Gastrointestinal Physiology - Digestive System (GIT, Accessory Organs)
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of practice flashcards covering the major topics from the GI physiology lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What are the four basic digestive processes?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and defecation.
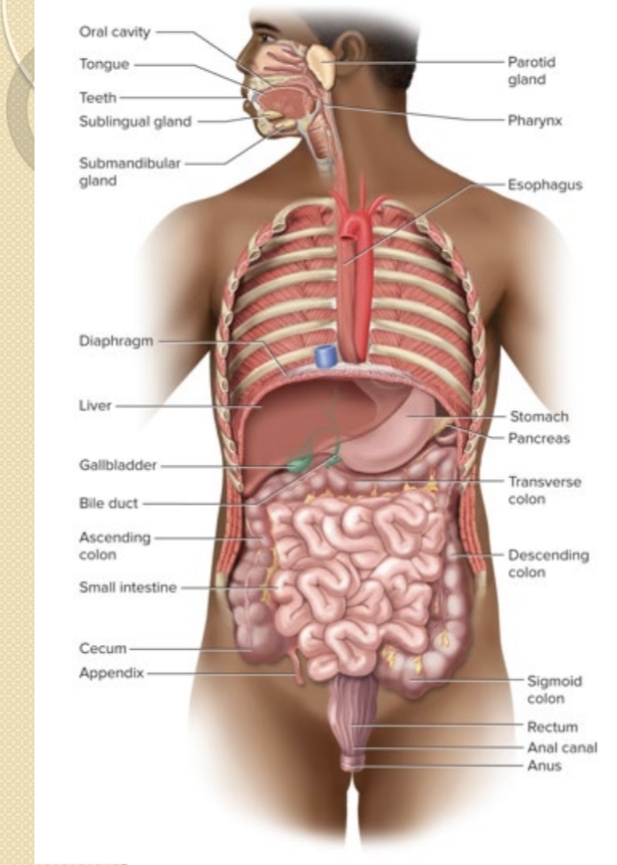
Which organs compose the GI tract?
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
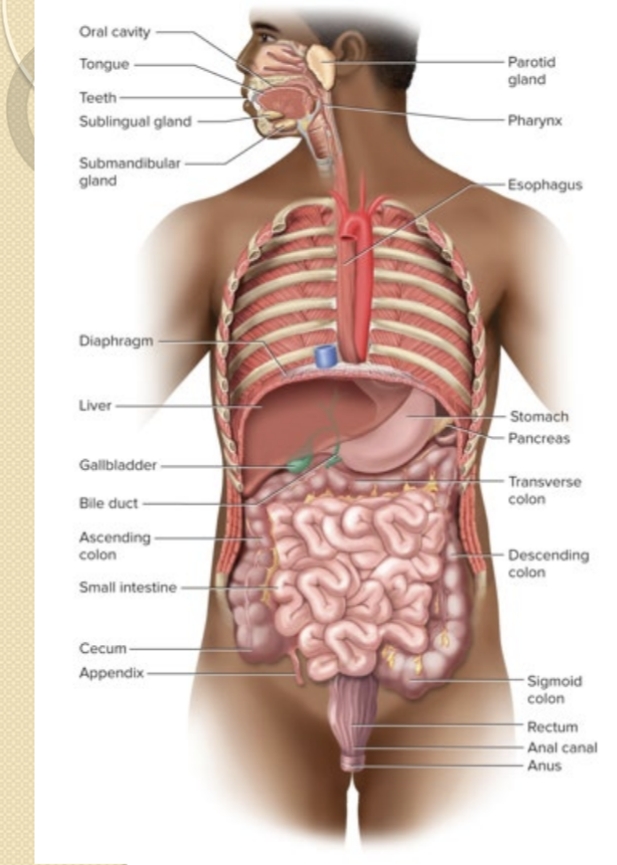
Which organs are considered accessory digestive organs?
Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What is gastric motility?
The GI tract’s ability to mix and move contents along its length.
What are the two major intrinsic neural networks of the GI tract and their roles?
