Exam 4, Chapters 11-15
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Know the functions of the nervous system.
maintain body homeostasis with electrical signals
sensation
higher mental functioning
emotional response
activate muscles & glands
sensory input & motor output
What are the functions of neuroglia cells: supporting cell of nervous system.
CNS | PNS |
Astrocytes: facilitates formation of blood brain barrier, regulates extracellular environment of brain, anchors neurons and blood vessels in place, repairs damaged brain tissue | Satellite Cells: surround and support cell bodies |
Microglial Cells: act as phagocytes | |
Ependymal Cells: line cavities, cilia circulate fluid around brain and spinal cord, some secrete this fluid | Schwann Cells: myelinate certain axons in PNS |
Oligodendrocytes: myelinate certain axons in CNS |
Describe myelin including functions, composition, and formation.
composed of repeating layers of plasma membrane of neuroglial cell
contain lipids unique to neurolemmocytes & oligodendrocytes
high lipid content makes myelin a great insulator
myelinated axons conduct action potentials faster than unmyelinated axons
myelination - process of formation of myelin sheath by neurolemmocytes or oligodendrocytes
Define an action potential.
uniform, rapid depolarization and repolarization of membrane potential of cell
long-distance signals
What are the 3 types of channels. Which substances use which channels?
Voltage-Gated Sodium and Potassium Ion Channels: open or close during AP to send signal to another cell
located on axon which sends signals to other cells by generating & transmitting APs
Voltage-Gated Calcium Ion Channels: trigger exocytosis of synaptic vesicles
located on axon terminal
Leak Channels & Na+/K+ Pump: generate resting membrane potential & maintaining ion gradients
located on every part of neuron because resting membrane potential applies to entire neuron
What is a resting membrane potential? What is the charge inside the cell?
voltage difference across plasma membrane of cell when not being stimulated
about -70 mV
negative number because cell loses small numbers of positively charged potassium ions
Define depolarization, hyperpolarization, repolarization.
depolarization - temporary increase in cell’s membrane potential; becomes less polarized as reaching 0 mV
Na+ enters
hyperpolarization - change in membrane potential of excitable cell to a value more negative than its resting potential
repolarization - movement of cell’s membrane potential back toward resting level after depolarization happened
K+ exits
Know what occurs at each phase of the action potential graph: resting state, depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization.
Resting → Depolarization → Repolarization → Hyperpolarization
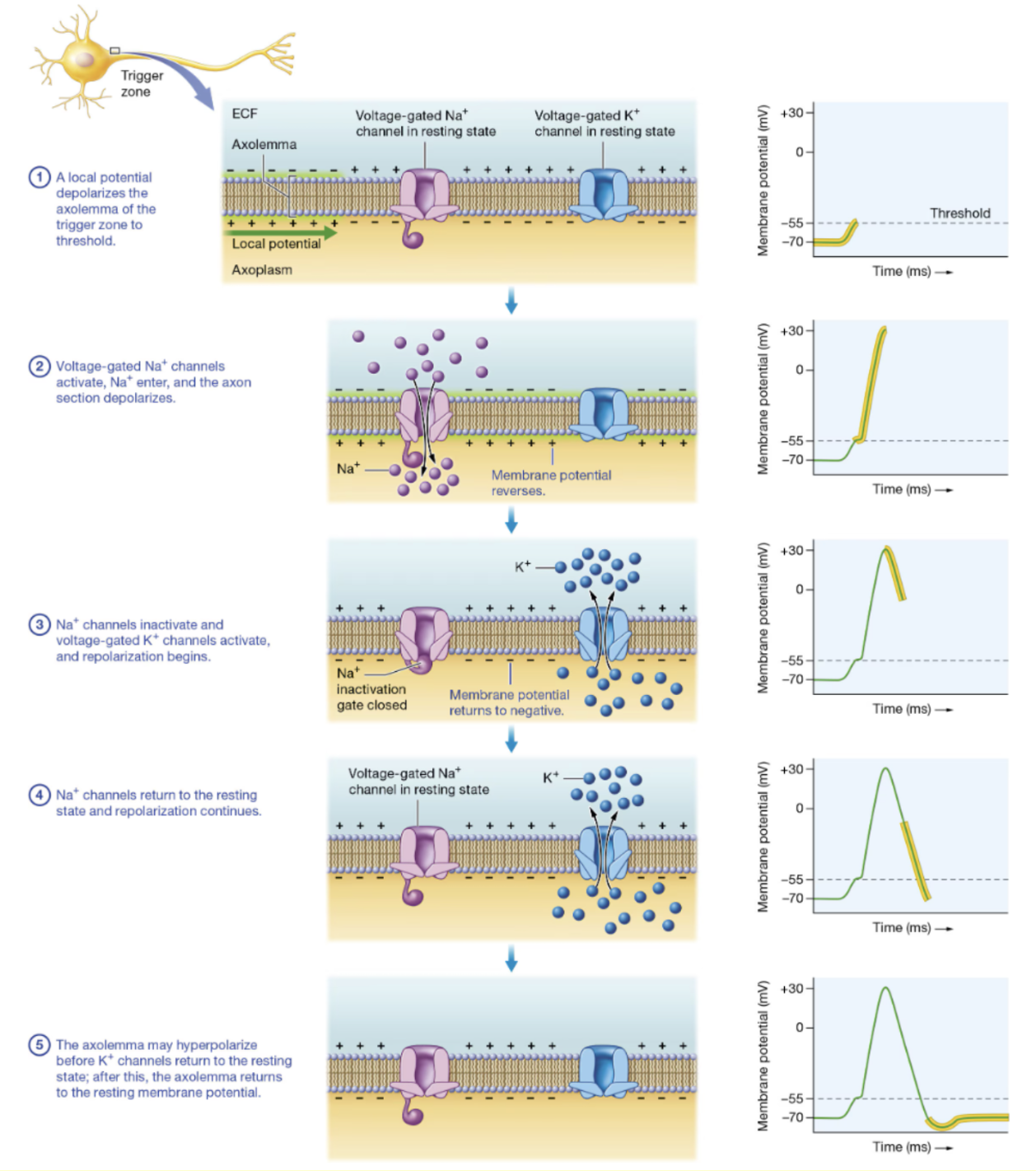
What is meant by “all or none” in regard to action potentials.
