HESI A2 Anatomy and Physiology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/199
Last updated 9:08 AM on 12/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
1
New cards
What is histology?
The study of tissues
2
New cards
What is a tissue?
A group of cells that act together to perform a specific function.
3
New cards
What are the fundamental tissues?
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nerve
(Elephants Can Make News)
Connective
Muscle
Nerve
(Elephants Can Make News)
4
New cards
What is the function of epithelial cells?
Cover, line, and protect the body and the internal organs.
5
New cards
What is the function of connective tissue?
Framework of the body. Provides support and structure to organs.
6
New cards
What is neuroglia?
The neurons and connective tissue cells that compose nerve tissue.
7
New cards
What ability does muscle tissue have?
Ability to contract and shorten.
8
New cards
What is muscle tissue classified as?
Voluntary(skeletal muscles) and involuntary(smooth & cardiac)
9
New cards
What is meiosis?
The cell division that takes place in the gonads, i.e. the ovaries and testes.
10
New cards
What two layers compose the skin?
Epidermis and dermis.
11
New cards
What is the epidermis?
The outermost protective layer of dead keratinized epithelial cells.
12
New cards
What is the dermis?
The underlying layer of connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and the associated skin tissues.
13
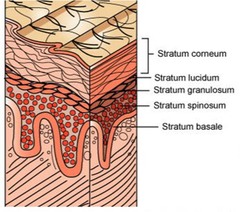
New cards
What are the layers of the epidermis?
Corneum
Lucidum
Granulosum
Germivatum ( basale & spinosum)
Mnemonic: Candy Lions Growl Great.
Lucidum
Granulosum
Germivatum ( basale & spinosum)
Mnemonic: Candy Lions Growl Great.
14
New cards
What does the protein pigment melanin protect against?
Radiation from the Sun
15
New cards
What is the dermis composed of?
Fibrous connective tissue with nerve endings, blood vessels, sensory nerve endings, hair follicles, and glands.
16
New cards
What are the 2 types of sweat glands?
ecrine & apocrine
17
New cards
What do ecrine sweat glands produce?
Sweat. Regulate body temperature.
18
New cards
What do apocrine sweat glands produce?
Secretions contain bits of cytoplasm from cells, attracting bacteria that produces body odor.
19
New cards
What do sebaceous glands secrete?
They secrete sebum through the hair follicles, which lubricates the skin and prevents drying.
20
New cards
What secretion produces oil?
Holocrine secretion.
21
New cards
What are sebaceous glands prone to during adolescence?
Becoming clogged and attracting bacteria.
22
New cards
What protein composes the hair and skin?
Keratin
23
New cards
What makes the body's framework?
Bone, cartilage, ligaments & joints.
24
New cards
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
Support, movement, blood cell formation, protection of internal organs, detoxification, muscle attachment, mineral storage. *A MIME BATHED SEALS SINGING "MY PONY"*
25
New cards
How are bones classified?
By shape.
Long
Short
flat
irregular
sesamoid
*LEMURS SING SALSA FOR INDIANS*
Long
Short
flat
irregular
sesamoid
*LEMURS SING SALSA FOR INDIANS*
26
New cards
What is the name for the cells that compose compact bone?
Osteoblasts
27
New cards
What occurs to osteoblasts when they become fixed in the dense bone matrix?
They stop dividing but continue to maintain body tissues as osteocytes.
28
New cards
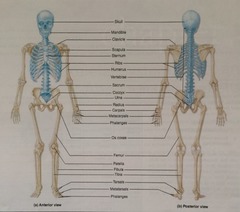
How many bones make up the axial skeleton?
28 bones of the skull. 14-facial, 14-cranium.
29
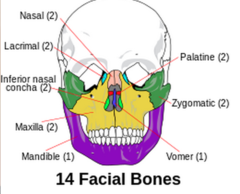
New cards
How many bones make the facial skeleton?
