(MCQ) 2 - Financial Statements Analysis pt. 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
C) earlier year amount from the later year amount and divide by the earlier year amount
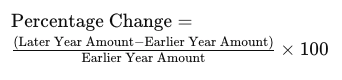
When preparing a horizontal analysis of financial statements, subtract the:
A) later year amount from the earlier year amount and divide by the later year amount
B) earlier year amount from the later year amount and divide by the later year amount
C) earlier year amount from the later year amount and divide by the earlier year amount
D) later year amount from the earlier year amount and multiply by the earlier year amount
C) the base year
When calculating trend percentages, all percentages shown are relative to:
A) an average index calculated for all the years shown
B) the current year
C) the base year
D) the immediately preceding year
A) The trend of the amounts is decreasing but all amounts are positive
When all amounts are positive, even if the trend is decreasing, you can calculate the percentage change accurately. The presence of negative amounts in the base or subsequent year complicates the computation of percentage changes and may lead to misleading results or require special handling
Under which of the following cases may a percentage change be computed?
A) The trend of the amounts is decreasing but all amounts are positive
B) There is no amount in the base year
C) There is a negative amount in the base year and a negative amount in the subsequent year
D) There is a negative amount in the base year and a positive amount in the subsequent year
D) to determine the amount and/ or percentage increase or decrease that has taken place
Horizontal analysis is a technique for evaluating a series of financial statement data over a period
A) that has been arranged from the highest number to the lowest number
B) that has been arranged from the lowest number to the highest number
C) to determine which items are in error
D) to determine the amount and/ or percentage increase or decrease that has taken place
C) calculation of peso amount changes and percentage changes from the previous to the current year
This involves comparing financial data across different periods to determine how much the amounts have changed both in absolute terms and as a percentage of the base period
Horizontal analysis of comparative financial statements includes the
A) development of common size statements
B) calculation of liquidity ratios
C) calculation of peso amount changes and percentage changes from the previous to the current year
D) evaluation of financial statement data that expresses each item in a financial statement as a percentage of a base amount
D) relationships
Ratios help to establish relationships between different financial statement items, which can provide insights into a company's financial health, performance, and operational efficiency
Ratios are most useful in identifying
A) trends
B) differences
C) causes
D) relationships
B) liquidity
Liquidity measures a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations with its most liquid assets. Short-term creditors need to ensure that the company can quickly convert its assets into cash to cover its immediate liabilities
Short-term creditors are usually most interested in assessing
A) solvency
B) liquidity
C) marketability
D) profitability
C) profit margin
A common measure of profitability is
A) return on assets
B) receivable turnover
C) profit margin
D) debt to equity
C) return on common stockholders’ equity ratio
This ratio assesses the profitability of a company by comparing net income to the average stockholders' equity, reflecting how effectively the company is using shareholders' equity to generate profit
A common measure of profitability is
A) the acid test or quick ratio
B) current cash debt coverage ratio
C) return on common stockholders’ equity ratio
D) debt to total assets
A) cash debt coverage ratio
The cash debt coverage ratio assesses a company's ability to cover its total debt with its cash flows from operating activities, providing insight into its long-term solvency
A common measure of long-term solvency is
A) cash debt coverage ratio
B) current ratio
C) asset turnover ratio
D) inventory turnover
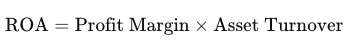
B) profit margin and asset turnover ratio
The give formula shows that ROA is influenced by both how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales (asset turnover) and its ability to convert sales into profit (profit margin)
Return on assets ratio is most closely related to
A) profit margin and debt to total assets ratio
B) profit margin and asset turnover ratio
C) times interest earned and debt to stockholders’ equity ratios
D) profit margin and free cash flow
D) return on asset ratio and leverage (debt to total asset ratio)
The return on common stockholder’s equity (ROE) is influenced by the return on assets (ROA) and the leverage used by the company. ROE can be affected by the company's use of debt and its ability to generate returns on its assets, as leverage amplifies the effects of profitability on stockholder's equity
Return on common stockholder’s equity ratio is most closely related to
A) gross profit rate and operating expenses to sales ratio
B) profit margin and free cash flow
C) times interest earned and debt to stockholder’s equity ratios
D) return on asset ratio and leverage (debt to total asset ratio)
D) solvency
Solvency assesses a company’s ability to meet its long-term obligations and survive over the long term. Long-term creditors need to ensure that the company can sustain its operations and manage its long-term debts effectively
Long-term creditors are usually most interest in evaluating
A) liquidity
B) marketability
C) profitability
D) solvency
D) Debt to total asset ratio
The debt to total assets ratio measures the proportion of a company's assets that are financed by debt, providing insight into the company's long-term solvency and financial leverage
Which one of the following would be considered a long-term solvency ratio?
