Meninges, ventricles, and CSF
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/132
Last updated 3:49 PM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
1
New cards
Epidural space
potential space between dura and calvaria
2
New cards
Subdural space
potential space in the innermost dural layer, near the dura-arachnoid interface
3
New cards
subarachnoid space
normally present space, CSF filled, space enlarges in cisterns
4
New cards
What happens if the epidural space opens up
arterial bleeding
5
New cards
What happens if the subdural space opens up
venous bleeding
6
New cards
What are the types of cerebral hemorrhages?
subdural, subarachnoid, epidural, intracerebral
7
New cards
Decorticate rigidity
destructive lesion of the corticospinal tracts near cerebral hemispheres
8
New cards
Decerebrate rigidity
lesion of the diencephalon, midbrain, vestibulospinal pathways
9
New cards
epidural hematoma physical features
* skull fracture
* rapid expanding with arterial blood
* torn middle meningeal artery
* dura pushed away from hematoma
* rapid expanding with arterial blood
* torn middle meningeal artery
* dura pushed away from hematoma
10
New cards
subdural hematoma physical features
* slowly expanding with nexus blood
* torn bridging vein
* dura is attached, so cannot cross falx, tentorium
* torn bridging vein
* dura is attached, so cannot cross falx, tentorium
11
New cards
Shape of an epidural hematoma
local and biconvex (lemon)
12
New cards
Shape of subdural hematoma
diffuse and concave (banana)
13
New cards
What part of the brain would an epidural hematoma be located?
temporal or temporo-parietal
14
New cards
What part of the brain would a subdural hematoma be located?
entire brain surface
15
New cards
What type of consciousness can we expect with an epidural hematoma?
lucid interval
16
New cards
What type of consciousness can be expected with a subdural hematoma?
severe brain damage **immediately present**
17
New cards
Prognosis for epidural hematoma
related to pre-surgical status
18
New cards
Prognosis for subdural hematoma
poor
19
New cards
Amount of patients with epidural hematoma
0\.5% head injury patients
20
New cards
Amount of patients with subdural hematoma
30% head injury patients
21
New cards
Falx cerebri
dural folds that separate the two cerebral hemispheres
22
New cards
Tentorium cerebelli
dural fold between the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum
23
New cards
Diaphragm sellae
dural fold that covers the pituitary fossa and admits the infundibulum through a small perforation
24
New cards
Anterior attachment of falx cerebri
crista galli of ethmoid bone
25
New cards
Posterior attachment of falx cerebri
internal occipital protuberance
26
New cards
What part of the tentorium does the brainstem travel through?
tentorium notch AKA tentoria incisura
27
New cards
Anterior (and inferior) attachment of tentorium
petrous bone
28
New cards
Posterior attachment of the tentorium
occipital bone
29
New cards
What type of compartments does the tentorium create?
supratentorial and infratentorial compartments
30
New cards
contents of the supretentorial compartment
forebrain
31
New cards
contents of the infratentorial compartment
* brainstem and cerebellum
32
New cards
What fossa is the infratentorial compartment found in?
posterior fossa
33
New cards
What majorly supplies the dura mater
middle meningeal arter
34
New cards
Anterior blood supply of the dura mater
ophthalmic artery
35
New cards
posterior blood supple of the dura mater
branches of the occipital and vertebral artery
36
New cards
Venous sinuses
between cerebral hemispheres
37
New cards
What parts of the brain/matter do not feel pain?
brain, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
38
New cards
what parts of the brain are pain sensitive?
dura mater, proximal portions of blood vessels at base of brain
39
New cards
What CN does the cranial fossa receive sensory innervation from?
CN V - trigeminal
40
New cards
Where do dural nerves end?
1. near middle meningeal arteries
2. near dural sinuses
41
New cards
What do the dural dural nerves follow?
meningeal arteries
42
New cards
What happens when there is pain near the meningeal arteries
dural nerves perceive pain as localized
43
New cards
What happens when there is pain near the dural sinuses?
dural nerves perceive pain to the peripheral distribution of the CN V
44
New cards
What is the posterior fossa innervated by?
