chapter 3 Crystal systems
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Material and structure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Crystal face
A plane surface on the exterior of a crystal where unrestricted crystal growth has ceased.
CRYSTAL FORM
A set of crystal faces dictated by the internal structure of a single crystal e.g. bipyramidal form.
Crystal habit
the form, or combination of forms, exhibited by any crystal that determines its characteristic shape
It reflects the arrangement of its crystal faces and internal structure. .
surface markings
etch pits growth marks fine parallel lines; surface grains or striation
Prismatic Habit
When a crystal forms in such a way that the prism form is the most dominant
Crystal shape resembling a prism.
Pinacoid
A crystal form composed of a pair of parallel faces.
Prism
A crystal form consisting of 3 or more faces parallel to a line
tabular habit
short prism faces and large pinacoid faces
rhombic
3 unequal axes at right angle to each other with the same length
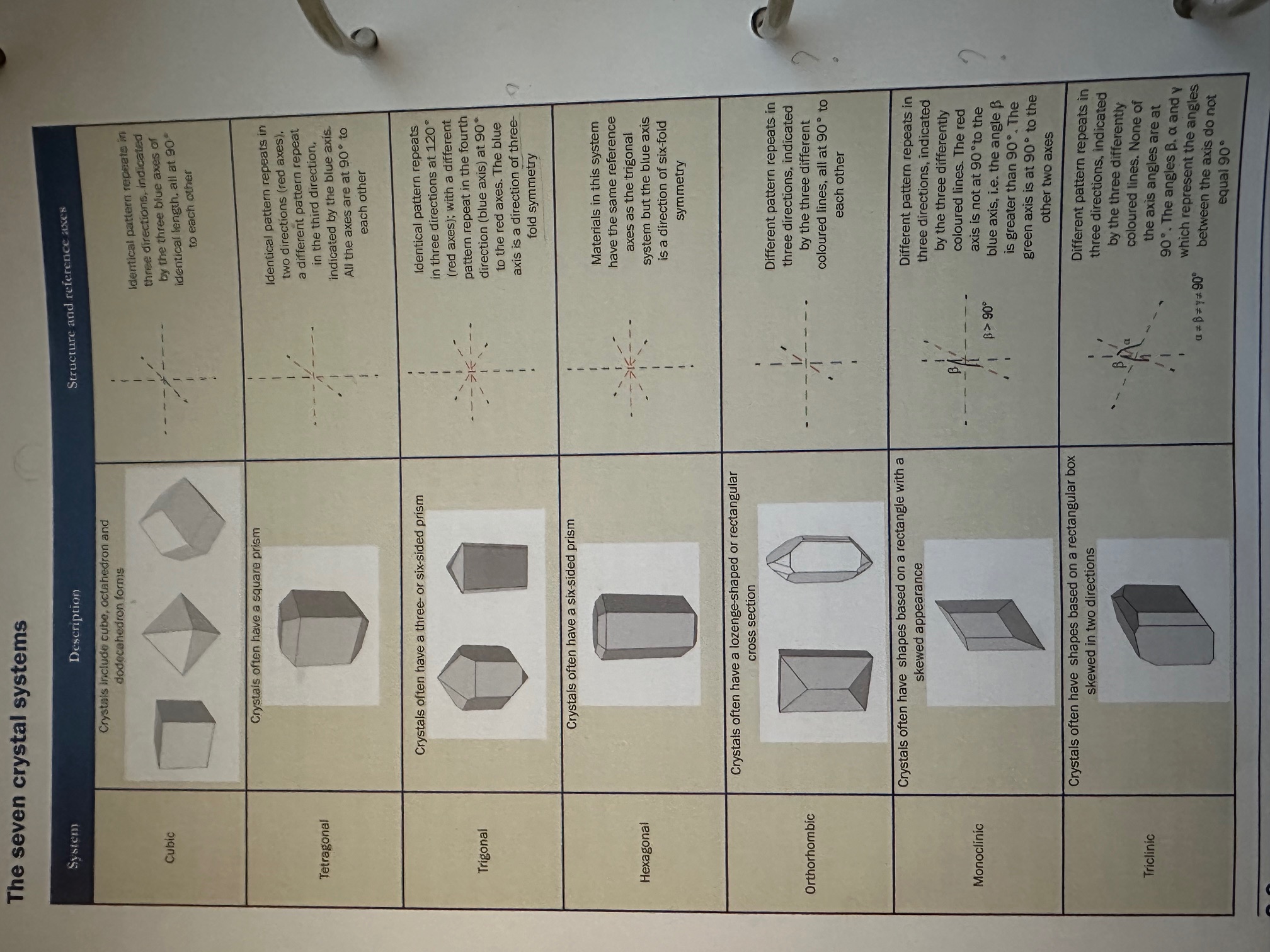
Cubic
Diamand= octahedron
Spinel = octahedron
Garnet = dodecahedron
Fluorite = cubic

