Week 8 - Eyewitness Testimony
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What does it mean for eyewitness testimony to be unreliable? (2 points)
Eyewitnesses often get it wrong
Eyewitness confidence is not a good indicator of accuracy
not true, but this is just for the sake of understanding why we came to the incorrect conclusion that it was unreliable
why do people think eyewitness testimony is unreliable?
Innocence Project Statistics
375+ DNA exonerations
69% of these cases involved eyewitness misidentification
Ronald Cotton
Cotton incorrectly identified as rapist by Jennifer Thompson. She was confident when testifying.
Experts (Elizabeth Loftus, Penrod & Cutler, opinion of APA)
Loftus stated that confidence is not indicative of a real memory
Penrod & Cutler found in their research paper that there was a weak correlation between confidence and accuracy
APA stated that eyewitness testimony is unreliable
what went wrong? why did all the experts get it wrong?
1) Researchers used the wrong measurement in lab-based studies when examining the confidence-accuracy relationship
2) People treat(ed) eyewitness confidence at trial as uncontaminated evidence
In the simultaneous lineup experiment (Wixted, 2016) what statistical test did researchers use? What test should they have used instead?
Researchers were correlating confidence accuracy scores or using a calibration calculation to determine accuracy
They should have instead been using a confidence-accuracy characteristic (CAC)
uses a percent-correct to measure accuracy
What does a CAC analysis on the simultaneous lineup experiment tell you about the reliability of eyewitness testimony?
The CAC analysis tells you that eyewitness testimony is reliable when they are extremely confident
how do real world conditions such as cross-race effect, weapon focus effect, time of day, etc. affect eyewitness reliability?
Wixted and Wells (2017) shows that it DOES NOT affect eyewitness reliability
Research shows that these real world conditions lower confidence
how does memory get contaminated in the context of police collecting evidence to prosecute?
The testing and retesting of memory contaminates memory itself. When presenting a lineup with a suspect, initially you may be reluctant. Upon further retesting you will become more confident in the suspect out of sheer familiarity.
What details about the conviction of Ronald Cotton showed low confidence with the initial test of memory?
Thompson selected two photos from the lineup
She spent 4-5 minutes looking at those two pictures (very long indicates low confidence)
Stated as saying “Yeah. This is the one . . . I think this is the guy.”
What is a non-ID? What is it evidence of for the suspect?
A non-id is when the eyewitness does a lineup rejection or a filler ID
These non-IDs are evidence of INNOCENCE
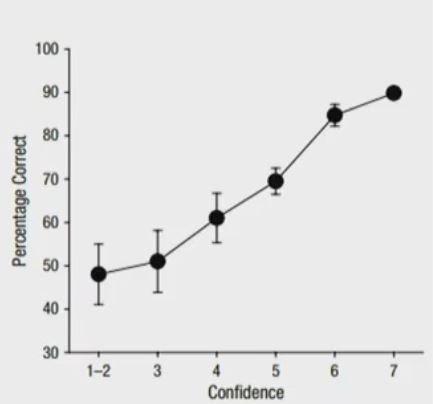
The following graph shows larger errors bars at the data points associated with lower levels of confidence. How do we interpret these error bars?
The wider error bars with the lower levels of confidence can be interpreted to mean that there’s larger variability associated with low confidence. In that same note, more precision accompanies high confidence
This is further evidence of the reliability of high confidence eyewitness testimony
Will memory be contaminated if a second lineup is shown, but with all new fillers AND a new suspect (the lineup contains all new people)?
The memory will be contaminated, HOWEVER it will not be contaminated in a way that is problematic for a suspect
What false assumption do we typically make when looking at the CAC graph and seeing a low accuracy with low confidence?
A witness may be less accurate if a weapon is present; it’s dark outside, a cross-race ID, etc. Is the witness more likely to make a false ID when they have low confidence?
We assume that the eyewitness is misidentifying an innocent person when we see low accuracy. What is actually happening is that accuracy is low because eyewitnesses are failing to identify a guilty suspect. This would include conditions such as rejecting a lineup with a guilty suspect or picking a filler,