Chapter 20: Antimicrobial drugs
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Selective toxicity
selectively finding and destroying pathogens without damaging the host
Chemotherapy
the use of chemicals to treat a disease
Antibiotic (AKA antibacterials)
a type of antimicrobial drug
it is a substance produced by a microbe that, in small amounts, inhibits another microbe
Antimicrobial drugs
synthetic substances that interfere with the growth of microbes
Who discovered penicillin in 1928 and produced Penicillium?
Fleming
1932: Prontosil red dye is a compound, sulfanilamide-containing dye used widely in WWII for ___________________ infections.
streptococcal
The first clinical trials of penicillin was in what year?
1940
Antibiotic resistance
formerly effective medications have less and less impact on bacteria
A growing problem today
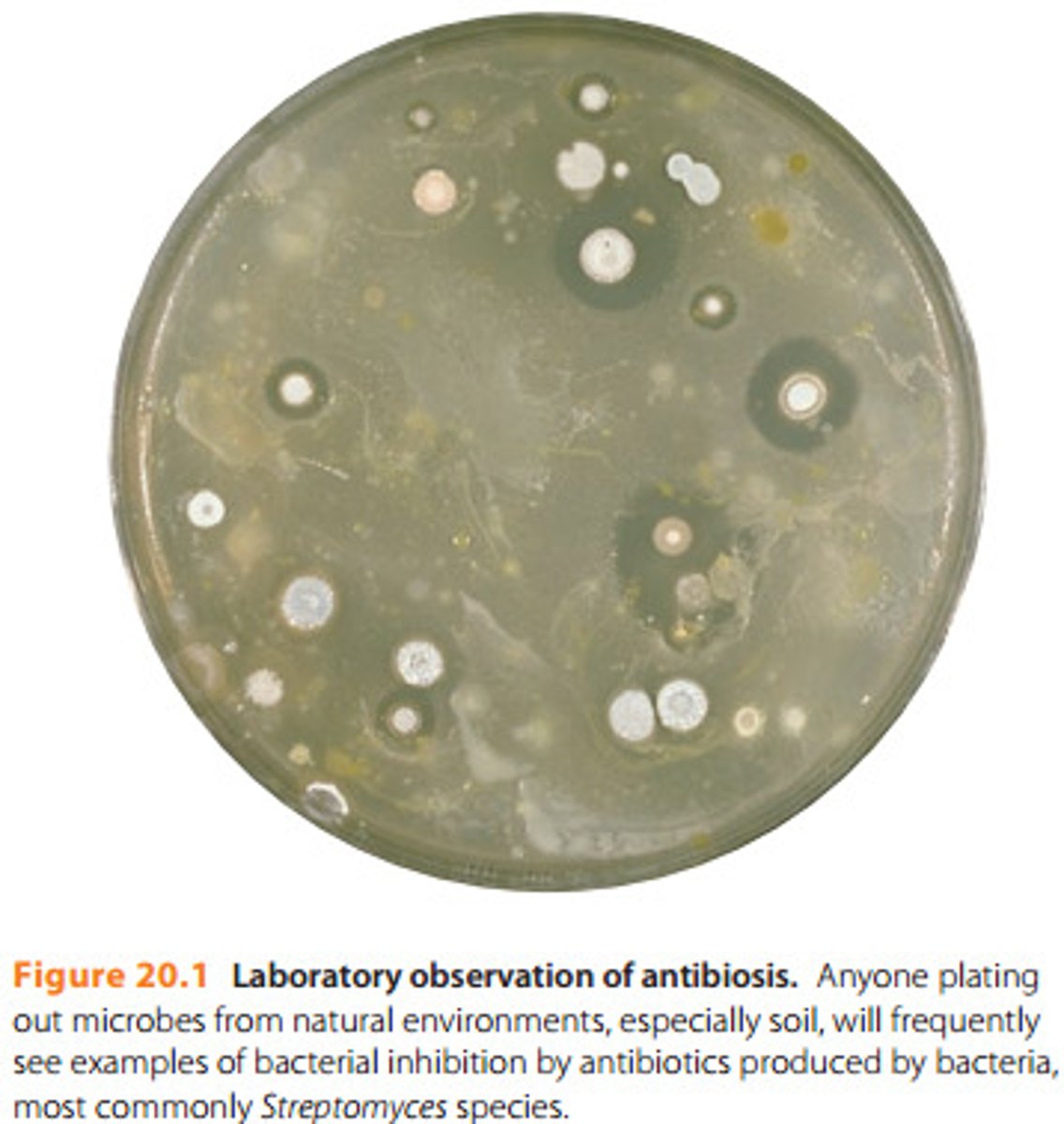
Antibiosis: Figure 20.1
Representative Sources of Antibiotics: Table 20.1
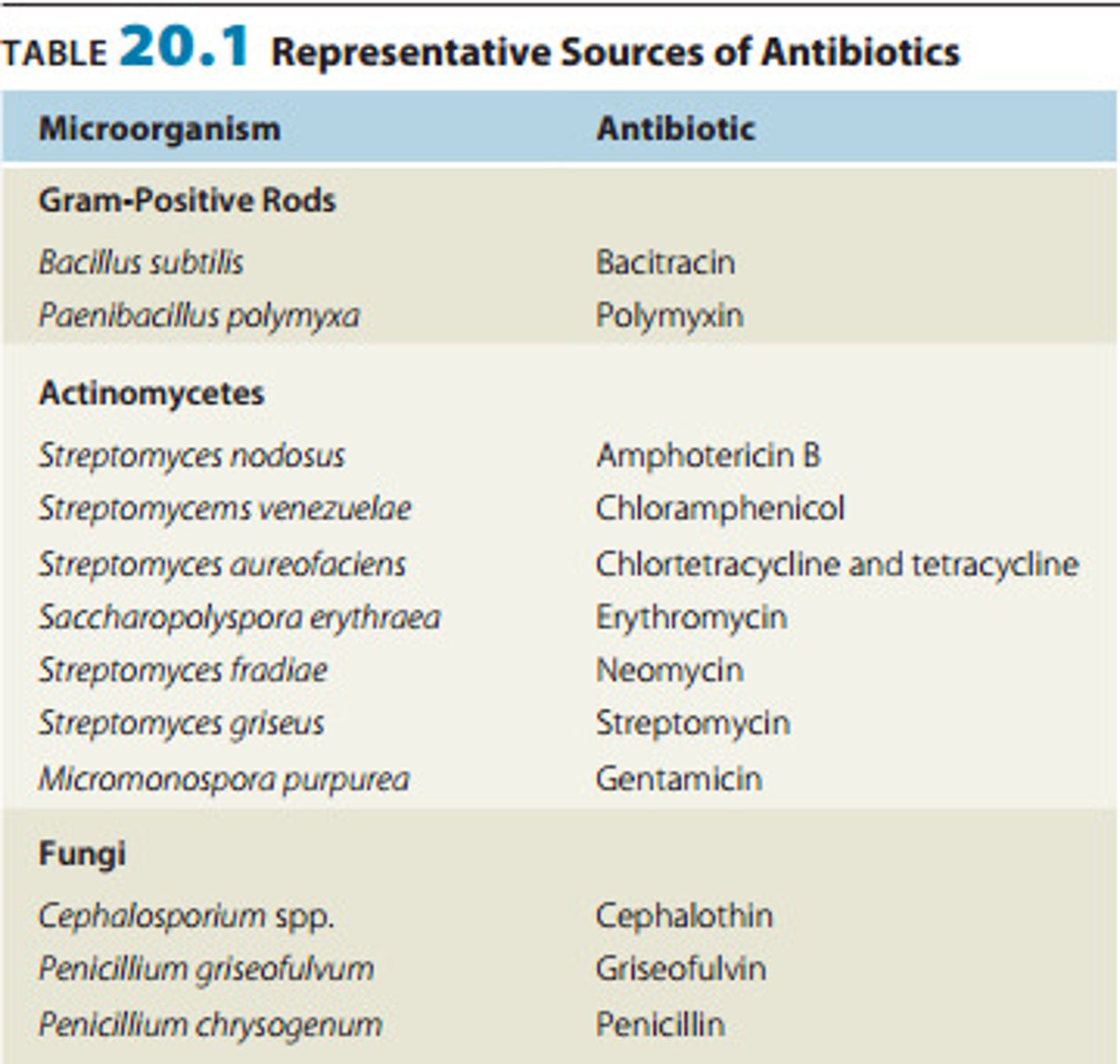
More than half of our antibiotics are produced by species of ________________________
Streptomyces
Narrow spectrum of microbial activity
drugs that affect a narrow range of microbial types
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
affect a bread range of gram positive or gram negative bacteria
Superinfection
overgrowth of normal microbiota that is resistant to antibiotics
The spectrum of activity of antibiotics and other antimicrobial drugs: Table 20.2
List the five ways of action of antimicrobial drugs
1. Inhibiting the cell wall synthesis
2. Inhibiting protein synthesis
3. Injuring the plasma membrane
4. Inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis
5. Inhibiting the synthesis of essential metabolites
Antimicrobial drugs are either bacteri______ or bacteri_________
bactericidal or bacteriostatic
What type of antimicrobial drug kills microbes directly?