action potential either happens completely or does not happen at all
Why are absolute refractory periods important?
no additional stimulus is able to produce additional action potential
creates limit to how many action potentials happen
What are the functions of the dorsal root, dorsal root ganglia, and the ventral root?
dorsal root - sensory input
dorsal root ganglia - sensory cell bodies
ventral root - motor output
Describe the 3 layers of meninges.
dura mater - tough outer layer
arachnoid mater - middle, CSF circulation
pia mater - delicate inner layer
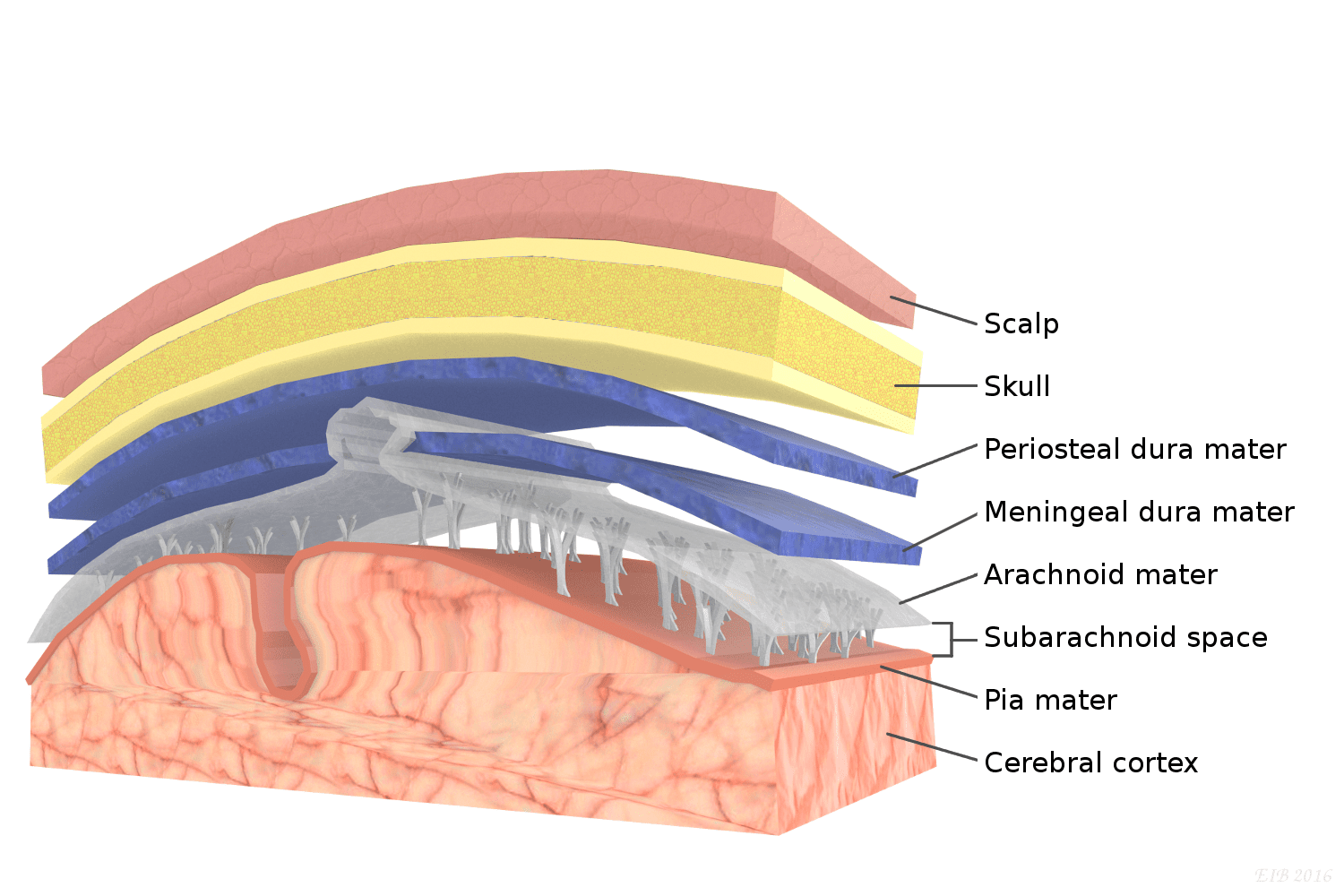
What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
cushioning
protection
nutrient & waste transport
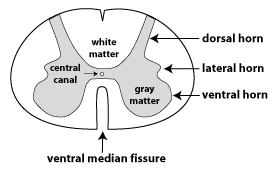
What are the functions of the posterior, anterior, and lateral horns of the gray matter?
