physiology exam 1
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
nervous system (NS)
one of two main control systems in body
NS responds to stimulus from inside or outside the body
inside ex: felling full
outside ex: stepping on a pin
NS functions
sensory function
integrative function (carried out by CNS)
motor function
NS sensory function
detection of internal and external stimuli by sensory receptors
nerve impulses travel toward CNA along sensory neurons
NS integrative function
carried out by CNS
processing of sensory information, sending messages to appropriate effector
effectors - targets (ex: muscles, glands)
NS motor function
generation of responses to initial stimulus
nerve impulses travel away from CNS along motor neurons which lead to effectors throughout the body
effectors carry out the response
CNS-PNS neuron organization
sensory and motor neurons — peripheral NS
interneurons — central NS
CNS
brain and spinal cord
integrative and control centers
PNS
cranial nerves, spinal nerves, sensory receptors in skin
communication lines between CNS and rest of body
PNS organization
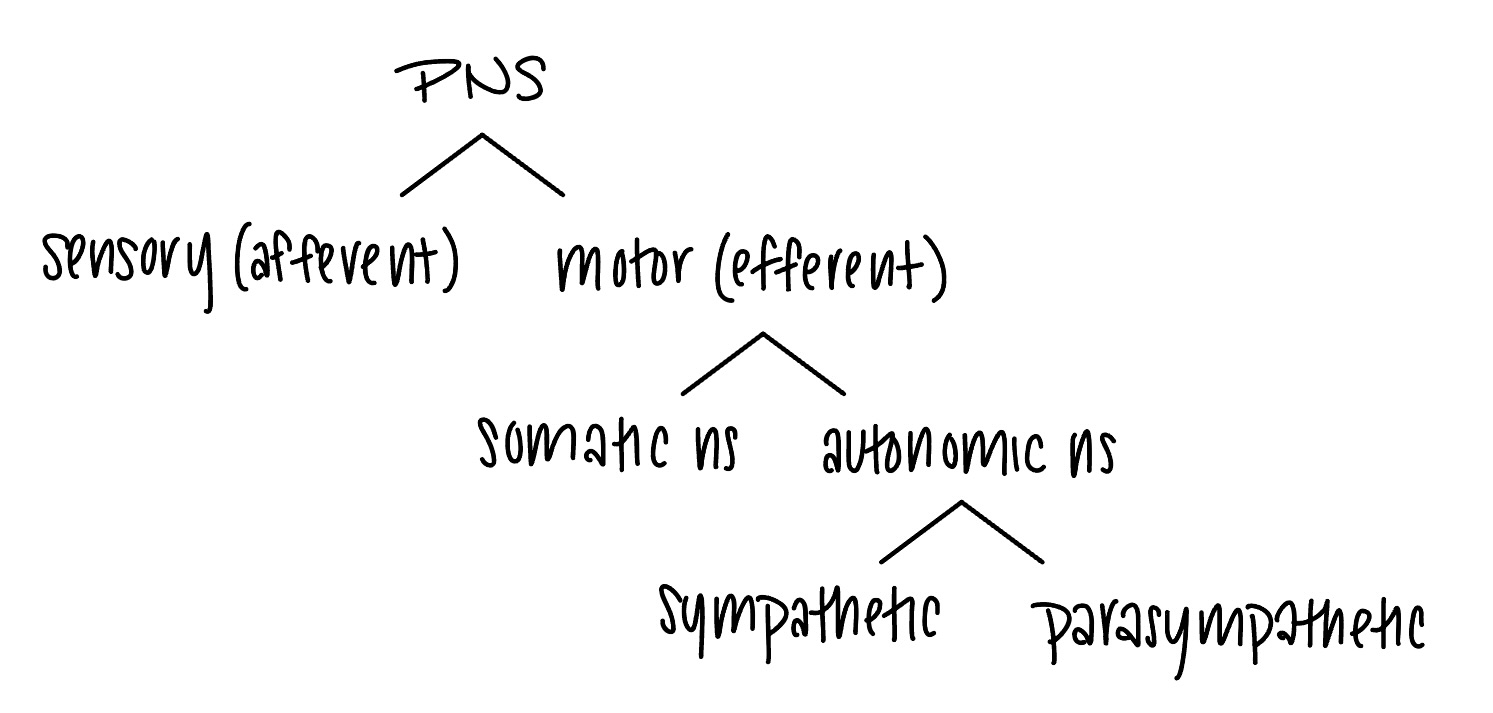
sensory (afferent) division
somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibers
conducts impulses from receptors to the CNS
motor (efferent) division
motor nerve fibers
conducts impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands)
somatic ns
somatic motor (voluntary)
conducts impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
skin, skeletal muscles, joints
autonomic ns
visceral motor (involuntary)
conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, and glands
coming from internal organs
sympathetic divison
mobilizes body systems during activity
parasympathetic division
conserves energy
promotes house-keeping functions during rest
neuron
nerve cell
conducts electrical impulses and releases chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) to communicate with other cells
neuron parts
cell body (soma)
dendrites
axon
axon hillock
axon terminals/synaptic bulbs
cell body (soma)
contains organelles, makes NT
cluster of cell bodies in PNS - ganglia
cluster of cell bodies in CNS - nuclei
dentrites
receiving end of a neuron
receive signals from other neurons or from stimuli in the environment
axon
transmits impulses away from cell body
<1mm to >1m in length
bundle of axons in PNS - nerve
bundle of axons in CNS - tract
axon hillock
area where impulses (action potentials) are initiated
mixed/single nerves
contain both sensory and motor fibers (axons)
referred pain
pain stimuli from visceral organs are perceived at a site other than the place of origin
