewing threatening faces
the amygdala is more activated when viewing threatening scenes
the ventral visual stream is more activated when viewing threatening faces
the amygdala is more activated when viewing threatening faces
In Williams Syndrome, the orbitofrontal cortex over-inhibits the activity of the amygdala
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
The chromosomal abnormality causing Williams Syndrome occurs on the q arm of chromosome 7
Individuals with Down Syndrome have three copies of chromosome 21
In Williams Syndrome, the orbitofrontal cortex over-inhibits the activity of the amygdala
The ventral visual stream is preferentially involved in object recognition and is also known as the “what?” stream
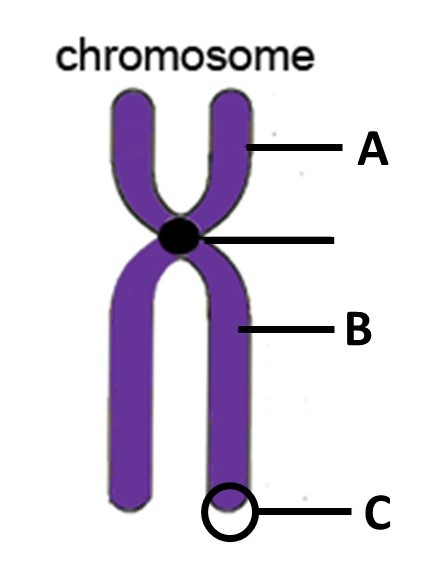
A) p arm; B) q arm; C) telomere
The correct labels for the features indicated at points A, B, and C in the figure above are
A) p arm; B) q arm; C) telomere
A) q arm; B) p arm; C) telomere
A) p arm; B) q arm; C) centromere
A) q arm; B) p arm; C) centromere
completing a visuoconstruction task
Hypoactivation in the parietal lobe of people with Williams Syndrome would most likely be observed when
viewing threatening faces
completing a visuoconstruction task
viewing pictures of snakes or spiders
completing a word association task
is caused by deletion of approximately 28 different genes on a single chromosome
Williams Syndrome
is the most common chromosomal abnormality
is caused by deletion of a single gene from approximately 28 different chromosomes
produces the same stereotypical facial features as Down Syndrome
is caused by deletion of approximately 28 different genes on a single chromosome
Many cardiovascular problems associated with Williams Syndrome are due to haploinsufficiency for elastin protein
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Individuals with Williams Syndrome tend to feel less empathy for other people
Individuals with Williams Syndrome tend to be fearless in all contexts, similar to individuals with amygdala lesions
Many cardiovascular problems associated with Williams Syndrome are due to haploinsufficiency for elastin protein
Many visual problems associated with Williams Syndrome are due to having an extra copy of chromosome 7
requires that symptoms persist for a minimum of 6 months
Schizophrenia
requires that an individual exhibit all of the following symptoms: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, disorganized/abnormal behavior, and negative symptoms
is clinically homogeneous across individuals in terms of symptoms
requires that symptoms persist for a minimum of 6 months
is classified as a neurodevelopmental disorder in the DSM-5
females tend to have more negative symptoms than males
Which of the following statements about negative symptoms of schizophrenia is FALSE?
