chemistry investigation 9 - 11 questions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
The current average global atmospheric CO2 concentration is approximately 415 ppm. The concentration has been increasing at a rate of 0.5% each year. Identify the approximate CO2 concentration in 5 years, if CO2 levels continue to increase at the current rate.
a. about 425 ppm
b. about 440 ppm
c. about 475 ppm
d. about 513 ppm
a. about 425 ppm
Which of the following occurrences have been presented in the form of data as evidence of climate change? Sort the descriptions into the correct boxes: Evidence of Climate Change or Not Evidence of Climate Change.
1 | CO2 concentration in ice cores | 2 | Current solar output levels |
3 | Disappearing glaciers | 4 | Rising sea levels |
5 | Longer solar cycles | 6 | Changes in tree ring width |
Evidence of Climate Change | Not Evidence of Climate Change |
CO2 concentration in ice cores Disappearing glaciers Rising sea levels Changes in tree ring width | Current solar output levels Longer solar cycles |
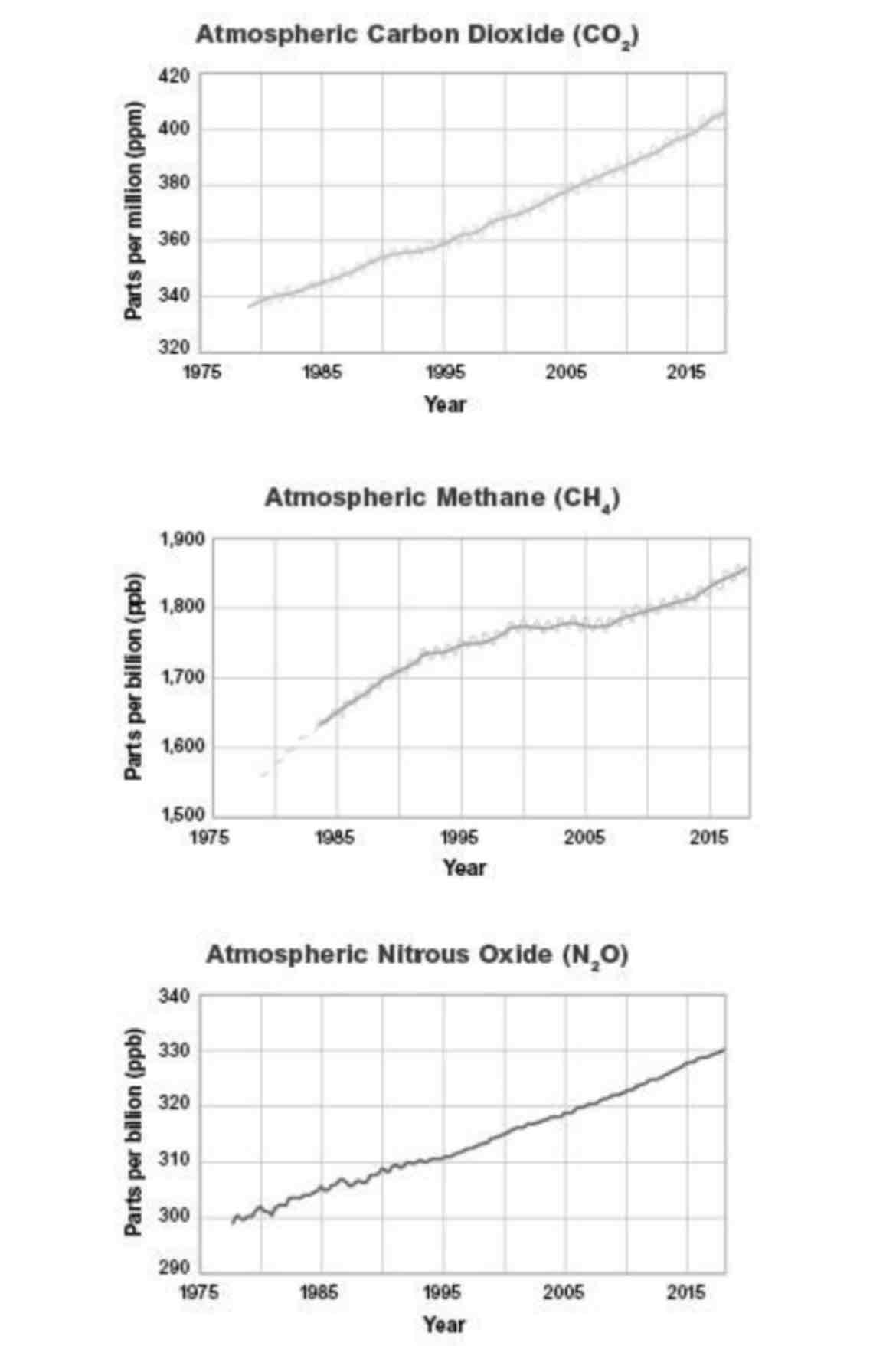
In each of the graphs, the lines corresponding to atmospheric CO2, atmospheric methane, and atmospheric nitrous oxide move up and down as they show a general increase over time. Choose the statement that best explains what the variations in the curves show as they increase over time.