axon terminals/synaptic bulbs
store NT molecules in synaptic vesicles
secrete NT via exocytosis
synapse
where a neuron meets its target
cells in neuroglia
nourish, protect, and support neurons
maintain homeostasis of cerebrospinal fluid\
oligodendrocytes - surround CNS axons, form myelin sheaths
schwann cells - surrounds PSN axons, form myelin sheaths
myelin
lipid and protein wrapping that surrounds the axon
myelin functions
electrically insulates the axon
increases speed of nerve impulse conduction
nodes of ranvier - areas without myelin
myelin - faster conduction
occurs along myelinated, larger diameter axons
myelin - slower conduction
occurs along unmyelinated, smaller diameter axons
opening of ion channels (integral membrane protiens)
allows charge flow across membrane
type of ion channel - leak channel
transiently open and close
type of ion channel - gated channel
open in response to a stimulus
gated ion channels - chemically gated ion channels
open in response to binding of the appropriate neurotransmitter (facilitated diffusion)
gated ion channels - voltage gated ion channels
open in response to changes in membrane potential (facilitated diffusion)
other types of gated ion channels
mechanically gated
thermally gated
graded potentials
occurs mainly in cell bodies and dendrites
types of graded potentials:
depolarizing and hyperpolarizing
vary in size/amplitude according to the strength of the stimulus
stronger stimuli open more ion channels, leading to a larger graded potential
can summate (they can add together)
names according to their location
on motor end plate of skeletal muscle = end plate potential
after a synapse on a postsynaptic cell/target = postsynaptic potential
depolarizing graded potential
potential becomes less negative compared to resting potential
> -55mV
are excitatory and are essential for triggering action potential
more likely to fire impulse
hyperpolarizing graded potential
potential becomes more negative compared to resting potential
< -55mV
are inhibitory and neuron are less likely to fire impulse (AP)
EPSP
excitatory postsynaptic potential
depolarizing
bring the neuron closer to AP threshold (-55mV)
IPSP
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
polarizing
drive the neuron away from AP threshold (-55mV)
action potential
series of rapidly occurring events that cause a large change in membrane potential
always same size/amp regardless of stimulus strength
has refractory periods
always begins as an excitatory (depolarizing) graded potential
occurs if depolarization brings membrane potential to threshold potential
What are the differences/ similarities between graded and action potentials?
