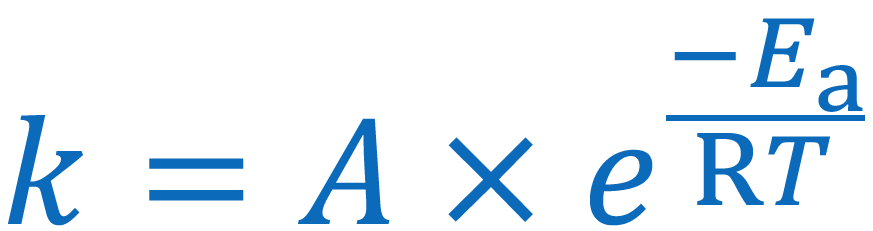general chemistry 5: chemical kinetics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
[...] is a number that relates the rate of a chemical reaction to the concentrations of the reacting substances
reaction order
the sum of all the exponents of the concentrations of substance determines the rate of the reaction
overall order = a+b
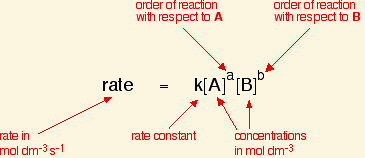
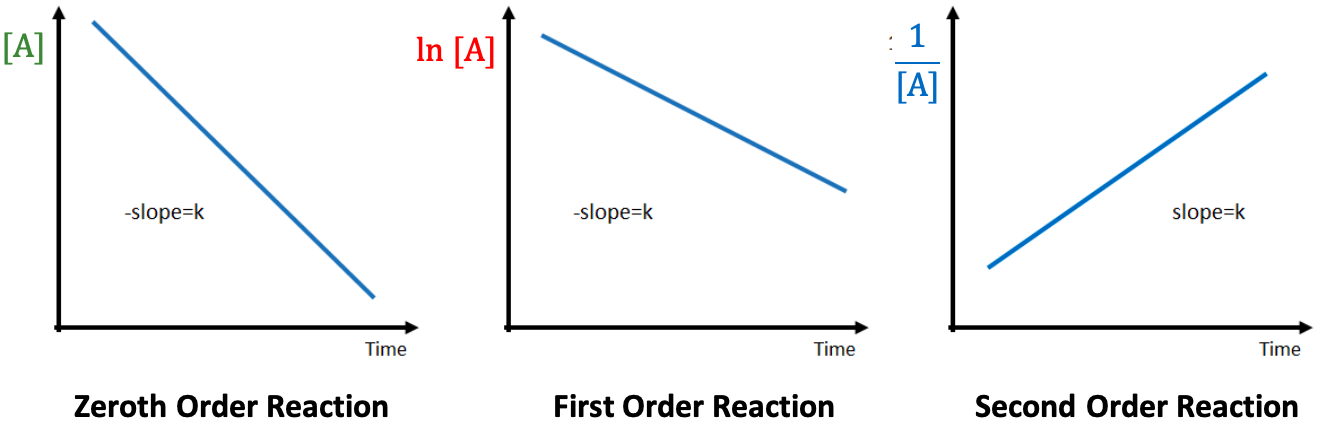
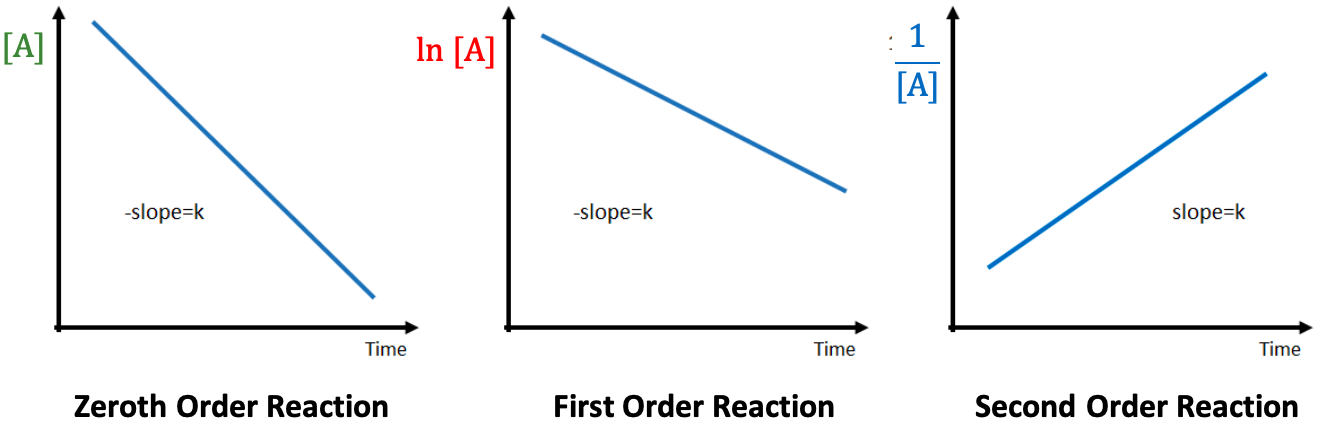
For a zeroth order reaction:
Rate Law: [...]
Integrated Rate Law: [...]
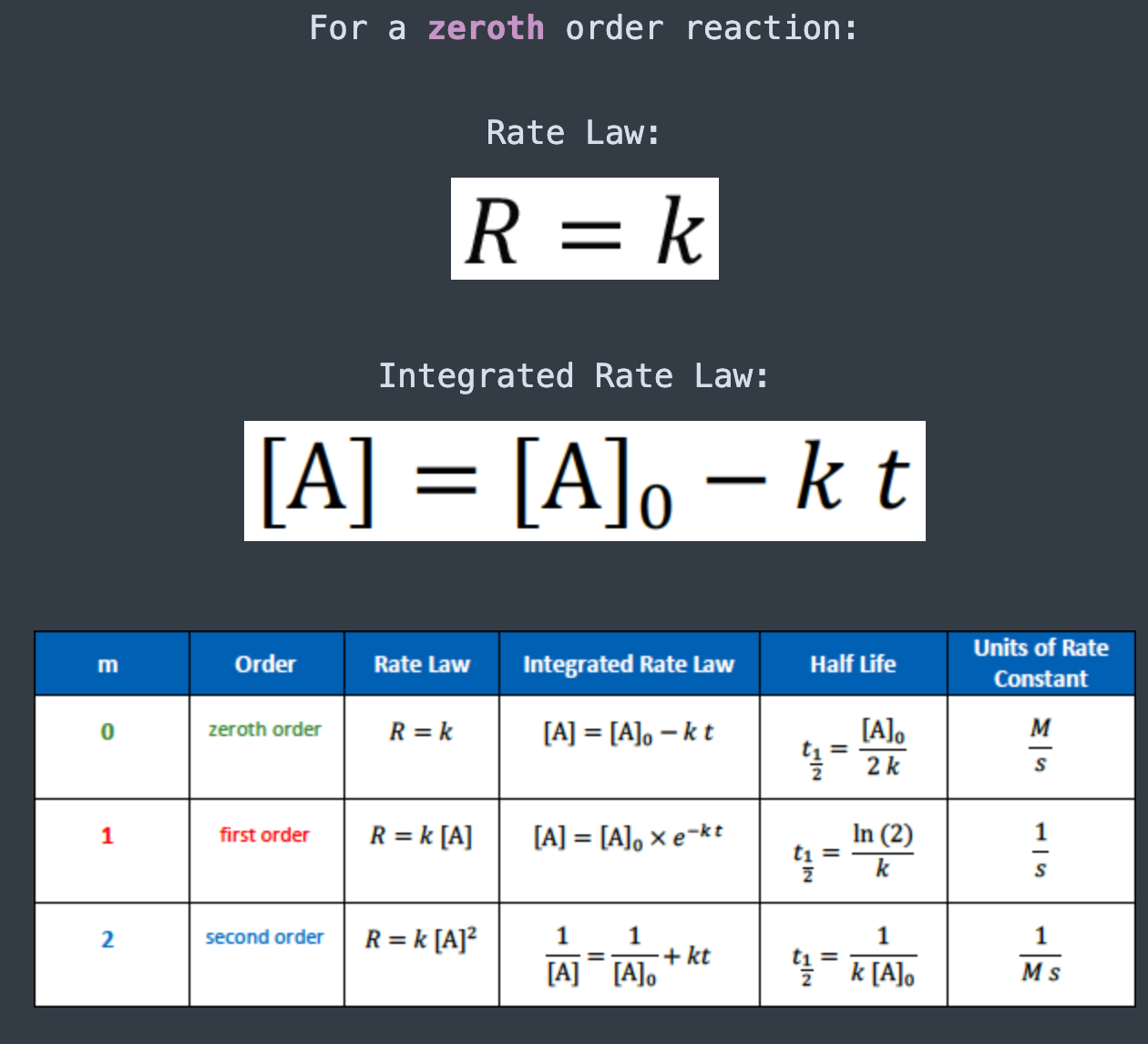
For a first order reaction:
Rate Law: [...]
Integrated Rate Law: [...]
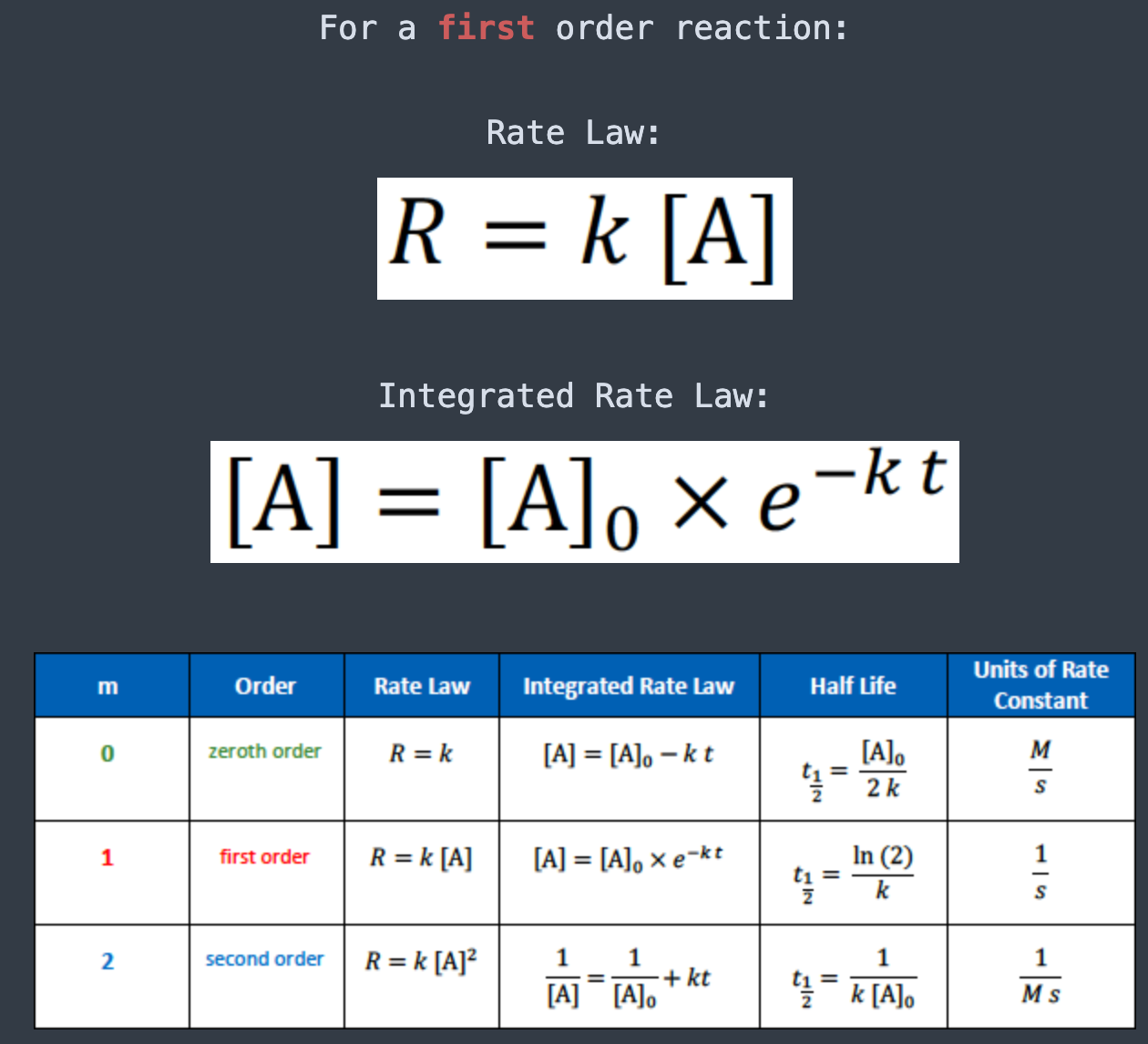