a. The variations are seasonal or annual patterns for each of the gases.
b. The variations are certain times when less of the gases are emitted.
c. The variations are due to the mixture of other chemicals reacting with the gases.
d. The variations are due to differences in the locations that are monitored.
a. The variations are seasonal or annual patterns for each of the gases.
Global climate change has many potential consequences. Identify which of the following sentences best describes some of the consequences of global climate change. Select all that apply.
a. The loss of Himalayan glacier ice threatens human water supplies. If glaciers disappear, then groundwater reservoirs will no longer be recharged.
b. Climate models suggest that the trend of extreme precipitation events will subside as global temperatures increase; regions that were predicted to receive less overall rainfall will have normal amounts of rain.
c. Rising global temperatures will not have any impact on the spread of infectious diseases because bacteria and viruses thrive best in cooler temperatures.
d. Dry areas will become more likely to have wildfires, especially if climates shift to periods of intense precipitation followed by drought.
a. The loss of Himalayan glacier ice threatens human water supplies. If glaciers disappear, then groundwater reservoirs will no longer be recharged.
d. Dry areas will become more likely to have wildfires, especially if climates shift to periods of intense precipitation followed by drought.
This is the computer output for the RCP model for future CO2 emissions based on human impact. Look at the graph and choose the quantitative data to finish the sentences.
900 ppm 800 ppm 600 ppm 400 ppm
400 ppm 500 ppm 600 ppm 700 ppm
According to the RCP model output, the highest predicted CO2 concentration for 2100 is approximately __________ . If we stop emitting CO2 right now, the CO2 concentration in 2100 is predicted to be approximately __________ .
900 ppm, 400 ppm
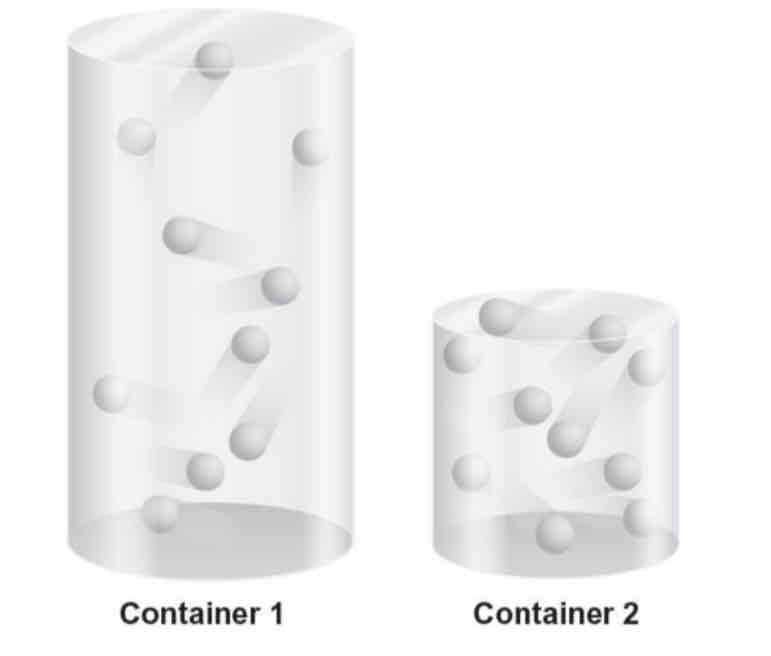
Select the best statement that describes the number of collisions among the gas molecules in the containers.
a. The number of collisions among the gas molecules is the same in both containers because volume does not affect collisions.
b. The number of collisions among the gas molecules is greater in container 1 than in container 2 because the volume is larger.
c. The number of collisions among the gas molecules is greater in container 2 than in container 1 because the volume is smaller.
d. The number of collisions among the gas molecules is greater in container 2 than in container 1 because volume does not affect collisions.
c. The number of collisions among the gas molecules is greater in container 2 than in container 1 because the volume is smaller.
