AFOQT Aviation Section (revised)
0.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/617
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything. And I mean everything from my AFOQT aviation info book
Last updated 3:20 PM on 8/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
618 Terms
1
New cards
Absolute accuracy
The ability to determine present position in space independently, and is most often used by pilots
2
New cards
Absolute Altitude
The actual distance between an aircraft and the terrain over which it is flying
3
New cards
Absolute Pressure
Pressure measured from a reference of zero pressure, or a vacuum
4
New cards
Acceleration Error
A magnetic compass error apparent when the aircraft accelerates while flying on an easterly or westerly heading, causing the compass to rotate towards north
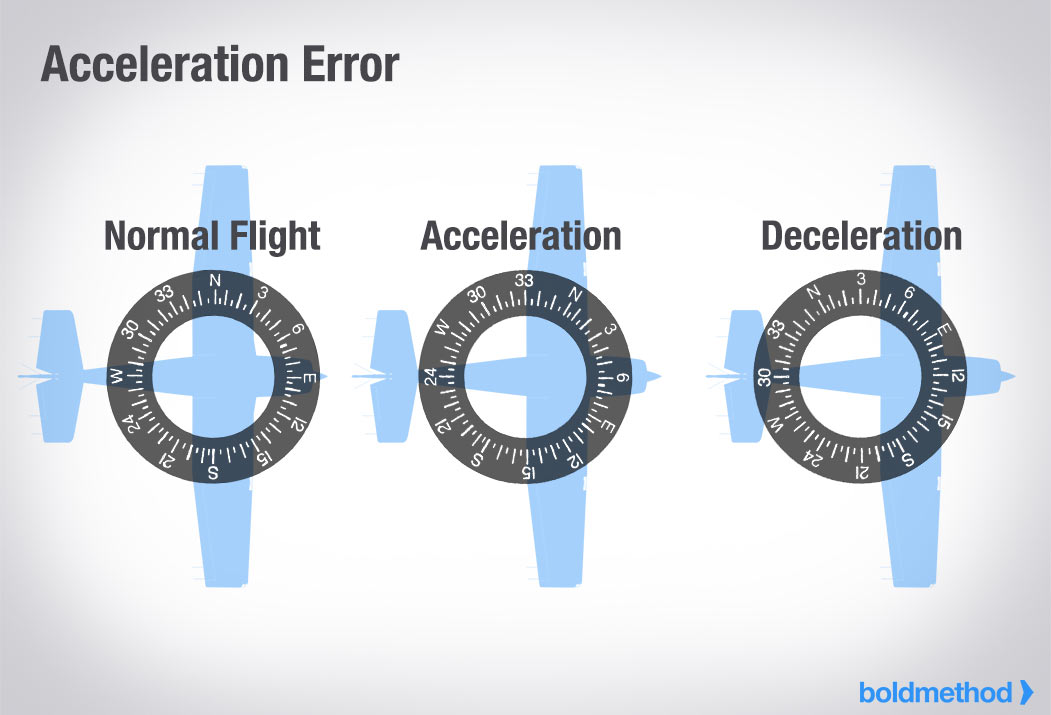
5
New cards
Accelerate-Go Distance
The distance required to accelerate to V1 with all engines at takeoff power, experience an engine failure at V1, and continue the takeoff on the remaining engine(s). The runway required includes the distance required to climb to 35 feet by which time V2 speed must be attained
6
New cards
Accelerate-Stop Distance
The distance required to accelerate to V1 with all engines at takeoff power, experience an engine failure at V1, and abort the takeoff and bring the airplane to a stop, using braking action only (Thrust reversing not considered)
7
New cards
Accelerometer
A part of an Inertial Navigation System (INS) that accurately measures the force of acceleration in one direction
8
New cards
ADC (Air Data Computer)
An aircraft computer that receives and processes pitot pressure, static pressure, and temperature to calculate very precise altitude, indicated airspeed, true airspeed, and air temperature
9
New cards
Automatic Direction Finder (ADF)
Electronic navigation equipment that operates in the low-and medium-frequency bands. Used i conjunction with the ground based non directional beacon (NDB), the instrument displays the number of degrees clockwise from the nose of the aircraft to the station being received
10
New cards
Attitude Director Indicator (ADI)
An aircraft attitude indicator that incorporates flight command bars to provide pitch and roll commands
11
New cards
Adjustable-Pitch Propeller
A propeller with blades whose pitch can be adjusted on the ground with the engine not running, but which cannot be adjusted in flight. Also referred to as ground adjustable propeller. Sometimes also used to refer to constant-speed propellers that are adjustable in flight
12
New cards
Adjustable Stabilizer
