HLSC 3P02 Ch 6 The development of B lymphocytes - final
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1. What is phase 1 of the development of B cells in the bone marrow?
2. What two things can this result in?
3. In what case does development move into the secondary lymphoid tissue?
1. Diverse and clonally expressed B-cell receptors in the bone marrow (repertoire assembly)
2. negative selection (phase 2) and positive selection (phase 3)
3. if it is selected (phase 3)
In secondary lymphoid tissues
1. What is phase 4 of B cell development?
2. What is phase 5 of B cell development?
3. What is phase 6 of B cell development?
1. recirculation of mature B cells between lymph, blood, and secondary lymphoid tissues searching for infection
2. Infection is found, activation and clonal expansion of B cells by pathogen derived antigens in secondary lymphoid tissues
3. Differentiation to antibody-secreting plasma cells and memory B cells in secondary lymphoid tissue. Attack infection!!
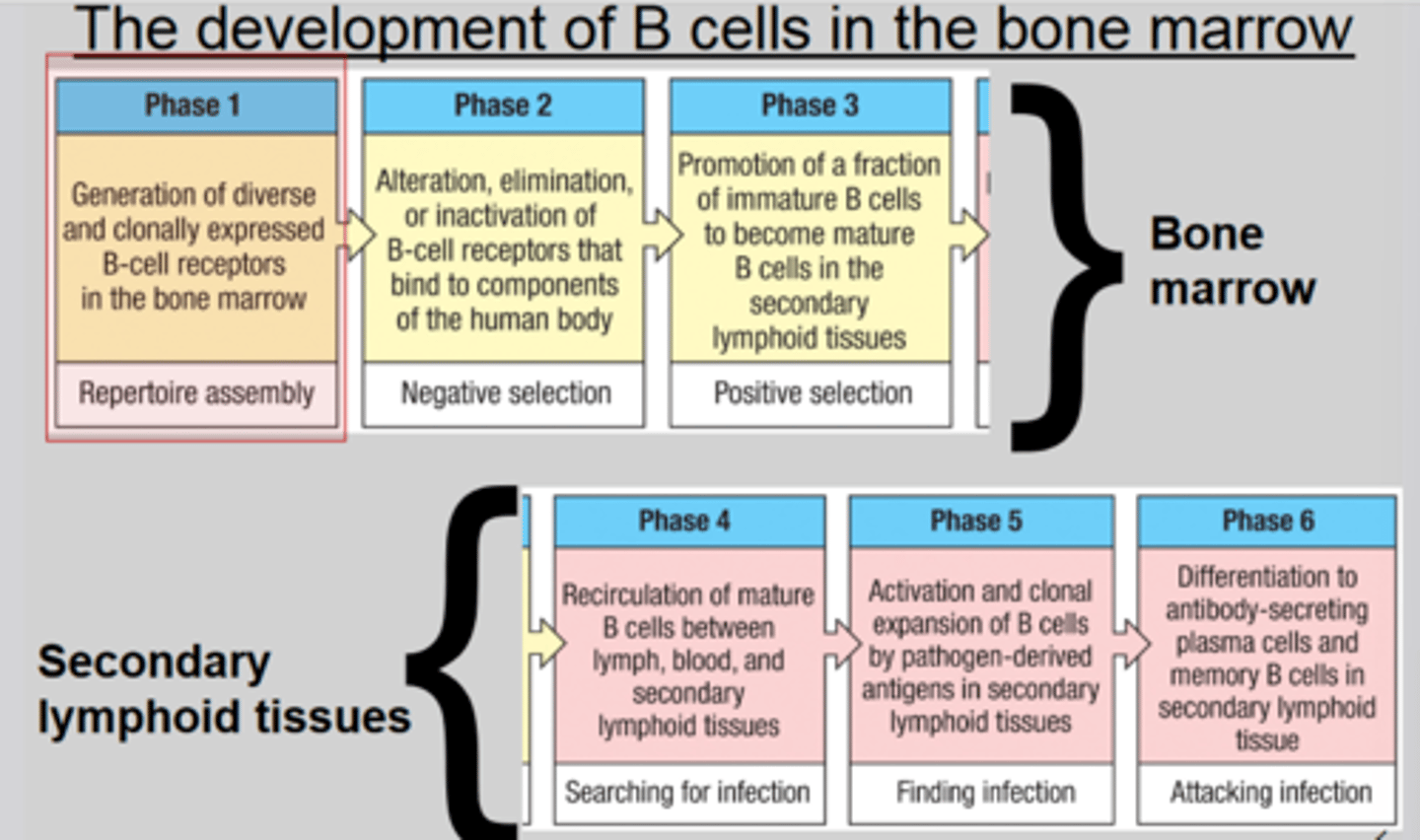
1. Describe the earliest identifiable stages of the B cell lineage?
2. This starts with what CD?, what is the order in which CDs are added?
1. 1) pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell 2) common lymphoid progenitor 3) B cell precursor 4) pro-B cell
2. 1) CD34 2) CD10 3) CD127 4) CD19
In the bone marrow, what occurs in the H-chain genes in early pro-B cell?