A balloon will float in the air as long as:
a. the mass of the gas inside the balloon is equal to the mass of the air outside it.
b. the temperature inside the balloon is the same as the temperature outside.
c. the number of collisions of particles inside the balloon is greater than those outside the balloon.
d. the number of collisions of particles inside the balloon is the same as outside of the balloon.
d. the number of collisions of particles inside the balloon is the same as outside of the balloon.
A given mass of gas at constant pressure was found to have a volume of 120 mL at 300K. When the same sample of gas was heated to 500K, its volume changed to ____. The same sample of gas had a volume of 160 mL when its temperature changed to ____.
a. 300 mL;400K
b. 200 mL; 400K
c. 400 mL;300K
d. 500 mL; 600K
b. 200 mL; 400K
Food cooks faster in a pressure cooker. Why is this, and what law does it represent?
a. Because the temperature increases and pressure increases. This is according to
Boyle's law.
b. Because the temperature increases and pressure decreases. This is according to
Charles’ law.
c. Because the temperature increases and pressure increases. This is according to
Gay-Lussac´s law.
d. Because the temperature increases and pressure decreases. This is according to
Avogadro's law.
c. Because the temperature increases and pressure increases. This is according to Gay-Lussac´s law.
The empirical van der Waals constant value, a, (in L2atm/mol2) for steam, methane, hydrogen fluoride, and ammonia are as follows:.
Steam 5.536
Methane 2.273
Hydrogen fluoride 9.565
Ammonia 4.170
Place the gases in order, from left to right, by increasing intermolecular force of attraction. The gas with the lowest intermolecular force of attraction should be on the far left, and the gas with the highest intermolecular force of attraction should be on the far right.
a. hydrogen fluoride, steam, ammonia, methane
b. methane, ammonia, steam, hydrogen fluoride
c. ammonia, methane, steam, hydrogen fluoride
d. steam, hydrogen fluoride, methane, ammonia
b. methane, ammonia, steam, hydrogen fluoride
The percentages by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in air are 78.08% and 20.95%. The partial pressures of the gases are 78.11 kPa and 21.22 kPa, respectively. Select the partial pressures that nitrogen and oxygen would exert if the atmospheric pressure was 404.32 kPa.
a. 300.00 kPa and 80.00 kPa
b. 315.69 kPa and 84.71 kPa
c. 278.12 kPa and 78.25 kPa
d. 318.18 kPa and 87.29 kPa
b. 315.69 kPa and 84.71 kPa
Which of the following statements compares the rates of effusion of helium and methane? a. Methane effuses 0.200 as fast as helium.
b. Helium effuses 0.250 as fast as methane.
c. Methane effuses 0.500 as fast as helium.
d. Helium effuses 0.400 as fast as methane.
c. Methane effuses 0.500 as fast as helium.
Death Valley in California is 86 m below sea level. Select the option that describes the partial pressure of oxygen in Death Valley.
a. The partial pressure will be the same as at sea level at all times.
b. The partial pressure will be lower than at sea level at all times.
c. The partial pressure will be higher than at sea level at all times.
d. The partial pressure will be higher than at sea level at some times and lower at other times.
c. The partial pressure will be higher than at sea level at all times.