A) Receivable turnover
B) Return on total assets
C) Current cash debt coverage ratio
D) Debt to total asset ratio
C) profitability
Stockholders are primarily concerned with a company's profitability because it affects their returns on investment, such as dividends and stock price appreciation. Profitability indicates how well the company is performing financially and its potential to generate returns for its shareholders
Stockholders are most interested in evaluating
A) liquidity
B) solvency
C) profitability
D) marketability
B) used to evaluate a company’s liquidity and short-term debt paying ability
The current ratio is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. It measures a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations with its short-term assets
The current ratio is
A) calculated by dividing current liabilities by current assets
B) used to evaluate a company’s liquidity and short-term debt paying ability
C) used to evaluate a company’s solvency and short-term debt paying ability
D) calculated by subtracting current liabilities from current assets
D) remain the same and decrease, respectively

A company with ₱60,000 in current assets and ₱40,000 in current liabilities pays a ₱1,000 current liability. As a result of this transaction, the current ratio and working capital will
A) both decrease
B) both increase
C) increase and remain the same, respectively
D) remain the same and decrease, respectively
C) liquidity
These ratios assess how effectively a company manages its receivables and inventory, which are crucial for evaluating its ability to convert assets into cash and manage short-term obligations
The receivable turnover and inventory turnover ratios are used to analyze
A) long-term solvency
B) profitability
C) liquidity
D) leverage
A) customers are making payments quickly
A high receivable turnover ratio means that a company is efficiently collecting its receivables, which suggests that customers are paying their invoices promptly
A high receivable turnover ratio indicates
A) customers are making payments quickly
B) a large portion of the company’s sales are on credit
C) many customers are not paying their receivables
D) the company’s sales have increased
B) how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales
This ratio indicates how well a company is utilizing its assets to produce revenue, reflecting the efficiency of asset use in generating sales
The assets turnover ratio measures
A) how often a company replaces its assets
B) how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales
C) the portion of the assets that have been financed by creditors
D) the overall rate of return on assets
D) net income by net sales
The profit margin ratio measures how much net income is earned for each dollar of net sales, indicating the percentage of sales that has been converted into profit
The profit margin ratio is calculated by dividing
A) sales by cost of goods sold
B) gross profit by net sales
C) net income by stockholders’ equity
D) net income by net sales
D) the percentage of the total assets provided by creditors
This ratio indicates the proportion of a company’s assets that are financed by debt, reflecting the level of financial leverage and risk associated with the company’s capital structure
The debt to total assets ratio measures
A) the company’s profitability
B) whether interest can be paid on debt in the current year
C) the proportion of interest paid relative to dividends paid
D) the percentage of the total assets provided by creditors
C) use of borrowed money to increase the return to owners
Leverage involves using borrowed funds to amplify potential returns on equity. By using debt, a company can increase its capacity to generate higher returns for its shareholders, although it also increases financial risk
Trading on the equity (leverage) refers to the
A) amount of working capital
B) amount of capital provided by owners
C) use of borrowed money to increase the return to owners
D) number of times interest is earned
B) contains debt financing
Leverage refers to the use of borrowed funds (debt) in a company's capital structure to amplify potential returns on equity. High leverage means that a significant portion of the company's capital comes from debt financing
A company that is leveraged is one that
A) has a high earnings per share
B) contains debt financing
C) contains equity financing
D) has a high current ratio
B) it doesn’t take into account the composition of the current assets
The current ratio provides a general measure of liquidity but does not distinguish between different types of current assets. It treats all current assets as equally liquid, which may not accurately reflect the company’s true ability to meet short-term obligations if a large portion of assets are not easily convertible to cash
A weakness of the current ratio is
A) the difficulty of the calculation
B) it doesn’t take into account the composition of the current assets
C) it is rarely used by sophisticated analysts
D) it can be expressed as a percentage, as a rate, or as a proportion
C) current ratio
The current ratio provides insight into a company’s liquidity and ability to meet its short-term obligations, which is crucial for suppliers who need to ensure that the company can pay for the goods or services provided in a timely manner
A supplier to a company would be most interest in the
A) asset turnover ratio
B) profit margin ratio
C) current ratio
D) earnings per share
C) Asset turnover ratio
While the current ratio, inventory turnover ratio, and receivables turnover ratio are directly related to a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations and manage short-term assets, the asset turnover ratio is more focused on how efficiently the company uses its assets to generate sales and is less relevant for assessing short-term creditworthiness
Which one of the following ratios would not likely be used by a short-term creditor in evaluating whether to sell on credit to a company?
