Chapter 17 & 18: Carboxylic Acids, Carboxylic Anhydrides, Esters and Amides
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Carboxylic acids
organic compound containing carbonyl group
Carbonyl group
functional group of a carboxylic acid
can be represented in 3 ways
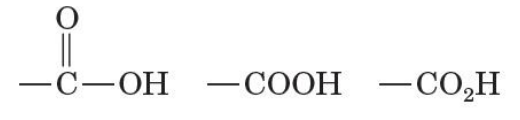
anhydrides, esters, and amides
3 classes of compounds derived from carboxylic acids
each is related to a carboxyl group by loss of H2O
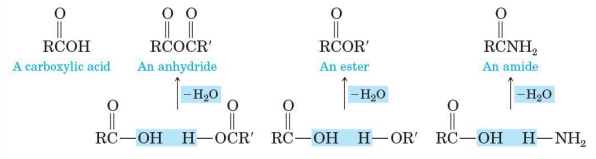
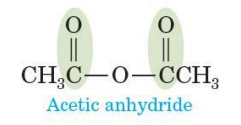
Anhydrides
functional group is 2 carbonyl groups bonded to the same oxygen
symmetrical or mixed
To name it, drop the word “acid” and add the word “anhydride”
Esters
functional group is a carbonyl group bonded to an -OR group
R may be alkyl or aryl
IUPAC and common names are derived from the names of the parent carboxylic acids
“-ic” becomes “-ate”
Lactone
cyclic ester
Amide
functional group is a carbonyl group
To name it, drop the ‘oic” acids
also bonded to an alkyl or aryl group, name the group and show its location on nitrogen by N-; two alkyl or aryl groups by N,N-di-
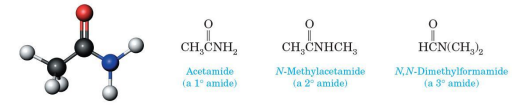
Lactam
cyclic amide
Penicillin
referred to as β-lactam antibiotics
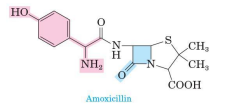
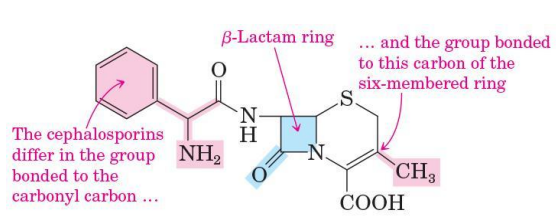
Cephalosporins
are also β-lactam antibiotics
C=O, C-O, O-H
3 polar covalent bonds in carboxyl group
polarity of these bonds determines the major physical properties of carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids
have significantly higher boiling points than other types of organic compounds of comparable molecular weight
more soluble in water than are alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones of comparable molecular weight
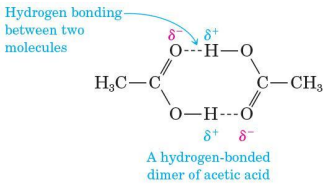
Polarity and hydrogen bonding
causes the higher boiling points of carboxylic acids
creation of dimer
Dimer
behaves as a higher-molecular-weight compound
Fatty acids
long chain carboxylic acids derived from animal fats, vegetable oils, or phospholipids of biological membranes
more than 500 have been isolated from various cells and tissues
most have between 12 and 20 carbons in an unbranched chain
Unsaturated fatty acids
cis isomer predominates, trans isomers are rare
generally have lover melting points than their saturated counterparts
Saturated fatty acids
lauric acid
myristic acid
palmitic acid
stearic acid
arachidic acid
Unsaturated fatty acids
palmitoleic acid
oleic acid
linoleic acid
linolenic acid
arachidonic acid
Saturated fatty acids
solids at room temperature
the regular nature of their hydrocarbon chains allows them to pack together in such a way as to maximize interaction (by london dispersion forces) between their chains