D-J rearrangment
In the bone marrow, what occurs in the Ig status in Large pro-B cell?
u (mew) heavy chain is made
In the bone marrow, what occurs in the 1) H-chain genes 2)L-chain genes 3) Ig status in Immature B cell?
1) VDJ rearranged 2) VJ rearranged 3) u (mew) heavy chain, lambda or kappa light chain, IgM on surface
B cells must keep contact with the stromal cell when developing, what molecules sustain this contact?
Besides SCF, what is the other growth factor here?
CAM and SCF
IL-7
What growth factor do stromal cells secrete?
In B cell development, is there any contact with antigens?
IL-7
no
Rearrangement of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus occurs in what stage of B cells?
Pro-B cells
Pro-B cells have how many chances at productive rearrangement? Why is this?
two, V-DJ on one chromosome and the same rearrangement on another
What monitors the quality of immunoglobulin heavy chains?
pre-B cell receptor
What is required for a pro-B cell to become a pre-B cell?
What are the Igs bound beside the B cell receptor?
A signal including the surrogate light chain (preB and lambda 5)
Ig alpha and Ig beta
The pre-B cell receptor causes what at the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus?
allelic exclusion
1. What are the three steps of how Allelic exclusion occurs?
2. What does allelic exclusion give?
3. What does no allelic exclusion give?
1. 1) RAG gene expression stops 2) RAG proteins degraded 3) Other DNA locus is reorganized to prevent rearrangement
2. gives homogeneous B-cell receptors with high-avidity binding
3. Gives heterogeneous B-cell receptors with low-avidity binding
Rearrangement of the light-chain loci occurs in what B cells?
The light chain loci gets rid of what in each rearrangment (3 rearrangments).
What is left at the end?
Third rearrangement called what?
pre-B cells
1V + 1J
2V + 1J + 1C
successive/productive
Does rearrangement occur for immature B cells?
no
In pre-B cell L-chain rearrangement what two genes are rearranged?
kappa and lambda
In pre-B cell L-chain rearrangement what does the IgM cell express if the kappa gene has productive rearrangement?
In pre-B cell L-chain rearrangement what does the IgM cell express if the lambda gene has productive rearrangement?
What is the outcome if rearrangements are non-productive?
u (mew) and kappa
u (mew) and lambda
apoptosis
In pre-B cell L-chain rearrangement what fraction of genes are kappa, what fraction are lambda?
This causes what % increase because there are two alleles?
What is the ultimate success rate for this light chain rearrangement?
2/3 kappa, 1/3 lambda
50%
85%
B cells have to pass two main checkpoints in their development in the bone marrow. These checkpoints occur after what two events?
What happens at these two checkpoints? What can be outcomes?
The first checkpoint is after the heavy-chain gene arrangement. The second checkpoint is after the light-chain gene arrangement.
At the first checkpoint, there is selection for functional heavy chains, those that have no pre-B cell receptor go through apoptosis. At the second checkpoint, there is selection for functional light chains, those that have no pre-B cell receptor go through apoptosis.