bactericidal
What type of antimicrobial drug prevents microbes from growing?
bacteriostatic
Major action modes of antibacterial drugs: Figure 20.2
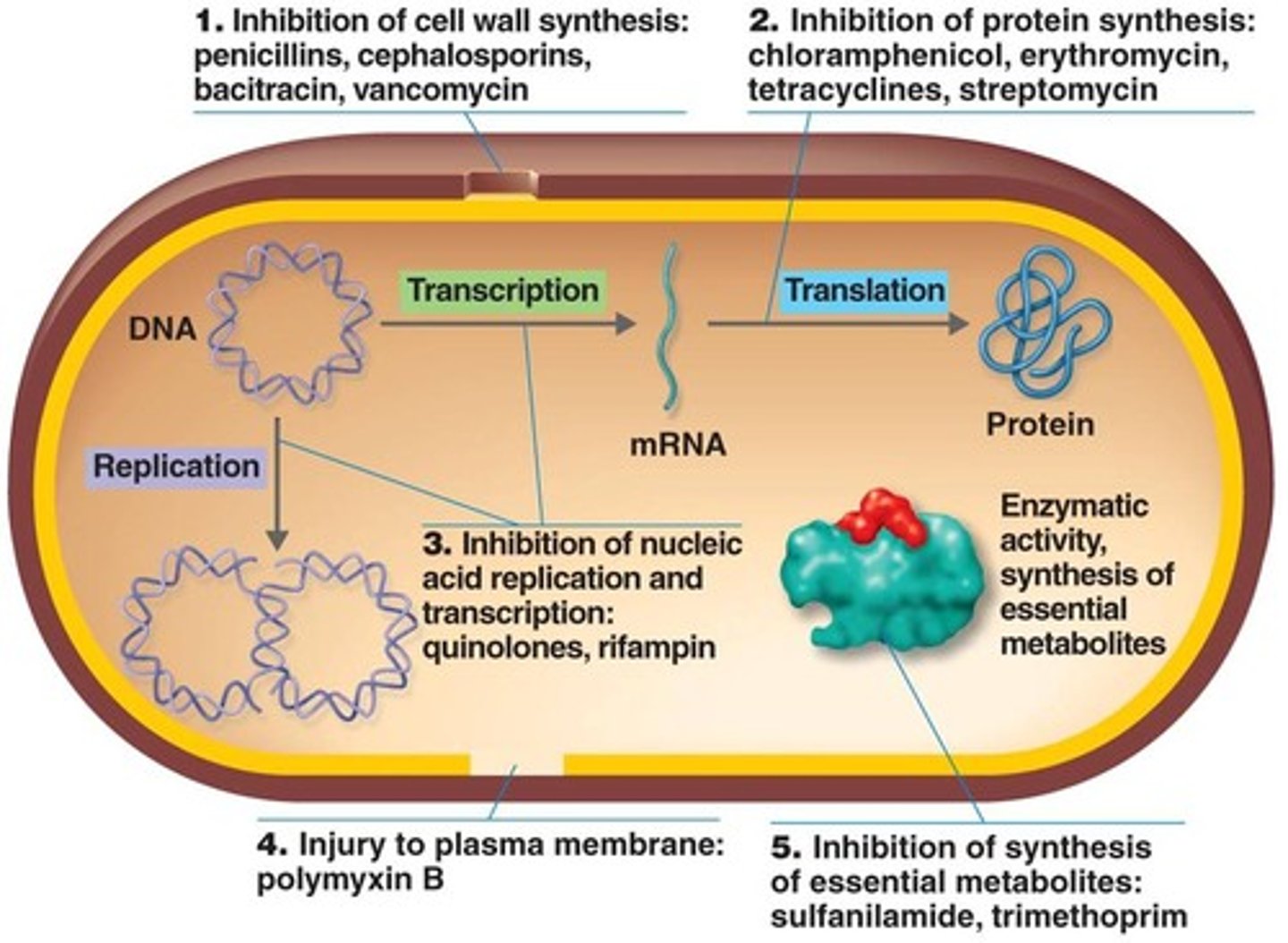
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis: How and what drugs are involved?
Penicillins, cephalosporins, bacitracin, vancomycin, bacitracin, antimycobacterial antibiotics
Prevent the synthesis of peptidoglycan of the cell wall
Inhibition of protein synthesis: How and what drugs are involved?