posterior horn - receive sensory information
anterior - sends out motor signals
lateral - autonomic functions
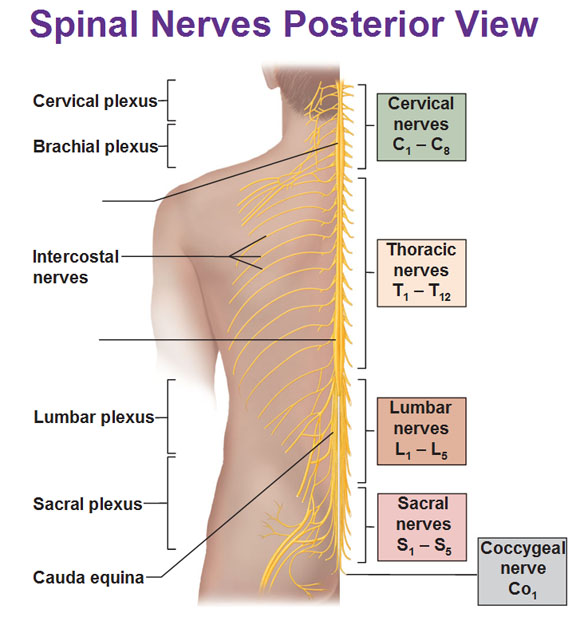
List the 4 major plexuses. What are the functions of the plexuses: cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral. Name at least one major nerve for each plexus.
Cervical (C1-C4) - innervates structures around head and neck
phrenic nerve
Brachial (C5-T1) - innervates skin and muscles of upper limb
axillary nerve, radial nerve
Lumbar (L1-L4) - innervates pelvis and lower limb
obturator nerve, femoral nerve
Sacral (L4-S4) - innervates pelvis, gluteal region, and much of lower limb
sciatic nerve
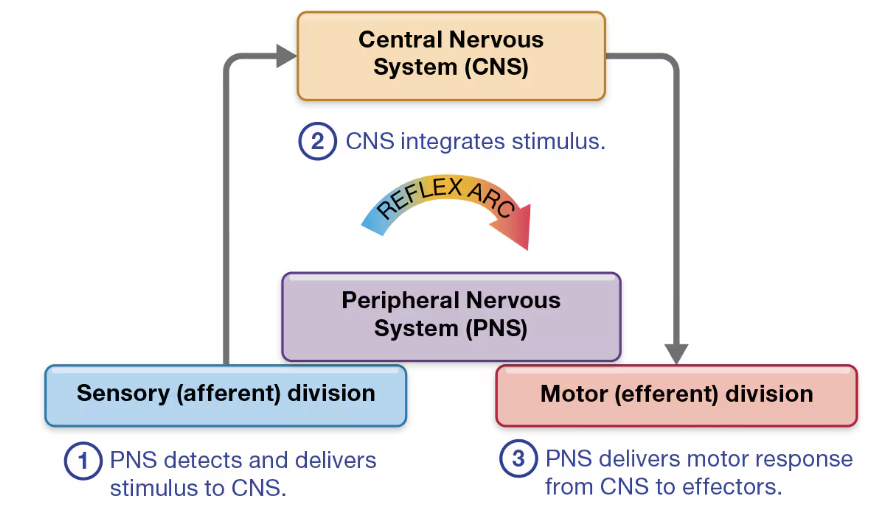
Know the 5 steps of a reflex arc.
Receptor - PNS detects
Sensory Neuron - delivers stimulus to CNS
Integration - CNS integrates stimulus
Motor Neuron - PNS delivers motor response from CNS to effectors
Effector - carries out response
What is the stretch reflex? Provide an example. Describe the withdrawal reflex and the crossed extensor reflex.
stretch reflex - monosynaptic reflex triggered by muscle stretch producing automatic contraction of muscle to counter stretch
knee-jerk
withdrawal reflex - polysynaptic reflex initiated by painful stimuli triggering withdrawal of affected body part
touch hot object