Myenteric (Auerbach) plexus controls motility; Submucosal (Meissner) plexus controls secretions.
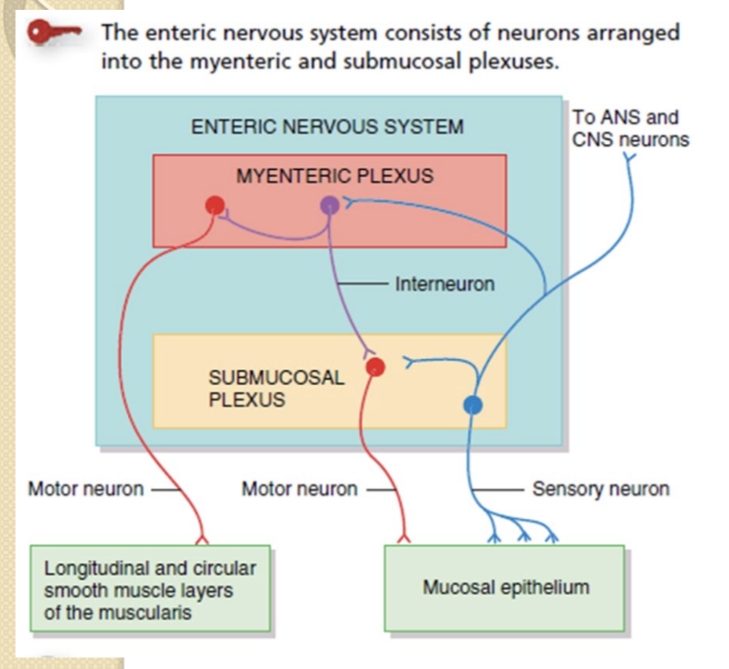
What are the effects of the parasympathetic (vagal) and sympathetic innervation on GI secretion and motility?
Parasympathetic via vagus increases secretion and motility; sympathetic suppresses GI activity.
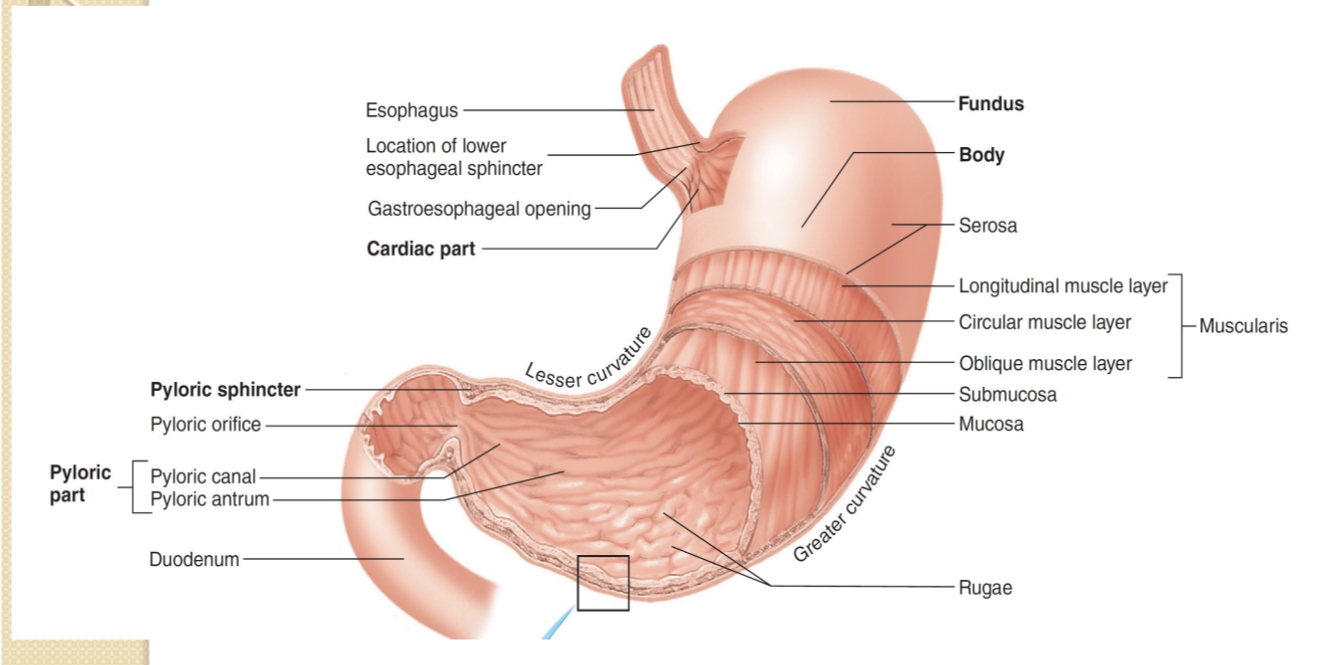
Name the major regions of the stomach.
