Bacterial Growth, Nutrition, and Culturing Techniques
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Microbial Growth
Increase in microbial cell numbers over time.
Biofilms
Communities of bacteria adhering to surfaces.
Cultured Bacteria
Bacteria isolated and grown in laboratory conditions.
Pathogens
Microbes that cause disease in hosts.
Escherichia coli
Bacterium capable of dividing every 20-30 minutes.
Limiting Nutrients
Nutrients that restrict bacterial population growth.
Chemically Defined Medium
Minimal medium with precise nutrient composition.
Fastidious Organisms
Microbes requiring specific growth factors from environment.
H. influenzae
Requires NAD and heme to grow.
Pure Culture
Genetically homogeneous strain of a single species.
Agar
Solidifying agent derived from seaweed for cultures.
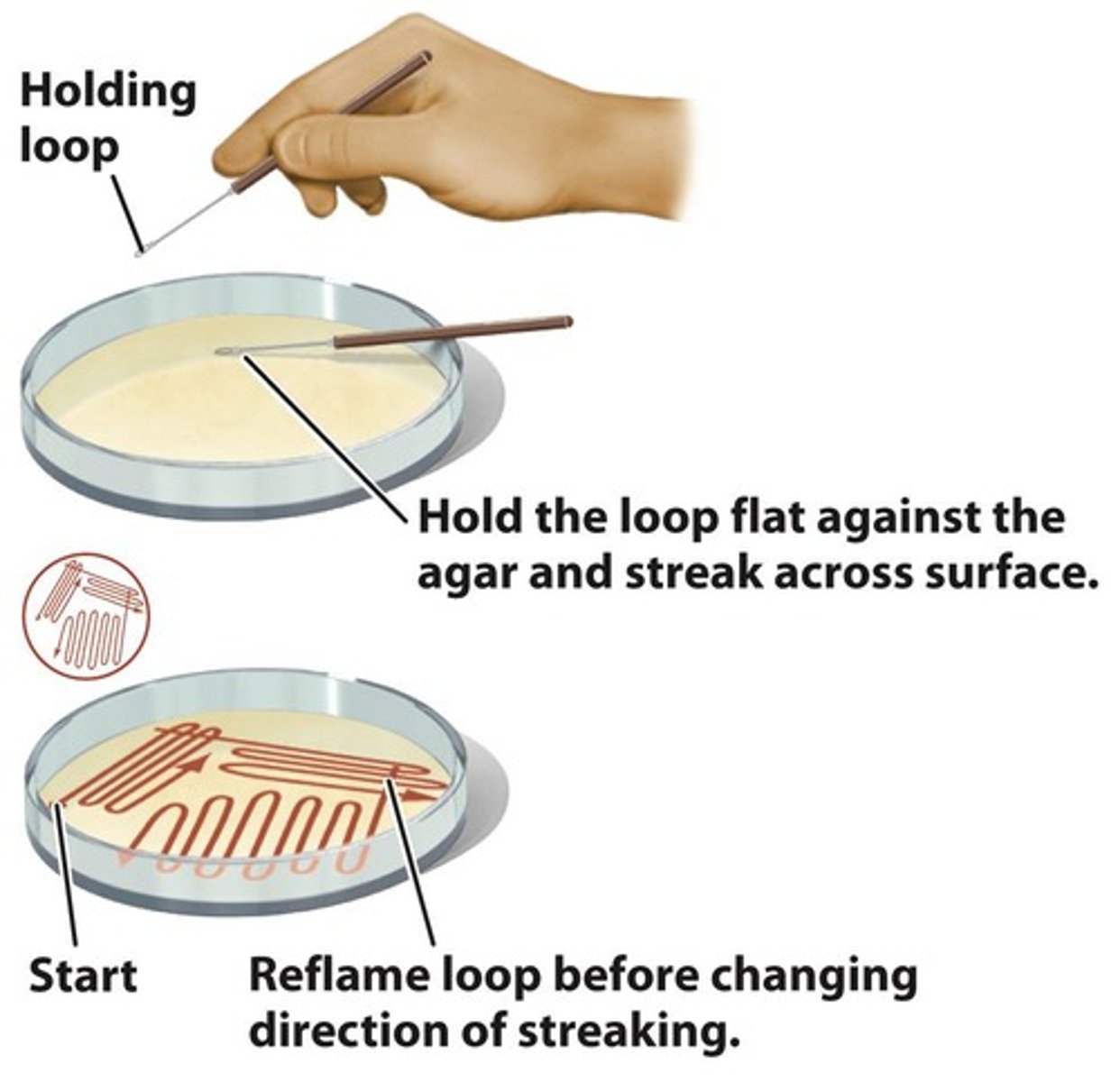
Isolation Streaking
Technique to dilute cells on agar surface.
