Module 4 - General Patient Care I
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
supine position
patient lies flat on their back with hands at their sides.
examine front of the body: head, chest, stomach, and some x-rays.
prone position
patient lies face down, flat on the stomach, head turned to onside, arms alongside the body.
examine back and some surgeries.
dorsal recumbent position
patient lies flat on the back with knees bent and feet flat on the examine table.
examine the head, neck, chest, vaginal, rectal, perineal areas.
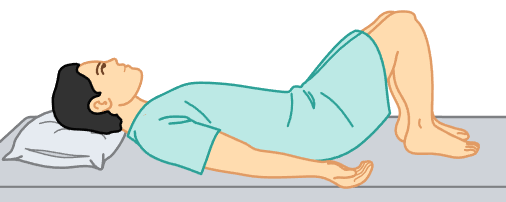
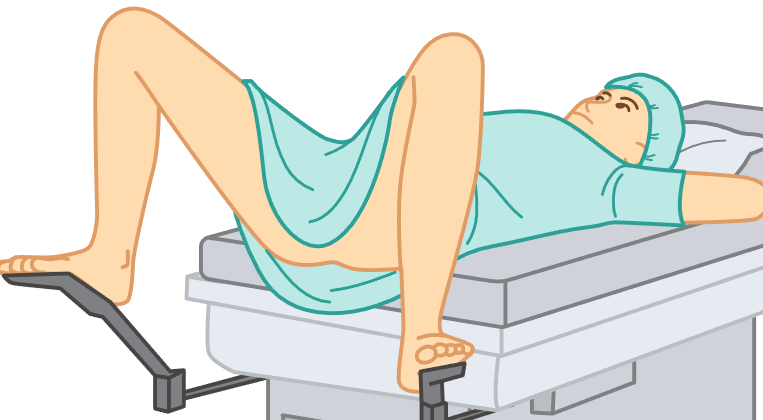
lithotomy position
patient lies flat on their back with knees bent and feet in stirrups attached to the table.
vaginal examinations.
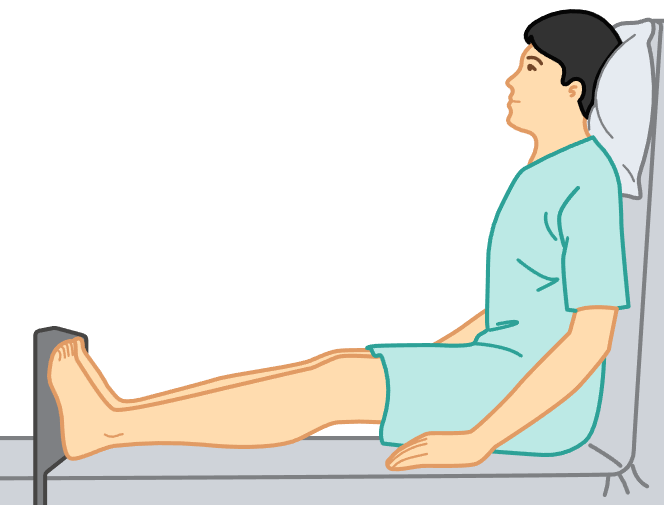
fowler’s position
patient sits upright at 90-degree angle.
examine head, neck, upper body.
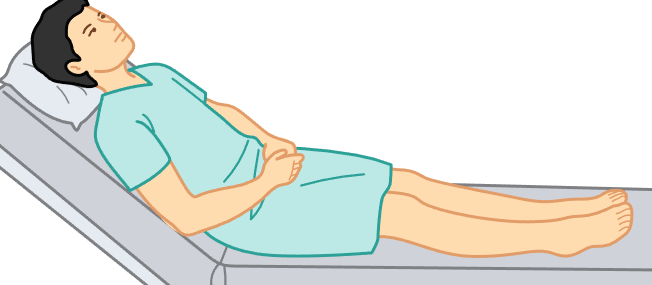
semi-fowler’s position
patient sits atop exam table at 45-degree.
postsurgical exams, lower back injuries, patients with breathing difficulties.
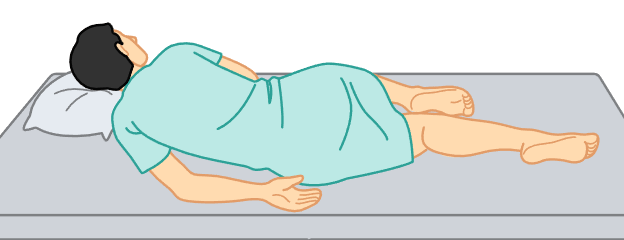
left lateral position
patient lies on their left side with the right leg sharply bent at the knee and left leg slightly bent.
rectal exams/temperatures, enemas, perineal or pelvic exams.