Cardia, fundus, body, antrum, and pyloric region (plus the gastroesophageal opening).
What is intrinsic factor and where is it produced?
A glycoprotein essential for vitamin B12 absorption, produced by parietal cells.
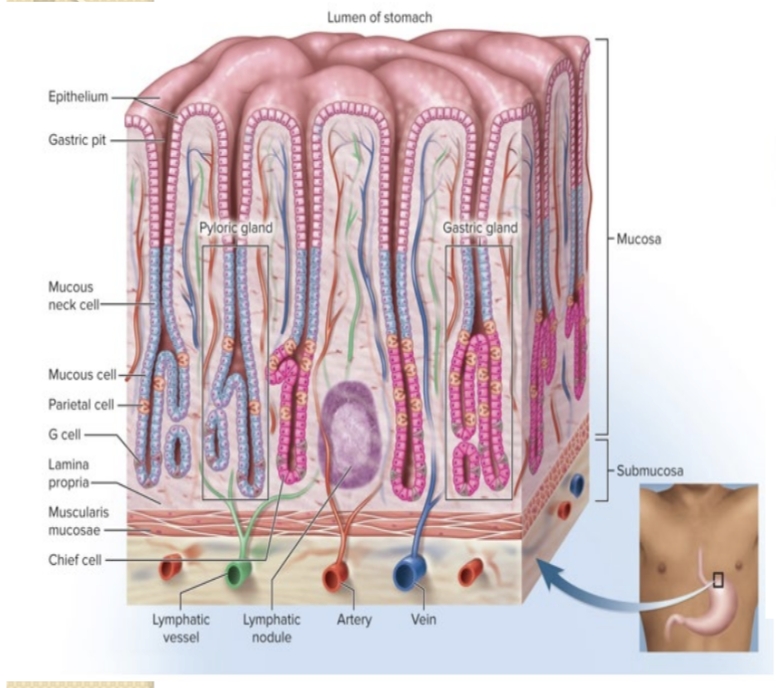
What secretions do parietal cells produce?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor.
What cells secrete pepsinogen?
Chief cells of the gastric glands.
What cells secrete gastrin?
G cells (enteroendocrine cells) of the gastric glands.
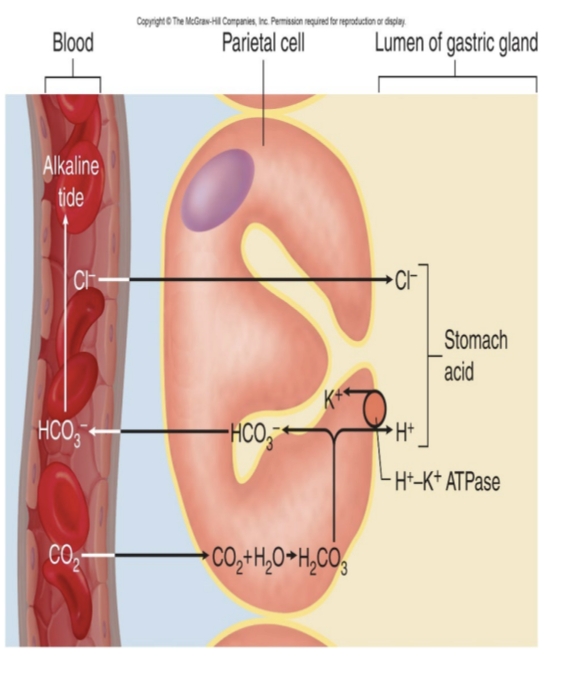
What is the function of HCl in the stomach?