A stabilizer that can be adjusted in flight to trim the airplane, thereby allowing the airplane to fly hands-off at any given airspeed
13
New cards
ADM (Aeronautical Decision Making)
A systematic approach to the mental process used by pilots to consistently determine the best course of action in response to a given set of circumstances
14
New cards
Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B)
A function of an aircraft or vehicle that periodically broadcasts its state vector (i.e., horizontal and vertical position, horizontal and vertical velocity) and other information
15
New cards
Advection Fog
Fog resulting from the movement of warm, humid air over a cold surface
16
New cards
Adverse Yaw
A condition of flight in which the nose of an airplane tends to yaw towards the outside of the turn. This is caused by higher induced drag on the outside wing. Which is also producing more life. Induced drag is a byproduct of the lift associated with the outside wing
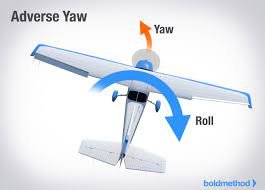
17
New cards
Aerodynamics
The Science of the action of air on an object, and with the motion of air on other gases. Deals with the production of lift by the aircraft, the relative wind, and the atmosphere
18
New cards
Aeronautical Chart
A map used in air navigation containing all or part of the following: topographical features, hazards or obstructions, navigational aids, navigation routes, designated airspace, and airports
19
New cards
Agonic Line
An irregular imaginary line across the surface of the earth along which the magnetic and geographic poles are in alignment, and along which there is no magnetic variation
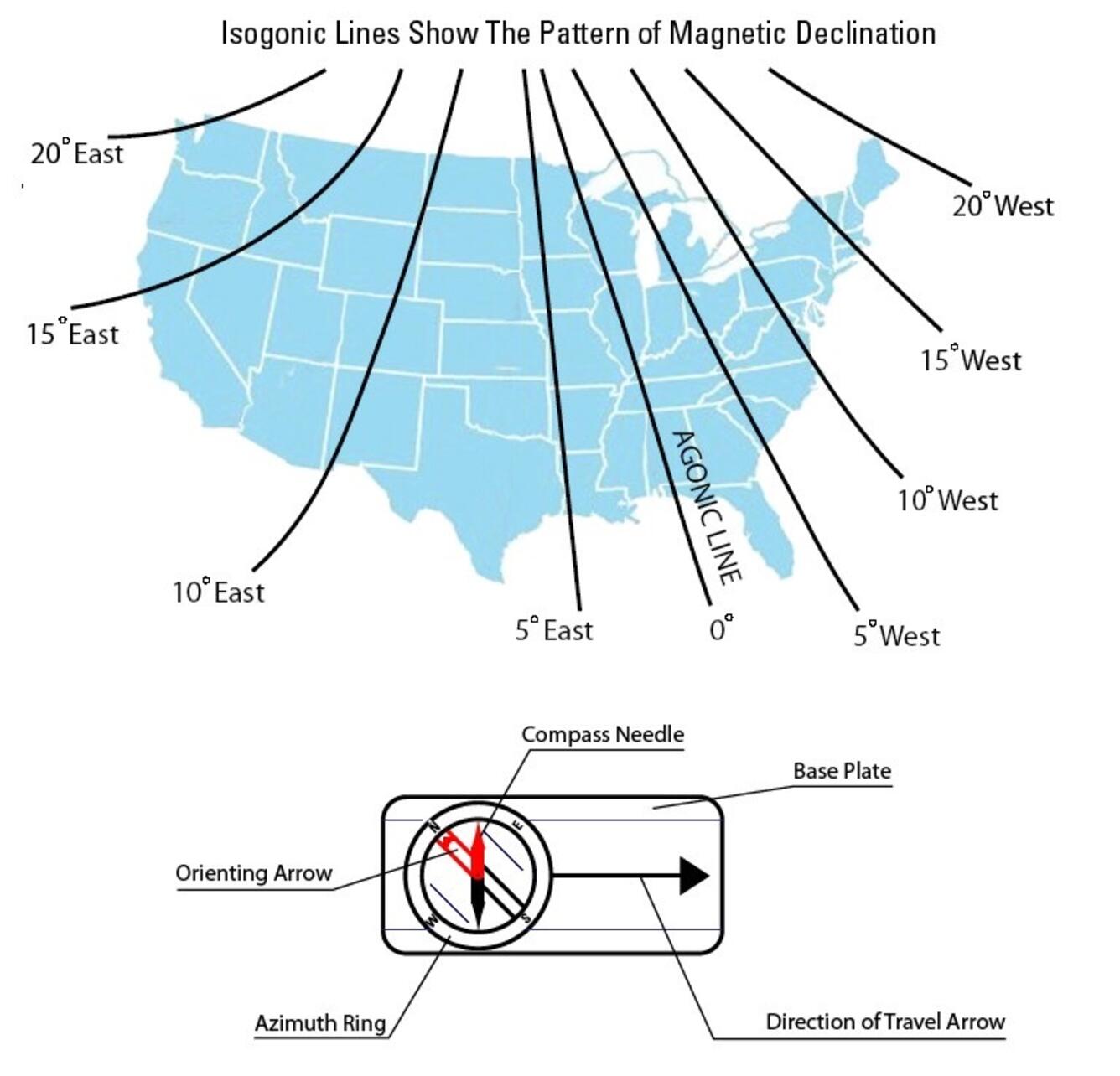
20
New cards
Ailerons
Primary flight control surfaces mounted on the trailing edge of an airplane wing, near the tip. Ailerons control roll about the longitudinal axis
21
New cards
Aircraft Altitude
The actual height above sea level at which the aircraft is flying
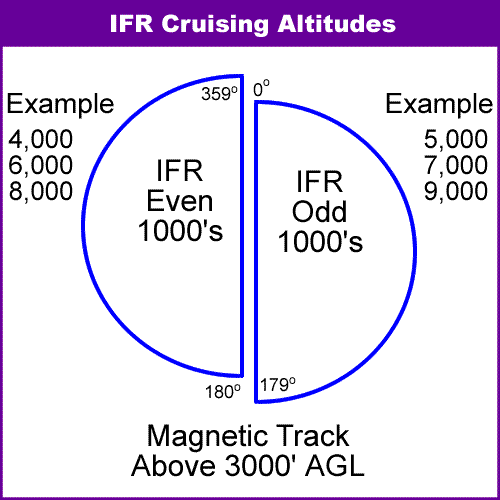
22
New cards
Aircraft Approach Category
A performance grouping of aircraft based on a speed of 1.3 times the stall speed in landing configuration at maximum gross landing weight
23
New cards
Airfoil
Any surface, such as wing, propeller, rudder, or even a trim tab, which provide aerodynamic force when it interacts with a moving stream of air
24
New cards
AIRMET
Inflight weather advisory issued as an amendment to the area forecast, concerning weather phenomena of operational interest to all aircraft and that is potentially hazardous to aircraft with limited capability due to lack of equipment, instrumentation, or pilot qualifications
25
New cards
Airport Markings
See Airport markings quizlet
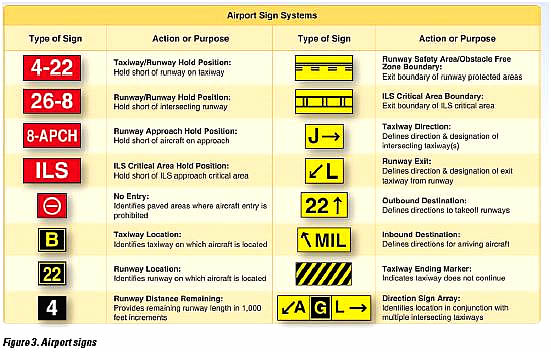
26
New cards
Airport signs
