Security+ Study Shortcomings
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This study-set is to help bring me up in the areas I am struggling
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
TPM
Trusted Platform Module
Hardware CHIP on the motherboard
Stores keys for local encryption
Provides FDE (full disk encryption)
Is the root of trust for a system / secures boot process
HSM
Hardware Security Module
External device
Provides cryptographic operations
Stores keys for multiple systems
MSA
Master Service Agreement
Overarching framework / terms for ongoing relationship between two organizations.
Billing / payment
General service expectations
SOW
Service Level Agreement
Statements of Work
Document that outlines specific activities, deliverables, and timelines for a particular project/task within larger MSA
SLA
Document that specifies the minimum level of service a provider will provide
Often quantifiable performance metrics (uptime, response times, data preservation requirements)
MOU
Memorandum of Understanding
Less formal document that expresses intent to collaborate on certain terms
Not legally enforceable
MOA
Memorandum of Agreement
More formal document detailing specific terms that both parties agree to
NDA
Non-Disclosure Agreement
Signed when two organizations are exploring business partnership. Ensures confidential information remains secret.
BPA
Business Partnership Agreement
Agreement defines the relationship, ownership structure, financial details, profit-sharing, and how partners operate / make decision within a business
Forward Proxy
Protects clients by sitting on client’s private network (controls outbound traffic)
Can filter outbound traffic to certain servers (policy enforcement)
Masks clients IP addresses
Reverse Proxy
Protects servers by sitting on server’s private network (controls inbound traffic)
Masks servers IP addresses
Protects against DDos / can load balance
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
An architecture where you “assume breach”. To connect with any application or database you need to authenticate each time.
Never trust, always verify
Least privilege
Explicit verification (not implicit except in trusted zones only)
How can we apply Zero Trust?
Control Planes
Break up devices and processes into 2 planes of operation:
Data Plane (Doing)
Handles data movement
Enforces policies on live traffic
Control Plane (Planning)
Manages configurations / policies for data plane
What is adaptive identity?
When security controls are elevated based on additional information. Looks at more information than just what the user is providing.
Example: someone logging into database in US, system might see they are reaching from China and employ extra security.
What are security zones?
They are zones of operation within a system.
Untrusted (external)
Trusted (internal)
DENY untrusted-trusted
ALLOW implicit trust if trusted-trusted
What are the 3 policy components?
Policy Enforcement Point (PEP), Policy Decision Point (PDP - PA/PE)
What does PEP do?
Policy enforcement point serves as the gatekeeper. All traffic going over network needs to go through this.
Inspects users, processes, and apps (gathers info but doesn’t decide)
What does PDP (or PE) do?
Policy decision points actually analyze the request information gathered from the PEP and then decide to trust or not.
Decide whether or not something / someone is to be trusted
MAKES THE DECISION
Policy Administrator
Establishes communication path between requester and the system resource by dispensing access tokens. MAKES IT HAPPEN
What is the overall flow of steps through a zero trust (PEP/PDP/PA) system?
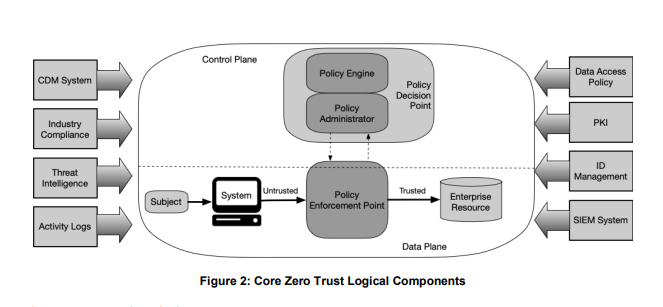
User hits PEP
PEP refers to PDP (PA/PE)
PDP refers back to PEP and allows access

What is the Policy Engine?
Component that actually decides to grant/deny access to a resource for a requester
Which plane is PEP in? PDP? PA? PE?
Data Plane
PEP
Control Plane
PDP, PA, PE
Who is the data owner and what do they do?
Data Owner
Senior Executive or Manager
Classify data
Determine access levels
Ensure protection aligns with business needs
Who is the data controller and what do they do?
HR/ Payroll Department
Decides the purposes and means of processing personal data
Ensure compliance with laws (example people above payroll processors)
Define how data is used/collected
Oversee the data processors
Who is the data processor and what do they do?
Individual / Team/ 3rd party service
Processes data on behalf of the controllers (example payroll processing)
Implement security measures
Report breaches
Who is the data custodian/steward and what do they do?
Individual / Team
Responsible for operational security
Storage and backups
Keep data accurate, available, and compliant
What’s the difference between risk acceptance and risk tolerance?
Risk Acceptance
Conscious decision to take on risk after assessment
Choosing to not mitigate or transfer the risk
Risk Tolerance
The LEVEL of risk a company will tolerate before addressing it
So risk > risk tolerance ≠ Risk acceptance
What are some examples of indicators of compromise?
Unusual network traffic
Unusual user activity
Anomalous logs
Unauthorized processes
Modified system files / registries