Activates pepsin, helps liquefy food, kills pathogens, and aids iron absorption.
Which enzyme digests proteins in the stomach?
Pepsin (activated from pepsinogen by HCl).
Which enzyme digests fats in the stomach?
Gastric lipase.
Which substances are absorbed in the stomach?
Limited absorption: water, ions, some short-chain fatty acids, certain drugs (e.g., aspirin), and alcohol.
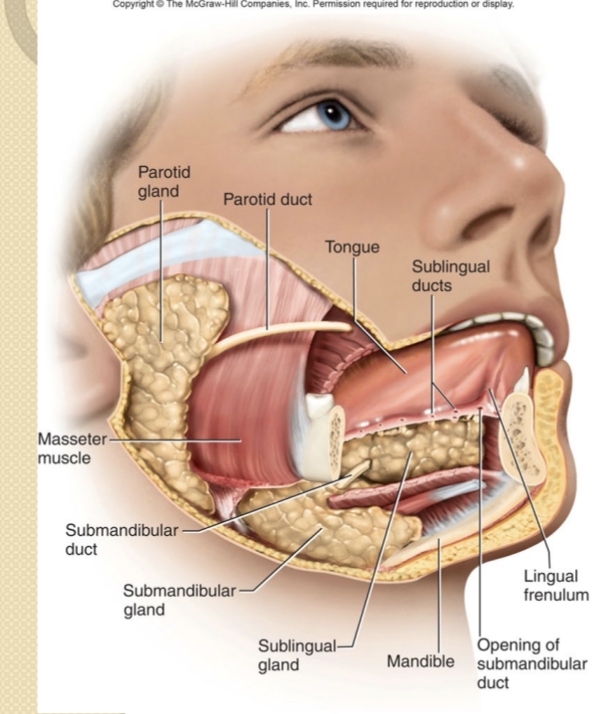
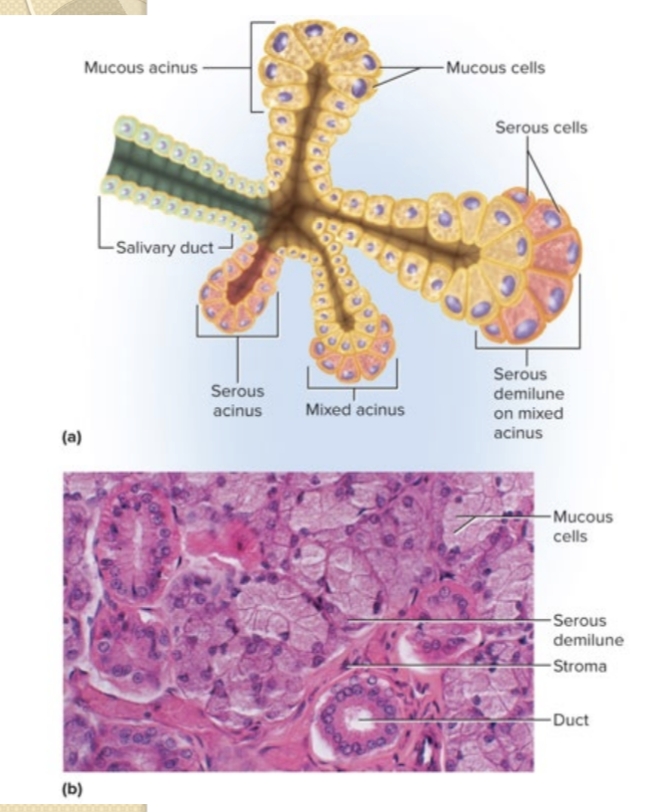
What is the role of saliva in digestion?
Moistens and lubricates food; contains salivary amylase and lingual lipase; forms a bolus.