Unsaturated fatty acids
are liquids in room temperature because the cis double bonds interrupt the regular packing of their hydrocarbon chains
Natural soaps
sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids
prepared from a blend of tallow and palm oils (triglycerides)
Tallow
insoluble triglyceride layer that forms on the top when solid fats from cattle are melted with steam
Triglycerides
triesters of glycerol
Preparation of soaps
begins by boiling the triglycerides with NaOH
Saponification
the reaction that takes place in preparation of soaps by boiling triglycerides with NaOH
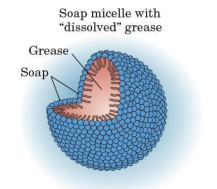
Micelles
in water, soap molecules spontaneously clusters into this
spherical arrangement of molecules such that their hydrophobic parts are shielded from the aqueous environment, and their hydrophilic parts are in contact with the aqueous environment
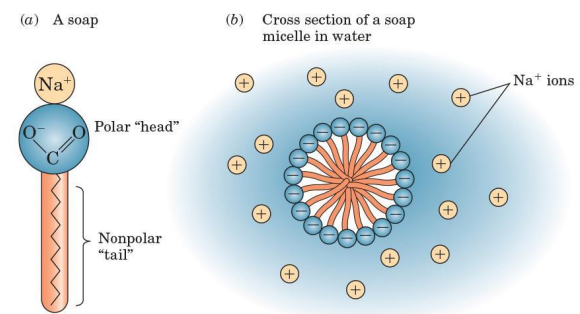
Nonpolar hydrocarbon inner parts
when soaps and dirt (grease, oil, and fats stains) are mixed in water, this part of the soap micelles “dissolve” the nonpolar substances
Natural soaps
from water-insoluble salts in hard water
Hard water
contains Ca2+, Mg2+, and Fe3+ ions
Sodium soap
soluble in water as micelles
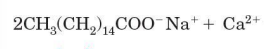
Calcium salt of a fatty acid
insoluble in water
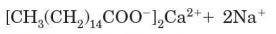
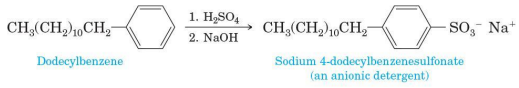
Sulfonate group (—SO3-)
the problem of formation of precipitates in hard water was overcome by using a molecule containing this group in the place of a carboxylate (—CO2-) group
Calcium, magnesium and iron salts of sulfonic acids (RSO3H)
more soluble in water than are their salts of fatty acids
SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate)
synthetic detergent
a liner alkylbenzenesulfonate (LAS), an anionic detergent
Foam stabilizers, bleaches, and optical brighteners
most common additives to detergents
Carboxylic acids
weak acids
Values of Ka for most unsubstituted aliphatic and aromatic carboxylic acids fall within the range 10^–4 to 10^–5 (pKa 4.0 – 5.0)
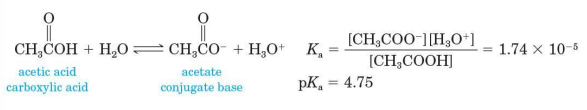
10^–4 to 10^–5 (pKa 4.0 – 5.0)
Values of Ka for most unsubstituted aliphatic and aromatic carboxylic acids fall within the range
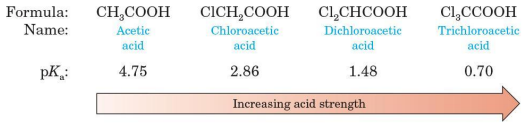
Substituents of high electronegativity (-OH, -Cl, -NH3+)
increase the acidity of carboxylic acids
Dichloroacetic acids and trichloroacetic acid
stronger acids than H3PO4 (pKa 2.1)
Increasing acid strength
acetic acid
chloroacetic acid
dichloroacetic acid
trichloroacetic acid
pH of the solution in which it is dissolved
when a carboxylic acid is dissolved in aqueous solution, the form of the carboxylic acid present depends on the,,,
