Autopsy: Peds
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
determine:
gestational age
time of death
underlying abnormalities
COD
evaluate:
pregnancy
obstetric care
assess diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, treatment courses
generate data
research
medical teaching
legal evidence gathering
provide genetic info for future pregnancies:
cytogenetic analysis
SNP microarray/LOH
discuss the purposes of performing a perinatal or infant autopsy (8)
body weight
body length (crown to heel and crown to rump)
head circumference (occipital-frontal)
chest circumference (nipple line)
nipple separation
arm span (3rd digits)
xiphoid → pubis
xiphoid → umbilicus
abdominal circumference (umbilicus)
umbilical cord stump (LxD, # of vessels)
penis length
hand length, bilateral
foot length, bilateral (most reliable)
list the body measurements taken during the external examination of perinatal autopsy (13)?
interpupillary distance
inner canthal
outer canthal
interalar distance (width of nose)
philtrum (nose to upper lip)
upper lip thickness
lower lip thickness
mouth commissure
palpebral fissure, bilateral
pupils, bilateral
external ear helix (2), bilateral
fontanelles in 2D (easier after skin reflection if possible)
list the face/head measurements taken during the external examination of perinatal autopsy (12)
May or may not have access
Causes of pregnancy loss in the second trimester are different from early pregnancy losses
Obstetric care/treatment and labor/delivery
How could the mother’s health affect the child?
Diabetes
Environmental factors - smoking, drinking
Family history and genetics that could impact the child
defend the significance of reviewing the mother’s medical chart prior to performing an infant autopsy.
Requires consent if:
Gestational age is greater than 20 weeks
Body weight is greater than 500 grams
Less than 20 weeks usually surg path
Talking to family for consent and disposition of body before performing the autopsy
Consent ONLY following death