Spread Plate
Technique for isolating colonies from liquid culture.
Colony Forming Unit (CFU)
One colony represents one viable organism.
Synthetic Medium
Contains precise amounts of basic nutrients.
Complex Medium
Nutrient-rich but poorly defined composition.
Enriched Medium
Contains blood components for fastidious organisms.
Selective Media
Promotes growth of specific organisms over others.
Differential Media
Reveals biochemical differences between species.
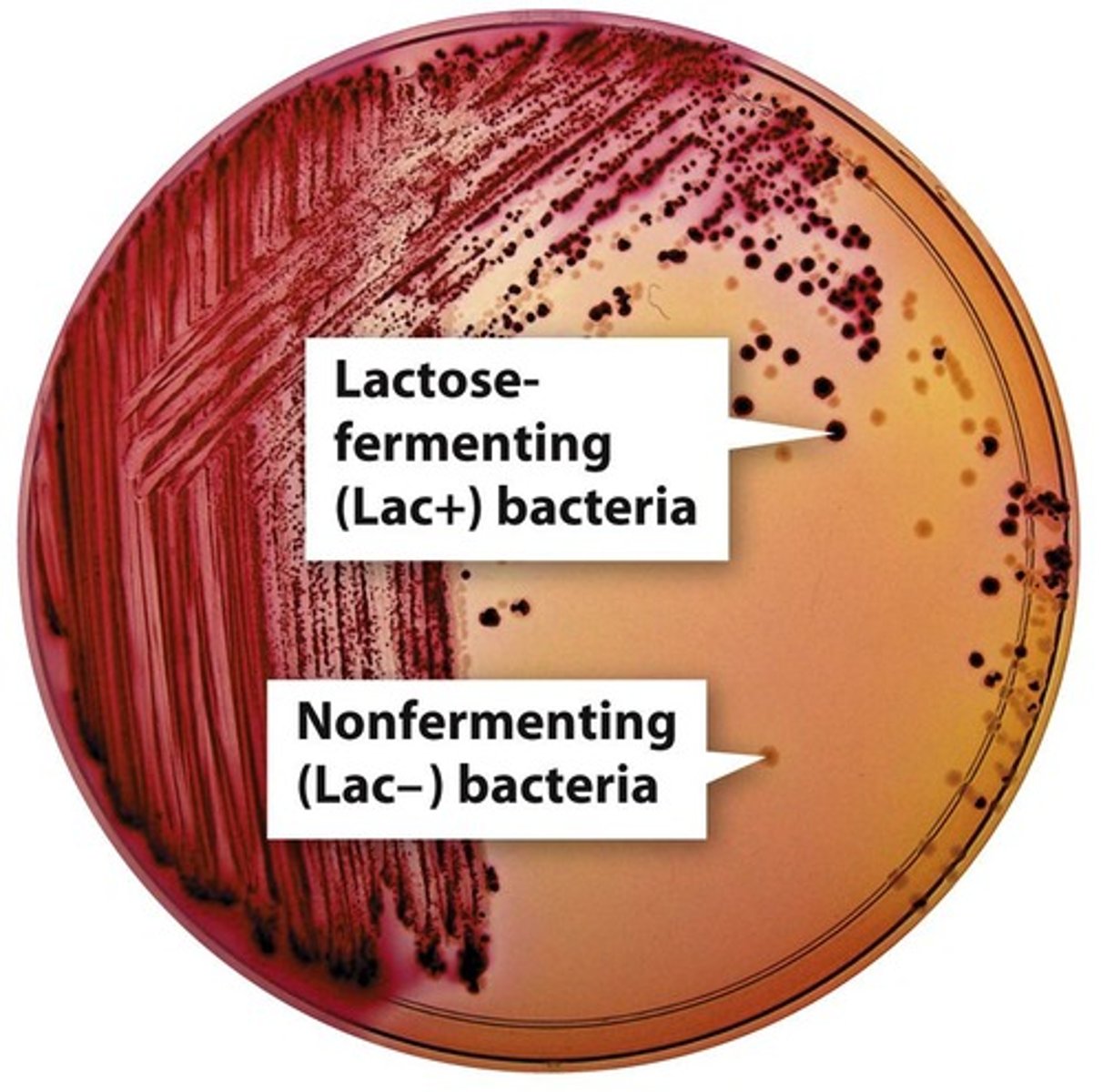
MacConkey Agar
Selective and differential medium for gram-negative bacteria.