Tetragonal
Zircon


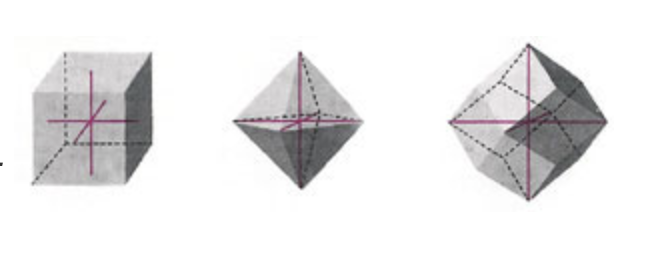
Trigonal
Corundum
Quartz; amethyst, Chalcedony, Citrine
Tourmaline
3-fold

Hexagonal
Beryl; emerald, aquamarine, heliodore, Morganite
6-fold


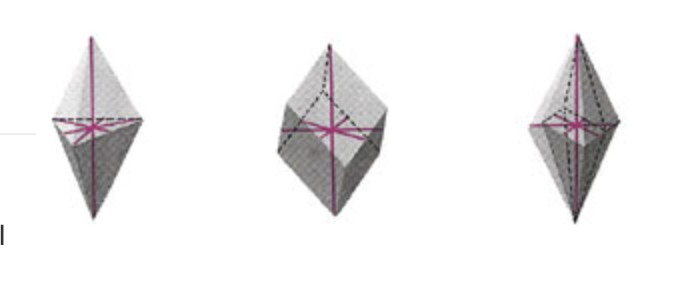
Orthorhombic
Peridot
Topaz
Chrysoberyl
Iolite
Tanzanite