For a second order reaction:
Rate Law: [...]
Integrated Rate Law: [...]
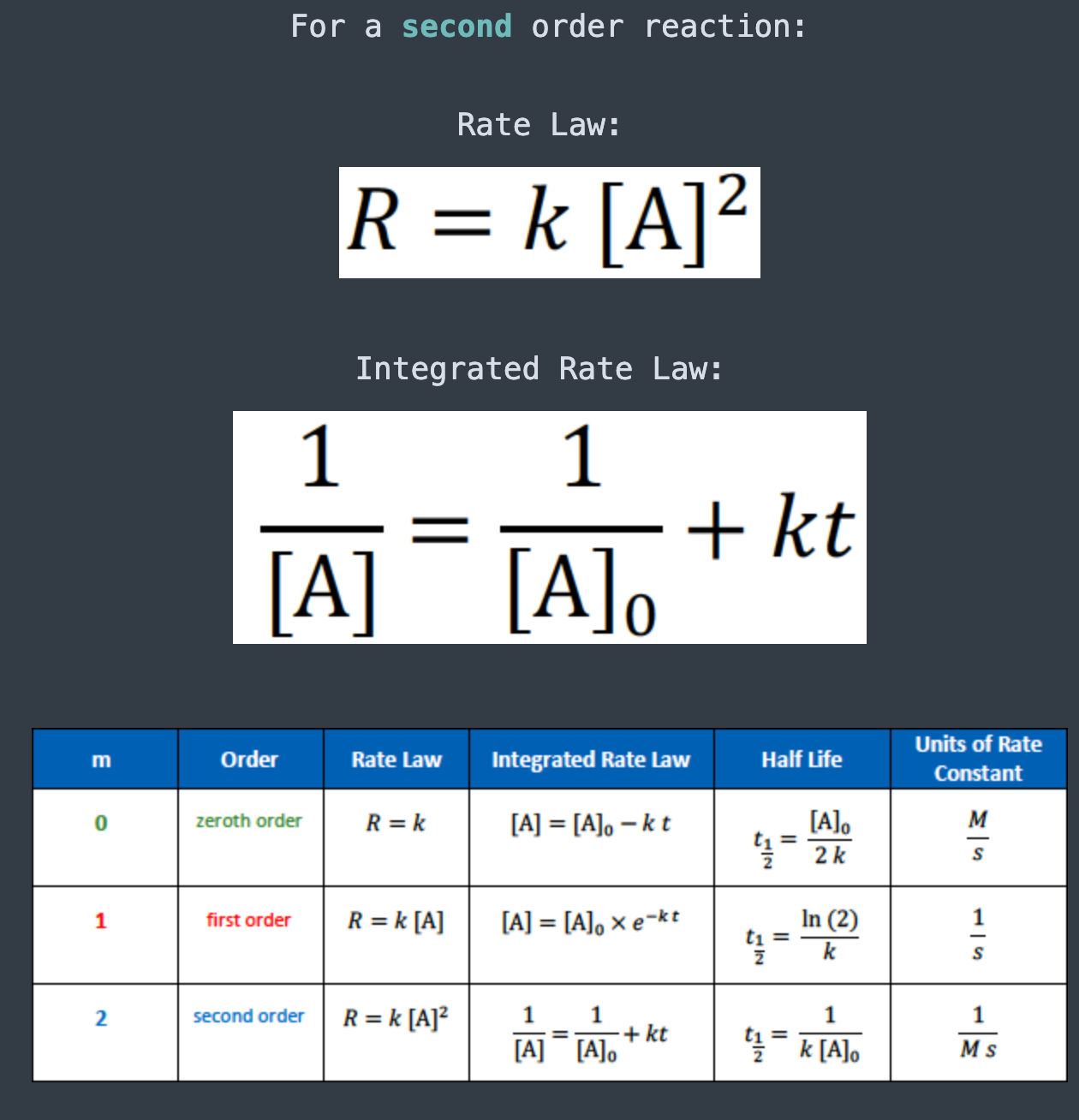
The units for the rate constant of a zeroth order reaction are
[...]
M/S
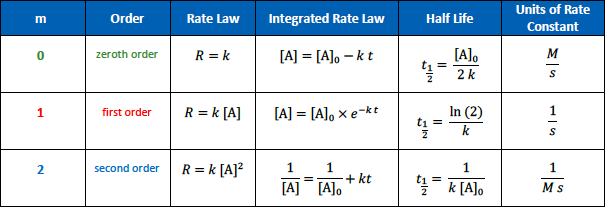
The units for the rate constant of a first order reaction are
1/S
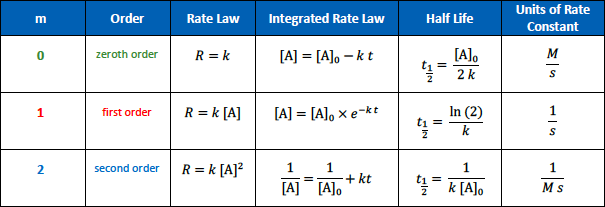
