6) B cells and antibodies
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the two types of light chains of an antibody?
Kappa and delta
Which antibodies have 4 constant domains rather than the standard 3 constant domains in it’s heavy chain?
IgM, IgE
Which chain determines the function of the antibody?
Heavy chain
What are the 2 points of flexibility in an antibody?
HInge region
At the V-C junction
Which CDR is most variable?
CDR3
What are all the ways BCR/ antibodies generate diversity of their binding sites?
1)somatic recombination
2)Different heavy and light chain combinations
3)Variable addition and loss of nucleotides at VDJ junctions: junctional diversity
4)Somatic hypermutation
5)Class-switch/isotype-switching recombination
Somatic recombination
Recombination in Ig genes of the variable, diversity and junctional gene segments of the heavy and light chains
Occurs in the bone marrow
Form unique variable regions of antibodies
How do heavy chain recombine?
RAG 1 and 2 recombinases first join the D and J segment and then the V segment joins to the DJ segment and all intervening genomic DNA is lost.
Somatic hypermutation + affinity maturation
Point mutations in the heavy and light chain variable regions by the AID enzyme.
AID (activation induced cytidine deaminase): cytosine to uracil deamination
Alters the antibody variable region to have increased or decreased affinity for antigen which can be selected for or against in germinal centres of secondary lymphoid tissue.
What happens in germinal centres?
1.Activated B-cells enter dark zone where they proliferate and somatic hypermutation occurs
2.Then the B-cell moves into the light zone where they compete for binding with antigens expressed by follicular dendritic cells
3.The B-cells with high affinity BCR can bind strongly and are selected for and receive survival signals from FDC and TFH which activate the B-cell for further proliferation