Monoclinic
feldspar
Jade
Nephrite
Moonstone
Triclinic
Feldspar
crystal reference axes
represent the patterns repeat in the lattices
Indicates the relative distance at which the crystal pattern repeats in that directionand the angles between them.
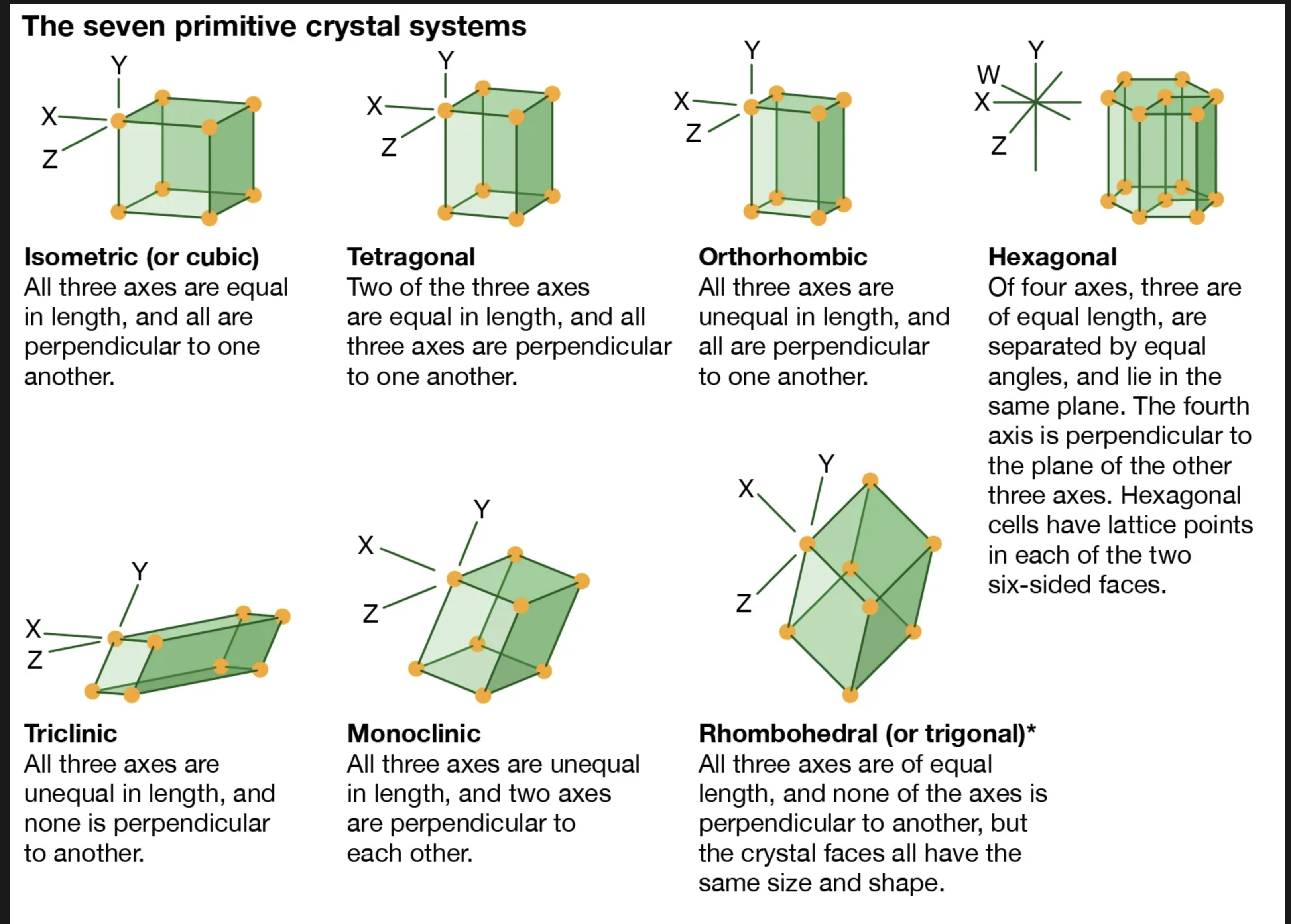
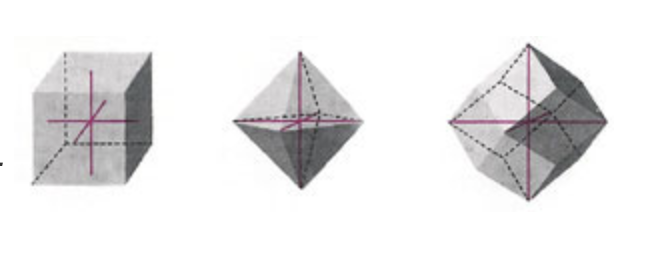
Crystal system: Cubic
a=b=c
All have the same length, all angles at 90 degrees, and the symmetry is high, resulting in a variety of shapes such as cubes and octahedra.

crystal system: Tetragonal
one difference with Cubic
the C axe can be longer or shorter
a=b but not equal to C
all angles are at 90 degrees to each other
Crystals often have square prims and can exhibit a variety of forms, including elongated shapes.

crystal system: Trigonal
a=b=d ongelijk aan C
Angles a,b and b,d = 120 degrees
3-fold
The identical pattern repeats in three directions at 120 degrees
with a different pattern repeats in the fourth direction(C axe) at 90 degrees to the red axes.
C-axe is a direction of 3-fold
symmetry, with a hexagonal arrangement of lattice points.

Hexagonal system
a=b=d ongelijk aan C
Angles a,b and b,d = 120 degrees
3-fold
The identical pattern repeats in three directions at 120 degrees
with a different pattern repeats in the fourth direction(C axe) at 90 degrees to the red axes. C-axe is a direction of 3-fold
The hexagonal crystal system features two distinct lengths where a=b, but both are unequal to C. The angles between a and b are 120 degrees, and the structure exhibits a three-fold symmetry along the C axis, which is perpendicular to the a-b plane.


