Chapter 20, Lesson 3: Capillaries and Fluid Exchange
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 20, Lesson 3 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Capillary exchange
The two-way movement of fluid across capillary walls between the blood and tissues; done through either:
diffusion
transcytosis
filtration
reabsorption
Diffusion
The most important form of capillary exchange
Glucose and oxygen diffuse out and carbon dioxide and wastes diffuse in the blood
Capillary diffusion requirements
The membrane must be permeable to the solute or passages must be available to pass through
lipid-soluble substances can diffuse through membranes
water-soluble membranes must go through pores
larger particles are held back
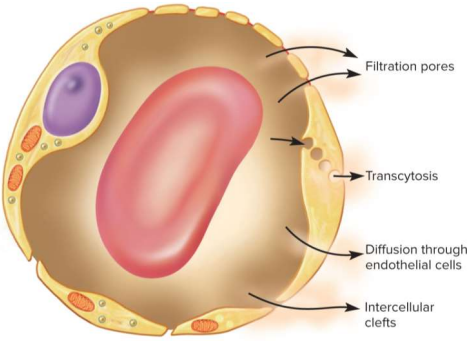
Transcytosis
Vesicle-mediated transport via endo- and exo-cytosis across the capillary wall; very small fraction of solute exchange but crucial for fatty acids, albumin, and hormones like insulin
Filtration and reabsorption
Fluid filters out of arterial end of capillary and osmotically enters venous end in reabsorption, delivering cell materials while removing wastes; can vary like in kidneys (more filtration) vs lungs (more absorption to avoid fluids)
Edema
The accumulation of excess fluid in a tissue; fluid filters in faster than it is reabsorbed and can causae tissue death, suffocation, headaches, or circulatory shock