4.Cytokines may also be released by the T-cells to allow class-switch recombination.
Isotype switching
Conversion from default antibodies to other types.
Defaults are generate by alternative splicing and co-expressed as BCR’s.
Initial RNA transcripts of the variable chains are processed, cleaved and polyadenylated which allows change of constant regions of B-cells
Which immunoglobulins are default?
IgM and IgD
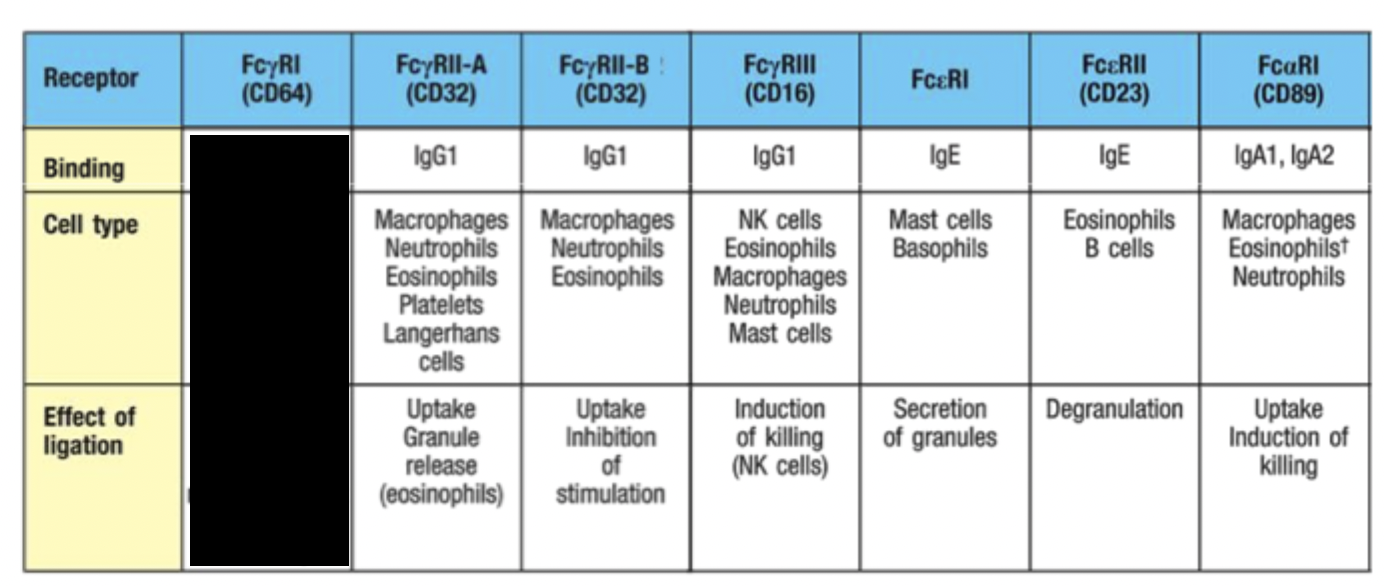
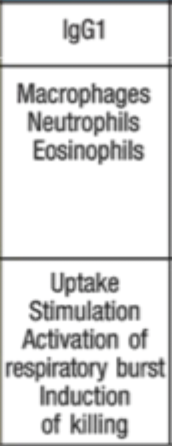
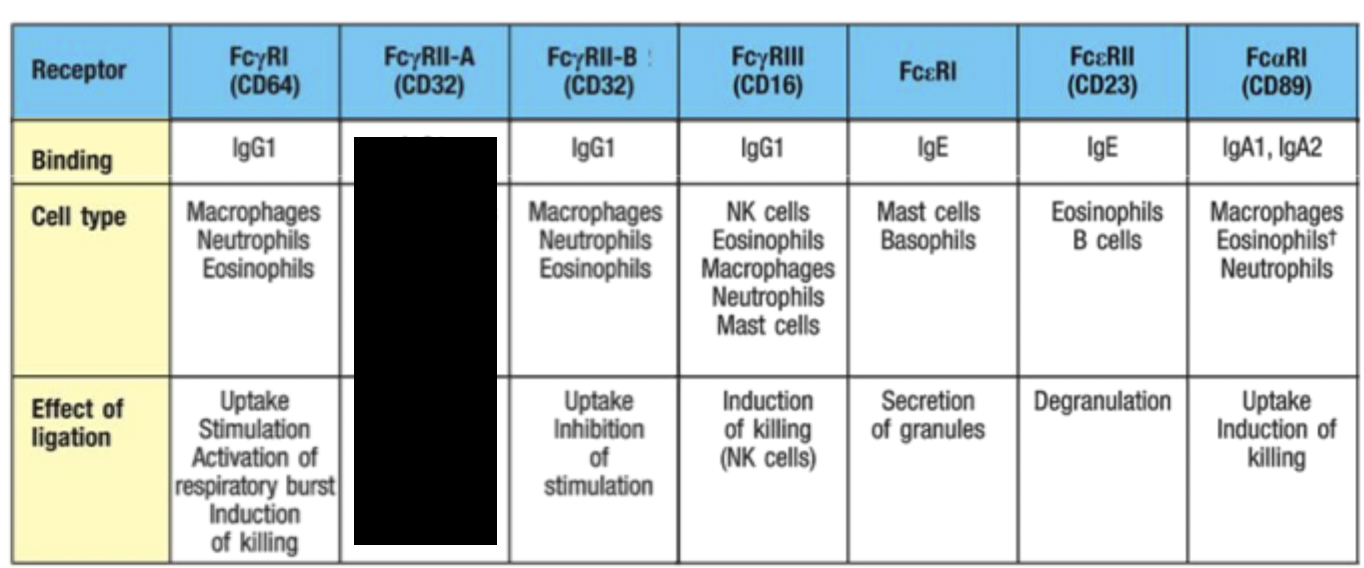

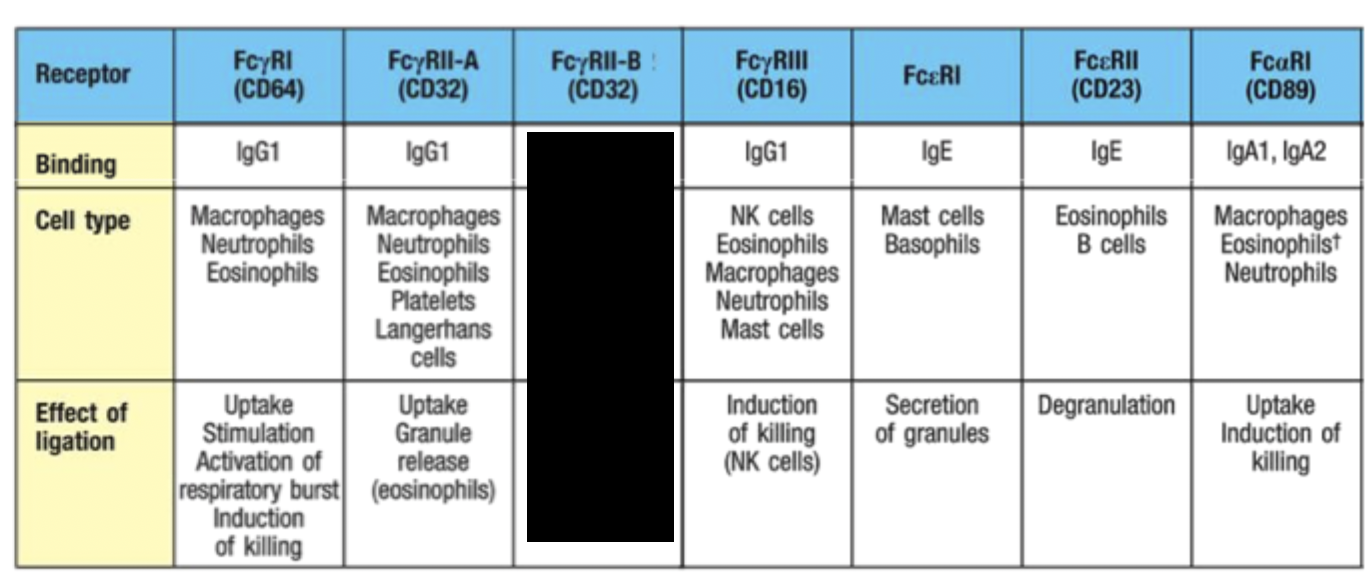

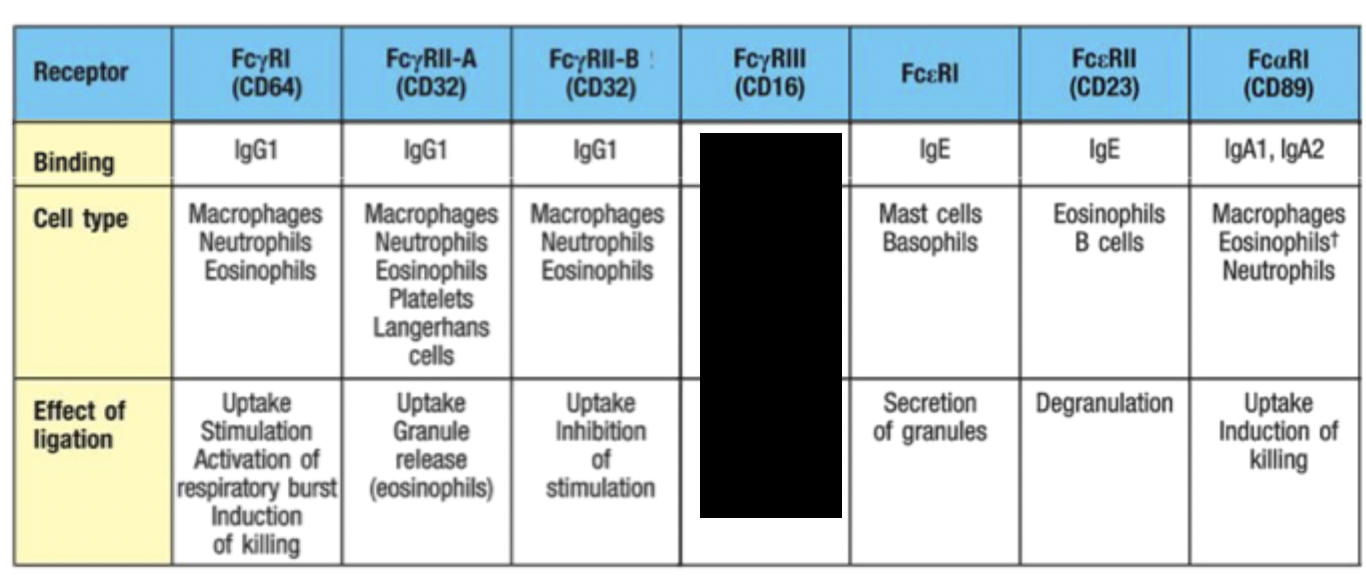

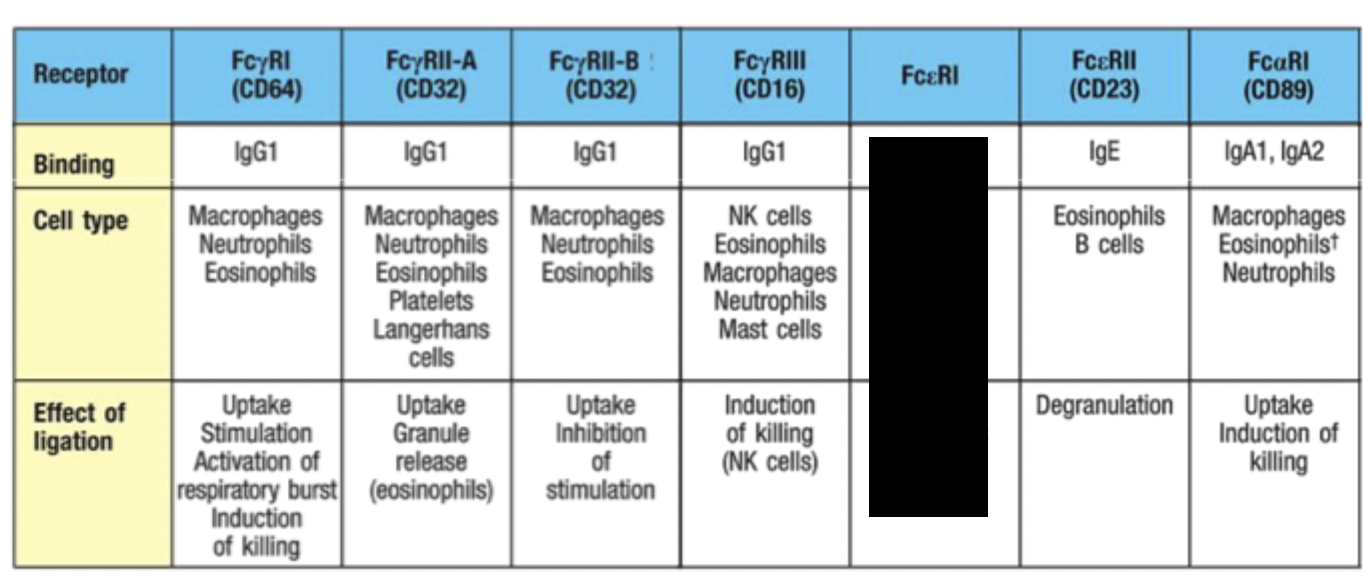

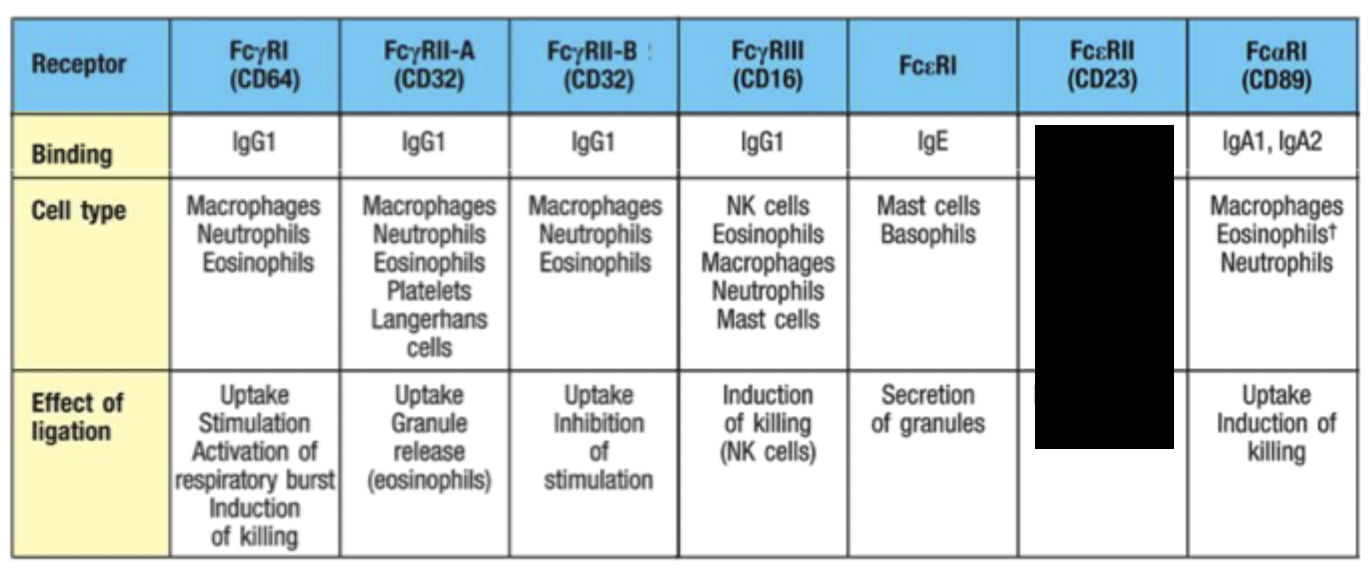

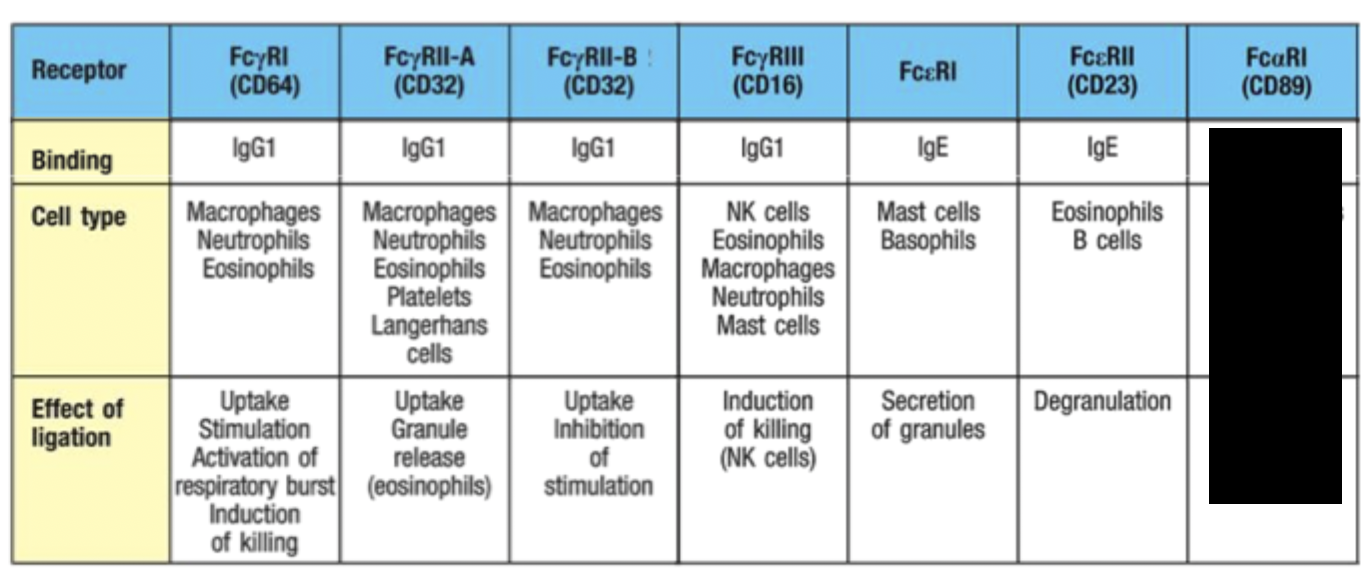

What role does RBC play in antibody opsonisation?
Binding of antigen/antibody complexes to complement receptors on RBC delivers immune complexes to the liver and spleen for removal by macrophages.
Activation of eosinophils