CN 2, 3, 10
45
New cards
What happens when there is pain by the dural arteries
pain is perceived as localized
46
New cards
What happens when there is pain near venous sinuses
pain is referred and perceived behind the **ear and back of neck**
47
New cards
Where can CN 2, 3, and 10 be found near?
1. dural arteries
2. venous sinuses
48
New cards
Arachnoid trabeculae
strains of CT extend to the pia mater and merge with the pia mater
49
New cards
Arachnoid mater
thin, a vascular membrane with few interspersed layers of cells
\
semi-transparent and **cobweb-like**
\
attached to the dura mater bu the **dural border cells**
\
semi-transparent and **cobweb-like**
\
attached to the dura mater bu the **dural border cells**
50
New cards
Subarachnoid space
where the arachnoid mater conforms with the brain but does not dip into the sulci
51
New cards
Subarachnoid cisterns
areas that contain substantial CSF
52
New cards
What separate arachnoid cisterns from each other
arachnoid trabeculae
53
New cards
What separates blood and CSF in the dural sinuses?
arachnoid mater
54
New cards
Arachnoid villi
herniate through the wall of dural sinus
55
New cards
Arachnoid granulations AKA pacchonian bodies
large clusters of arachnoid villi
56
New cards
What parts of the mater can calcify with age?
arachnoid villi
57
New cards
How does the arachnoid mater have its barrier function?
its cells are connected by tight junctions
58
New cards
How does CSF travel through the arachnoid mater?
one-way valve-type travel
59
New cards
Pathway of CSF through the arachnoid mater
1. allow CSF to flow from subarachnoid space into venous space
2. CSF pressure exceeds venous pressure
3. Never flows in reverse, even if pressure gradient reverses
60
New cards
Pia mater
invests all external surfaces of the CNS, delicate membrane
61
New cards
leptomeningeal complex
the area where the arachnoid trabeculae and pia mater merge, very difficult to distinguish the 2 apart
62
New cards
Virchow-Robin space
each vessel enters and leaves with a sleeve of perivascular space
63
New cards
How is the spinal dura different from the brain dura?
1. spinal dura has no periosteal component
2. cranial epidural is a **potential space**, while the spinal dura is **actual space**
64
New cards
how many denticulate ligaments are there in the spine?
21
65
New cards
filum terminale
anchors the conus medullaris to the caudal end of the spinal dural sheath
66
New cards
What is the function of the denticulate ligaments?
anchor the spinal cord to the arachnoid
67
New cards
Lumbar cistern
where lumbar puncture can be performed, **space in subarachnoid space in the lumbar region**
68
New cards
opening CSF of pressure
90-180 mmH20 while laying supine and lateral
69
New cards
What are the constituents of CSF like
plasma
70
New cards
Procedures that can be performed at the lumbar cisterns?
1. lumbar puncture
2. epidural anesthesia
71
New cards
Where is CSF formed?
lateral portions of 3rd and 4th brain ventricles
72
New cards
Where does CSF emerge from after being formed?
4th brain ventricle apertures → fill subarachnoid space
73
New cards
What is responsible for suspending the brain?
CSF
74
New cards
What is CSF’s role in brain communication?
route for chemical messengers to reach brain rapidly
75
New cards
What are the ventricles of the brain lined with?
ependymal cells
76
New cards
What does the neural tube develop into?