2 nasal bones
2 maxillary bones
2 zygomatic bones
1 mandible
2 palatine bones
1 vomer
2 lacrimal bones
2 inferior nasal bones
2 maxillary bones
2 zygomatic bones
1 mandible
2 palatine bones
1 vomer
2 lacrimal bones
2 inferior nasal bones
30
New cards
What are the bones of the cranium?
single occipital
frontal
ethmoid
sphenoid
paired parietal
temporal
ossicles
frontal
ethmoid
sphenoid
paired parietal
temporal
ossicles
31
New cards
What bone structures are in the ossicles (ears) ?
malleus, incus, stapes
32
New cards
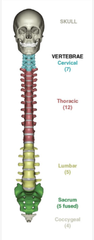
How many bones make the skeletal column?
33 bones
33
New cards
How many cervical vertebrae in the skeletal column?
7
34
New cards
How many thoracic vertebrae in the skeletal column?
12
35
New cards
How many lumbar vertebrae?
5
36
New cards
How many sacral vertebrae?
5
37
New cards
How many coccygeal vertebrae?
1-the tailbone
38
New cards
What makes up the final part of the axial skeleton?
the thorax
the sternum
12 pairs of ribs.
the sternum
12 pairs of ribs.
39
New cards
What makes up the appendicular skeleton?
the bones of the girdle and limbs
40
New cards
What bones make the upper appendicular skeleton?
pectoral & shoulder girdle
clavicle
scapula
upper extremities
clavicle
scapula
upper extremities
41
New cards
What are the bones of the arm?
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Carpals (wrist bones)
Metacarpals (hand bones)
phalanges (finger bones)
Radius
Ulna
Carpals (wrist bones)
Metacarpals (hand bones)
phalanges (finger bones)
42
New cards
What bones make the lower part of the appendicular skeleton?
The pelvic girdle or os coxae
43
New cards
What bones make the os coxae?
fused ilium
ischium
pubis
ischium
pubis
44
New cards
What bones make up the lower extremities?
femur
tibia
fibula
tarsals (ankle bones)
metatarsals (foot bones)
phalanges (toe bones)
tibia
fibula
tarsals (ankle bones)
metatarsals (foot bones)
phalanges (toe bones)
45
New cards
How do muscles make movement?
Contraction in response to nervous stimulation.
46
New cards
What occurs in muscle fibers during contraction?
Myosin & actin filaments slide together.
47
New cards
What structures make up muscle cells?
Myofibrils made up of sarcomeres.
48
New cards
What must be present for a muscle cell to contract?
Calcium and ATP
49
New cards
What does nervous stimulation from motor neurons cause in the muscles?
Release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
50
New cards
What is the function of calcium in muscle contraction?
Attach to inhibitory proteins on the actin filaments of the muscle cell, moving them aside.
This forms cross bridges between actin and myosin filaments.
This forms cross bridges between actin and myosin filaments.
51
New cards
Why are the skeletal muscles of the muscular system considered voluntary?
Because they are under conscious control.
52
New cards
How do skeletal muscles work?
In pairs: the prime mover and the antagonist.
53
New cards
What is the function of the prime mover?
The muscle that executes a given movement.
54
New cards
What is the function of the antagonist?
The muscles that executes the opposite movement of the prime mover.
55
New cards
What are synergists?
Muscles that work together with the prime mover.
56
New cards
How are muscles classified?
According to the movements they elicit
57
New cards
What are the two classifications of muscles?
Flexors and extensors.
58
New cards
What is the function of flexors?
Reduce the angle at the joint.
59
New cards
What is the function of extensors?
Increase the angle at the joint.
60
New cards
What is the function of an abductor muscle?
Draw a limb away from the midline of the body.
61
New cards
What is the function of adductors?
Return the limb back toward the body.
62
New cards
What makes up the nervous system?
The brain, spinal cord & nerves.
63
New cards
What are the functional units of the nervous system?
The neuron.
