DND ID (midterm): Therapeutics 1- general principles
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What are the 3 types of antimicrobial therapy?
Pt, bug, then drug
1.) Prophylaxis
2.) Empiric
3.) Definitive
Prophylactic Therapy
prevents an infection that has NOT YET developed
- high risk pts!
- CD4 <200
- surgical prophylaxis
Empiric Therapy
Suspected or proven infection
- responsible pathogen NOT YET identitfied
- best guess of agents most active against likely pathogens
Definitive Therapy
antibiotic therapy targeted to a specific microorganisms AFTER culture and antimicrobial susceptibility results are known
Which of the following scenarios most describes a pt w. an infectious disease?
A) 72 year old male, T 98.6, WBC 6,000, neutrophils 50%, bands 2%
B) 54 year old female, T 100.4, WBC 15,000, neutrophils 88%, bands 14%
C) 42 year old male, T 99, WBC 9,000, CRP 5 mg/dL, ESR 15 mm/hr
D) 23 year old female, T 98.7, WBC 8,000, procalcitonin <0.01 ng/mL
B) 54 year old female, T 100.4, WBC 15,000, neutrophils 88%, bands 14%
What is a fever?
elevation of body temp above NL
- oral= 98-98.6F
- CDC def= 100.4F
- non-specific symptom of infection
T or F: WBCs are leukocytes
True
- protects against infectious diseases and foreign invaders
What is Leukocytosis?
High WBC count
- in response to infection
- non-specific causes= stress, corticosteroids, malignancy
- normal range= 4000-10000 cells/mm
What do each part of a WBC differential tell you about infections?
Neutro: acute bacterial infections
- viral, fungal
- segs (mature) and bands (immature)
Lympho: viral or fungal infections
- TB
Monocytes: Chronic infections
- TB and lymphoma
Eosino: Parasitic Infections
- also allergic rxns
Baso: RARE allergic rxns
Are CRP and ESR biomarkers of infection?
YES!
- non-specific markers
- does not confirm infection
- RA, acute MI, and Crohn's
- Normal CRP= <10 ng/mL
- Normal ESR= <22 mm (M)/hr <29 (F)
T or F: Lactate is a biomarker for sepsis
true
- impaired tissue oxygenation
- normal= 0.5-1 mmol/L
T or F: Procalcitonin is a more specific marker of "bacterial" infections
True
- used to discontinue antibiotics
- need clinical judgement
- normal= <0.25 ng/mL
What are some local signs of infection?
1) @ site of infection
- pain, erythema, swelling, tenderness, purulent discharge
2) Imaging: x-ray, CT, MRI, echi
- inflammation, infiltrate, collection of lfuid
3) Tissue or fluid sample
- presence fo WBCs and bacteria
- ie) sputum, urine, SF, joint fluid
What changes indicate a more severe infection?
Hemodynamic changes
- HR and BP
Respiratory changes
- RR, rapid breathing, SOB
Neurologic
- altered mental status, lethargy, confusion, psychosis
Establish site of infection:
•Dysuria, flank pain, abnormal urinalysis?
Urinary Tract (UTI)
- Dysuria --> bladder involvement (cystitis)
- flank pain --> upper urinary tract infection (Pyelenophritis)
- and obvs abnormal urinalysis
Establish site of infection:
•Cough, chest pain, sputum, +CXR?
Lungs (Pneumonia)
- positive findings in chest X-ray
- obvs cough, chest pain, sputum
Establish site of infection:
•Headache, altered mental status, +LP?
CNS (meningitis/encephalitis)
- positive findings in lumbar puncture
- AMS and headache
Establish site of infection:
Fever, heart murmur, +blood cultures, +TTE?
Heart (Infective Endocarditis)
- positive findings in blood culture and transthoracic echocardiogram
Establish site of infection:
•Pain at IV site (central line), swelling, erythema, +cultures?
Central Line Catheter Infection
- infection in bloodstream
Non-lactose fermenting, gram-negative rods suggest:
A.Pseudomonas aeruginosa
B.Staphylococcus aureus
C.Streptococcus pneumoniae
D.E. coli
A.Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Gram-positive cocci in clusters suggest:
A.Pseudomonas aeruginosa
B.Staphylococcus species (S. aureus, S. epidermidis)
C.Streptococcus species (S. pneumoniae)
D.E. coli
B.Staphylococcus species (S. aureus, S. epidermidis)
What are the 2 specimen types?