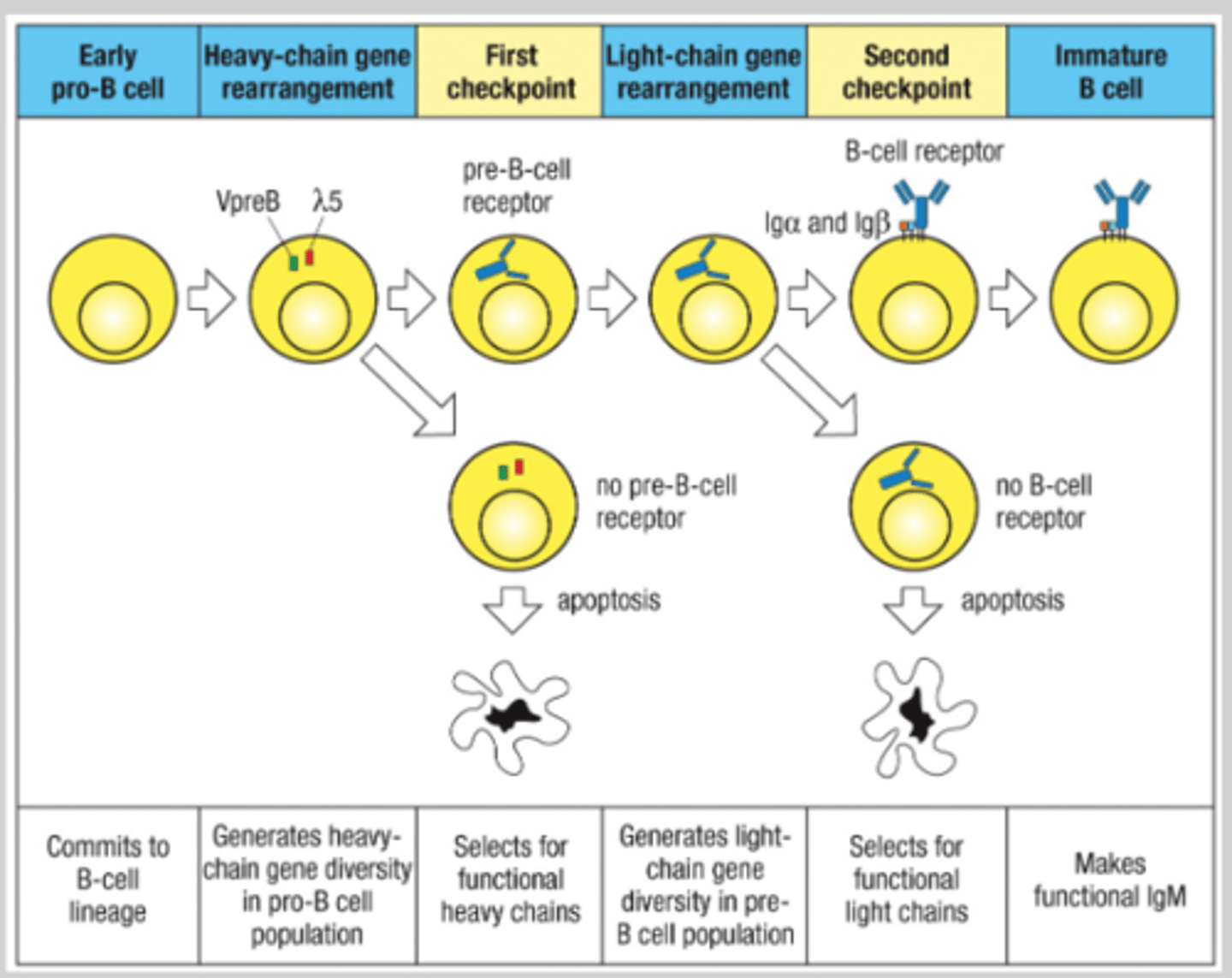
For what B cell development one protein is expressed twice in in development. What stages does it occur in? What protein is expressed and what is it's function?
Late pro-B cell and immature B cell. RAG-1 and RAG-2, lymphoid-specific recombinase
Many B cell tumours carry
chromosomal translocations that join what?
What two chromosomes are in this example?
What is the most associated oncogene with cancers?
that join immunoglobulin genes to genes that regulate cell growth
8 and 14
myc gene
What cells in the bone marrow screen for self-reactive B cells?
What occurs in the case of no reaction and reaction?
stromal cells and blood cells
No reaction: immature B cell moves into the blood and expresses IgD and IgM
Reaction: Immature B cell is retained in the bone marrow
The antigen receptors of autoreactive immature B cells can be modified by what?
What happens if this fails? How many cells die like this each day?
receptor editing, they go through recombonation to produce a non-reactive cell
clonal deletion, 55 billion
Immature B cells specific for monovalent self antigens are made ____________/____________ to antigen
nonresponsive/anergic aka can bind but not send singalling cascade to activate immune system
1. Encounter with antigen leads to the differentiation of activated B cells into what cells?
2. What cell are required for this interaction?
3. Where does this interaction take place?
4. to cross the endothelial barrier, a folicular DC has expression of what?
1. plasma cells and memory B cells
2. CD4 helper T cells
3. in secondary lymph tissue
4. CXCL13
For plasma cells, what % of all protein is antibody?
10-20%
Why is antigen-specific IgG is much higher than IgM in secondary immune responses?
memory B cells!
Do memory B cells require persistent folicular stimulation to survive?
no
Where do memory B cells come from?
germinal center
Do tumours retain characteristics and location of the stage of B cell they originate from?
Yes