The units for the rate constant of a second order reaction are
[...]
1/Ms
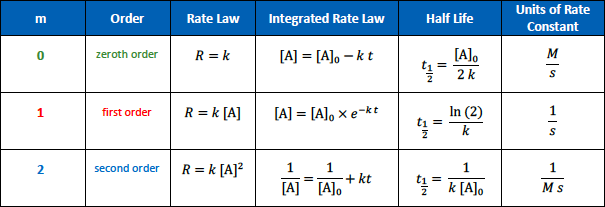
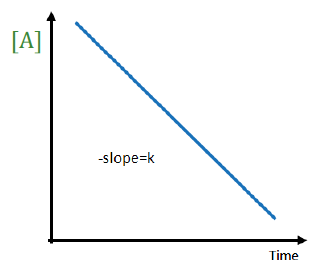
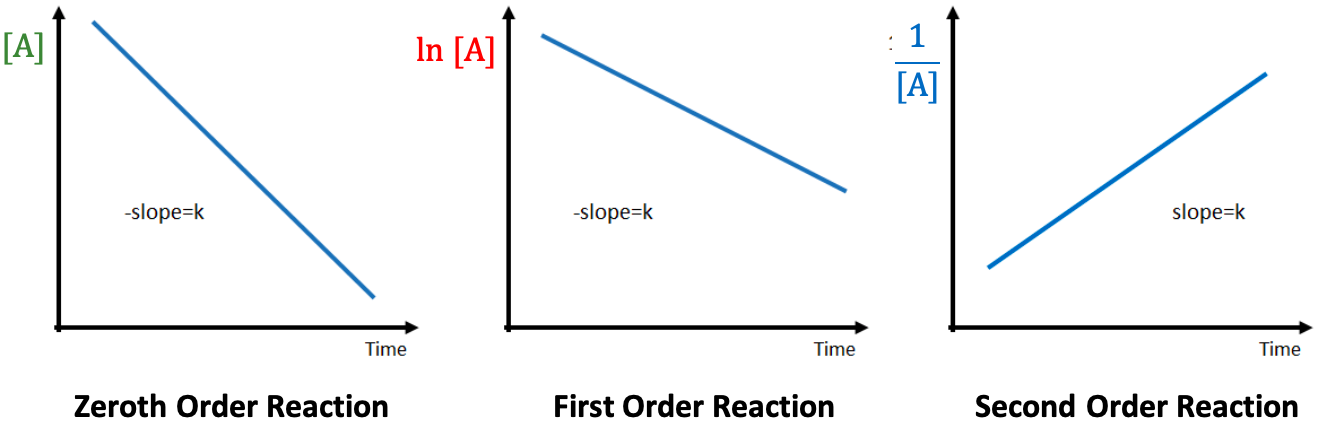
The order of this reaction is
zeroth order
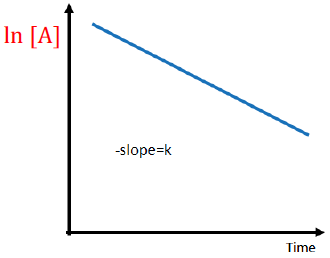
the order for this reaction is
first order
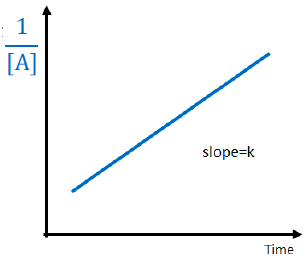
The order for this reaction is