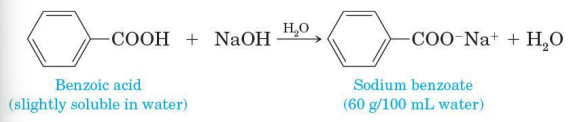
NaOH, KOH, and other string bases
all carboxylic acids, whether soluble or insoluble in water, react with these to form water soluble salts
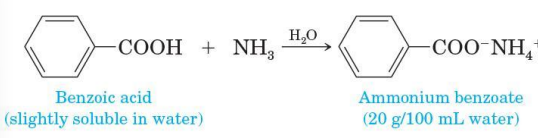
Ammonia and amines
carboxylic acids also form water-soluble salts with them
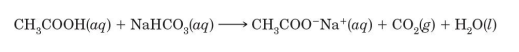
Sodium bicarbonate and sodium carbonate
like inorganic acids, carboxylic acids react with these to form water soluble sodium salts and carbonic acids
Carbonic acid
decomposes to give water and carbon dioxide, which evolves as a gas
Fischer esterification
one of the most commonly used methods for the preparation of esters
a carboxylic acid is treated with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, most commonly concentrated sulfuric acid
reversible
possible to drive it in either direction by the choice of experimental conditions (Le Chatelier’s principle)
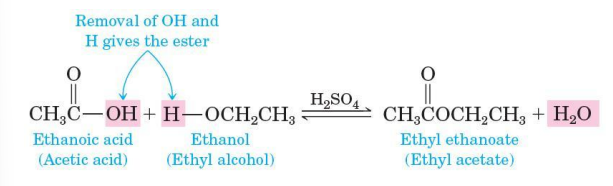
Tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate
in fischer esterification, the alcohol adds to the carbonyl group of the carboxylic acid to form a,,,
Ester
the intermediate loses H2O to give an,,,
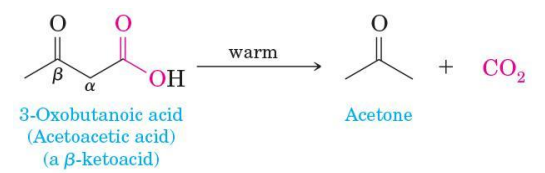
Decarboxylation
loss of CO2 from a carboxyl group
Thermal decarboxylation
almost all carboxylic acids, when heated to a very high temperature will undergo this
Most carboxylic acids
resistant to moderate heat and melt and even boil without undergoing decarboxylation
an exception is any carboxylic acid that has a carbonyl group on the carbon β to the COOH group
Decarboxylation of a β-ketoacid
Mechanism of thermal decarboxylation
involves (1) redistribution of electrons in a cyclic transition state followed by (2) keto-enol tautomerism
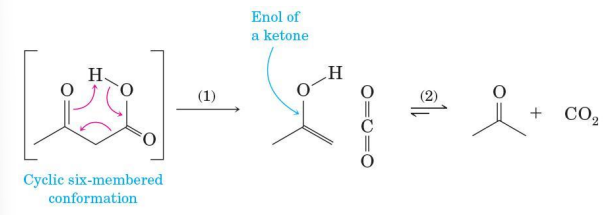
Oxidation of foodstuff in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle
an important example of decarboxylation of a β-ketoacid in biochemistry
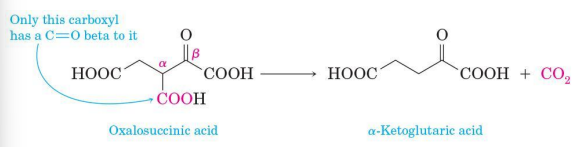
Oxalosuccinic acid
one of the intermediates in this cycle
has a carbonyl group (in this case a ketone) β to one of its three carboxyl groups
Amides
can be formed with an amine and removing -OH from the acid and an -H from the amine
In practice, what occurs if the two are mixed is an acid-base reaction to form an ammonium salt
if this slat is heated to a high enough temperature, water is eliminated and an amide forms
Ammonium salt
occurs if the carboxylic acid and amine are mixed in an acid base reaction
Amide
if ammonium salt is heated to a high enough temperature, water is eliminated and it is formed,,,
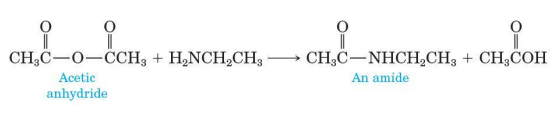
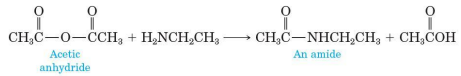
Treating an anhydride with an amine
much more common way of preparation of amides