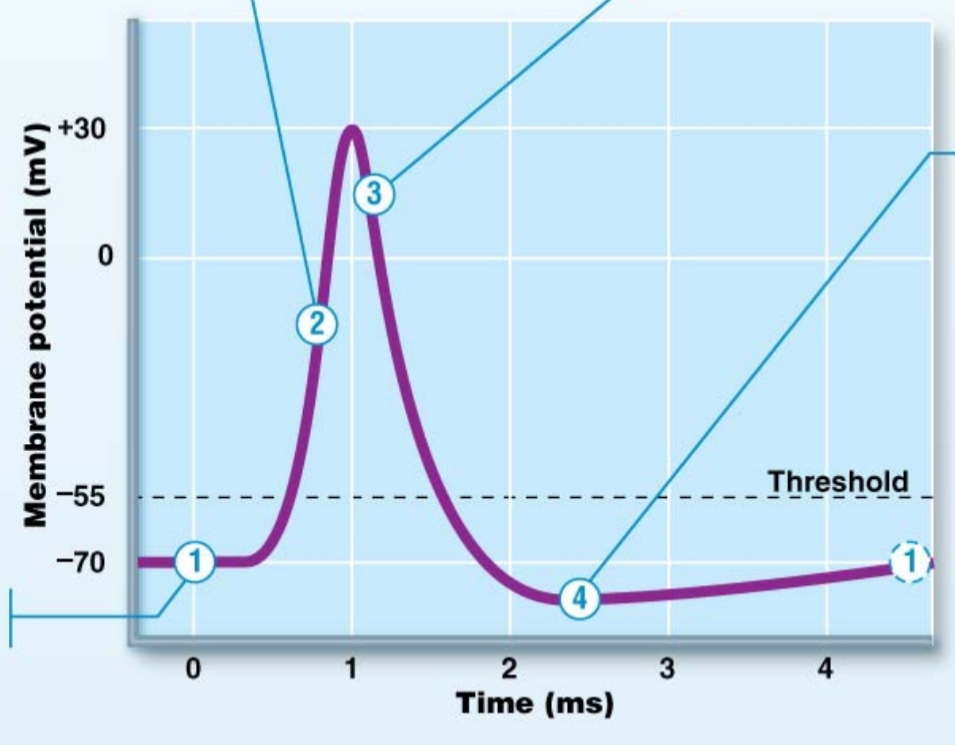
action potential diagram
AP voltage changes occur as a result of the opening and closing of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels in the neuronal membrane
voltage grated Na+ channels during AP
Na+ down its gradient (into cell) - facilitated diffusion
closed - not crossing; activation gate is closed
opened - crossing; activation gate is open
inactivated - prevents Na+ from crossing; inactivation gate blocking
inactivation will switch back to closed when potential returns to -70mV
voltage grated K+ channels during AP
K+ down its gradient (out of cell) - facilitated diffusion
closed - not crossing; activation gate is closed
opened - crossing; activation gate is open
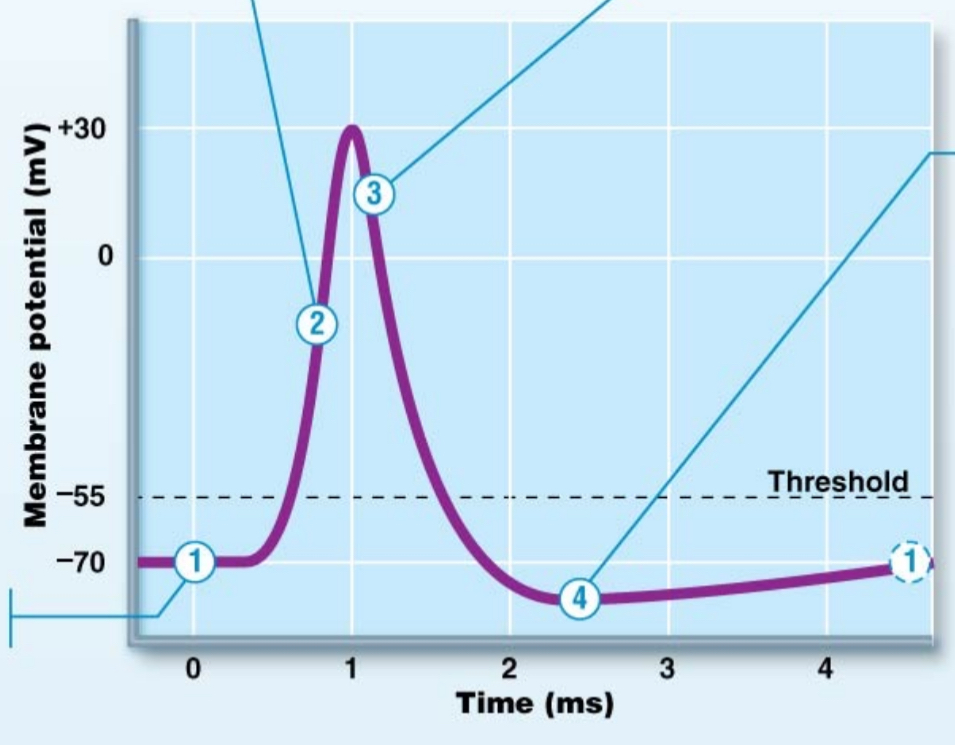
action potential - #1