second order
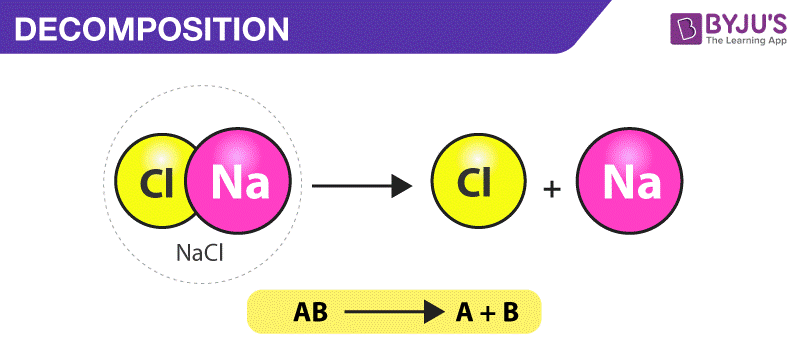
In [...] reactions, a single reactant breaks down
decomposition
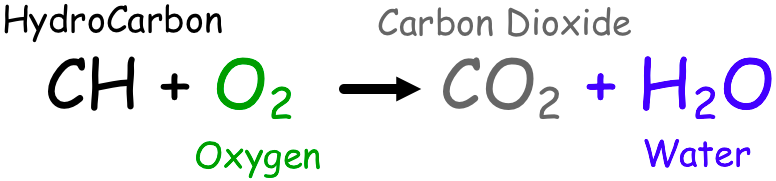
[...] are exothermic reactions in which something reacts with oxygen
Combustion reactions
commonly known as burning
A/an [...] reaction is when an acid and base react to form water and salt