What are the major salivary glands?
Parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
What are the main components of saliva composition?
About 97–99.5% water; 0.5% solutes including mucus, ions, lysozyme, IgA, salivary amylase, and lingual lipase.
What is the purpose of the pharynx and esophagus in swallowing?
Propel food via muscular contractions; lower esophageal sphincter prevents reflux.
What are the phases of deglutition?
Oral phase (voluntary), pharyngeal phase (involuntary), and esophageal phase (involuntary).
What is the primary function of the stomach?
Store and mix ingested food with gastric juice to form chyme; reservoir before small intestine.
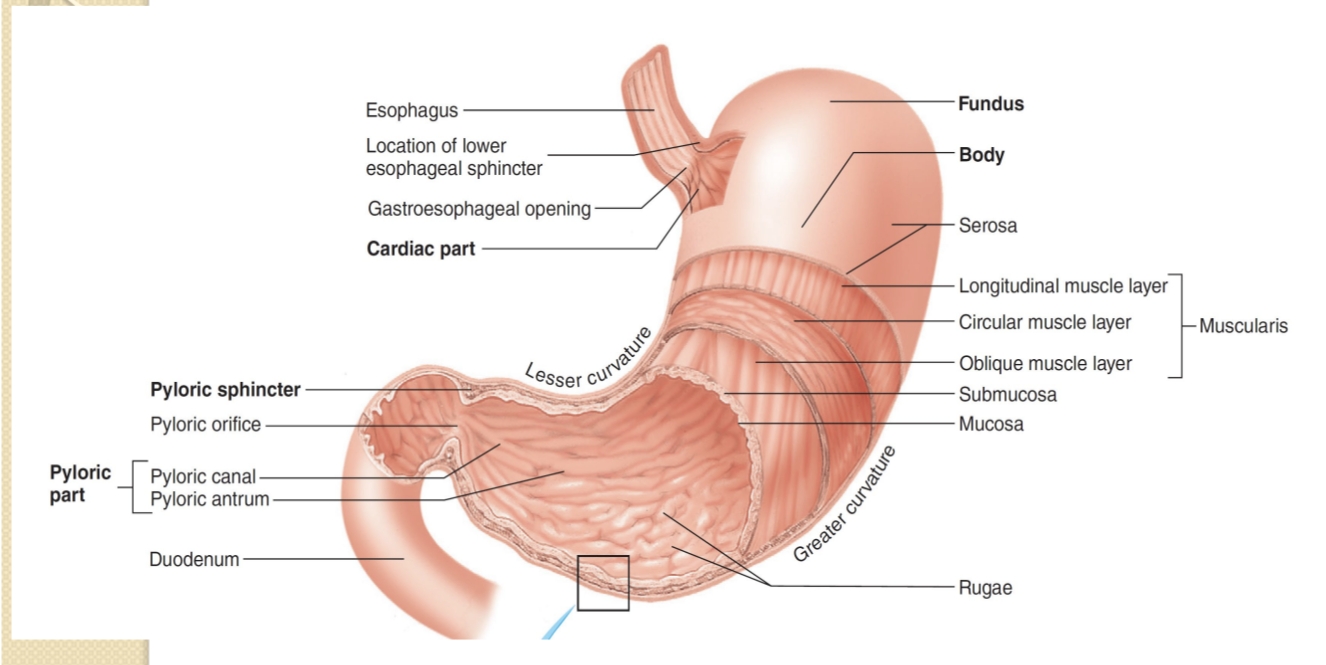
What is the role of the pyloric sphincter and pyloric canal?
Regulates passage of chyme from stomach to duodenum and controls gastric emptying.