Chloramphenicol, tetracylines, streptomycin, erythromycin, azithromycin
Target bacterial cells 70S ribosomes
Adverse effects: Eukaryotic organelle mitochondria has 70S ribosomes and can have an affect on the host
Inhibition of protein synthesis by antibiotics; figure 20.4
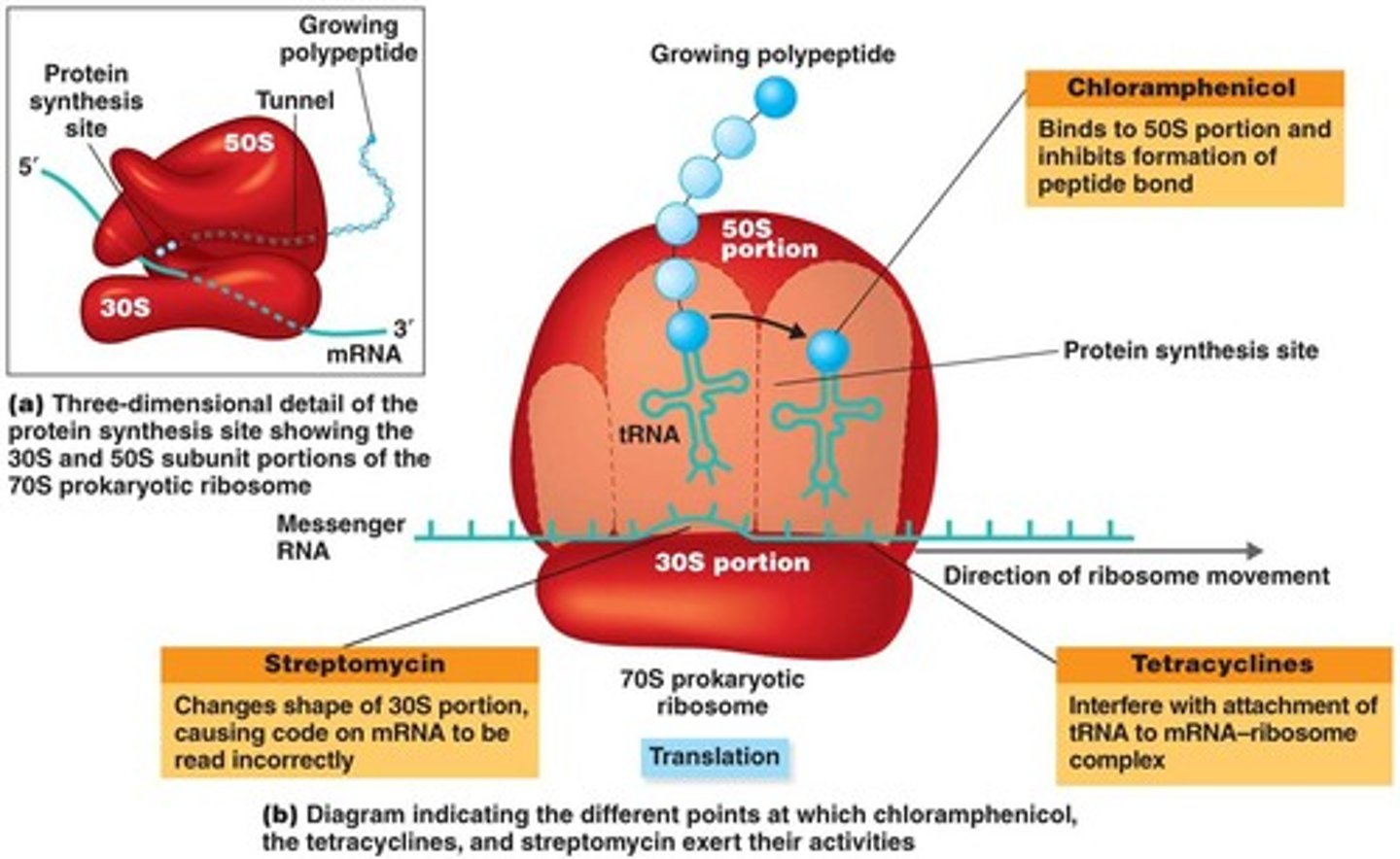
Injuring the plasma membrane: How and what drugs are involved?
Polypeptide antibiotics = Polymyxin B
Changes the bacterial cell membrane permeability
Antifungal drugs like amphotericin B, miconazole, ketoconazole =
Combine with membrane sterols in the fungal plasma membrane and disrupts
Bacteria lack sterols therefore not effective
Inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis: How and what drugs are involved?
Quinolones, fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin) & rifampin
Interfere with DNA replication and transcription
Inhibiting the synthesis of essential metabolites: How and what drugs are involved?
Sulfanilamide and trimethoprim
Competitively inhibited: Antimetabolites compete with normal substrates for an enzyme
Sulfanilamide competes with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) - stopping the synthesis of folic acid
The term penicillin refers to a group of over _____ chemically related antibiotics
50
All penicillin contain a __________ ring
Beta-lactam ring
Types are differentiated by the chemical side chains attached to the ring
Penicillin prevent the _____________ of peptidoglycans, interfering with the cell wall construction (especially gram-__________ bacteria)
cross-linking
gram-positive
Penicillins extracted from cultures of the mold Penicillium are known as __________ penicillins