If the volume of freshwater lakes were to increase over the next few years due to climate change, what event occurring in the biosphere would most likely be the cause?
a. receding oceans
b. eroding mountains
c. changing river courses
d. melting glaciers
d. melting glaciers
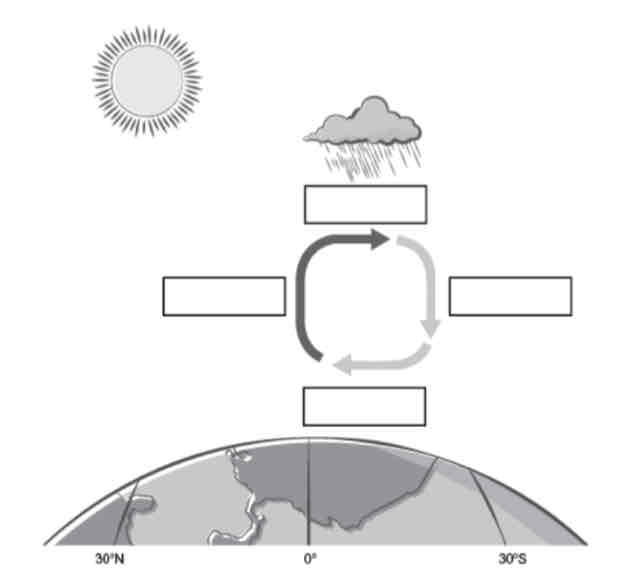
Use the air flow descriptions to fill in the diagram and show a simplified process of how air can move as a result of convection in the atmosphere.
a. Dry air becomes heavier
b. Cool air condenses as precipitation
c. Warm air expands and rises
d. air flows back towards equator
In the last 100 years, Arctic sea ice extent has decreased by more than 2 million square kilometers. Choose the answer that best explains how this impacts the overall albedo of Earth’s surface.
a. Albedo decreases because ice is very reflective.
b. Albedo does not change because water is just as reflective as ice.
c. Albedo increases because ice is very reflective.
d. Albedo remains stable in the summer and increases in the winter.
a. Albedo decreases because ice is very reflective.
What is the relationship between ocean temperature and carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere? Is it a reinforcing feedback or a counterbalancing feedback loop?
a. A warmer ocean holds less dissolved CO2. So it is a counterbalancing feedback loop.
b. A colder ocean holds less dissolved CO2. So it is a counterbalancing feedback loop.
c. A warmer ocean holds less dissolved CO2. So it is a reinforcing feedback loop.
d. A colder ocean holds less dissolved CO2. So it is a reinforcing feedback loop.
c. A warmer ocean holds less dissolved CO2. So it is a reinforcing feedback loop.
Climate is a pattern that happens over a longer period of time, while weather involves short-term conditions.
Read each of the sentences that describe either a climate pattern or weather-related factor.
Classify each description in the corresponding box.
1 A supercontinent creating alternating monsoon periods
2 Regional air pressure during storm
3 Increase in solar output
4 Current air temperature and moisture
5 Period of large glacial formation
6 Cold and warm fronts meeting
Climate Pattern | Weather-related factor |
A supercontinent creating alternating monsoon periods Increase in solar output Period of large glacial formation | Regional air pressure during storm Current air temperature and moisture Cold and warm fronts meeting |
If clam shells contain a large amount of the oxygen-18 isotope, what could this indicate about the ocean water during the Phanerozoic Eon?
a. Ocean water was getting more diluted with melted water from glaciers.
b. The oxygen-18 isotopes were not as prevalent in ocean water during that time period.
c. Ocean water was evaporating, thus increasing the concentration of the oxygen-18 isotope.
d. Ocean water was getting colder because of all of the glaciers forming.
a. Ocean water was getting more diluted with melted water from glaciers.
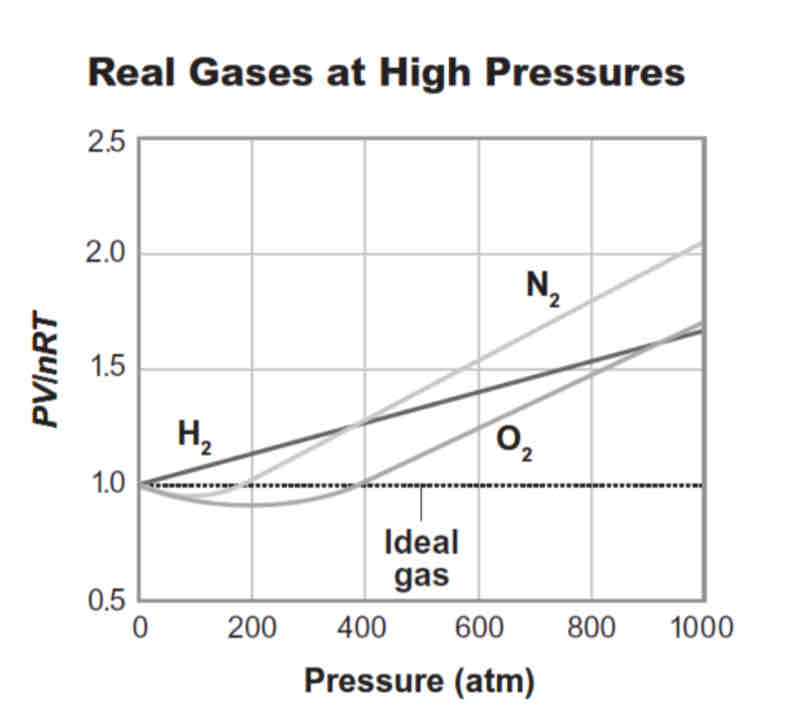
The image shows how real gases deviate from ideal gas behavior. What two particle properties of an ideal gas are different from the properties of a real gas? How are these two properties different in an ideal gas?