crossed extension reflex - polysynaptic reflex that occurs concurrently with withdrawal reflex triggering extension of limb on opposite of body from painful stimulus
maintain balance when pulling away from stimuli
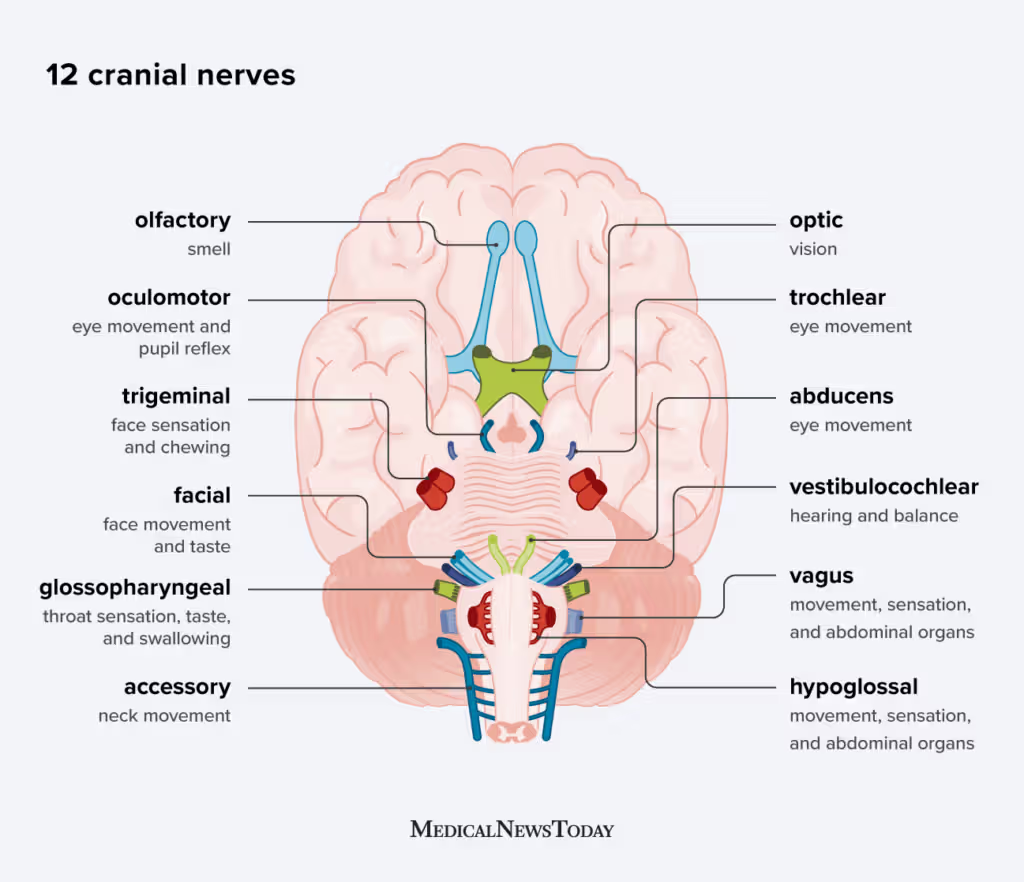
Know the names. numbers, and functions of the 12 cranial nerves. (CH 12)
oh, oh, oh to touch and feel very good vagina AH
some say marry money, but my brother says big boobs matter more
Olfactory - sense of smell; SENSORY
Optic - vision; SENSORY
Oculomotor - eye movement, pupil control; MOTOR
Trochlear - eye movement (looking down and moving eyes toward/away nose); MOTOR
Trigeminal - sensation in face, mouth, and head; chewing muscles; BOTH
Abducens - lateral eye movement; MOTOR
Facial - facial expression, salivation, taste; BOTH
Vestibulocochlear - hearing, balance; SENSORY
Glossopharyngeal - salivation, taste, swallowing; BOTH
Vagus - digestion, blood pressure, heart rate, breathing; BOTH
Accessory - head & shoulder control; MOTOR
Hypoglossal - tongue movements, speech, swallowing; MOTOR
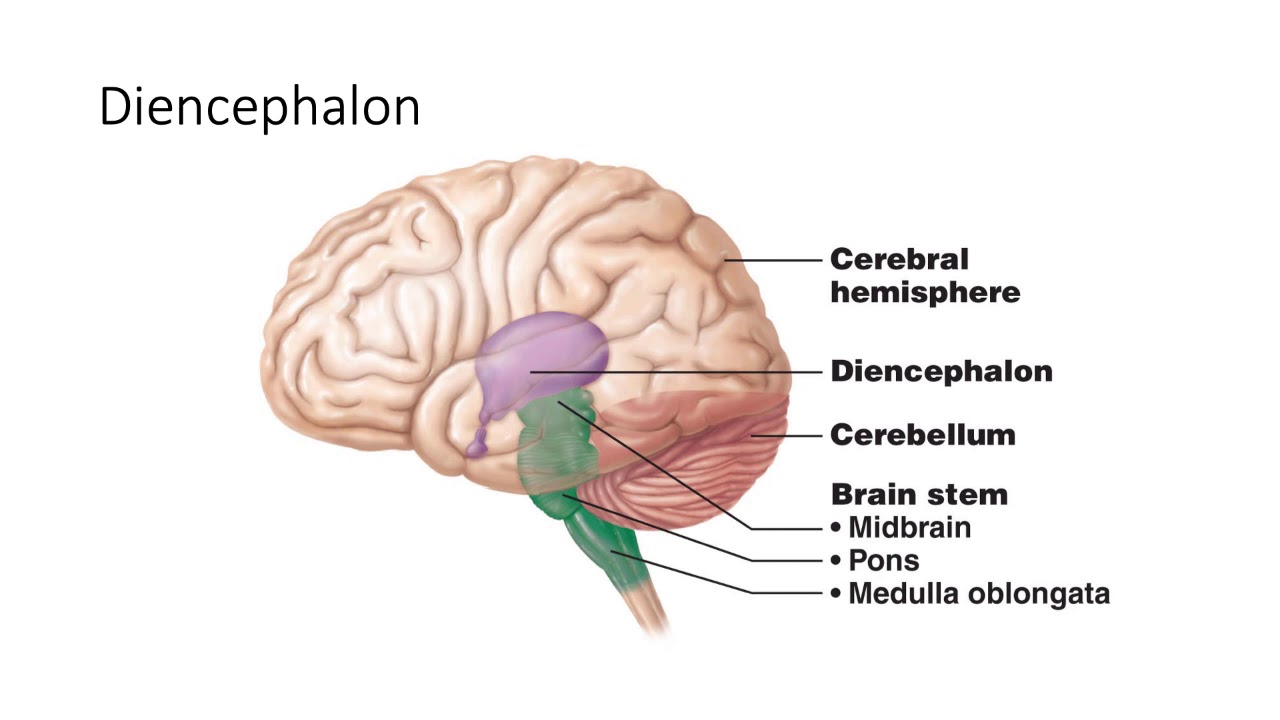
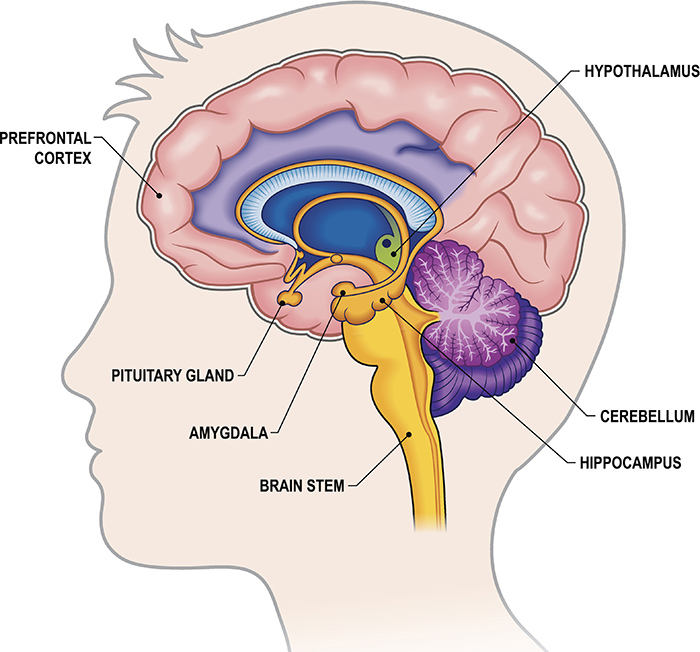
Identify the 4 parts of the brain along with major functions.
Cerebrum - higher mental functions
five lobes
Diencephalon - primary relay & processing center for sensory information and autonomic control