Eosinophils have similar mechanism to ADCC where they secrete granules (degranulation) that contain free radical and toxic proteins that destroy worms
Mobilisation of inflammatory mediators
Mast cells and basophils have receptors against antibodies and when they crosslink, inflammatory mediator signals released.
Degranulation may occur and release of arachadoinic derivatives and TNF-alpa.
Response is also triggered during allergic reactions with IgE on mast cells.
Antibody transport

Regulation of humoural immune responses
Negative feedback mechanism to regulate B-cell levels involves immune complexes binding to Fc receptors at the same time as the antigen binds to the BCR on a B-cell which generates a negative signal that terminates B-cell responses in naive B-cells.
Affinity
Interaction between a single antibody binding site and a single monovalent epitope.
Avidity
Measure of strength of interaction due to recognition of polyvalent epitopes based on multiple simultaneous bindings.
IgG
-Good at crossing placenta
-Most abundant
-Monomer
-More abundant in secondary immune response than primary
-Involved in opsonisation and MAC formation
-Allow macrophages to bind and detect pathogens
-Can be transported across umbilical cord to provide new born passive immunity
IgA
-Dimer
-Found in saliva, skin, sweat, mucus linings and milk
-Maternal IgA passed onto baby
IgM
-Monomer/pentamer
-Short-lived
-May also exist as BCR
-Made the earliest so not require recombination
-Potent activator of complement for opsonisation + MAC
-Agglugination
-10 antigen binding sites
-Involved in type 2 hypersensitivity
IgE
-Low serum conc.
-Very readily bound by mast cells
-Monomer
-Found in respiratory tract,GI tract mucosa,urogenital structures and lymphatics
-Involved in vasodilation which increase fluid outflow causing oedema and bronchoconstriction
-Part of anaphalaxis and type 2 hypersensitivity
IgD
-Monomer
-BCR