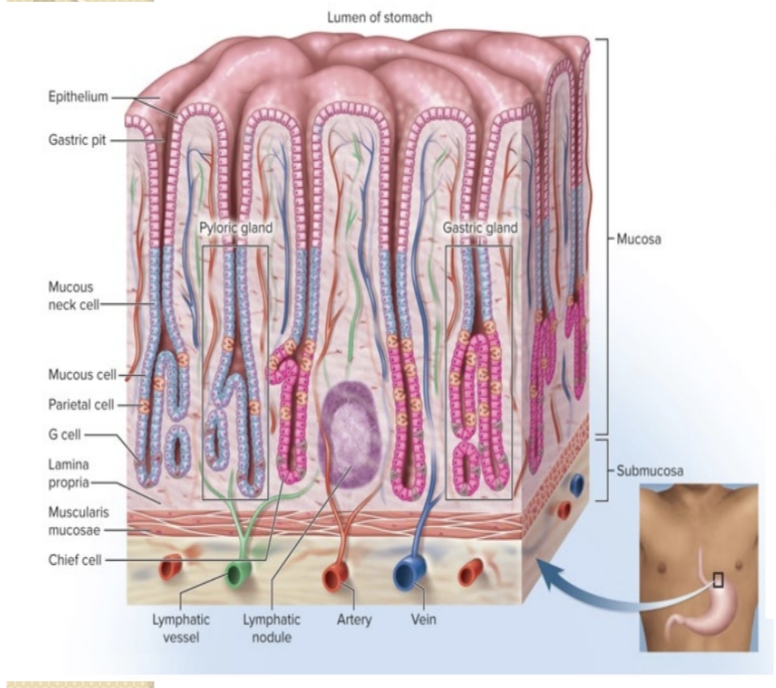
Which gastric secretions and their producing cells?
HCl and intrinsic factor (parietal cells); pepsinogen (chief cells); gastrin (G cells).
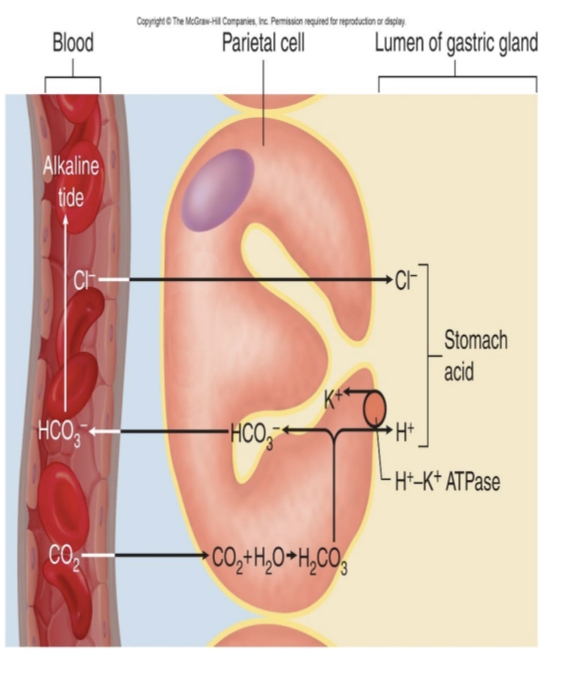
What stimulates HCl secretion?
Acetylcholine, histamine, and gastrin (triggered by cephalic and gastric phases).
What inhibits gastric secretion during the intestinal phase?
Secretin, CCK, and the enterogastric reflex; plus sympathetic input and vagal inhibition.
Role of secretin and CCK in digestion?
Secretin stimulates pancreatic bicarbonate secretion; CCK stimulates pancreatic enzymes and gallbladder contraction. CCK also promotes satiety and slows gastric emptying.