natural
The prototype compound of all penicillin is known as penicillin ___
G (injected)
Penicillin ____, which is stable in the stomach acids and can be taken orally.
V
Disadvantages to natural penicillins
-Narrow spectrum of activity
-Susceptible to penicillinases (beta-lactamases) which are enzymes produced by many bacteria especially Staphylococcus species
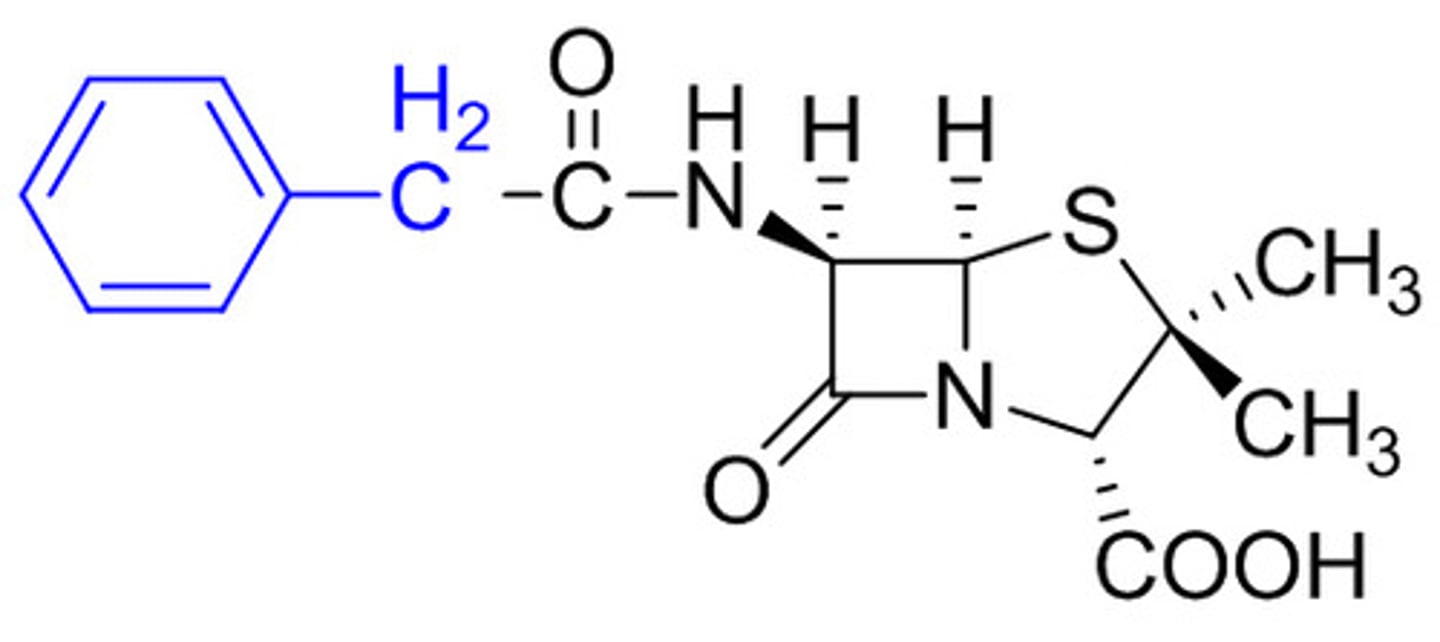
Natural penicillin G
Requires injection
Beta-lactam ring in the center square
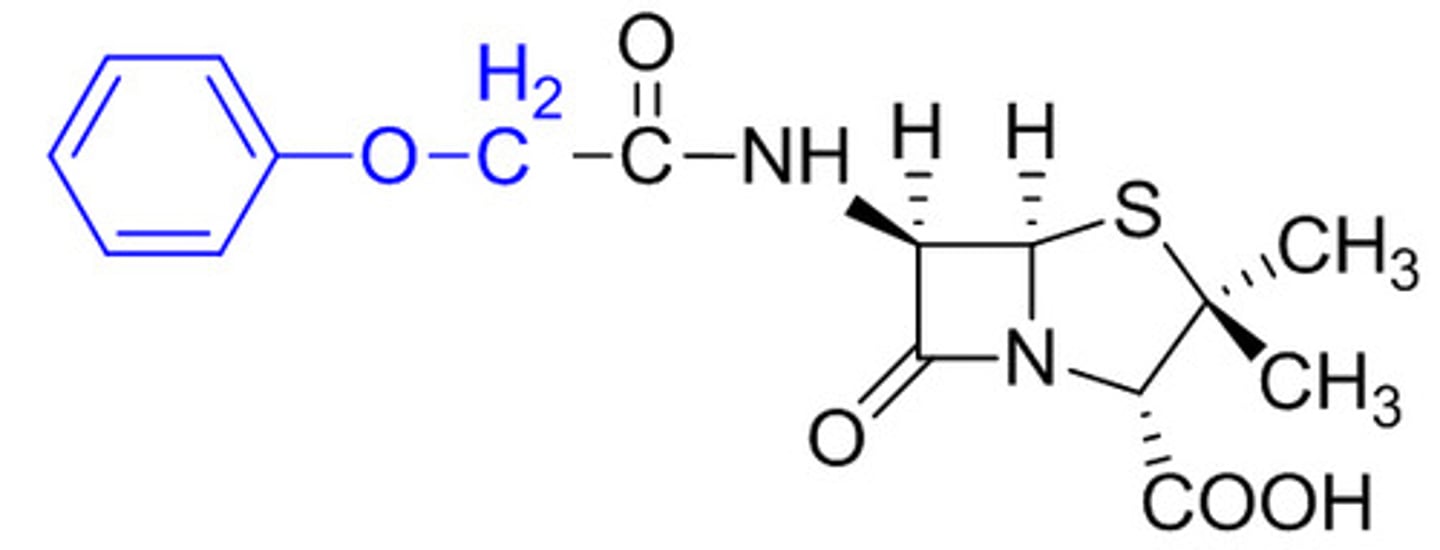
Natural penicillin V
Can be taken orally
Beta-lactam ring in the center square
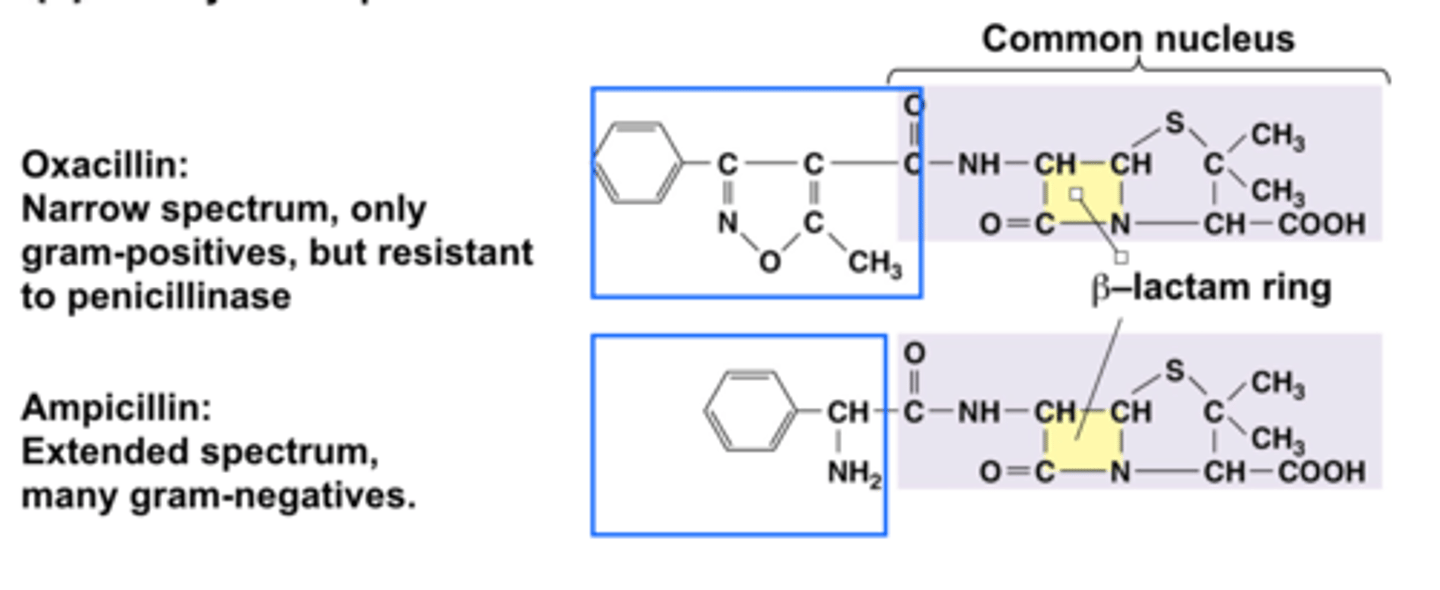
Semisynthetic penicillins: What are they?
Oxacillin and ampicillin
Why make semisynthetic penicillins?
Developed in attempts to overcome the disadvantages of natural penicillins:
1. Interrupt synthesis of the molecule by Penicillium and obtain only the common penicillin nucleus for use
2. Can remove the side chains from the completed natural molecules and then chemically add other side chains that make them more resistant to penicillinase
What makes them semisynthetic?
part of the penicillin is produced by mold and the other part is added synthetically
Which type of semisynthetic is narrow spectrum, only gram positives, but resistant to penicillinase?
oxacillin
Which type of semisynthetic is extended spectrum and targets many gram-negatives?
ampicillin
semisynthetic penicillins: Figure 20.6b
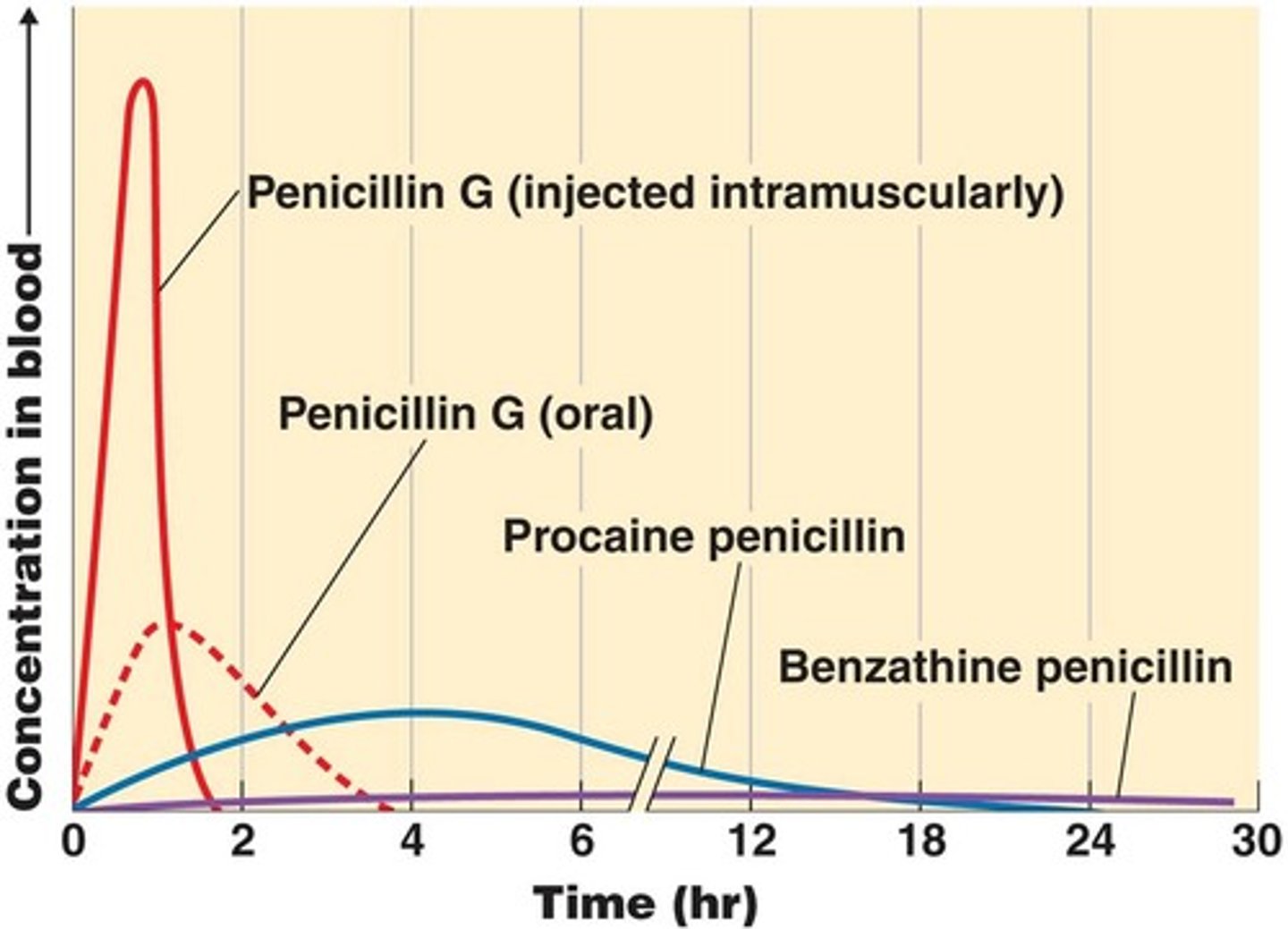
Retention of penicillin G: Figure 20.7
Drug is present in high concentrations in the blood (solid red line) when administered by injection, but disappears quickly.