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus
Brainstem - connects brain and spinal cord; regulates involuntary bodily processes
midbrain, pons, medullar oblongata
Cerebellum - balance
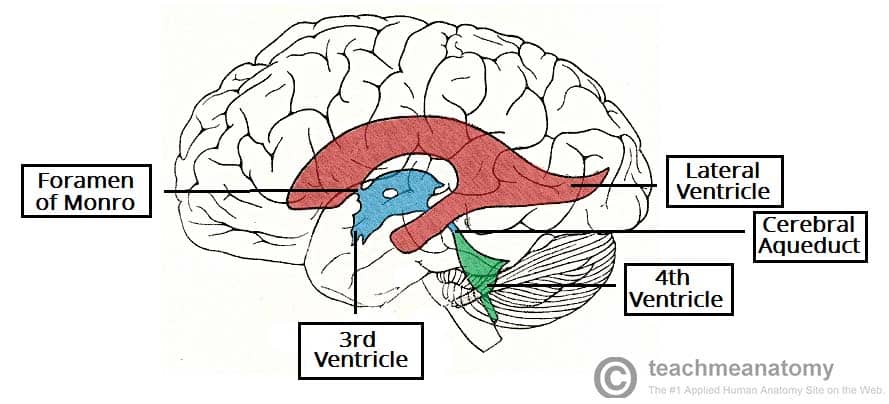
Know the 4 ventricles and where each is found. What fills the ventricles?
hollow cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid
Right Lateral Ventricle - in right cerebral hemisphere
Left Lateral Ventricle - in left cerebral hemisphere
Third Ventricle - in diencephalon
Fourth Ventricle - in hindbrain
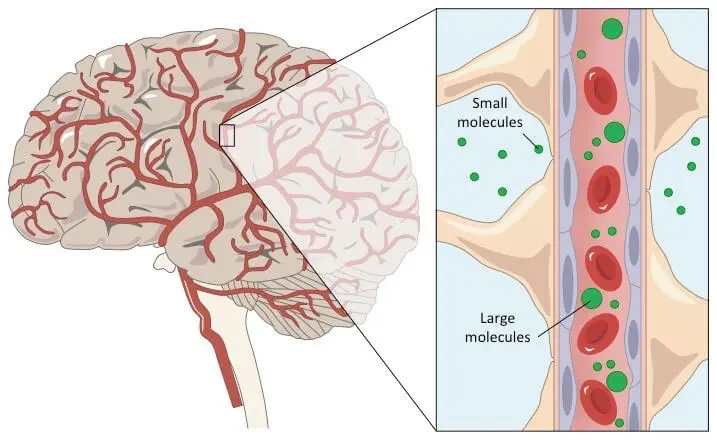
Define the blood-brain barrier. Which substances are allowed to pass through the barrier? (remember, large molecules such as proteins and urea are unable to enter)
keeps cerebrospinal fluid & brain extracellular fluid separate from blood, protecting brain from certain substances in blood
prevents substances (large, polar molecules) in blood from gaining access to cells of brain
allow water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and non-polar lipid-based compounds to pass
allow glucose, amino acids, and ions to pass if there are protein channels or carriers
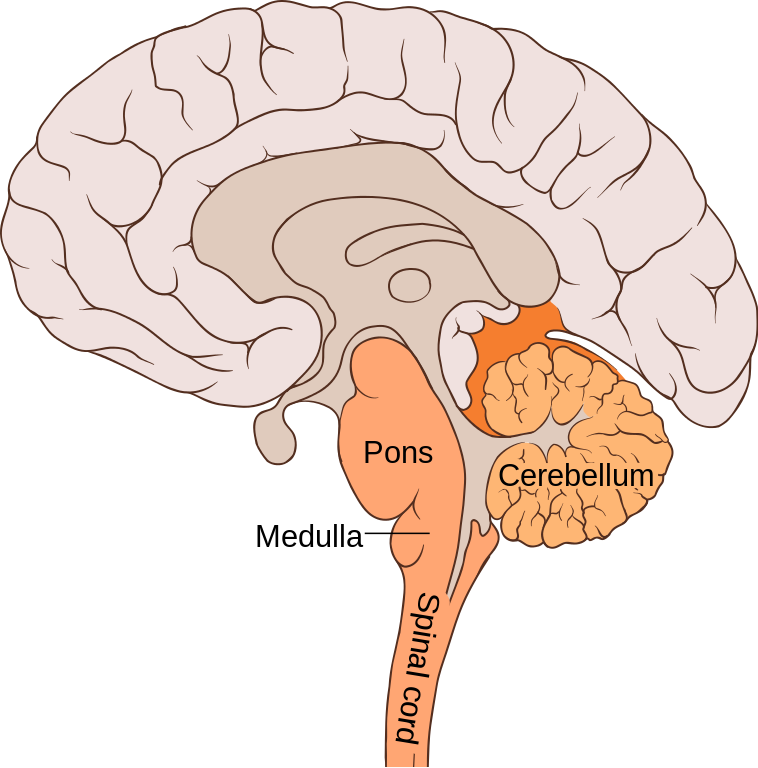
Know the functions of the brain stem (midbrain, pons, medulla) and the cerebellum.