see airport signs quizlet
27
New cards
Airport Surface Detection Equipment (ASDE)
radar equipment specifically designed to detect all principal features and traffic on the surface of an airport, presenting the entire image on the control tower console; used to augment visual observation by tower personnel of aircraft and/or vehicular movements on runways and taxiways
28
New cards
Airport Surveillance Radar (ASR)
Type of radar system used at airports to detect and track aircraft within its coverage area. It provides information on the aircraft's position, altitude, and velocity to air traffic controllers for safe and efficient air traffic management. ASR helps in monitoring and guiding aircraft during takeoff, landing, and taxiing operations.
29
New cards
Airport Surveillance Radar Approach
An instrument approach in which ATC issues instructions for pilot compliance based on aircraft position in relation to the final approach course ad the distance from the end of the runway as displayed on the controller’s radar scope
30
New cards
Air Route Surveillance Radar (ARSR)
Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) radar is used primarily to detect and display an aircraft’s position while en route between terminal areas
31
New cards
Air Route Traffic Control Center
Provides ATC service to aircraft operating on IFR flight plans within controlled airspace and principally during the en route phase of flight
32
New cards
Airspeed
Rate of the aircraft’s progress through the air
33
New cards
Airspeed indicator
A differential pressure gauge that measures the dynamic pressure of the air through which the aircraft is flying. DIsplays the craft’s airspeed, typically in knots to the pilot
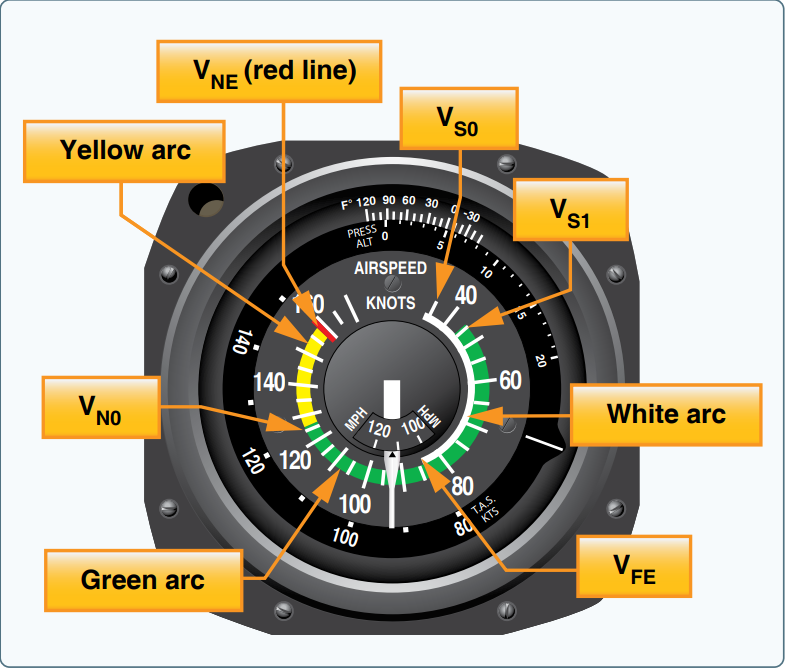
34
New cards
Air Traffic Control Radar Beacon System (ATCRBS)
secondary surveillance unit, utilizes the transponder in the aircraft. the ground equipment is an interrogating unit, in which the beacon antenna is mounted so it rotates with the surveillance antenna. This displays a coded sequence to ground equipment providing aircraft identification and other special data
35
New cards
Airway
based on centerline that extends from one navigation aid or intersection to another navigation aid; used to establish a known route for en route procedures between terminal areas
36
New cards
Alert Area
An area in which there is a high volume of pilot training or an unusual type of aeronautical activity
37
New cards
Approach Lighting System (ALS)
Provides lights that will penetrate the atmosphere fat enough from touchdown to give directional, distance, and glidepath information for safe transition from instrument to visual flight.