Taken orally (dotted red) it is destroyed by stomach acid = not effective
Blue and purple lines: Penicillin G is combined with compounds procaine and benzathine = possible to improve retention but blood concentration reached is low and the target bacterium needs to be extremely sensitive to the antibiotic.
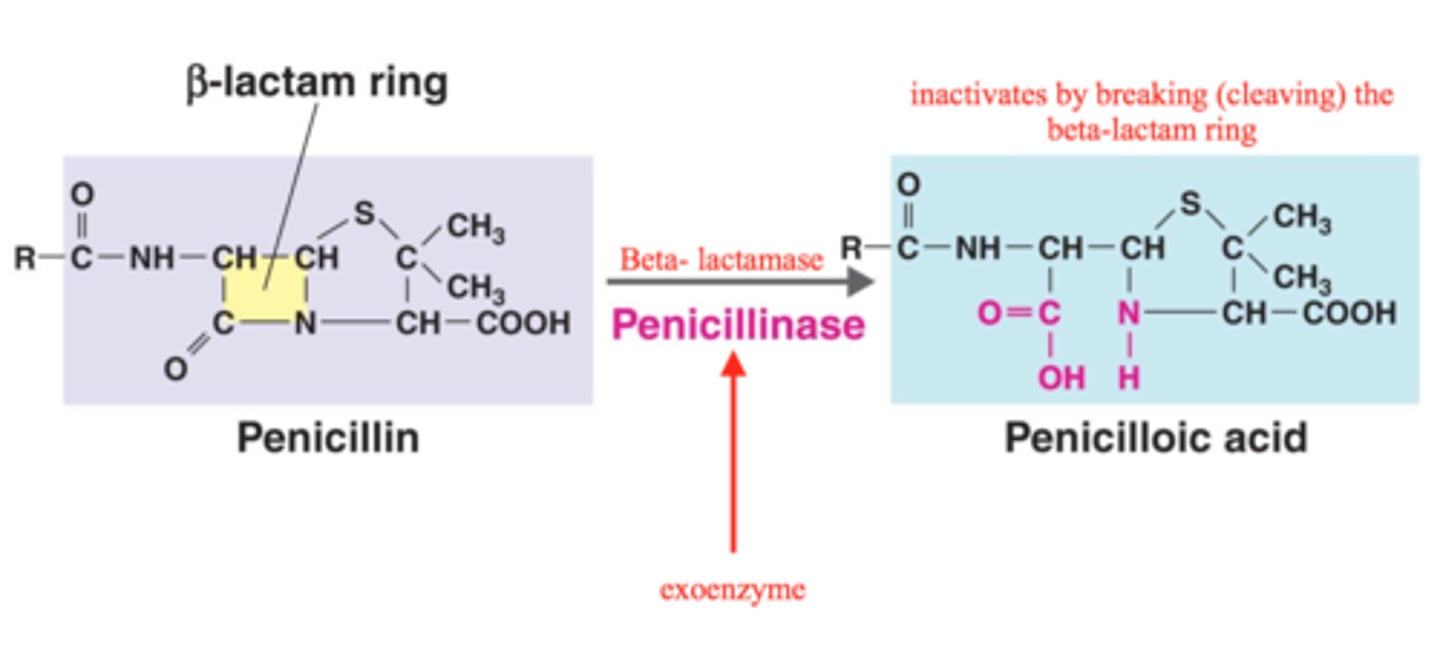
Effect of penicillinase on penicillins: Figure 20.8
Most common form of resistance to penicillins = breaking the beta-lactam ring
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins: What are they?
Resistance to the plasmid-borne gene for beta-lactamase. Antibiotics that are resistant are:
-Methicillin = organisms terms MRSA; so prevalent that methicillin has been discontinued in the U.S.
-Oxacillin
Extended-spectrum penicillins: What are they?
-To overcome the problem of narrow spectrum activity of natural penicillins, broader-spectrum semisynthetic penicillins created
-Effective against gram-negative bacteria as well as gram-positives
-They are not resistant to penicillinases
-First created were aminopenicillins: ampicillin & amoxicillin
Penicillins plus Beta-lactam inhibitors: A different approach to proliferating penicillinase is to combine penicillins with _______________ acid, a noncompetitive inhibitor of penicillinase
clavulanic acid
Carbapenems
-Class of beta-lactam antibiotics
-Substitute a carbon (C) for a sulfur (S) and add a double bond to the penicillin nucleus.
-Inhibit cell wall synthesis and have an extremely broad spectrum of activity
-Primaxin & doripenem
-Effective for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections
Monobactam
-New class of antibiotics; synthetic ; single ring instead of the beta-lactam double ring
-Aztreonam = has unusually low toxicity and affects only gram-negative bacteria = pseudomonads and E. coli
Cephalosporins
-Similar nuclei to penicillin; work similar
-Beta-lactam ring differs from penicillin
-Grouped according to their generation of development
-Inhibit cell wall synthesis similar to the way penicillins do
Name the two types of polypeptide antibiotics
Bacitracin and vancomycin
Bacitracin
topical application; works against gram-positives
Vancomycin
Glycopeptide; last line against antibiotic-resistant MRSA
What are the two types of antimycobacterial antibiotics?
-Isoniazid (INH)
-Ethambutol (secondary)
Isoniazid (INH) inhibits the _____________ _______________ synthesis in mycobacteria
mycolic acid
Ethambutol inhibits ________________ of the mycolic acid into the cell wall
incorporation
What are the 8 antibiotic groups that inhibit protein synthesis?