more negative symptoms suggest a poorer prognosis
females tend to have more negative symptoms than males
anhedonia is a common negative symptom
negative symptoms often present before positive symptoms
are generally ineffective at treating negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Typical antipsychotic drugs
have fewer side effects than atypical antipsychotic drugs
are powerful dopamine agonists
are also prescribed to treat tardive dyskinesia
are generally ineffective at treating negative symptoms of schizophrenia
fixed beliefs that are not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence
Delusions are
perception-like experiences that occur without an external stimulus
fixed beliefs that are not amenable to change in light of conflicting evidence
the tendency to provide bizarre explanations for things
illogical connections in chains of thought
hyperactive
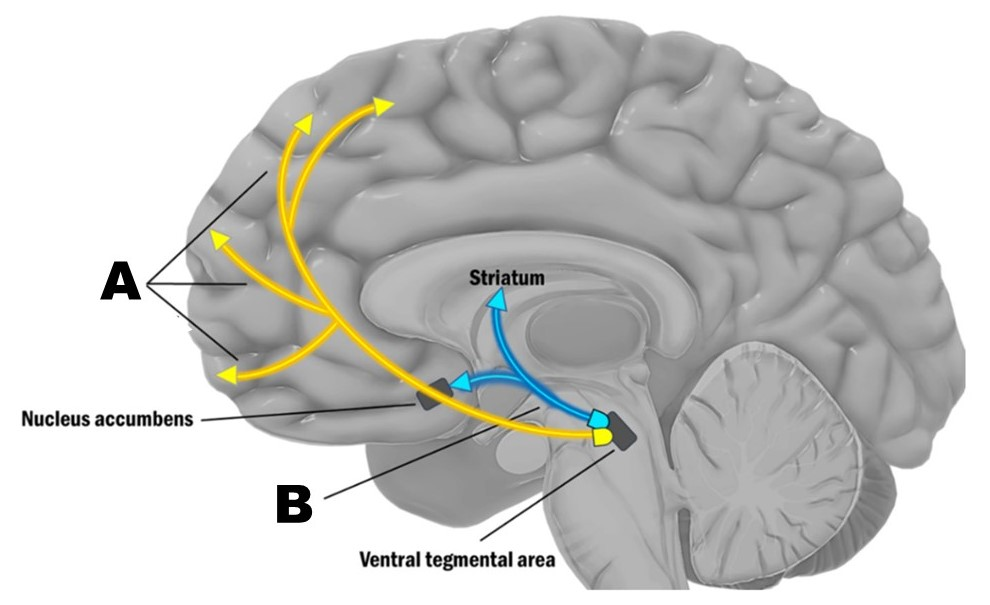
According to the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia, pathway B in the figure above is
hyperactive
hypoactive
missing
congenitally deformed
Catatonic excitement
Common negative symptoms seen in patients with schizophrenia include all of the following except
Avolition
Catatonic excitement
Anhedonia
Diminished emotional expression
are often partial dopamine agonists
Atypical antipsychotic drugs
include cocaine and amphetamines
are often partial dopamine agonists
are free of side effects
target GABA instead of dopamine
copy number variants
Variations, deletions, or duplications of larger chromosomal segments that may affect one or multiple genes
copy number variants
single-nucleotide polymorphisms
exons
introns
Williams Syndrome
All of the following are examples of complex diseases except for
Williams syndrome
schizophrenia
multiple sclerosis
asthma
adopting a precision medicine approach
The reading for this week suggests that clinical treatment for schizophrenia might be made more effective by
increased use of the general linear model to simplify research findings
“lumping” schizophrenia together with bipolar disorder due to their shared genetic overlap
adopting a precision medicine approach
making NIH funding for basic research contingent upon showing effectiveness in reducing the negative symptoms of schizophrenia
living in a rural area
Environmental factors that are correlated with higher rates of schizophrenia diagnoses include all of the following EXCEPT for
living in a rural area
cannabis abuse
complications during childbirth
prenatal malnutrition
exons
DNA regions that contain instructions for making proteins
copy number variants
megatrons
exons
introns
single-nucleotide polymorphisms
Variations in a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome
copy number variants
single-nucleotide polymorphisms
exons
introns
does not interfere with activities of daily living (ADLs)
Mild cognitive disorder
always precedes major cognitive disorder
always occurs following recovery from major cognitive disorder
does not interfere with activities of daily living (ADLs)
is characterized by major decline in multiple cognitive domains
Alzheimer’s disease
Potential causes of traumatic brain injury (TBI) include all of the following EXCEPT
contact sports (American football, rugby, boxing, etc)
Alzheimer’s disease
automobile accidents
falls
a more genetically influenced condition than late onset Alzheimer’s disease
Early onset Alzheimer’s disease is
more common than late onset Alzheimer’s disease
a more genetically influenced condition than late onset Alzheimer’s disease
defined as onset of symptoms after age 65 but before age 85
classified as a neurodevelopmental disorder in the DSM-5
delusional disorder
According to the DSM-5, subtypes of neurocognitive disorder include all of the following EXCEPT
traumatic brain injury (TBI)
vascular disorder
Parkinson’s disease
delusional disorder
the most common form of traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a concussion
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
an ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel bursts within the brain
a hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks the blood flow in an artery within the brain
the most common form of traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a concussion
L-dopa (levodopa), used to treat Parkinson’s disease, works by blocking dopamine receptors
delirium, major neurocognitive disorder, mild neurocognitive disorder
According to the DSM-5, neurocognitive disorders include
delirium, major neurocognitive disorder, mild neurocognitive disorder
schizophrenia, major neurocognitive disorder, Parkinson’s disease
delusional disorder, delirium, dementia
delusional disorder, schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s disease
Psychosis
Based on the research we presented, which peripartum disorder is not definitively linked to pro-inflammatory cytokine activity?
Anxiety
Depression
Anorexia
Psychosis
All of the above
What outcomes are associated with high levels of inflammatory cytokines?
High blood pressure
Poor digestive health
Mood dysregulation
All of the above
Strong social support
Which preventative factor is shared by all peripartum psychiatric disorders presented?
High levels of estrogen
Strong social support
Greater household income
Fewer previous pregnancies
Diet
Which of these is not strongly associated with the development of Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)?
Genetic factors
Childhood trauma
Attachment styles
Diet
Williams Syndrome
Which of these disorders is not commonly comorbid with Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)?
Bipolar Disorder
Antisocial Personality Disorder
Borderline Personality Disorder
Williams Syndrome
Cognitive behavioral therapy or schema therapy
Which of the following is considered the most appropriate treatment for Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)?
Cognitive behavioral therapy or schema therapy
Occasional participation in general support groups without structured therapy
Stimulant medications like methylphenidate as first-line treatment
Surgical intervention to reduce narcissistic traits
Optic nerve
The following brain areas are implicated in BPD EXCEPT:
Hippocampus
Optic nerve
Insular cortex
Amygdala
The DSM-5 states that personality disorders can only be diagnosed in adults
Which of the following is NOT a reason that a clinician may not diagnose BPD in a young adolescent?
The personality may not be fully developed by this age
BPD is a stigmatized condition
The DSM-5 states that personality disorders can only be diagnosed in adults
The emotional instability found in BPD can occur naturally in adolescent development
Differences in social communication, sensory processing, and repetitive behaviors
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of BPD?
Unstable interpersonal relationships
Recurrent suicidal behavior
An inability to regulate emotions
Differences in social communication, sensory processing, and repetitive behaviors
Cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuit
What cortical pathway is most associated with OCD?
Cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuit
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
Retino-tectal pathway
Eating
Which of the following is not a common compulsion in OCD?
Cleaning
Eating
Counting
Ordering and reorganizing
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
What is the best treatment for OCD in both children and adults?
SSRIs
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
SNRIs
Genetic predisposition
Which is NOT a possible environmental risk factor of adolescent drinking?
Peer influence/pressure
A family history of alcoholism
Peer and family relationships
Genetic predisposition
Social media
Smaller hippocampal volume
What is one brain related effect of adolescent drinking?
Smaller hippocampal volume
Larger amygdala
Larger frontal lobe
Smaller brainstem
Decreased white matter growth
Decreased anxiety
What is NOT one behavioral effect of adolescent drinking?
Increased aggression
Increased impulsive behavior
Heightened sensation seeking
Compromised executive functioning
Decreased anxiety