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction method in bacteria.
Budding
Asymmetrical reproduction method in some bacteria.
Asymmetrical Budding
Division method in marine bacterium Hyphomicrobium.
Exponential Growth
Population doubles at a fixed rate.
Generation Time
Time interval for bacterial cell division.
Exponential Curve
Graphical representation of population growth over time.
Nutrient Depletion
Limited resources slow bacterial growth rate.
Toxic By-products
Waste products that inhibit further bacterial growth.
Bacterial Growth Curve
Graph showing phases of bacterial population growth.
Chemostats
Our bodies act as controlled environments for microbes.
Extremophiles
Organisms thriving in extreme environmental conditions.
Temperature Extremes
Microbes' growth temperature matches their environment.
Optimum Temperature
Ideal temperature for maximum microbial growth.
Psychrophiles
Bacteria growing at 0°C, optimum at 14°C.
Mesophiles
Bacteria thriving between 20-40°C, with limits 15-45°C.
Thermophiles
Bacteria adapted to high temperatures, above 55°C.
Hyperthermophiles
Bacteria growing at temperatures up to 121°C.
Water Activity
Measure of water availability for microbial growth.
Osmolarity
Concentration of solute molecules in a solution.
pH Influence
Hydrogen ion concentration affects microbial growth.
Homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal pH in microbes.
Aerobes
Bacteria that require oxygen for energy extraction.
Anaerobes
Bacteria that cannot tolerate oxygen, often pathogenic.
Strict aerobes
Require oxygen for growth and metabolism.
Strict anaerobes
Cannot survive exposure to oxygen.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Toxic oxygen molecules harming anaerobes.
Superoxide dismutase
Enzyme that removes superoxide radicals.
Peroxidase
Enzyme that removes hydrogen peroxide.
Catalase
Enzyme that converts hydrogen peroxide to water.
Facultative anaerobes
Can use oxygen or fermentation for energy.
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Only use fermentation but detoxify ROS.
Microaerophiles
Grow at low oxygen concentrations only.
Biofilm
Mass of bacteria adhering to surfaces.
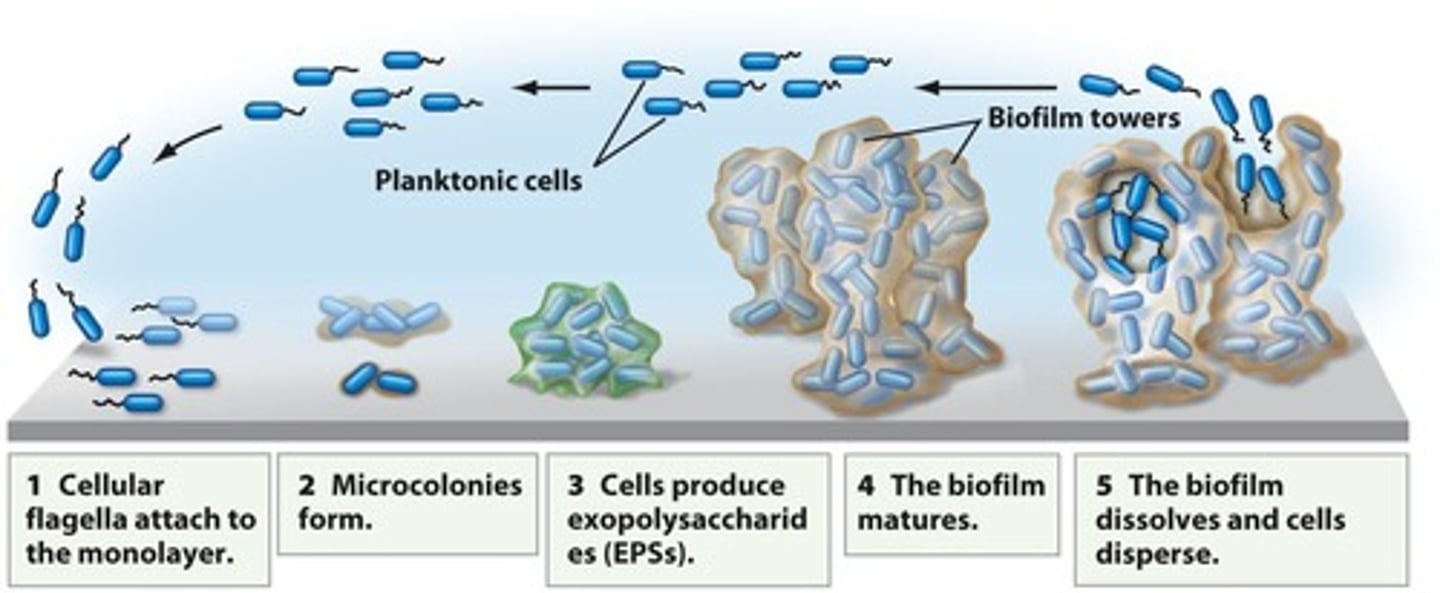
Planktonic cells
Free-living cells not attached to surfaces.