midbrain - processes & routes visual and auditory stimuli to thalamus, mediates reflexes
pons - regulate breathing & sleep/wake cycle
medulla - regulate many autonomic functions (heart rate, blood pressure, respiration)
cerebellum - coordinates ongoing voluntary movement to reduce motor error; balance, coordination
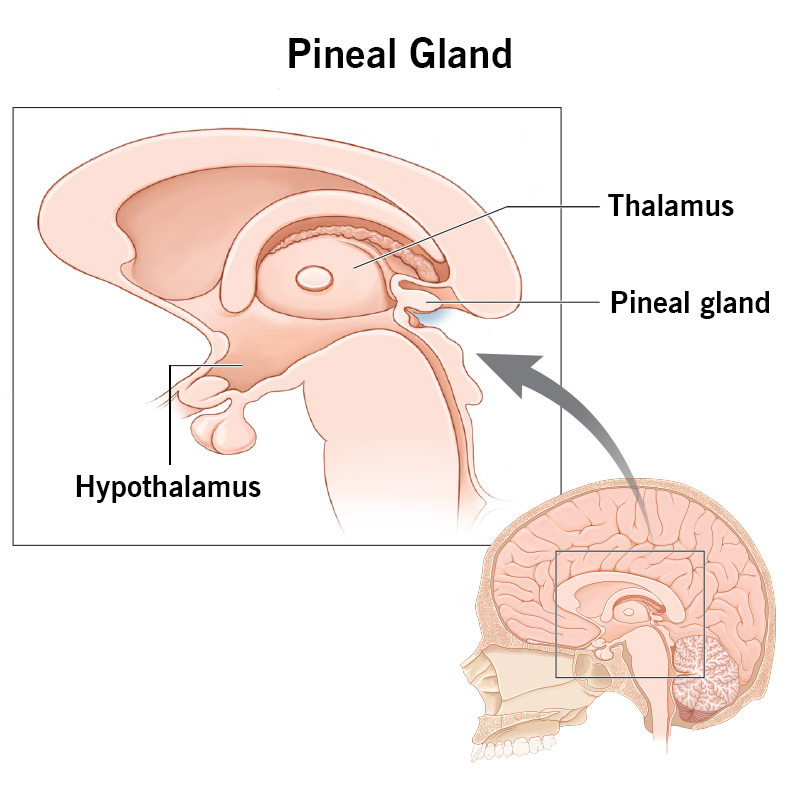
Understand these structures of the diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, pineal gland. What are their functions?