Mother and father have equal rights - need agreement
Ability to accept/decline, choose limitations:
“Minimize disfigurement”
External only
Certain organs only
Research only
No extremities or head
May or may not want to know the sex
No photos
All tissue returned with body
examine the unique importance of verifying consent with perinatal specimens
Assessment of anomalies/malformations vs. medical disease
Letulle method almost always - important to preserve anatomic relationships
defend the significance of an extensive external examination.
maceration
degenerative changes in fetal tissue when retained in utero
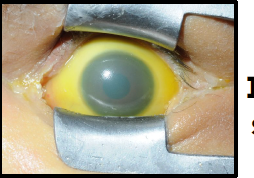
icteric sclera
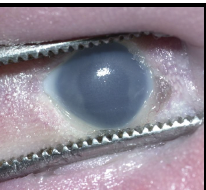
iris coloboma
missing iris portion of eye
moebius sequence
paralysis of facial nerves, unable to form facial expressions
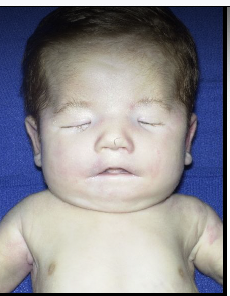
cloverleaf deformity
enlarged anterior fontanelle, other cranial sutures fused, hydrocephalus, macrocephaly
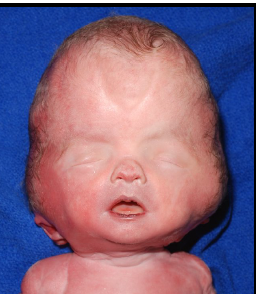
nuchal cord
umbilical cord around neck
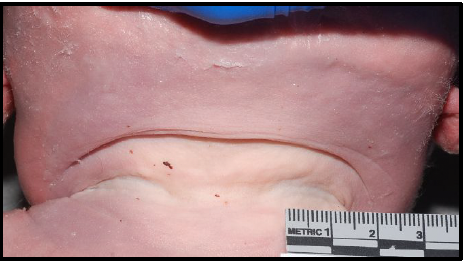
cystic hygroma
lymphatic obstruction leading to fluid accumulation
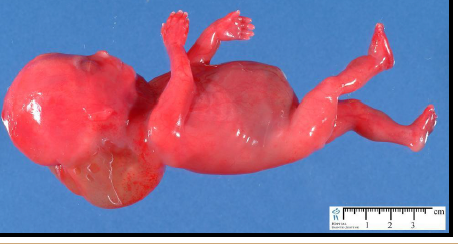
cleft palate
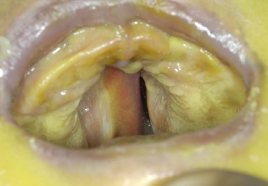
high arch
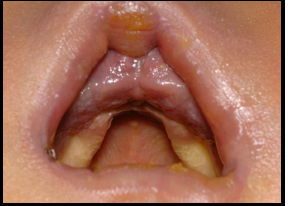
macrognathia
abnormally large jaws
clinodactyly
abnormal curvature of 5th digit associated with down syndrome
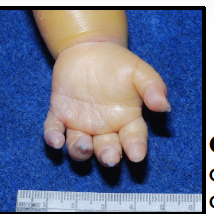
amniotic band syndrome
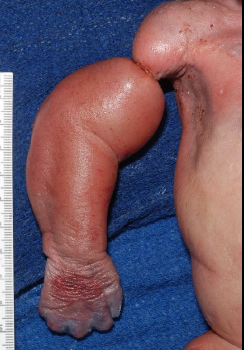
osteogenesis imperfecta
abnormally formed bones due to insufficiency or absent type I collagen production; most severe form is lethal
short, bent limbs
multiple fractures
short, beaded ribs
reduction or absence of cranial vault ossification
blue sclera
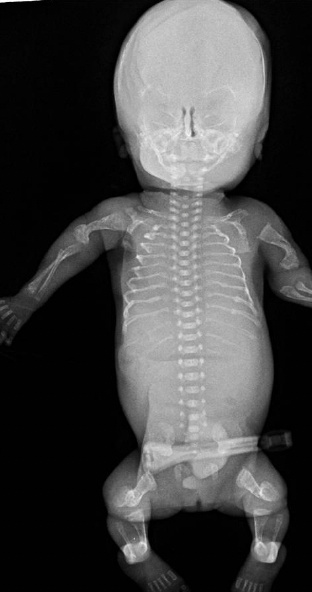
thanatophoric dysplasia (TD)
most severe subtype of osteogenesis imperfecta
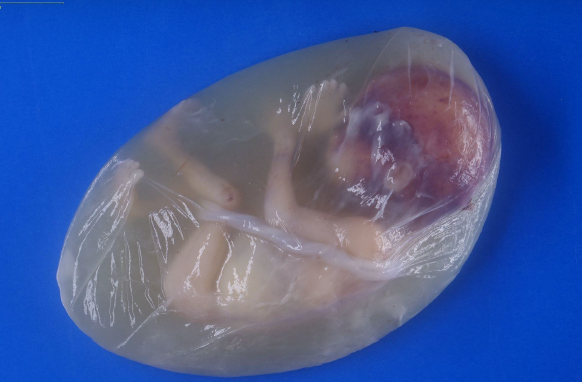
birth with intact amniotic membrane sac
what is an en caul birth?