1. Chloramphenicol
2. Aminoglycosides
3. Tetracyclines
4. Glyclyclines
5. Macroglides
6. Streptogramins
7. Oxazolidinones
8. Pleuromutilins
Chloramphenicol
-Inhibits peptide bond formation by binding to the 50S portion of the 70S prokaryotic ribosome
-Synthesized chemically; broad spectrum
-Serious adverse affects: can suppress bone marrow and affect blood cell formation
-Low cost
Aminoglycosides
-Amino sugars linked by glycoside bonds
-Interferes with the initial steps of protein synthesis by changing the shape of the 30S portion of the 70S prokaryotic ribosome
--mRNA is read incorrectly
-Significant against gram-negative bacteria
-Best known is streptomycin
-others: neomycin & gentamicin
-Can cause damage to hearing and also the kidneys (use has declined due to this)
Tetracyclines
-Closely related broad-spectrum antibiotics
-Produced by Streptomyces spp.
-Interfere with the attachment of the tRNA carrying the amino acids to the ribosome at the 30S portion of the 70S ribosome
-Do not interfere with mammalian 70S ribosomes however they do in small amounts enter the host cell making them valuable against rickettsias and chlamydias
-Effective against gram-positive, gram-negative and also penetrate body tissues well
Types: oxytetracycline, chlortetracycline, tetracycline
-Synthetic tetracyclines: docycycline & minocycline
-Treat UTI's, mycoplasma pneumonia, chlamydial & rickettsial infections.
-Suppress the normal intestinal microbiota = GI upset = superinfections called Candida albicans
Glyclyclines
-Broad spectrum; newer class (2000)
-Similar to tetracyclines
-Bacteriostatic
-Best known: tygecycline
-Binds to the 30S ribosomal unit = blocking protein synthesis
-Inhibits rapid efflux
-Slow IV infusion
-Useful against MRSA
Macrolides
-Macrocyclic lactone ring (star-shaped)
-Best known: erythromycin
-Others: azithromycin, clarithromycin
-Narrow spectrum against gram-positives
-Inhibits protein synthesis by blocking the tunnel
-Similar to penicillin G and used as an alternative
-Treats legionellosis, mycoplasma pneumonia, and other infections
Streptogramins
-Synercid: combination of two cycline peptides: quinupristin and dalfopristin (distantly related to macrolides
-Block protein synthesis by attaching to the 50S portion of the ribosome
-Works against gram-positives that are resistant to other antibiotics
Oxazolidones
-New class developed in response to vancomycin resistance (2001)
-Act on the ribosomes by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit close to the point where it interfaces with the 30S subunit
-Synthetic = resistance is slower to develop
- Linezolid = type to combat MRSA
Pleuromutilins
-New class (2000)
-Interferes with protein synthesis
-First antibiotic for human use = retapamulin, a topical and effective against gram-positives
Lipopeptide
-Daptomycin: gram-positive bacteria only
-Produced by a streptomycete
-Used for skin infections
-Attacks the bacterial cell membrane (affects synthesis)
Polymyxin B
-Bactericidal; topical; effective against gram-negative bacteria
-Combined with bacitracin and neomycin in nonprescription ointments
Rifamycin
-Inhibits mRNA synthesis
-Penetrates tissues; antitubercular activity
-Rifampin
-Structurally related to macrolides
-Treats mycobacteria infections: TB and leprosy
-Side effect: orange-red urine, feces, saliva, sweat and tears
Quinolone & Fluoroquinolones
-1960's: synthetic drug nalidixic acid was developed = first in the quinolone group
-Synthetic and a bactericidal effect by inhibiting an enzyme DNA gyrase
-1980's: prolific group of synthetic quinolones = fluoroguinolones
-Norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin = treats anthrax infections
-Newer group: gemifloxacin and moxifloxacin
-Resistance can develop quickly; broad-spectrum & nontoxic
Sulfonamides
-sulfa drugs
-Inhibit the folic acid synthesis needed for nucleic acid and protein synthesis
-Competitively bind to the enzyme meant for PABA (structurally similar) = blocking folic acid production
-PABA = folic acid precursor
-Combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole = drug synergism
Many antifungal drugs target the ___________ in the plasma membrane, making it excessively permeable.
sterols (principal type: ergosterol)
Polyenes
-Amphotericin B: produced by Streptomyces & toxic to the kidneys
Azoles
Imidazoles: first type made which includes clotrimazole and miconazole
-No prescription; used topical to treat cutaneous mycoses (athlete's foot, vaginal yeast infections)
Triazole: fluconazole and itraconazole
-Treat systemic fungal infections
Allylamines
-For azole-resistant infections
-Inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterols
Agents affecting fungal cell walls
-Primary target other than ergosterol is beta-glucan compound
-Echinocandins - inhibits the biosynthesis of beta-glucans = incomplete cell wall and cell lysis
Agents inhibiting nucleic acids
-Flucytosine : cytosine analog interferes with RNA synthesis
Griseofulvin
-Produced by the species Penicillium
-Inhibits microtubule formation = interferes with mitosis and therefore fungal reproduction
-Active against superficial dermatophytic fungal infections of the hair and nails
-Binds to keratin
Tolnaftate
-For athlete's foot
-Alternative to miconazole
Pentamidine
-Anti-Pneumocystis; may bind to DNA
Antiviral drugs: Entry and Fusion Inhibitors
-Drugs that block the initial steps in viral infection: absorption and penetration
-Blocks the receptors on the host cell that bind to the virus
-Block fusion of the virus and cell
Antiviral drugs: Uncoating, Genome Integration & Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibition
--Prevent viral uncoating
-Inhibit viral DNA integration into the host genome
-Nucleoside analogs inhibit RNA and DNA synthesis
Antiviral drugs: Interference with Assembly and Release of Viral Particles
-Protease inhibitors: block the cleavage of protein precursors
Antiviral drugs: Exit inhibitors
-Inhibit neuraminidase, an enzyme required for some viruses to bud from the host cell
Antiviral drugs: Interferons
-Produced by viral-infected cells to inhibit further spread of infection
-Imiquimod: promotes interferon production
Antivirals for treating HIV/AIDS
*HIV is an RNA virus; it's reproduction depends on the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which controls the synthesis of RNA from DNA.