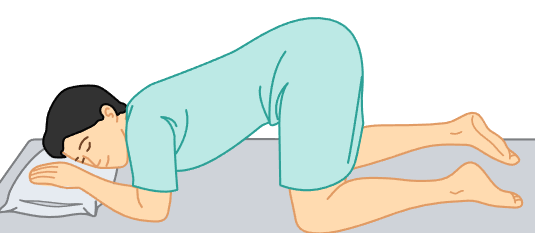
knee-chest position
patient kneels and lies their head on the exam table, with their buttocks in the air.
proctologic exams, sigmoidoscopy procedures, rectal or vaginal exams.
parenteral medication
non-oral medication administration bypassing the gastrointestinal tract, typically injected directly into the body.
nonparental medication (enteral)
medication given by mouth, delivered to the gastrointestinal tract.
subcutaneous injection
injection administered below the skin layer into the adipose (fat) layer at a 45 degree angle.
insulin, some vaccines, medications for slower absorption.
injected in upper thigh, upper/out arm, abdominal region.
intradermal injection
injection administered into the dermis, slightly beneath the skin, at a 5-15 degree angle.
allergy testing, tuberculosis screening.
injected in mid forearm.
intramuscular injection
injection administered into the muscle, at a 90 degree angle.
vaccines, hormones, medications for faster absorption or large doses.
deltoid (shoulder), outer hip, upper/outer thigh.
intravenous injection
injection delivered directly into the bloodstream through a vein, at a 15-30 degree angle. allows for immediate effect and rapid absorption.
fluids, nutrients, blood, IVs, fast acting medications, used in hospital/ER.
sublingual medication
medication placed under the tongue.
buccal medication
medication placed between the cheek and gums.
inhalation medication
inhaled through the mouth, passes the trachea into the lungs or inhaled through the nose and absorbed through the nasal mucous membrane.
ocular medication
drops of medication instilled directly into the eye.
otic medication
drops of medication instilled directly into the ear.
transdermal medication
medication/drug applied to the skin by an adhesive patch, designed to release slowly into circulation.
topical medication
medication applied to the skin or mucous membrane that acts locally, including creams, ointments, or emulsions.
three check medication
compare med to medication order.
check med when preparing to administer.
check med when discarding or storing.
rights of medication administration
ensure the right patient, medication, form, dose, route, time, technique, education, and documentation.
eye/ocular drop administration
patient tilts their head back. MA pulls down the lower lid of the eye to expose the conjunctival sac, dispense drops ½inches above the eye.
eye/ocular cream administration
patient tilts their head back, MA applies a thin ribbon of ointment along the inside edge of the lower eyelid near the nose, moving outward.
ear/octic drop administration
patient lies on their side with ear facing up. MA pulls the outwear ear outward and upward (adults) downward (children), administer drops 1/2inch above ear canal, patient remains lying down for at least 5 min.
anaphylactic shock
severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening without immediate intervention. can occur immediately or within a couple of hours.
abdominal pain, coughing, diarrhea, dyspnea, dysphagia, facial swelling, vomiting, convulsion, unconsciousness.
epinephrine autoinjector (EpiPen)
first line of treatment for anaphylactic shock, intramuscular injection into the thigh, hold the needle at least 10 seconds, then call 911.
reusable critical devices
devices that come in contact with blood or normally sterile tissue, must be sterilized in between use, such as surgical forceps.
reusable semi-critical devices
devices that come in contact with mucus membranes, require high-level disinfecting between use, such as endoscopes.
reusable non-critical devices
devices that come in contact with unbroken skin, require low-level disinfecting between use, such as stethoscopes.
sterilization instruments
sterilization is required for all instruments that will penetrate a patient’s skin, enter a patient’s body, or contact any sterile areas of the body. also required for all instruments used in a sterile field.
needle gauge
size of the opening of the needle, lumen, higher the gauge the narrower the lumen/opening. inject with the bevel facing up.
refrigerated medications storage
2-8 C
35-46 F
frozen medications storage
-50 to -15 C
-58 to - 5 F
MAR
medication administration records, serves as a legal records of meds administered to a patient by a provider. must be filled out each time administered.
PT, DOB, allergies, date, drug, dose, provider, how often/long, time, route.
eye irrigation
patient in supine or sitting position, cleanse eyelid from the inner to outer eye, tilt patient head back, open patient’s eye lids and gently flush with the sterile solution an inch above inner eye flowing the liquid outwards.
ear irrigation
patient titles their head toward the ear side being irrigated. gently introduce the solution into the ear canal, keep patient lying with that ear done for 15 minutes.
specialty pharmacies
dispense intricate medications for more complex conditions (cancer, HIV, immune diseases, hormone deficiencies, ect). they can compound medications by mixing or altering ingredients or form for specific conditions.
EMR
electronic medical record, version of a patient’s medical history used within a single organization.
EHR (electronic health record)
contains EMR and shares it across health care organizations, laboratories, specialists, and pharmacies.
CPOE system (computerized provider order entry)
healthcare providers enter, modify, and manage medication orders and other treatment instructions electronically, reducing errors and improving efficiency.