en caul birth
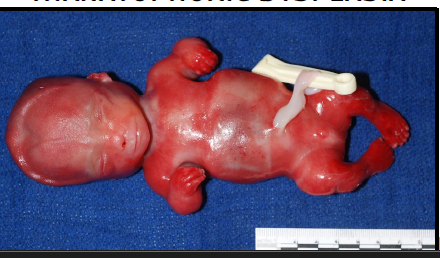
body stalk anomaly
abnormal development of body folds leading to absence/shortening of umbilical cord
organs lie outside the abdominal cavity directly attached to the placenta
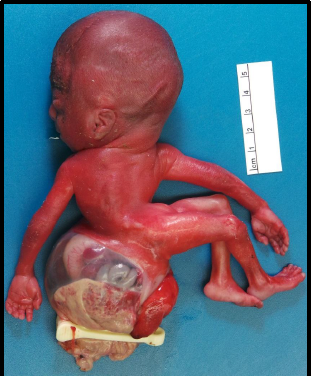
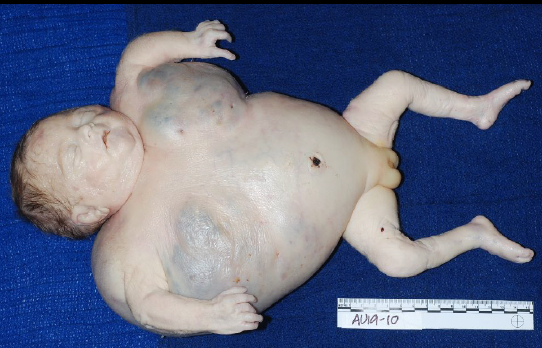
abnormal accumulation of fluid in two or more fetal compartments: ascites, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, skin edema; leads to heart failure
what is hydrops fetalis
hydrops fetalis
results from fetal anemia in the setting of chronic intrauterine anemia (immune or non-immune) or congenital heart anomalies
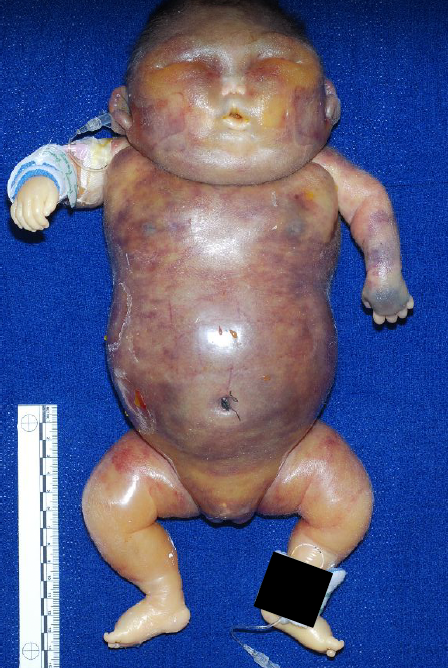
sirenomelia
“mermaid syndrome”
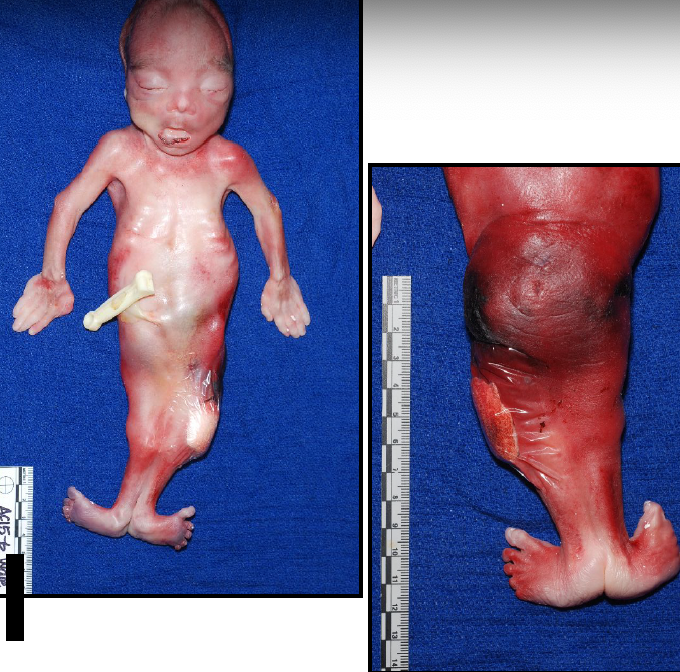
improperly formed lower vasculature leading to hypoperfusion and underdevelopment of lower limbs (caudal regression)
usually death due to GU complications
what is sirenomelia?