-Antiretroviral=a drug is used to treat HIV infection
1. Nucleoside analog is zidovudine
2. Nucleotide analog is tenofovir
3. Non-nucleoside inhibitors is nevirapine
4. Protease inhibitors is atazanavir
5. Integrase inhibitors is raltegravir
6. Entry inhibitors is miraviroc
7. Fusion inhibitors is enfuvirtide
Antiprotozoan drugs
-Quinine and chloroquine treat malaria
-Artemisinin kills Plasmodium that causes malaria
-Metronidazole (Flagyl) interferes with anaerobic bacteris and treats Trichomonas, giardiasis and amebic dysentery
Antihelminthic drugs
-Niclosamide prevents ATP production and treats tapeworms
-Praziquantel alters membrane permeability and treats tapeworms and flukes
-Mebendazole and albendazole interfere with nutrient absorption and treats intestinal helminths
-Ivermectin paralyzes helminths and treats roundworms and mites
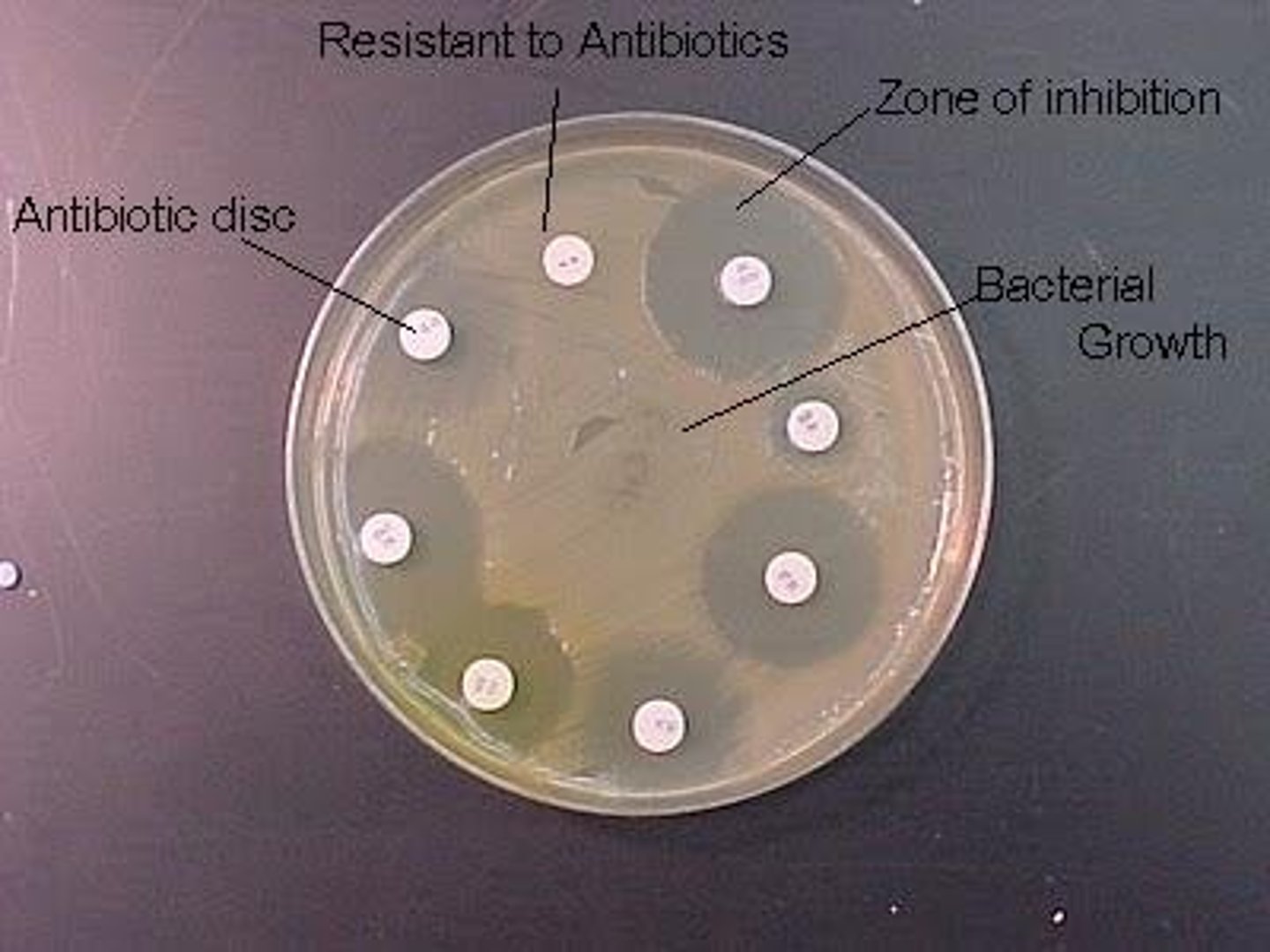
Disk-diffusion method (Kirby-Bauer test)
-Tests the effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents
-Paper disk with a chemotherapeutic agent are placed on agar containing the test organism
**Zone of inhibition around the disk determines the sensitivity of the organism to the antibiotic
Disk-diffusion: Figure
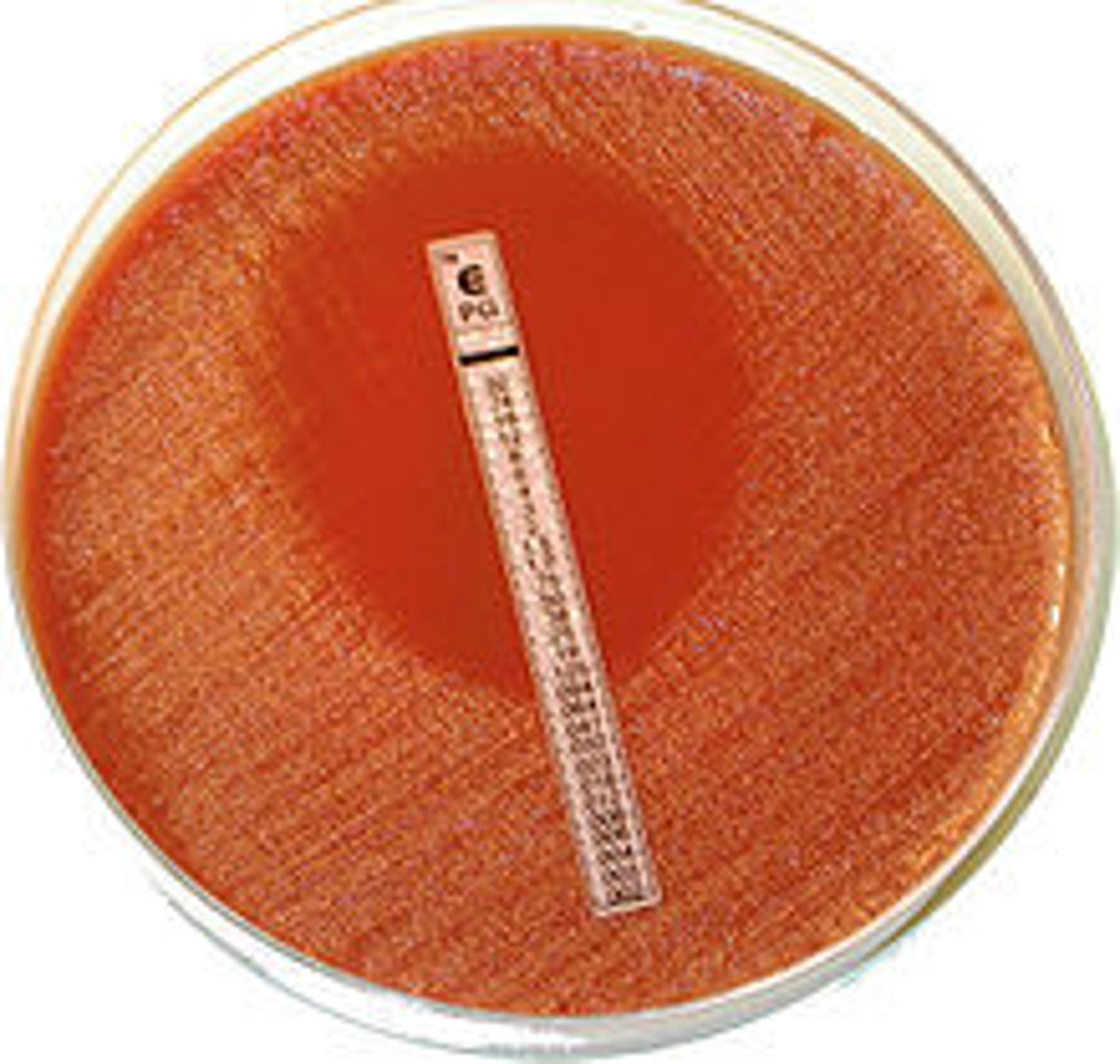
E test
Determines the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
-Lowest abx concentration preventing bacterial growth
E test Figure
Broth Dilution tests
Determine the MIC and minimal bactericidal concentration (MCB) of an antimicrobial drug