A) Current ratio
B) Inventory turnover ratio
C) Asset turnover ratio
D) Receivables turnover ratio
B) because they can provide information that may not be apparent from inspection of the individual components of the financial statements
Ratios help to reveal insights about a company's financial health and performance that might not be obvious from the raw financial statements alone. They allow for a more nuanced analysis by comparing different financial metrics
Ratios are used as tools in financial analysis
A) instead of horizontal and vertical analysis
B) because they can provide information that may not be apparent from inspection of the individual components of the financial statements
C) because even single ratios by themselves are quite meaningful
D) because they are prescribed by GAAP
D) current ratio, acid-test ratio, receivables turnover, and inventory turnover
These ratios help assess a company's liquidity and ability to manage and pay off short-term obligations
The ratios that are used to determine a company's short-term debt paying ability are
A) asset turnover, times-interest-earned, current ratio, and receivables turnover
B) times-interest-earned, inventory turnover, current ratio, and receivables turnover
C) times-interest-earned, acid-test ratio, current ratio, and inventory turnover
D) current ratio, acid-test ratio, receivables turnover, and inventory turnover
C) The ratio decreased

Sweet Company had P250,000 of current assets and P90,000 of current liabilities before borrowing P60,000 from the bank with a 3-month note payable. What effect did the borrowing transaction have on Sweet Company's current ratio?
A) The ratio remained unchanged
B) The change in the current ratio cannot be determined
C) The ratio decreased
D) The ratio increased
C) short-term ability of the enterprise to pay its maturing obligations and to meet unexpected needs for cash
Liquidity ratios assess a company's capacity to cover its short-term liabilities with its short-term assets, reflecting its ability to handle immediate financial obligations
A liquidity ratio measures the
A) income or operating success of an enterprise over a period of time
B) ability of the enterprise to survive over a long period of time
C) short-term ability of the enterprise to pay its maturing obligations and to meet unexpected needs for cash
D) number of times interest is earned
B) decrease
When you add the same amount to both the numerator (current assets) and the denominator (current liabilities) of the current ratio, the ratio will decrease because the denominator increases by the same amount, but the numerator's increase is relatively less impactful on the ratio
If equal amounts are added to the numerator and the denominator of the current ratio and the ratio is over one, the ratio will always
A) increase
B) decrease
C) stay the same
D) equal zero


If a company has a current ratio of 1.2:1, what respective effects will the borrowing of cash by short-term debt and collection of accounts receivable have on the ratio?

D) that it should not greatly exceed the credit term period
The average collection period should be relatively close to the credit term period offered to customers. If it significantly exceeds the credit terms, it may indicate issues with receivables collection
A general rule to use in assessing the average collection period is
A) that it should not exceed 30 days
B) it can be any length as long as the customer continues to buy merchandise
C) that it should not greatly exceed the discount period
D) that it should not greatly exceed the credit term period
C) cost of goods sold by the average inventory
This ratio measures how efficiently a company manages its inventory by showing how many times inventory is sold and replaced over a period
The inventory turnover is calculated by dividing
A) cost of goods sold by the ending inventory
B) cost of goods sold by the beginning inventory
C) cost of goods sold by the average inventory
D) average inventory by cost of goods sold