Orthorhombic crystal system
A niet b niet gelijk c
all angles are 90 degrees to each other
different patterns repeat in three directions
rhomb shaped prisma
basal cleavage
looks a bit like a Matchbox
The orthorhombic crystal system is characterized by three mutually perpendicular axes of unequal lengths (a, b, and c). It exhibits distinct rhomb-shaped prisms and often shows basal cleavage.
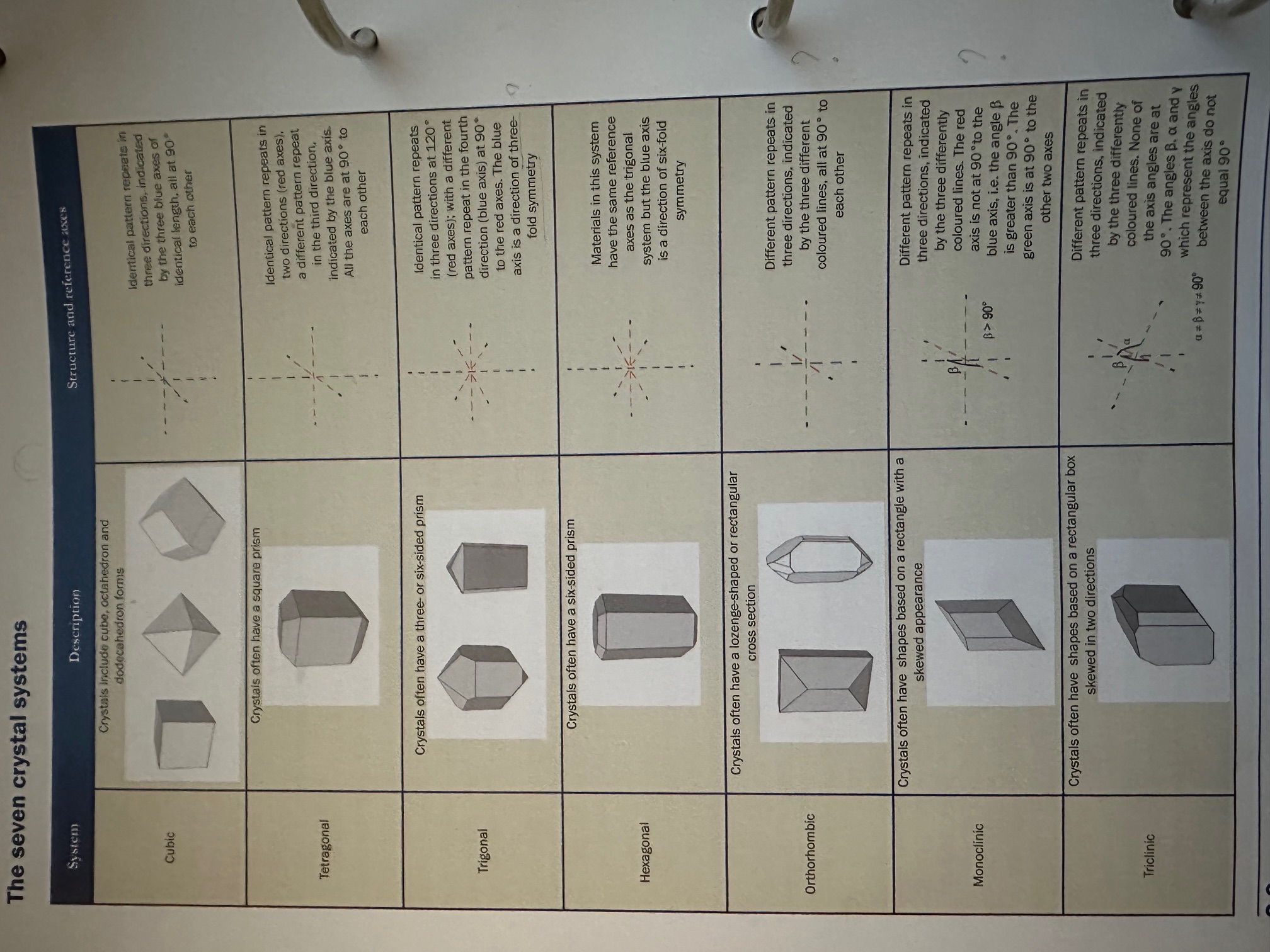