recipient → heart failure
donor → anemia and renal failure
COD of death in twin-twin transfusion syndrome
blood supply of twins becomes connected, allowing the movement of blood from one twin to the other across the placenta (monochorionic), causing circulation imbalance
define twin twin transfusion syndrome
acardius-acephalus
incomplete fetus with legs and possible caudal organs
cranially amorphous mass of tissue with no heart or brain
complete acardiac twin
fetus with recognizable body regions and some poorly developed, non-functioning organs
blood pumped from one twin to another by retrograde flow
omphalo-ischiopagus tripus
conjoined twins at the abdominal and lower extremity
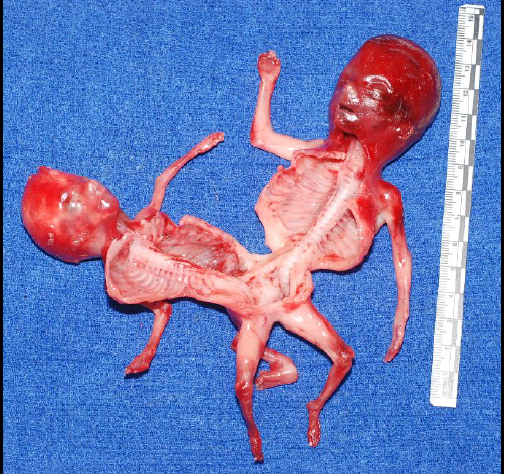
thoracopagus
conjoined twins at the chest
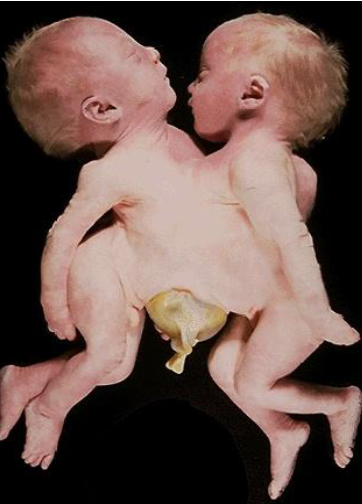
craniothoracopagus
conjoined twins at the head and chest
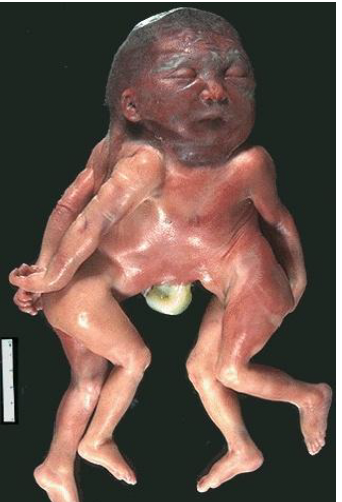
trisomy 13 - patau syndrome
microcephaly
mental retardation
microphthalmia
polydactyly
cardiac defects