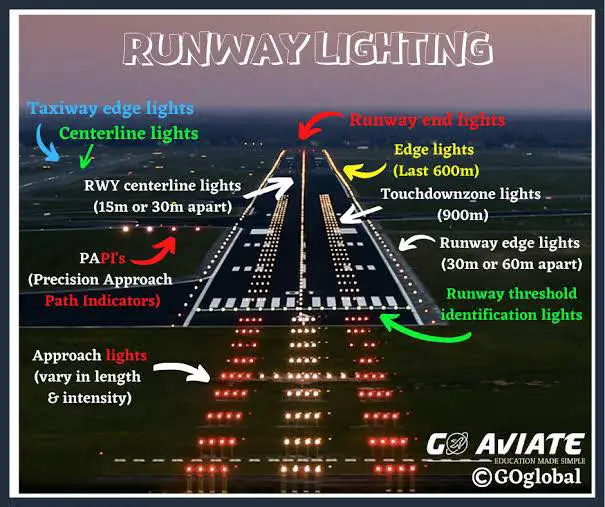
38
New cards
Alternate Airport
An airport designated in an IFR flight plan, providing a suitable destination if a landing at the intende airport becomes inadvisable
39
New cards
Alternate Static Source Valve
A valve in the instrument static air system that supplies reference air pressure to the altimeter, airspeed indicator, and vertical speed indicator if the normal static pickup should become clogged or iced over
40
New cards
Altimeter
A flight instrument that indicates altitude by sensing pressure changes
41
New cards
Altimeter Setting
Station pressure (The barometric pressure at the location the reading is taken) which has been corrected for the height of the station above sea level
42
New cards
Altitude engine
A reciprocating aircraft engine have a rated takeoff power that is producible from sea level to an established higher altitude
43
New cards
Aneroid
The sensitive component in an altimeter or barometer that measures the absolute pressure of the air. It is a sealed, flat capsule made of thin disks of corrugated metal soldered together and evacuated by pumping all of the air out of it
44
New cards
Aneroid Barometer
An instrument that measures the absolute pressure of the atmosphere by balancing the weight of the air above it against the spring action of the aneroid
45
New cards
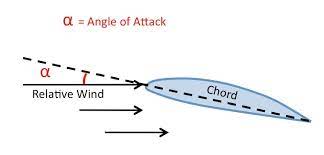
Angle of Attack
The angle between the chord line of an aircraft's wing and the oncoming airflow. It determines lift and stall characteristics.