continuous fluid-filled system of ventricles
77
New cards
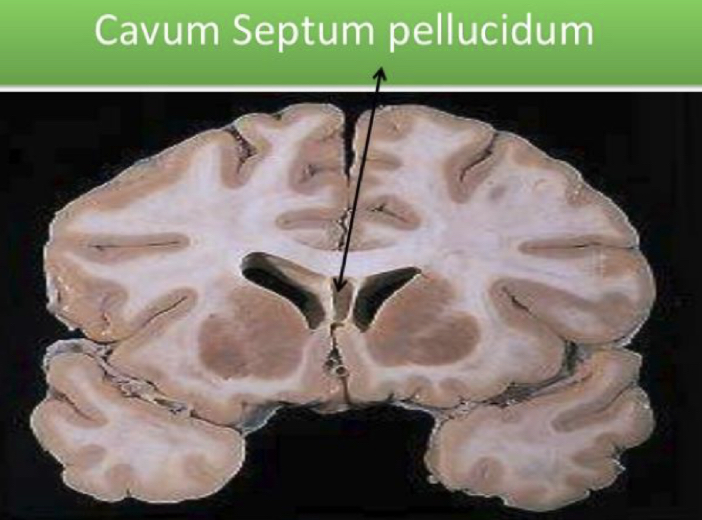
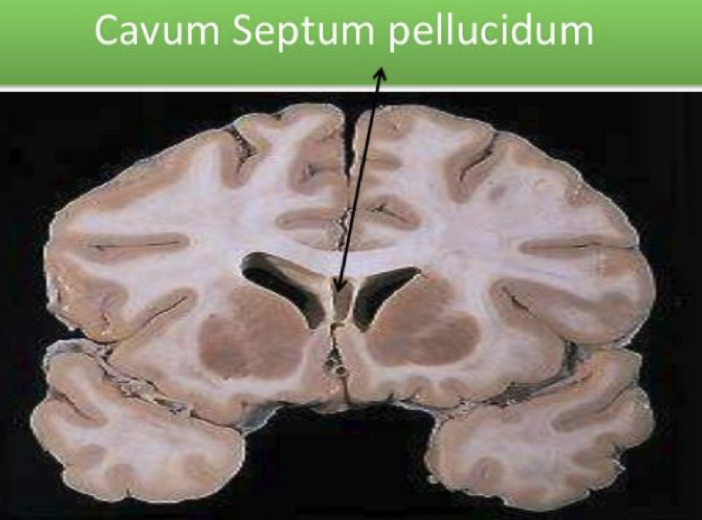
Cavum septum pellucidum
potential space in between the brain ventricles
78
New cards
how do the lateral ventricles communicate with he 3rd ventricle
inter ventricular foramina of Monroe
79
New cards
how does the 3rd ventricle communicate with the 4th ventricle
aqueduct of sylvius
80
New cards
What side of the lateral ventricles would be larger in a right-handed individual?
posterior horn on LEFT side
81
New cards
What form the lateral ventricles?
corpus callosum and septum pellucidum
82
New cards
What forms the floor and medial wall of inferior horn
hippocampus
83
New cards
What shape do the lateral ventricles make
C-shaped
84
New cards
What would a blockage of the *interventricular foramen of Monroe* cause?
obstructive hydrocephalus
85
New cards
What part of the brain does the 3rd ventricle mostly fill?
midline of diencephalon
86
New cards
interthalamic adhesion
hole found in the 3rd ventricle, where the 2 thalami join each other
87
New cards
Where does the 3rd ventricle end anteriorly?
*lamina terminalis*, remnant of rostral neuropore
88
New cards
what are the recesses of the 3rd ventricle
1. supraoptic recess
2. infundibular recess
3. pineal recess
4. supra-pineal recess
89
New cards
Limits of the 4th ventricle
anteriorly: pons/medulla
posteriorly: cerebellum
posteriorly: cerebellum
90
New cards
Diamond shaped hole in 4th ventricle
rhomboid fossa
91
New cards
Narrow tube in 4th ventricle
lateral recess
92
New cards
Roof of the 4th ventricle
superior medullary velum
93
New cards
Where does the lateral recess of the 4th ventricle end?
flocculus of the cerebellum
94
New cards
Apertures of 4th ventricle
1. unpaired median aperture - foramen of Magendie
2. 2 lateral aperatures - foramina of Luschka
95
New cards
Total volumes of CSF in brain and spinal cord
200mL
96
New cards
Volume of CSF in lateral ventricles
23mL
97
New cards
Volume of CSF in 3rd and 4th ventricles
2mL
98
New cards
Volume of normal ventricular CSF
approximately 10-30mL
99
New cards
How much does SNS stimulation reduce CSF production by?
30%
100
New cards
How many times does CSF completely turnover a day?
3-4 times, actively secreted product