umbilical hernia
renal defects
cleft lip/palate
rocker bottom feet
**majority die in utero
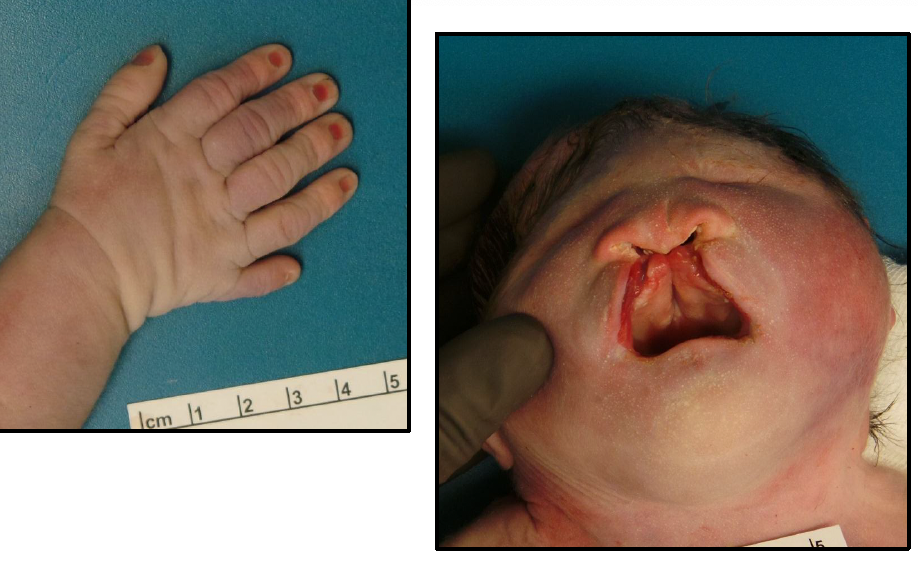
trisomy 18 - edwards syndrome
prominent occiput
mental retardation
micrognathia
low set ears
short neck
overlapping fingers
congenital heart defects
renal malformations
limited hip abduction
rocker bottom feet
more life threatening, majority die in uterus, AMA, female
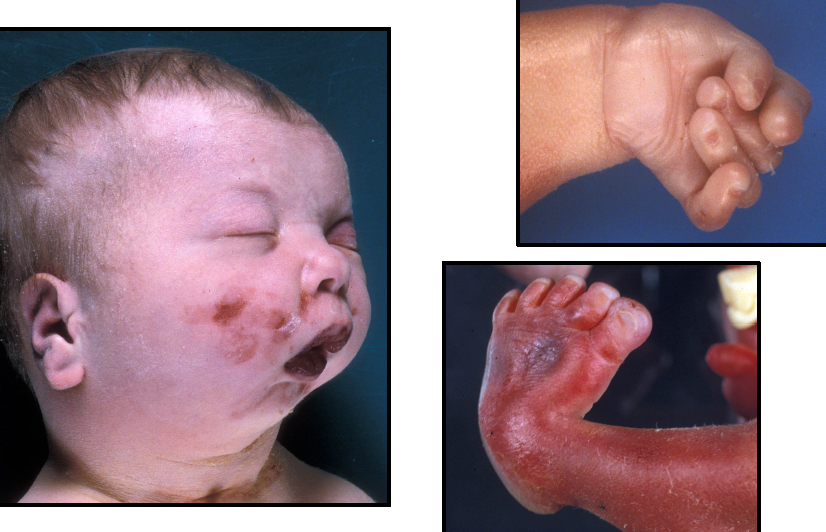
trisomy 21 - down syndrome
● epicanthic folds, upslanting palpebral fissures, flat facies
● macroglossia
● mental retardation
● simian crease
● abundant neck skin
● congenital heart defects
● intestinal stenosis
● umbilical hernia
● hypotonia
● gap between first and second toes (saddle)
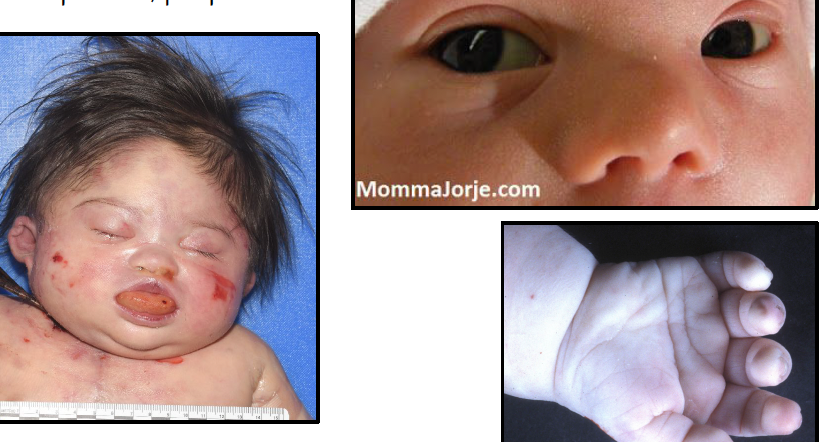
oligohydramnios
bilateral renal agenesis
pulmonary hypoplasia - usually lethal
low set ears
what are key findings in potter sequence
dandy-walker syndrome
cerebellum does not develop normally
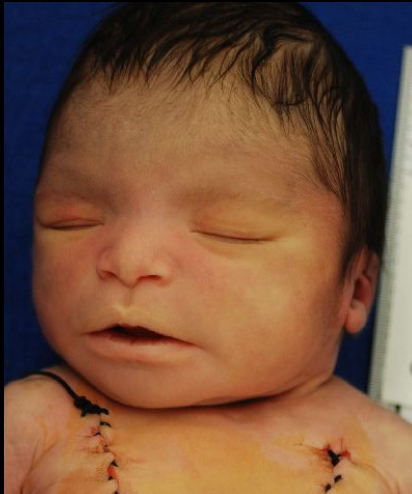