64
New cards
What are the main parts of the neuron?
Cell body
Axon
Dendrites
Axon
Dendrites
65
New cards
What is the function of the dendrites?
Transmit impulses toward the cell body
66
New cards
What is the function of the axon?
Transmit impulses away from the body
67
New cards
What two systems make up the nervous system?
CNS-Central nervous system
PNS-Peripheral nervous system
PNS-Peripheral nervous system
68
New cards
What makes up the PNS?
All the nerves that transmit information to and from the CNS.
69
New cards
What is the function of sensory (afferent) neurons?
Transmit information to and from the CNS.
70
New cards
What is the function of Motor (efferent) neurons?
Transmit nerve impulses away from the CNS toward the effector organs such as muscles, glands, and digestive organs.
71
New cards
What are the 3 major parts of the brain?
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Medulla Oblongata
Cerebellum
Medulla Oblongata
72
New cards
What is the function of the cerebrum?
Movement & sensory input.
73
New cards
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Muscular coordination.
74
New cards
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
Controls vital functions such as respiration and heart rate.
75
New cards
How long is the spinal cord?
18 inches long and extends from the base of the skull to the first or second lumbar vertebrae.
76
New cards
How many pairs of nerves exit the spinal cord?
31 pairs of nerves exit the spinal cord.
77
New cards
What are simple (spinal) reflexes?
Those in which nerve impulses travel through the spinal cord only and do not reach the brain.
78
New cards
What is the function of the endocrine system?
Assist the nervous system in homeostasis and plays important roles in sexual maturation.
79
New cards
Where do the endocrine and nervous system meet?
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland
80
New cards
What does the hypothalamus govern?
The pituitary gland and is controlled by the feedback of hormones in the blood.
81
New cards
Which has more long-lasting effects on the body, the endocrine or the nervous system?
The endocrine system
82
New cards
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers controlling growth, differentiation & metabolism of cells.
83
New cards
What are the two major groups of hormones?
Steroid and nonsteroid
84
New cards
What is the effect of steroid hormones?
Enter the cell and have a direct effect on the DNA of the nucleus.
85
New cards
What is the function of some nonsteroid hormones?
Serve as protein hormones.
86
New cards
What is the function of protein hormones?
Stay at the cell surface and act through second messenger.
87
New cards
What is the usual second messenger used by protein hormones?
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
88
New cards
How do hormones affect cell activity?
Alters the rate of protein synthesis.
89
New cards
Which gland is considered the "master gland"?
The pituitary gland
90
New cards
Where is the pituitary gland located?
Attached to the hypothalamus by a stalk called the infundibulum.
91
New cards
What are the two major portions of the pituitary gland?
Anterior lobe-adenohypophysis
Posterior lobe-neurohypophysis
Posterior lobe-neurohypophysis
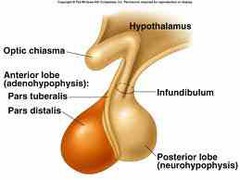
92
New cards
Why are the hormones of the adenohypophysis called *tropic hormones*?
Because they act mainly on other endocrine glands.
93
New cards
What are the tropic hormones?
STH
GH
ACTH
TSH
FSH
LH
GH
ACTH
TSH
FSH
LH
94
New cards
What is the STH or GH hormone?
Growth Hormone
95
New cards
What is the ACTH hormone?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
96
New cards
What is the TSH hormone?
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
97
New cards
What is the FSH hormone?
Follicle-stimulating hormone
98
New cards
What is the LH hormone?
Luteinizing hormone
99
New cards
What hormones are released from the posterior lobe of the pituitary?
Oxytocin (labor hormone)
ADH-Antidiuretic hormone.
ADH-Antidiuretic hormone.
100
New cards
What are some important endocrine glands?
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Adrenals
Pancreas
Gonads (ovaries & testes)
Parathyroid
Adrenals
Pancreas
Gonads (ovaries & testes)