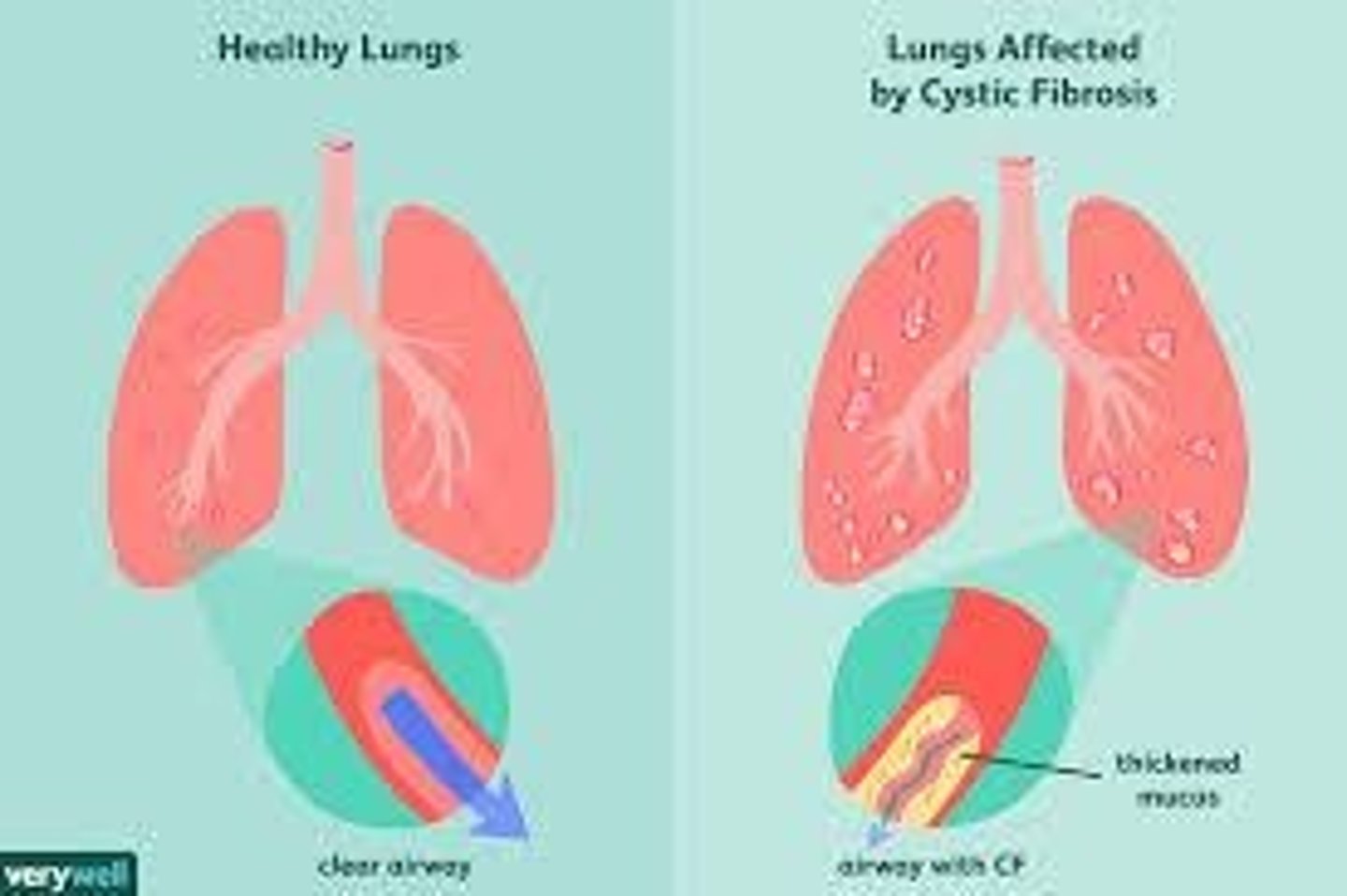
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
Genetic disorder causing thick mucus in lungs.