triploidy
additional set of chromosomes per cell
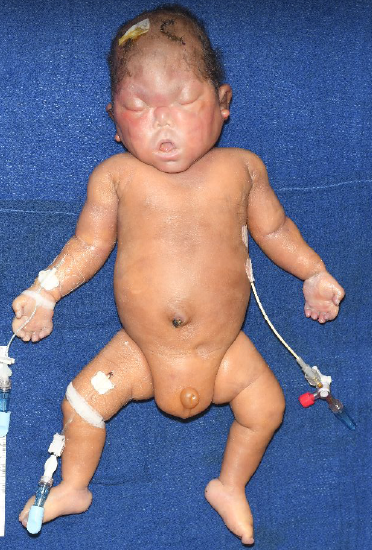
neu-laxova syndrome
severe growth delays; distinctive facial and head abnormalities
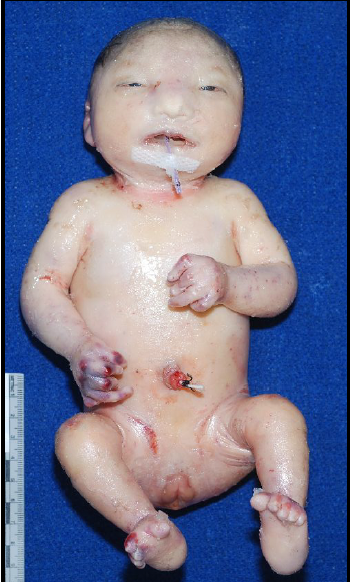
omphalocele
defect in the anterior abdominal wall at the insertion of the umbilical cord
incomplete closure of abdominal musculature
opening covered by amnion/peritoneum into which viscera protrude
gastroschisis
congenital paraumbilical defect of anterior abdominal wall
visceral organs are uncovered
all layers of the abdominal wall are involved
2% of population
2 feet proximal to ileocecal valve
2 inch length
2 types of common ectopic tissue (gastric/pancreatic)
2 years is most common age for presentation
2:1 male to female ratio
meckel’s rule of 2’s
diaphragmatic herniation
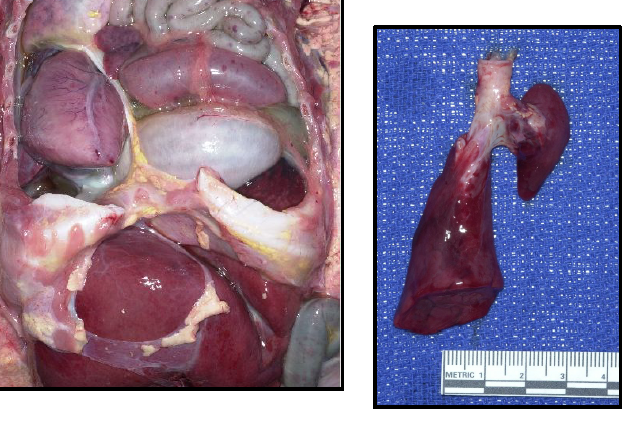
necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) totalis
inflammation/infection of bowel causing tissue death, perforation, sepsis; commonly affects premature infants.