46
New cards
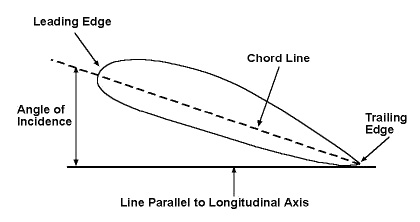
Angle of Incidence
The acute angle formed between the chord line of an airfoil and the longitudinal axis of the aircraft on which it is mounted
47
New cards
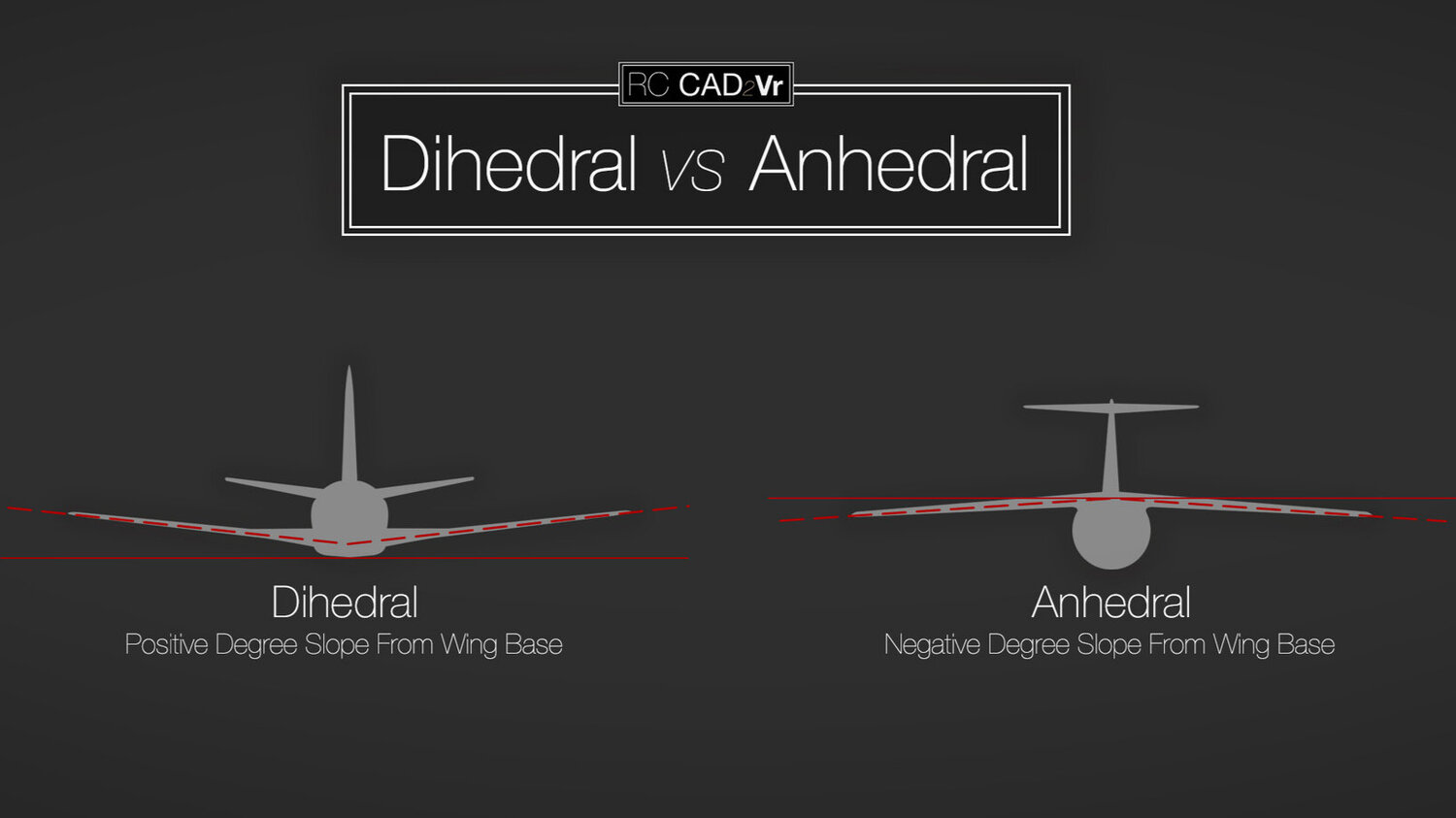
Anhedral
A downward slant from root to tip of an aircraft’s wing or horizontal tail surface
48
New cards
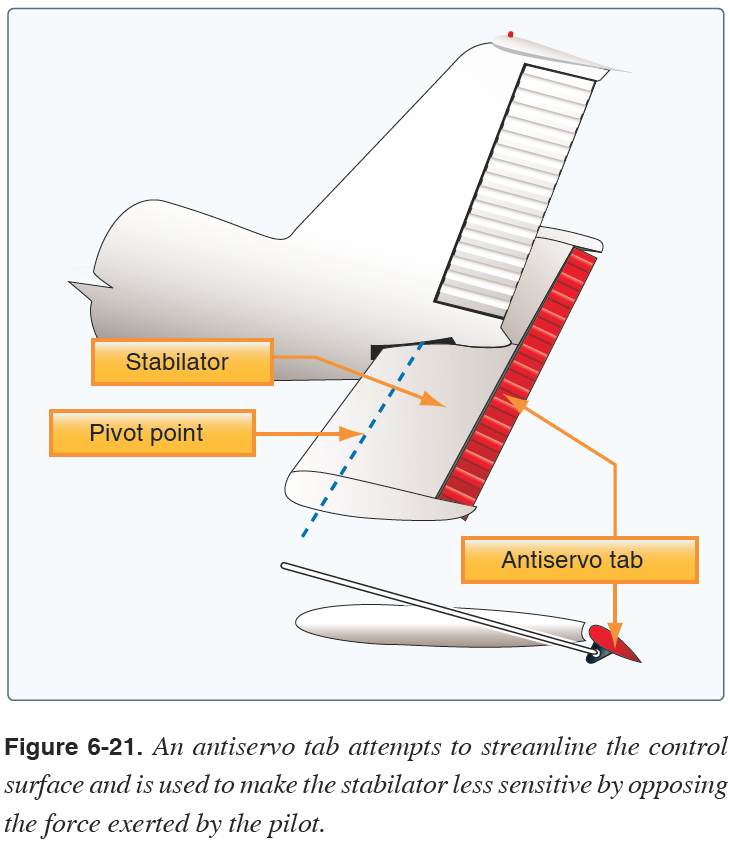
Antiservo Tab
An adjustable tab attached to the trailing edge of a stabilator that moves ini the same direction as the primary control. It is used to make the stabilator less sensitive
49
New cards
Area Chart
Part of the low altitude en-route chart series, this chart furnishes terminal data at a larger scale for congested areas
50
New cards
Area Forecast (FA)
A report that gives a picture of clouds, general weather conditions, and visual meteorological conditions (VMC) expected over a large area encompassing several states
51
New cards
Area Navigation (RNAV)
Allows a pilot to fly a selected course to a course to a predetermined point without the need to overfly ground-based navigation facilities, by using waypoints
52
New cards
Automated Surface Observing System (ASOS)
Weather reporting system which provides surface observations every minute via digitized voice broadcasts and printed reports
53