thalamus - controls sensory information entry into cerebral cortex
hypothalmaus - regulates autonomic nervous system, sleep/wake cycle, thirst & hunger, body temperature
processes ADH and oxytocin
controls secretion from anterior pituitary gland
limbic system - emotions, memory
pineal gland - sleep
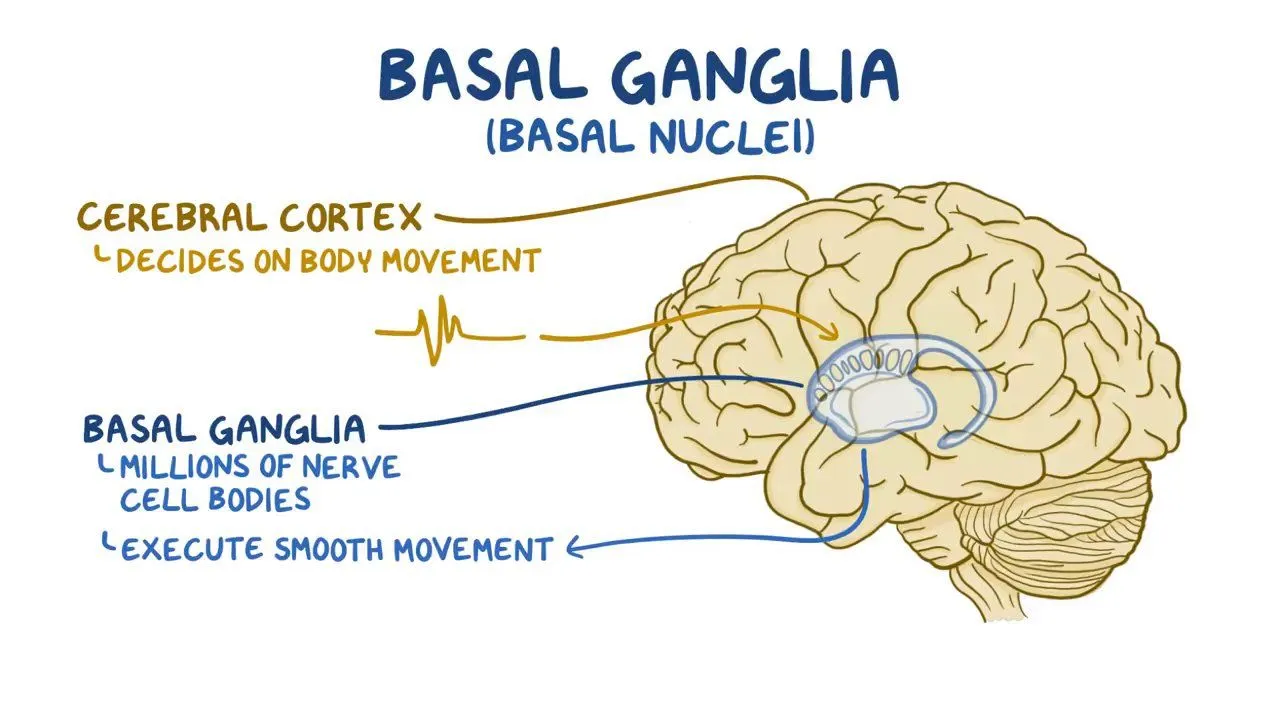
What are the functions of the basal nuclei? Which diseases may affect this area?
group of nuclei in cerebrum that function in movement (initiate voluntary motion)
(1) caudate nucleus, (2) putamen, (3) globus pallidus
Parkinson's Disease - movement difficult to initiate & difficult to end once started
tremor, minimal face expression
Huntington's Disease - jerky, involuntary movement
degeneration of basal nuclei
Differentiate between “left brain” and “right brain”. Define lateralization.
left - logic/language
right - creativity/spatial skills
lateralization - division of labor between the hemispheres
Define: concussion, contusion, subdural hemorrhage, and cerebral edema, paralysis, parasthesias, paraplegia, and quadriplegia.
concussion - mild brain injury
contusion - brain tissue bruising
subdural hemorrhage - bleeding between dura and brain
cerebral edema - swelling; buildup of excess fluid in brain
paralysis - loss of motor function
parasthesias - loss of sensation
paraplegia - paralysis of legs
quadriplegia - paralysis of all limbs
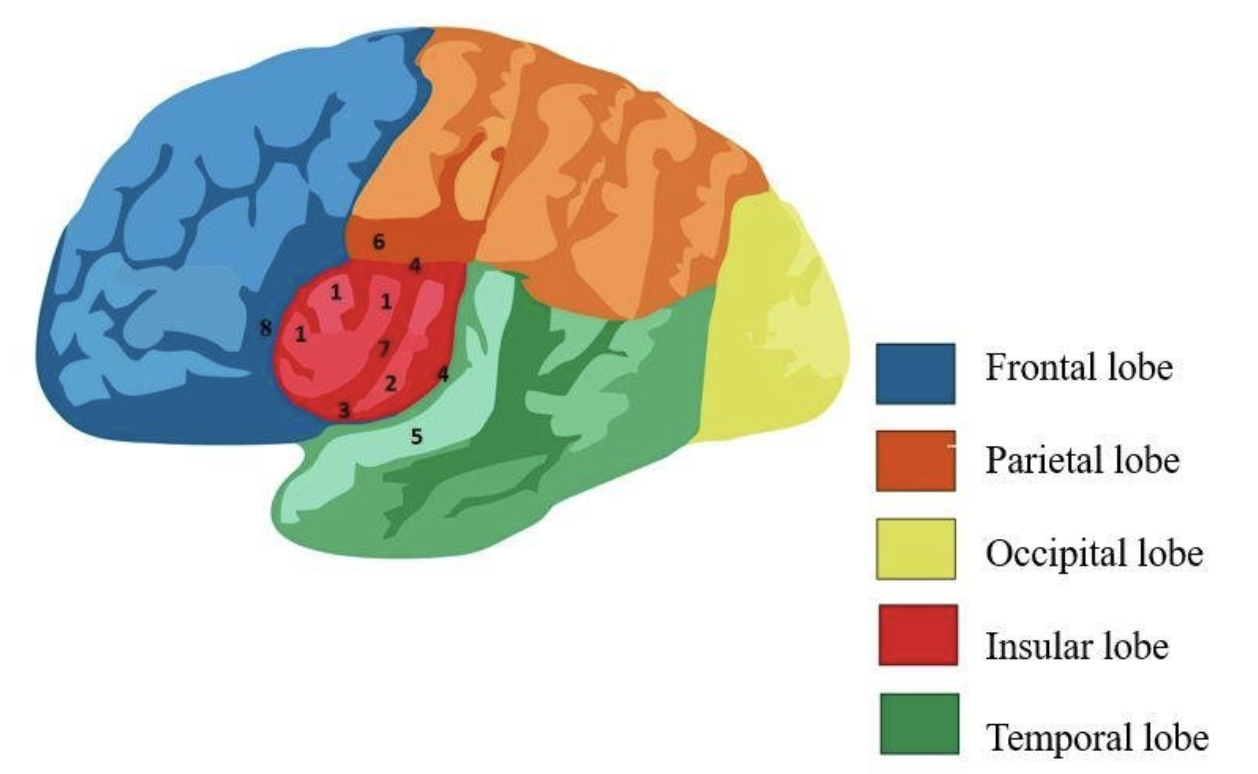
Know the functions of the lobes of the brain (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula).