Sterile
- blood
- sputum (deep)
- urine
- CSF and joint fluid
- tissue
- abscess
Non-sterile
- stool
- throat swab
- wound swab
- genital swab
T or F: Blood cultures are collected when pt is acutely ill
true
- incubated for 5-7 days
- 2 sets, 2 body sites
- 1 set= 1 aerobic and 1 anaerobic
How should urine cultures be collected?
clean catch midstream or via catheter
- never collect urine from catheter bag
- use needle to collect from tubing
Urine Dipstick vs Urinalysis
Dipstick: Rapid screening
- leukocytes, nitrites, blood, etc
Urinalysis: under microscope
- appearance and bacteria load
- WBCs (>4000 cells/mm)
- epithelial cells and RBCs
Gram stain on Gram (+) vs Gram (-)
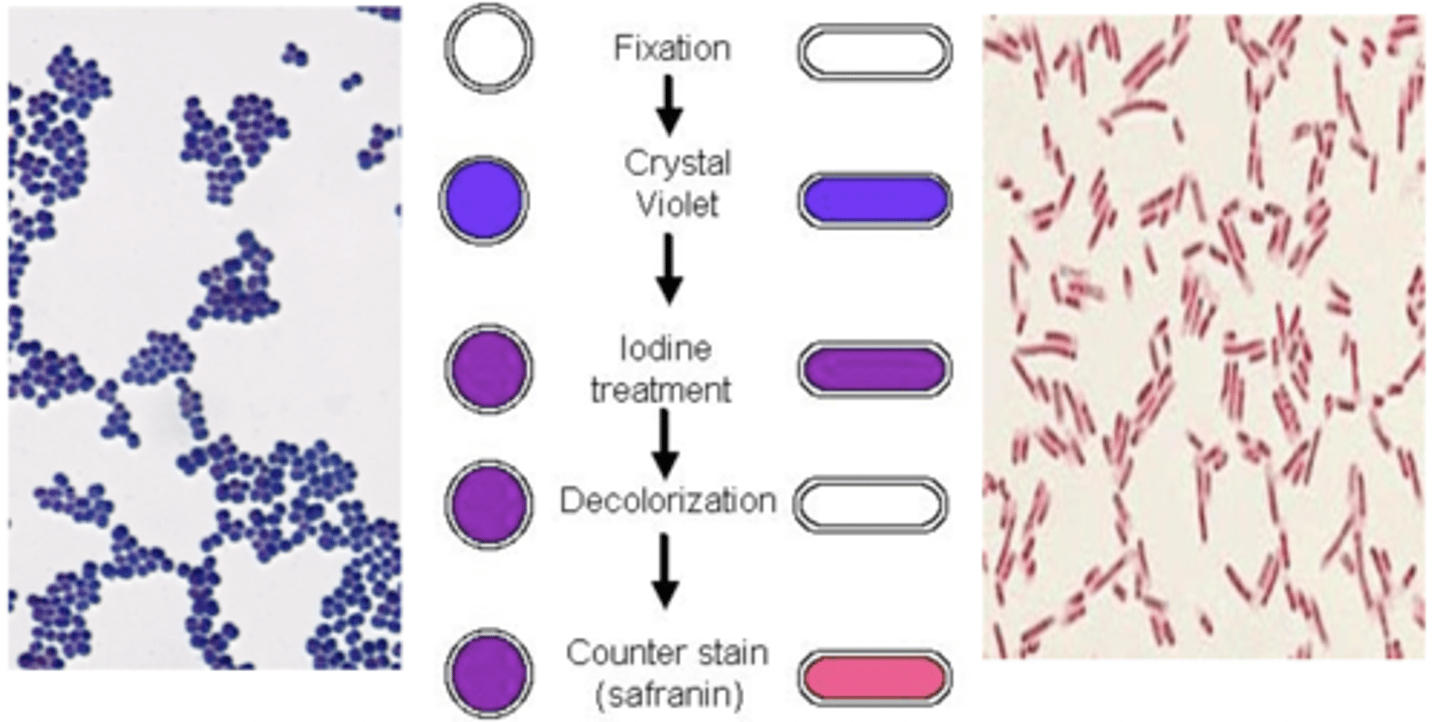
Cell Wall on Gram (+) vs Gram (-) Bacteria
Gram (+)
- no LPS
- no outer membrane
- THICK peptidoglycan layer
Gram (-)
- LPS
- outer membrane
- THIN peptidoglycan layer
Gram (+) aerobes
Cocci
- chains & pairs (strep/entero)
- clusters (stap A. staph ep.)