New cards
Aspect ratio
span of a wing divided by its average chord
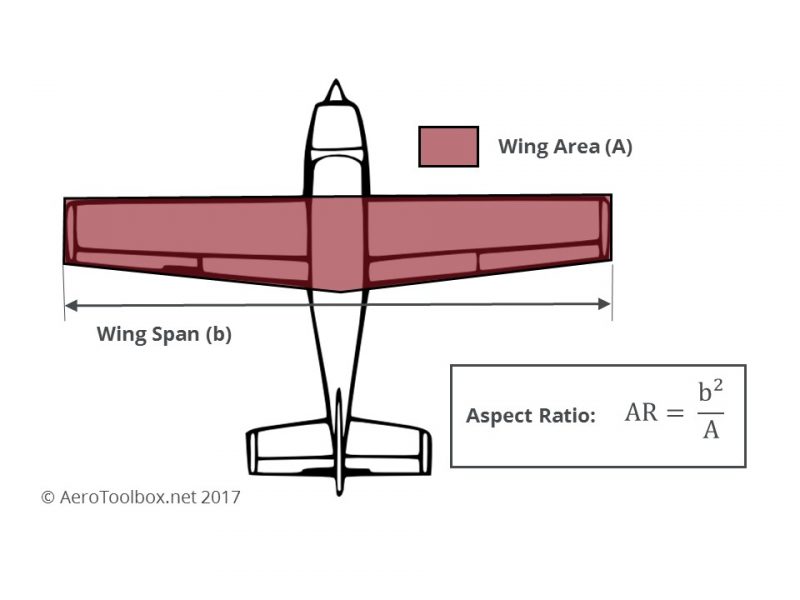
54
New cards
Asymmetric Thrust
Known as P-Factor. A tendency for the aircraft to yaw to the left due to the descending propeller blade on the right producing more thrust than the ascending propeller blade on the left. This occurs when the aircraft’s longitudinal axis is in a climbing attitude in relation to the relative wind. The P-Factor would be to the right if the propeller is spinning counter clockwise.
55
New cards
ATC
Air Traffic Control
56
New cards
Automatic terminal information service (ATIS)
The continuous broadcast of recorded non-control information in selected terminal areas. Its purpose is to improve controller effectiveness and relieve frequency congestion by automating repetitive transmission of essential but routine information
57
New cards
Attitude and Heading Reference System (AHRS)
A system composed of three-axis sensors that provide heading, attitude, and yaw information for aircraft. AHRS are designed to replace traditional mechanical gyroscopic flight instruments and provide superior reliability and accuracy
58
New cards
Attitude Indicator
The foundation for all instrument flight. this instrument reflects the airplane’s attitude in relation to the horizon.