frontal - planning, motor, complex mental functions
parietal - processing & integrating sensory information, attention
temporal - hearing, language, memory, emotions
occipital - vision
insula - deep lobes of cerebrum; have functions relating to taste and to viscera
Know the general function of the autonomic nervous system.
controls homeostatic responses of organs of many other systems
controls involuntary movement (heartbeat, breathing)
sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
Differentiate between the sympathetic NS and the parasympathetic NS. (See the 7 sympathetic responses and the 5 parasympathetic responses)
Sympathetic: fight or flight; speeds body functions up (heart rate, respiratory rate, dilate pupils, increase glucose)
heightened mental alertness
increased metabolic rate
reduced digestive and urinary functions
energy reserves activated
increased respiratory rate and respiratory passageways dilate
increased heart rate and pressure
sweat glands activated
Parasympathetic: rest and digest; slows things down (decreases HR, RR, increases digestion and elimination)
decreased metabolic rate
decreased heart rate and blood pressure
increased secretion by salivary and digestive glands
increased motility and blood flow in digestive tract
urination and defecation stimulation
Know the location of the ANS.
Sympathetic: T1-L2
Parasympathetic: Cranial and sacral regions
Know the functions of the following (some repeated information)
Medulla: vital center: regulates cardiac, vasomotor, respiratory system
Hypothalamus: regulates visceral functions, temperature, hunger, thirst, water, electrolyte balance Understand the important role of the hypothalamus “center of ANS activity”
Limbic: controls emotional responses and feelings.
What is meant by “dual innervation” in regards to sympathetic and parasympathetic NS.
SNS & PNS work together to maintain balance ensuring body’s needs are met
organs innervated by neurons from both systems
SNS becomes dominant & trigger effects to maintain homeostasis & PNS to regulate same organs and preserve homeostasis
Differentiate between the general senses and the special senses.
general - touch, pressure, pain, temperature; skin, various organs & joints
receptors: sensory neuron endings
stimuli transmitted through cranial and spinal nerves
special - vision, sound, taste, smell, balance; eyes, ears, nose, mouth
receptors: mostly specialized cells
stimuli transmitted only through cranial nerves
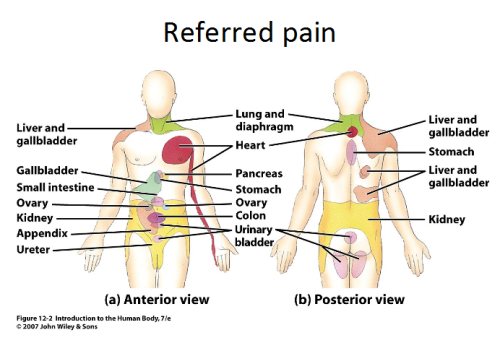
Why is perception of pain important? What is referred pain? Provide several examples.
perception of pain warns of damage
referred pain - pain that originates in organ is perceives as cutaneous pain due to sensory impulses from two regions following common nerve pathway to brain
heart attack → anterior chest wall & left arm
diaphragm → shoulder/back
kidney stones → lower back
Describe the olfactory nerve pathway.
receptors → olfactory bulb → tract → temporal cortex
Axons of olfactory neurons carry olfactory stimuli to olfactory bulb in CNS.
An olfactory stimulus travels from olfactory bulb to primary olfactory cortex in temporal lobe.
Describe the visual pathway. Include the basic eye and nervous structures: the eye: cornea, iris, pupil, retina, lens, anterior cavity, aqueous humor, posterior cavity, vitreous body; optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic radiations, thalamus, occipital cortex.
The retina of each eye detects visual stimuli from portions of the right and left visual fields.
Some visual stimuli cross at the optic chasma so that all stimuli from the right visual field are processed by the left hemisphere, and stimuli from the left visual field by the right hemisphere.
Visual stimuli travel from the thalamus to the primary visual cortex in the medial portion of the occipital lobe.
37. Describe the hearing pathway: include structures of the ear and nervous system: auricle, external acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane, auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), auditory tube, bony labyrinth (vestibule, semicircular canals, cochlea, perilymph), membranous labyrinth (endolymph), hair cells, otoliths, vestibulocochlear nerve, thalamus, temporal lobe.
Action potentials propagate through axons of the cochlear portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve to the cochlear nuclei at the medulla-pons junctions.
Axons from the cochlear nuclei synapse on the superior olivary nucleus in the pons.
Auditory stimuli are then sent to the inferior colliculus of the midbrain.
The auditory stimuli are relayed to the medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus.
The thalamus stimulates neurons of the primary auditory cortex in the superior portion of the temporal lobe.
Differentiate between static and dynamic equilibrium.
static - ability to maintain balance when the head & body are not moving
dynamic - ability to maintain balance when head & body are moving