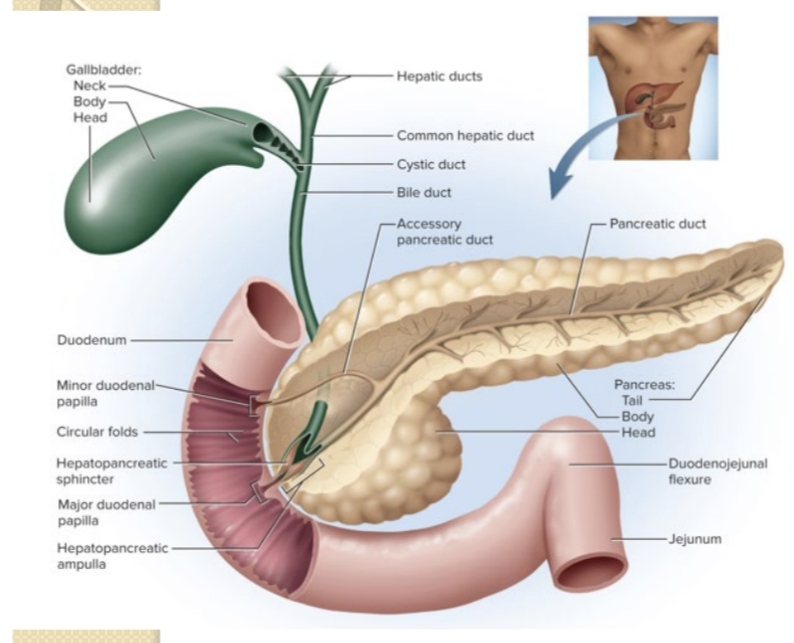
What pancreatic enzymes are secreted by the pancreas?
Pancreatic amylase; proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase); pancreatic lipase; ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease.
What is pancreatic juice composition?
Digestive enzymes plus sodium bicarbonate to neutralize acid and provide optimal pH for enzymes.
What is enterohepatic circulation of bile salts?
Bile salts are secreted into the duodenum, reabsorbed in the ileum, returned to the liver via portal blood, and resecreted.
What comprises a hepatic lobule?
Hepatocytes arranged around a central vein; liver lobes made of hexagonal lobules; hepatic portal triads supply blood.
What are Kupffer cells?
Hepatic macrophages that phagocytose bacteria and debris in blood.
What are the major functions of the liver?
Carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism; bile production and bilirubin excretion; detoxification; synthesis of plasma proteins; phagocytosis; vitamin/mineral storage.
Role of bile in digestion?
Emulsifies fats, aids micelle formation, and transports bilirubin and cholesterol; contains bile salts and phospholipids.
What is bilirubin fate?
Derived from heme; converted to stercobilin in the intestine (feces color) and urobilin in urine.
What is the gallbladder’s function?
Stores and concentrates bile; contracts to release bile into the duodenum when needed.
How is release of bile and pancreatic juice regulated?
CCK and secretin (and ACh) regulate hepatopancreatic sphincter relaxation and bile/pancreatic juice secretion; CCK also stimulates gallbladder contraction.
What are the three main regions of the small intestine and their roles?
Duodenum (chemical digestion by pancreatic enzymes), Jejunum (major digestion/absorption), Ileum (absorption and bile acid reabsorption).
What are intestinal villi and microvilli?
Villi are finger-like projections increasing surface area; microvilli (brush border) are on enterocytes to enhance absorption and host brush-border enzymes.
What are brush-border enzymes and their roles?
Carbohydrate-digesting enzymes (alpha-dextrinase, maltase, sucrase, lactase); protein-digesting enzymes (aminopeptidase, dipeptidase); nucleotide-digesting enzymes (nucleosidases, phosphatases).
What forms of absorption occur in the small intestine?
Diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport for absorbed nutrients and water.
How are monosaccharides absorbed from the intestine into blood?
Glucose and galactose via SGLT (secondary active transport with Na+); fructose via GLUT5; all exit via GLUT2 into blood.
How are lipids absorbed into lymphatics?
Lipids form micelles and diffuse into enterocytes; reassemble into triglycerides, form chylomicrons, and enter lacteals via exocytosis to the lymphatic system.
What are the major functions of the large intestine?
Absorb water and electrolytes; form and store feces; house gut microbiota; defecation.
What triggers mass peristalsis in the large intestine?
Gastrocolic and duodenocolic reflexes, with mass peristalsis occurring 1–3 times per day after meals.
What are some products of the gut microbiome in the large intestine?
Digestion of cellulose, synthesis of vitamins B and K, and production of intestinal gases.
What is the enterogastric reflex?
Duodenum sends inhibitory signals to the stomach to slow gastric secretion and motility during the intestinal phase.