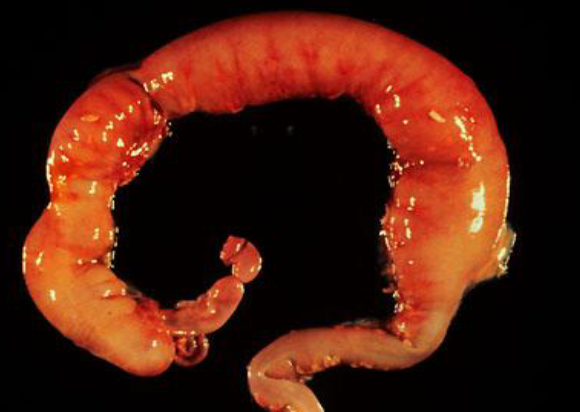
hirschsprung’s disease
migration of ganglion cells is incomplete; colon movement is improperly regulated causing stool obstructions
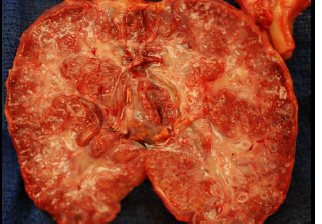
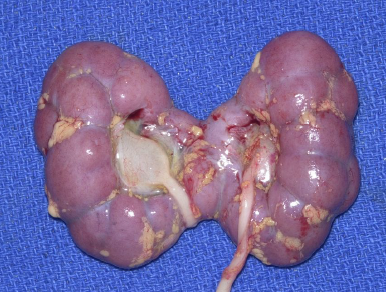
ARPKD
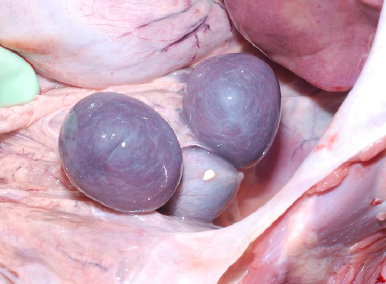
polysplenia
horseshoe kidney
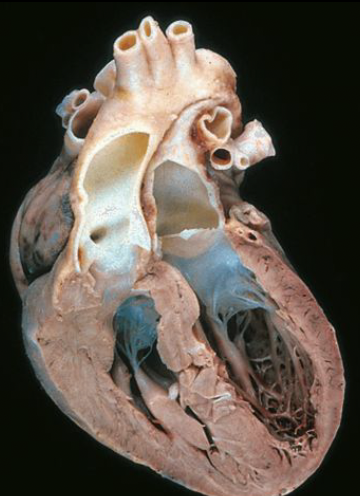
VSD
pulmonary stenosis
right ventricular hypertrophy
overriding aorta
tetralogy of fallot (TOF)
transposition of great vessels
lympho/vascular malformation
mirror development of SVC on the left side
drains the head/neck on left and allows it to return to right atrium via SVC
what is an innominate vein
situs inversus totalis
rare AR condition causing abdominal and thoracic organs to be mirrored in relation to normal
asymptomatic alone and often with other anomalies
malrotation
congenital anomaly of intestinal position
spina bifida
incomplete closure of the embryonic neural tube
iniencephaly
spina bifida of cervical vertebrae with defect in occipital protuberance; retroflexion
encephalocele
neural tube defect with membrane covered protrusions of brain through skull opening
hydrancephaly
cerebral hemispheres are absent; brain is filled with CSF within sacs
anencephaly
neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral end of the embryonic neural tube fails to close; incomplete development of brain, scalp, skull; most stillborn
cyclopia
single eye; most severe of facial defects and missing nose or proboscis
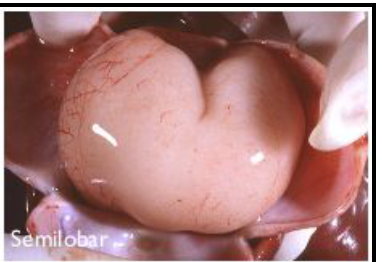
holoprosencephaly
cephalic disorder in which the embryo forebrain fails to develop into two hemispheres
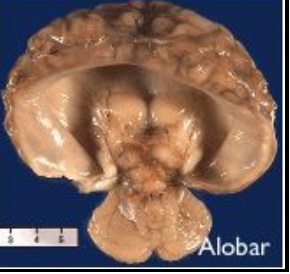
lissencephaly
rare brain disorder causing the brain’s surface to appear smooth due to lack of gyri and sulci; defective neuronal migration during 12-24 weeks gestation
premature (vasculature strength greatly increases in the last 10 weeks)
what makes babies more susceptible to intraventricular hemorrhage?
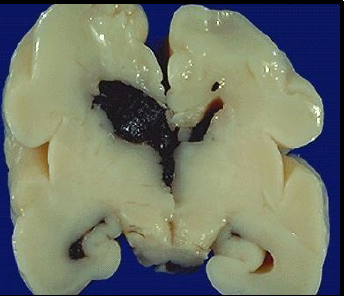
meningitis