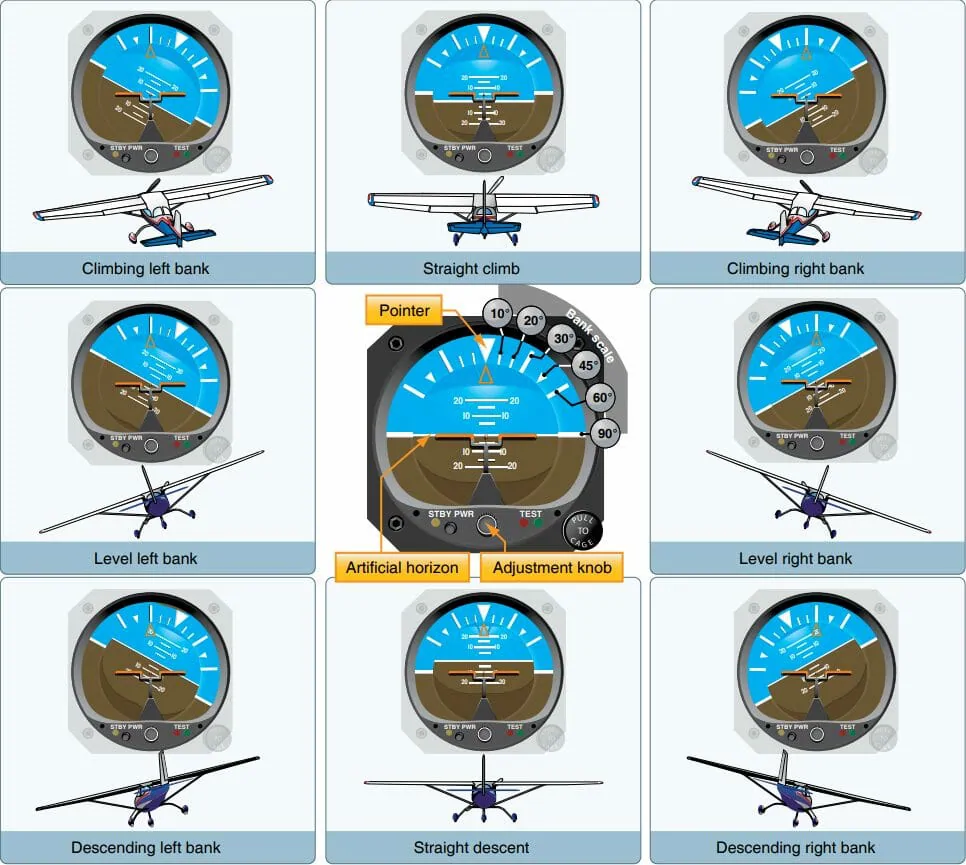
59
New cards
Attitude Instrument Flying
Controlling the aircraft by reference to the instruments rather than by outside visual cues
60
New cards
Autokinesis
Nighttime Visual Illusion that a stationary light is moving, which becomes apparent after several seconds of staring at the light
61
New cards
Automated Weather Observing System (AWOS)
Automated weather reporting system consisting of various sensors, a processor, a computer-generated voice subsystem, and a transmitter to broadcast weather data
62
New cards
Aviation Routine Weather Report (METAR)
Observation of current surface weather reported in a standard international format
63
New cards
Axes of an Aircraft
Three imaginary lines pass through an aircraft’s center of gravity. The axes can be considered as imaginary axles around which the aircraft rotates. The three axes pass through the center of gravity at 90-degree angles to each other. The axis from nose to tail is the longitudinal axis (pitch), the axis that passes from wingtip to wingtip is the lateral axis (roll), and the axis that passes vertically through the center of gravity is the vertical axis (yaw)
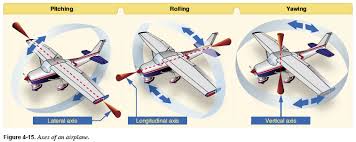
64
New cards
Axial Flow Compressor
A type of compressor used in a turbine engine in which the airflow through the compressor is essentially linear. an axial-flow compressor is made up of several stages of alternate rotors and stators. The compressor ratio is determined by the decrease in area of the succeeding stages
65
New cards
Back Course (BC)
The reciprocal of the localizer course for an ILD. When flying a back-course approach, an aircraft approaches the instrument runway from the end at which the localizer antennas are installed
66
New cards
Balance Tab
An auxiliary control mounted on a primary control surface, which automatically move in the direction opposite the primary control to provide an aerodynamic assist in the movement of control
67
New cards
Barometric Scale
A scale on the dial of an altimeter to which the pilot sets the barometric pressure level from which the altitude shown by the pointers is measured
68
New cards
Basic Empty Weight (GAMA)
includes the standard empty weight plus optional and special equipment that has been installed
69
New cards
Bernoulli’s principle
A principle that explains how the pressure of a moving fluid varies with its speed of motion. An increase in the speed of movement causes a decrease in the fluid’s pressure
70
New cards
Block Altitude
A block of altitudes assigned by ATC to allow altitude deviations; for example, “Maintain block altitude 9 to 11 thousand”
71
New cards
Cabin Altitude
Cabin Pressure in terms of equivalent altitude above sea level
72
New cards
Cage
The black markings on the ball instrument indicating its neutral position
73
New cards
Calibrated Orifice
A hole of specific diameter used to delay the pressure change in the case of a vertical speed indicator
74
New cards
Calibrated Airspeed (CAS)
The speed at which the aircraft is moving through the air, found by correcting IAS for instrument and position errors
75
New cards
Camber
The camber of an airfoil is the characteristic curve of its upper and lower surfaces. The upper camber is more pronounced, while the lower camber is comparatively flat. This causes the velocity of the airflow immediately above the wing to be much higher than that below the wing
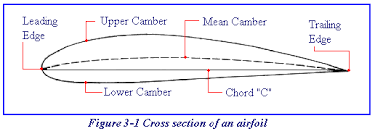
76
New cards
Canard
A horizontal surface mounted ahead of the main wing to provide longitudinal stability and control. It may be fixed, movable, or a variable geometry surface, with or without control surfaces

77
New cards
Canard Configuration
A configuration in which the span of the forward wings is substantially less than that of the main wing
78
New cards
Cantilever
A wing designed to carry loads without external struts
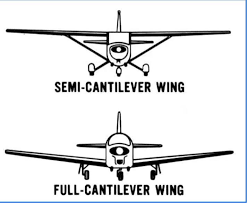
79
New cards
Curse Deviation Indicator (CDI)
A Course Deviation Indicator (CDI) is an instrument that shows if an aircraft is flying on the desired course or deviating from it. It provides visual cues, usually in the form of a needle or bar, to help pilots stay on track during navigation.