The two particle properties that are different in an ideal gas are the size of the particles and the intermolecular attractive forces between the particles. The particles in an ideal gas have an infinitesimal/insignificant size and no intermolecular attractive forces between the particles.
There are many different sources of greenhouse gases. Several of them are related directly or indirectly to human activity.
Which of the following is a correct list for the sources of emissions for the following gases: carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and CFCs? The answer must be in the same order as the gases.
a. fossil fuel burning, fertilizers, decay of biomass, refrigerants
b. fertilizers, refrigerants, decay of biomass, fossil fuel burning
c. fossil fuel burning, decay of biomass, fertilizers, refrigerants
d. fertilizers, decay of biomass, fossil fuel burning, refrigerants
c. fossil fuel burning, decay of biomass, fertilizers, refrigerants
Global climate change has many potential consequences that computer simulations can help predict.
Which of the following are consequences of climate change? Select all that apply.
a. spread of diseases
b. disappearing glaciers
c. vegetation shifts
d. magnetic pole reversal
e. longer solar periods
f. more frequent famines and fires
a. spread of diseases
b. disappearing glaciers
c. vegetation shifts
f. more frequent famines and fires
Which of the following are renewable resources? Select all that apply.
a. natural gas
b. biomass energy
c. oil and gas drilling
d. tidal energy
e. geothermal energy
b. biomass energy
d. tidal energy
e. geothermal energy
The figure shows the potential future outcome results of the Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) model scenarios. In this case the outcomes are for concentrations of carbon dioxide and carbon dioxide emissions. The RCP scenarios use different levels of radiative forcing to run their models.
The main graph shows the amount of carbon emissions required between now and 2100 in order to produce the CO2 pathways shown in the inset.
The four RCP scenarios show human-induced radiative forcing, in W/m2, in the year 2100. For each scenario, a line shows Earth’s mean atmospheric CO2 levels between now and 2100.
Examine the outcome of the RCP scenarios for carbon dioxide concentrations. Give a general explanation of why the concentration outcomes make sense given the different radiative forcing values.
The model data makes sense because the highest radiative forcing has the highest projected CO2 concentration, and the lowest radiative forcing has the lowest projected CO2 concentration.
A chemical company has developed scented air fresheners as their new product line. The company came up with four scented air fresheners containing different scents: lemon, vanilla, strawberry, and rose. The molar masses of each product are as follows: lemon (154 g/mol), vanilla (152 g/mol), strawberry (206 g/mol), and rose (155 g/mol). The products are packaged in closed containers and are stored in a storage room. One day, a technician walked by the storage room and noticed a strong strawberry scent. The technician discovered that the scent was coming from the storage room and one of the containers had been opened. None of the products had been damaged.
5. If the rose and strawberry containers were both found to be opened in the storage room, how would the kinetic energy and velocity of the particles in each container compare?
a. The velocity of the strawberry particles would be greater than the rose particles,
but the kinetic energy would be the same.
b. The kinetic energy of the strawberry particles would be greater than the rose,
particles but the velocity would be the same.
c. The velocity of the rose particles would be greater than the strawberry particles,
but the kinetic energy would be the same.
d. The kinetic energy of the rose particles would be greater than the strawberry
particles, but the velocity would be the same.
c. The velocity of the rose particles would be greater than the strawberry particles,