Detectors that rely on chemical changes- Neutron Detection
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
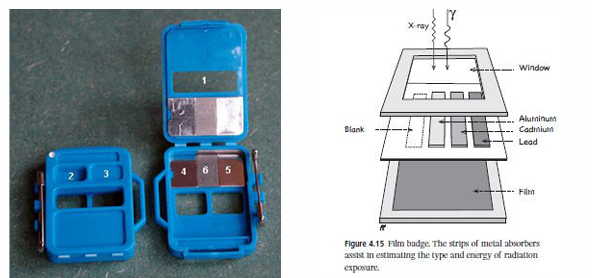
Film badge (photographic dosimeter).
Detectors that rely on chemical changes
Film emulsion
contains silver halide crystals (AgBr) — ionizing radiation produces latent image which develops to a darkening on chemicalprocessing.
exposure
Film badge (photographic dosimeter)
Optical density after development is proportional to ____.
energy discrimination, directional information
Film badge (photographic dosimeter)
Filters on the badge yield ____ and ____
Film badge (photographic dosimeter)
Advantages historically: low cost, permanent record (if stored)
Film badge (photographic dosimeter)
Disadvantages: limited dynamic range, energy dependence, fading, processing required, largely replaced by OSL/TLD.
Film badge (photographic dosimeter)
uncharged particles, ionize matter
Neutrons are ____ → they do not directly___
Neutron Detection
Detection must rely on secondary charged particles produced in nuclear reactions.
Elastic scattering, Neutron capture (absorption), Nuclear reactions
Neutron Detection Main interaction mechanisms:
Neutron capture (absorption)
Neutron Detection
nucleus emits charged particles or γ-rays.
Nuclear reactions
Neutron Detection
producing radioactivity (activation foils)
detector material
target nucleus
secondary charged particles
detector medium
ionization/scintillation; electrical signal
Neutron Detection
Step by step:
Neutron enters the___.
Interacts with ____(e.g., ¹⁰B, ³He, ⁶Li)
Produces ____ (protons, α, electrons).
These charged particles ionize the ___(gas, solid, or liquid).
Resulting____ converted into ____.
Conversion gas detectors, Activation methods
Neutron detection— two main approaches
Conversion gas detectors
Neutron detection— two main approaches
e.g., BF₃ (Boron Trifluoride) or ³He (Helium-3) detectors — neutrons captured by nucleus produce charged particles which ionize gas and are detected.
Activation methods
Neutron detection— two main approaches
irradiate foils — neutron absorption makes nucleus radioactive. (e.g., gold, indium) → induced radioisotopes measured by gamma spectrometry → infer neutron fluence