neutralization
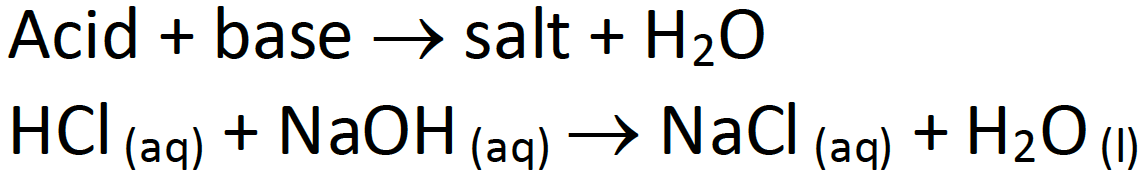
A/an [...] reaction uses water to break the bonds in a molecule
hydrolysis
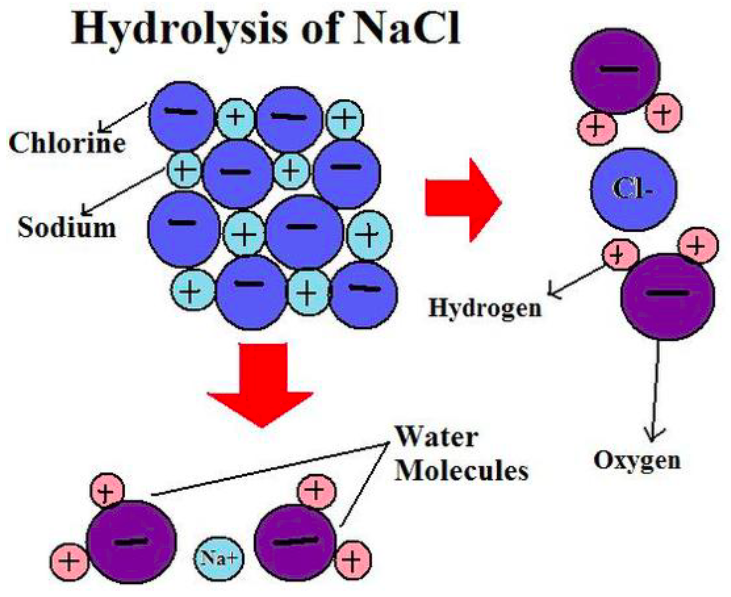
Give the Arrhenius equation:
you can use the arrhenius equation to show the effect of a change of temperature on the rate constant and therefore on the rate of the reaction
k = rate constant