Bacilli/rods
- corynebacterium
- listeria
Gram (+) anaerobes
Cocci
- pepto
- peptostrepto
Bacilli/rods
- clostridium
Gram (-) aerobes
Bacilli/rods
- lactose fermenting (e. coli, enterbac, klebsiella)
- non-lactose (pseudo a. and acinetobacter)
Cocci
- neisseria
- n. gonorrhoeae
- haemophilius influenzae
Gram (-) Anaerobes
Bacilli/rods
- Bacteroides spp
- fusobacterium spp
- prevotella spp
Atypical bacteria include...
- mycoplasma
- legionella
chlamydophila
Mycobacteria vs Fungi vs Viral Species
Mycobacteria
- mycobactrium tuber, mycobacterium avium
Fungi
- aspergillus, candida, cryptococcus, histoplasma, tinea
Viruses
- flue, hep A/B/C/D/E, HIV, herpes, RSV, EBV
Contaminate vs Colonizer vs Pathogen
Contaminate
- introduced into specimen from external source
- poor technique/sample/collection
Colonizer
- "normal flora" does not cause harm
Pathogen
- damages tissue, elicits host response
Respiratory cultures were sent. Preliminary microbiology report reveals gram negative rods, non-lactose fermenting. Final report: Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Two sets of blood cultures were also sent. Preliminary microbiology report 1 out of 2 sets of blood cultures reveals gram positive cocci in clusters, coagulase negative. Final report: Staphylococcus epidermidis
Patient is currently on piperazillin-tazobactam and vancomycin.
Which of the following is the most appropriate antibiotics for RJ based on his cultures?
A.Continue piperacillin-tazobactam and vancomycin
B.Continue piperacillin-tazobactam and discontinue vancomycin
C.Continue piperacillin-tazobactam, start amikacin, and discontinue vancomycin
D.Discontinue piperacillin-tazobactam and vancomycin and start ciprofloxacin
B.Continue piperacillin-tazobactam and discontinue vancomycin
Which antibiotics cover P. Aeruginosa?
- beta-lactams
- floroquinolones
- aminglycosides
- combination drugs
What is the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)?
Lowest drug conc that prevents visible growth of an organism after 24 hrs in vitro
- good indicator of antibiotic potency
- MIC values are different for each organism-antibiotic pair
What is the CLSI? What do they do?
Clinical Lab Standards Institute
- establish MIC breakpoints for each organism to each antibiotic
- updated annually
What are antibiograms used for?
deciding empiric antimicrobial therapy
- cumulative report of antibiotics
- % susceptible or resistant
Vancomycin was discontinued. S. epidermidis was determined to be a contaminate since it only grew in 1 out of 2 sets of blood cultures and it is a common normal skin flora. Respiratory cultures were sent. Preliminary microbiology report reveals gram-negative rods, non-lactose fermenting. Final report: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Is piperacillin-tazobactam the best choice for empiric antimicrobial therapy for nosocomial gram-negative coverage?
Yes!
- If the strain is susceptible, therapy can continue
- In resistant cases, alternatives may be used
Is it a true allergy, toxicity, or intolerance:
nephrotoxicity w/ gentamicin?
True allergy
Is it a true allergy, toxicity, or intolerance:
diarrhea w/ doxycycline?
Intolerance
Is it a true allergy, toxicity, or intolerance::
Hives and SOB w/ penicillin?
true allergy
Is it a true allergy, toxicity, or intolerance::
thrombocyptopenia w/ linezolid?
toxicity
Is it a true allergy, toxicity, or intolerance::
SJS w/ TMP/SMX?
true allergy
What % of the US reports they're allergic to penicillin? What % is TRULY allergic?
10% reports PCN allergy
- 1% is truly allergic
- if pt is TRULY allergic, use alternative meds, graded challenge, and desensitization
T or F: 80% of pts w/ IgE-mediated PCN allergies lose their sensitivity after 10 years
true
- decreases by 10% per year of avoidance
T or F: Certain antimicrobial drug tx should be avoiding in certain age groups
true
- ie) ceftriaxone in neonates should be AVOIDED
- WHY? hyperbilirubinemia and interactions w/ Ca
What numerical value assesses hepatic function?