Test organism is placed into the wells of a tray containing dilutions of a drug; growth is determined
Antibiograms
Reports that record the susceptibility of organisms encountered clinically
Microdilution plate used for testing the MIC of antibiotics
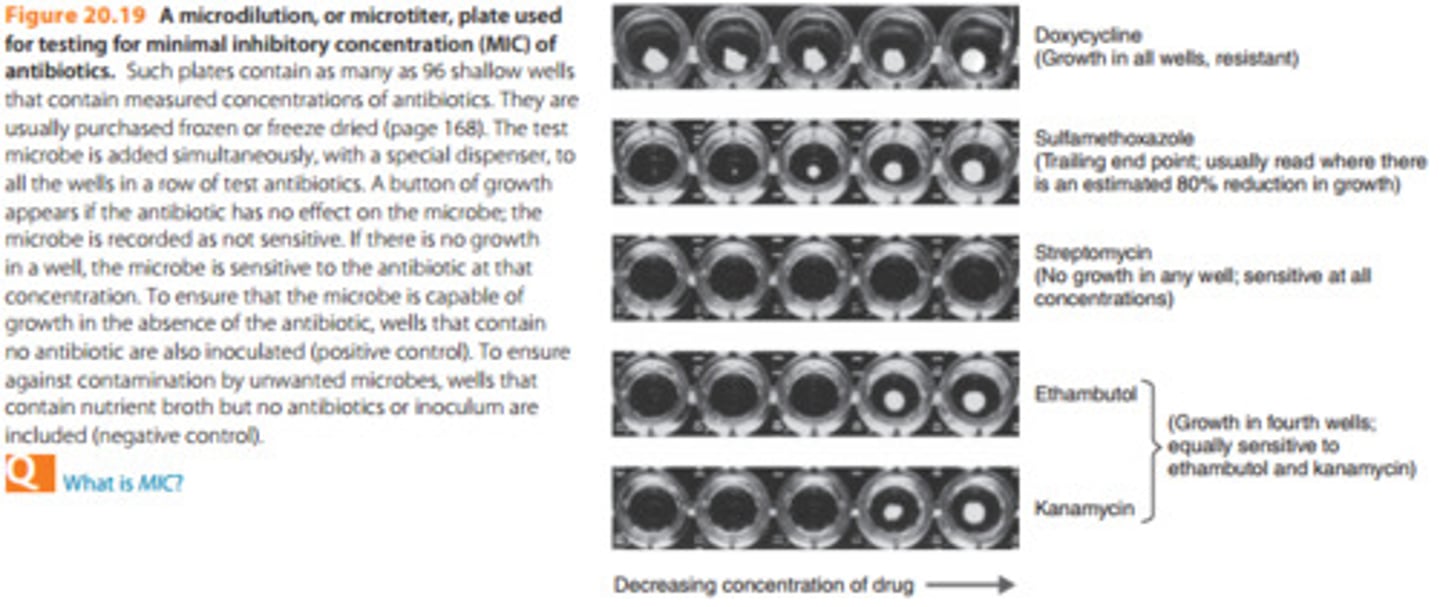
Persister cells
microbes with genetic characteristics allowing for their survival when exposed to an antibiotic
Superbugs
bacteria that are resistant to large number os antibiotics
Resistance genes are often spread horizontally among bacteria on plasmids or transposons via ________ or _______
conjugation or transduction
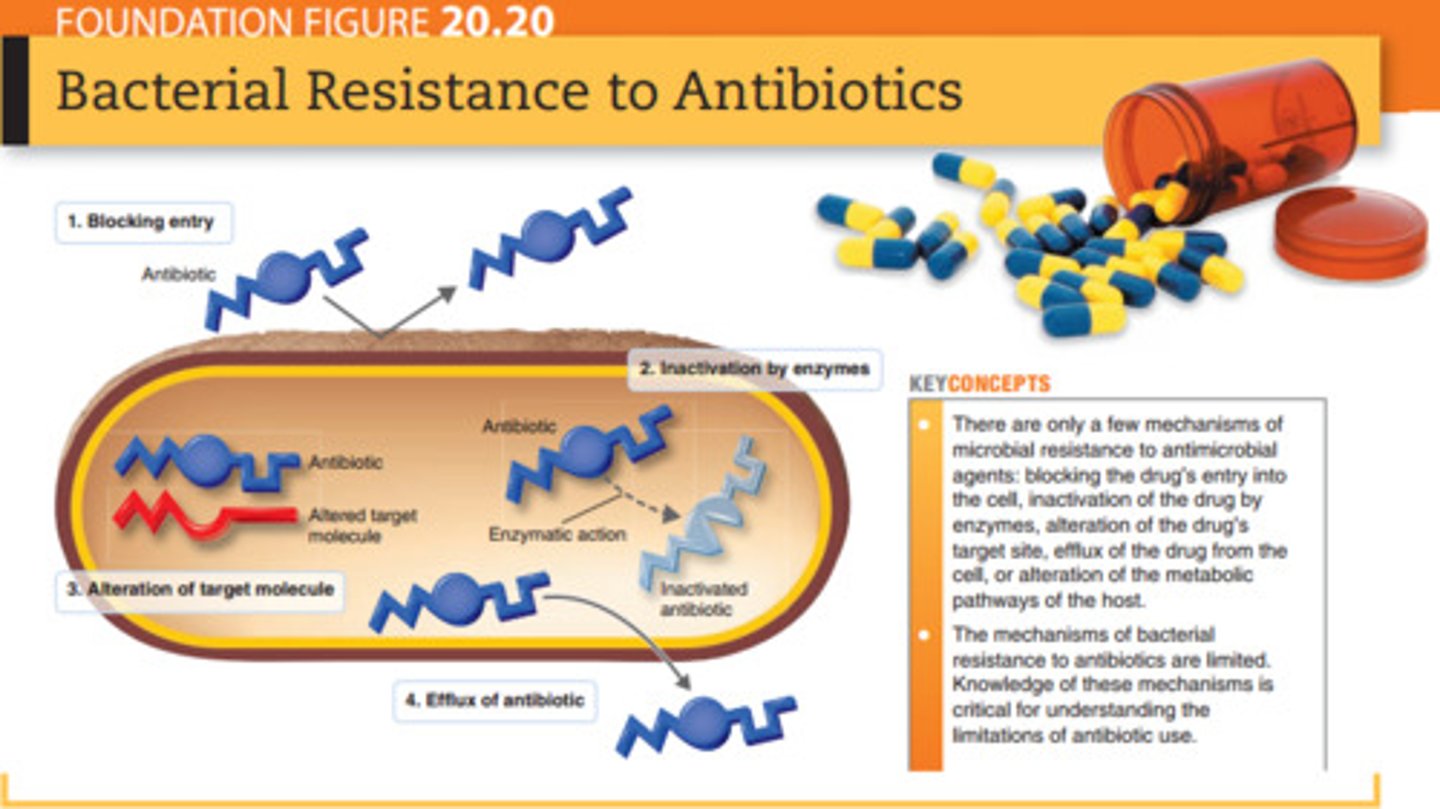
Name the 5 mechanisms of resistance
1. Enzymatic destruction or inactivation of the drug
2. Prevention of penetration to the target site within the microbe
3. Alteration of the drug's target site
4. Rapid efflux (ejection) of the antibiotic
5. Variations of mechanisms of resistance
Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics : Figure20.20
Misuse of antibiotics selected for resistance mutants
Misuse includes:
-using outdate or weakened antibiotics
-using antibiotics for the common cold and other inappropriate conditions
-using antibiotics in animal feed
-failing to complete the prescribed regimen
-using someone else's leftover prescription
Antibiotic Safety
-Therapeutic index: Risk versus benefit
-Reaction of antibiotics with other drugs
-Damage to organs
-Risk to fetus