P. aeruginosa
Bacteria often fatal in cystic fibrosis patients.
Quorum sensing
Chemical communication among bacteria in biofilms.
Sporulation
Process of forming dormant spores.
Endospores
Heat-resistant spores from certain bacteria.
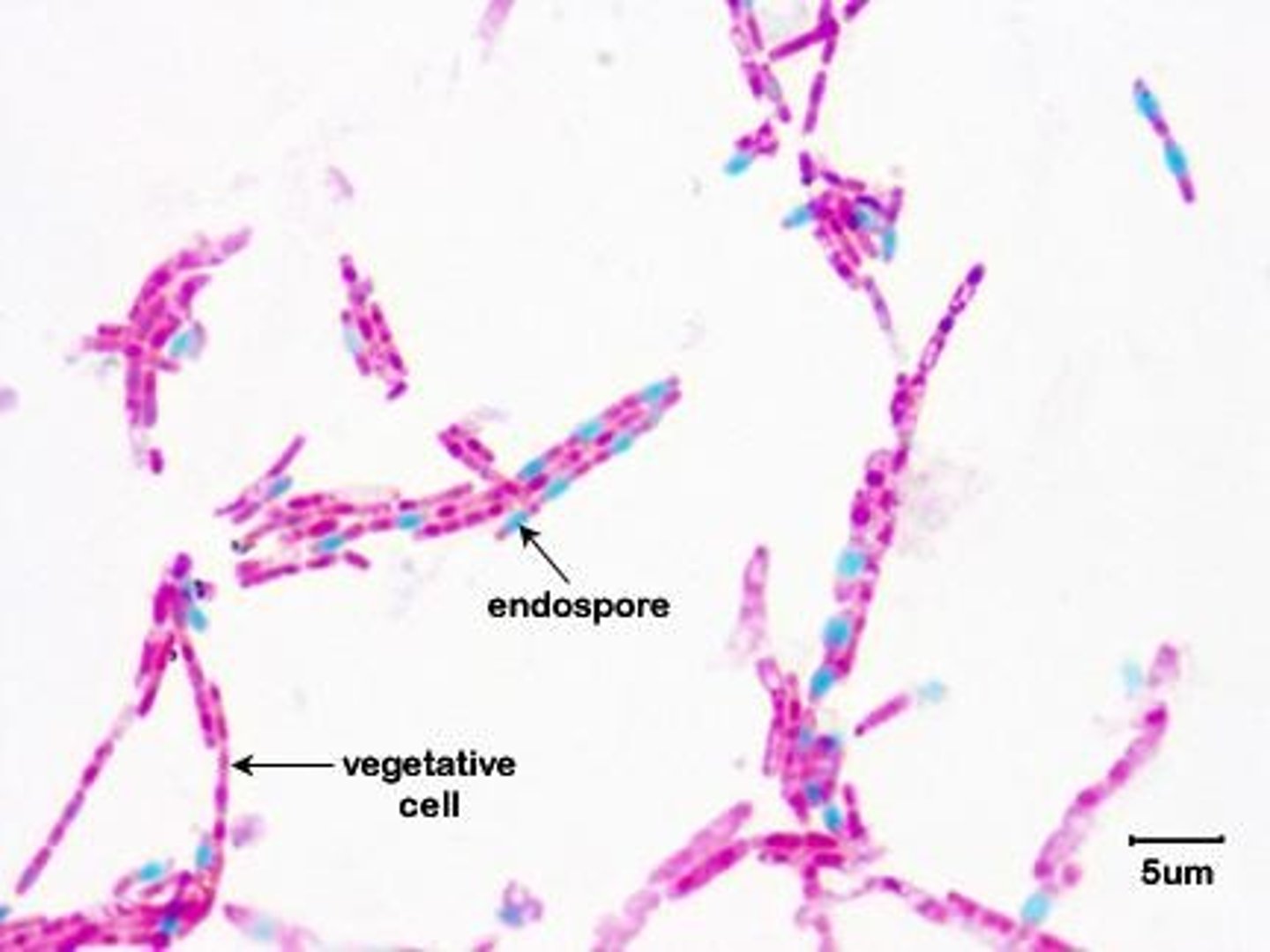
Vegetative state
Active growth phase of bacteria.
Germination
Process of a spore becoming a vegetative cell.
Biofilm formation
Bacteria attach and multiply on surfaces.
Environmental stress
Conditions that threaten bacterial survival.
Communication in biofilms
Cells send signals to coordinate behavior.
Biofilm resistance
Biofilms protect bacteria from antibiotics.