Child Pugh Score
T or F: Pregnant and lactating women can shouldn't take certain drugs because it puts them and their child at risk
True
- teratogenicity
- altered PK (increased Vd, renal blood flow, hep and metab activities)
- antibiotics conc. in breast milk
Pts with G6PD may experience hemolytic anemia when taking...
- dapsone
- primaquine
- nitrofurantoin
Pts w/ HLA-B*5701 allele may experience a hypersensitivity reaction with what drug?
Abacavir
Why are diabetes pts more susceptible to infection?
they have poor peripheral blood flow
- causes higher risk of infection
- more difficult to treat
Why are pts w/ chronic lung disease/cystic fibrosis more susceptible to infection?
There are different microorganisms
Why are HIV/AIDS pts more susceptible to infection?
their immune system is suppressed
T or F: different antibiotic dosing is required depending on the location of the infection
True
- aminoglycosides in uncomplicated UTI vs severe infection
Which antibiotic has better penetration/concentration:
Cefepime vs piperacillin/tazobactam in CNS?
Cefepime
Which antibiotic has better penetration/concentration:
Polymyxin B va Colistin in URINE?
Colistin
Which antibiotic has better penetration/concentration:
Daptomycin in PNEUMONIA?
Daptomycin is NOT EFFECTIVE in pneumonia
T or F: You should start antibiotic treatment with IV then switch to PO if an infection is severe
True
What is time-dependent killing (T>MIC)?
Rate/extent of bacterial killing depends on the time the active drug conc remains above MIC
- ie) Beta-lactams
What is concentration-dependant killin (Cmax:MIC)?
Rate/extent of bacterial killing depends on antimicrobial conc
- ie) aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones
Benefits of prolonged infusion of Beta-Lactams
maximize the duration that pathogen is exposed to beta-lactam
- time-dependent
- T>MIC
- prolonged infusion over 3-4 hrs (not 30 min)
- good for critically ill pts and pathogens w/ high MICs
Benefits of Extended Interval Aminoglycoside Dosing
Decreases nephrotoxicity
- Cmax:MIC for rapid killing
- high dose ONCE daily
- Gentamicin 5-7 mg/kg q24h
- Amikacin 15 mg/kg q24hr
- easy admin and drug monitoring
Why is combination therapy preferred?
Broad spectrum coverage (esp for mixed/nosocomial infection)
- SYNERGISTIC (1+1=2)
- prevent resistance
What is an example of a synergistic drug combo?
Beta-lactam + aminoglycoside
- enterococcal endocarditis --> rapid killing!
What are some disadvantages of combo drug therapy?
- superinfection
- toxicities
- antagonistic effects
- $$$
When do we know its ok to switch antibiotic from IV to PO?
- overall clinical improvement
- no fever for 24 hrs
- decrease WBC
- functioning GI tract
Which antibiotics have great oral bioavailability?
- ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin
- clindamycin
- doxycycine
- metronidazole and moxifloxacin
- linezolid
- TMP/SMX
What antibiotics cover MRSA?
- Vancomycin/Clindamycin/Daptomycin
- Linezolid Tedizolid
- TMP/SMX
- Doxycycline/Tigecycline
- etc!
What is intrinsic resistance?
resistance is natural to the organism
- ie) vancomycin vs gram (-) bacteria
- ie) cephalosporins vs enterococcus
What is acquired resistance?
caused by prior exposure to the antibacterial (inappropriate use of abx)
- decreased permeability
- efflux pump
- drug inactivation/mod
- altered target site
What is MRSA?
methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- altered target site: PBP2 --> PBP2a
- resistant to meth, oxa, nafc
- 1st line: VANCOMYCIN
- alt: dapto, linezolid, ceftatro
What is VRE?
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
- altered target site: D-ala-D-ala --> D-ala-D-lac
- 1st line: Dapto, linezolid
What is EBSL?
Extended spectrum beta-lactamases
- hydrolyze beta-lactam ring
- inactivate most beta-lactams
- gram (-) bacteria
- 1st line: carbapenams
What is CRE?
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales
- carbapenamases inhibit ALL beta-lactams
- 1st line: combo drugs like polymyxin, ceftazidime/avibactam, meropenem/vaborbactam