80
New cards
Center of Gravity (CG)
The point at which an airplane would balance if it were possible to suspend it at that point. It is the mass center of the airplane, or the theoretical point at which the entire weight of the airplane is assumed to be concentrated. It mat be expressed in inches from the reference datum, or in percentage of mean aerodynamic chord (MAC). The location depends on the distribution of weight in the airplane
81
New cards
Center of Gravity Limits
THe specified forward and aft points within which the CG must be located during flight. These limits are indicated on pertinent airplane specifications
82
New cards
Center of Gravity Range
The distance between the forward and aft CG limits indicated on pertinent airplane specifications
83
New cards
Center of Pressure
A point along the wing chord line where lift is considered to be concentrated. For this reason, the center of pressure is commonly referred to as the center of lift.
84
New cards
Centrifugal Flow Compressor
An Impeller-shaped device that receives air at its center and slings the air outward at high velocity into a diffuser for increased pressure. Also referred to as a radial outflow compressor
85
New cards
Centrifugal Force
An outward force that opposes centripetal force, resulting from the effect of inertia from a turn
86
New cards
Centripetal Force
A center-seeking force directed inward toward the center of rotation created by the horizontal component of lift during flight
87
New cards
Changeover point (COP)
A point along the route or airway segment between two adjacent navigation facilities or waypoints where changeover in navigational guidance should occur
88
New cards
Chord Line
An imaginary straight line drawn through an airfoil from the leading edge to the trailing edge
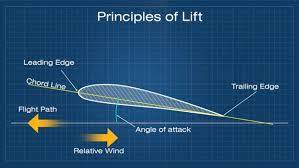
89
New cards
Circling Approach
A maneuver initiated by the pilot to align the aircraft with a runway for landing when a straight-in landing from an instrument approach is not possible or is not desirable
90
New cards
Class A Airspace
Airspace from 18000 feet MSL up to and including FL 600, including the airspace overlying the waters within 12 NM of the coast of the 48 contiguous states and Alaska; and designated international airspace beyond 12 NM of the coast of the 48 contiguous states and Alaska within areas of domestic radio navigational signal or ATC radar coverage, and within which domestic procedures are applied

91
New cards
Class B Airspace
Airspace from the surface to 10000 feet MSL surrounding the nation’s busiest airports in terms of IFR operations or passenger numbers. The configuration of eac Class B airspace is individually tailored and consists of a surface area and two or more layers, and is designed to contain all published instrument procedures once an aircraft enters the airspace. FOr all aircraft, ATC clearance is required to operate in this area, and aircraft so cleared receive separation services within the airspace.

92
New cards
Class C Airspace
Airspace from the surface to 4000 feet above the airport elevation (Charted in MSL) surrounding those airports having an operational control tower, serviced by radar approach control, and having a certain number of IFR operations or passenger numbers. Although the configuration of each Class C airspace area is individually tailored, the airspace usually consists of a 5NM radius core surface area that extends from the surface up to 4000 feet above airport elevation, and a 10 NM radius shelf area that extends from 1200 feet to 4000 feet above the airport elevation

93
New cards
Class D Airspace
Airspace from the surface to 2500 feet above the airport elevation (charted in MSL) surrounding those airports that have an operational control tower. The configuration of each Class D airspace area is individually tailored, and when instrument procedures area published, the airspace is normally designed to contain the procedures.

94
New cards
Class E Airspace
Airspace that is not Class A, Class B, Class C, or Class D, and is controlled airspace

95
New cards
Class G Airspace
Airspace that is uncontrolled, except when associated with a temporary control tower, and has not been designated as Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, or Class E airspace

96
New cards
Clean Configuration
A configuration in which all flight control surfaces have been placed to create minimum drag. In most aircraft this means flaps and gear retracted
97
New cards
Clearance
ATC permission for an aircraft to proceed under specified traffic conditions within controlled airspace, for the purpose of providing separation between known aircraft
98
New cards
Clearance Delivery
Control tower position responsible for transmitting departure clearances to IFR flights
99
New cards
Clearance Limit
The fix, point, or location to which an aircraft is cleared when issued an air traffic clearance
100
New cards
Clearance on Request
An IFR clearance not yet received after filing an IFR flight plan