Monoclinic System
basically the same as orthorhombic
Difference angles A,C are not equal to 90 degrees
one axe is at 90 degrees to the C axe, hence the skewed shape Often, it has shapes based on a rectangle with a skewed appearance
The monoclinic crystal system has three unequal axes where two axes are perpendicular while the third is inclined, resulting in non-right angles between them. This leads to a skewed rectangular appearance in its crystal forms.
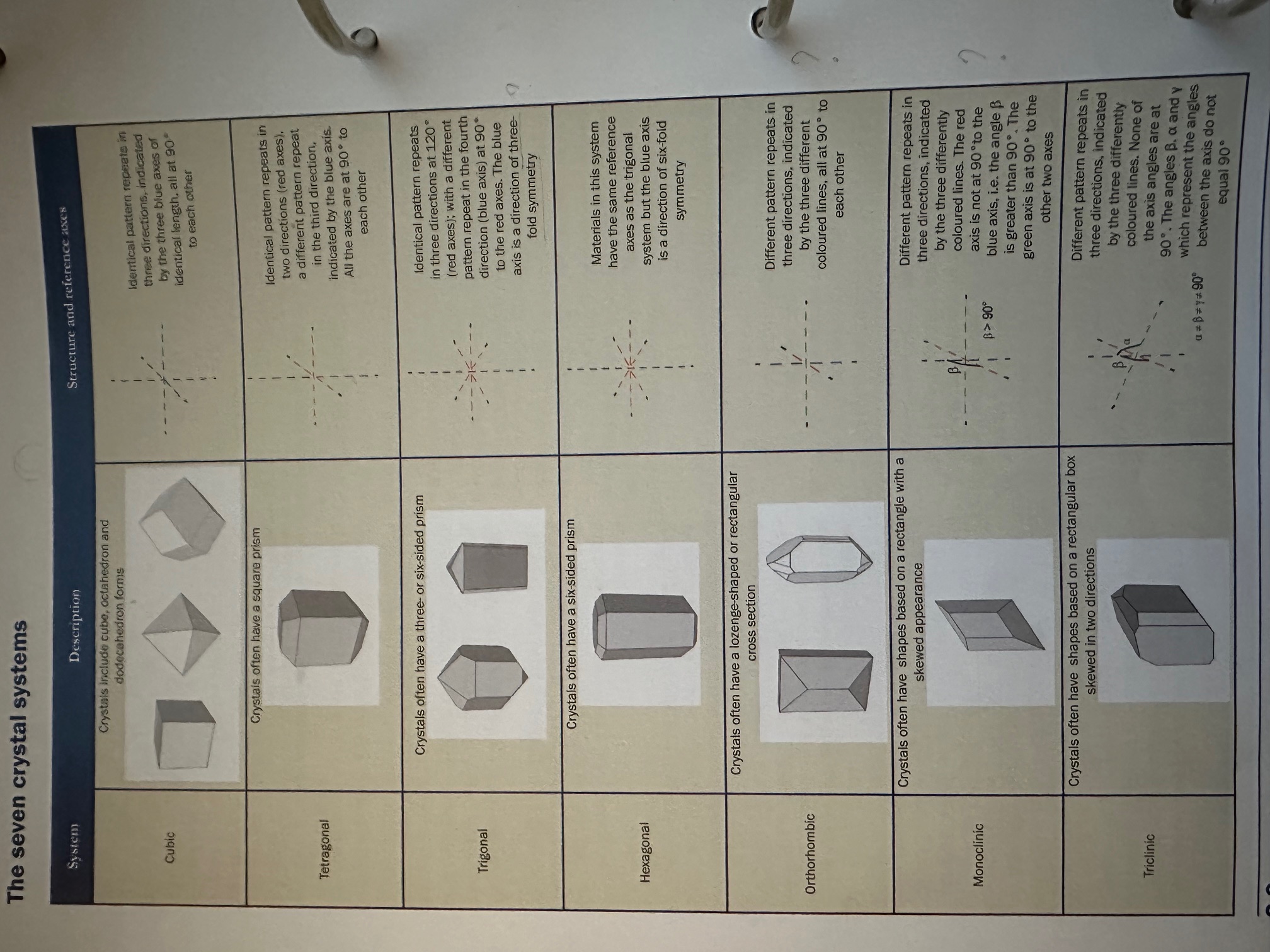

Triclinic Crystal System
angles of a,c and a,b not equal to 90 degrees
basically the same as orthorhombic
Often has shapes based on a rectangular box skewed in two directions.
The triclinic crystal system is characterized by three unequal axes with no angles equal to 90 degrees, resulting in a skewed rectangular box shape. It lacks any symmetry and exhibits the most general form of crystal structure.