A = frequency factor
Ea = activation energy
R - gas constant
T te
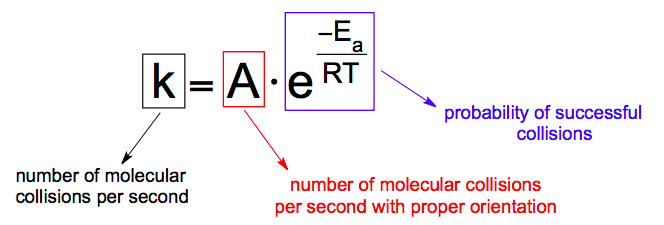
mperature in K (+273)
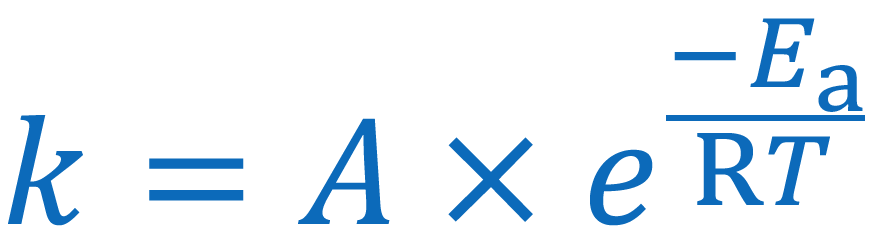
If temperature goes up, the rate constant goes [up or down] and the reaction speed goes [up or down]
up, up
this is because the exponent gets closer to 0. the exponent becomes less negative