resting state / resting potential
-70mV
gated channels closed
action potential - #1a
stimulus has opened gated channels (not voltage; either chemical or mechanical)
depolarization occurs and spreads to axon hillock (current flow)
threshold potential = -55mV
once threshold potential is reached, AP will occur
if stimulus isn’t powerful enough to get membrane to -55mV, it returns to rest (no AP)
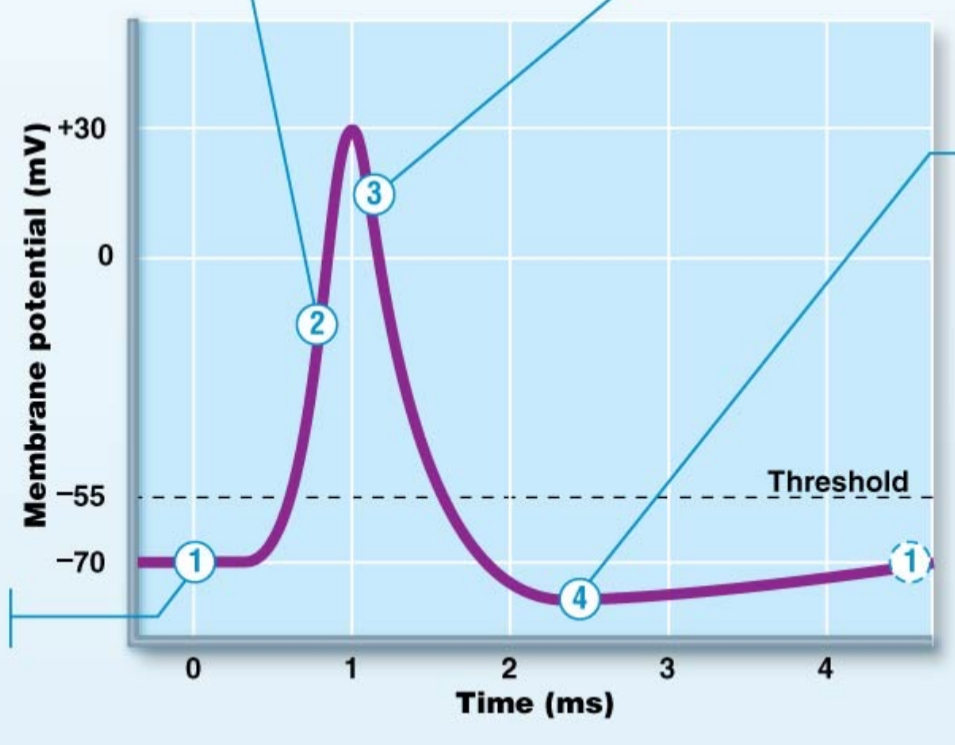
Action potential - #2
depolarization
voltage gated Na+ channels open
Na+ rushes in > rapid depolarization
positives are getting added inside so it gets less negative

action potential - #3
voltage gated Na+ channels inactive
voltage gated K+ channels open
K+ flows out of neuron > rapid repolarization
positives are leaving the neuron
repolarization
returning to resting potential
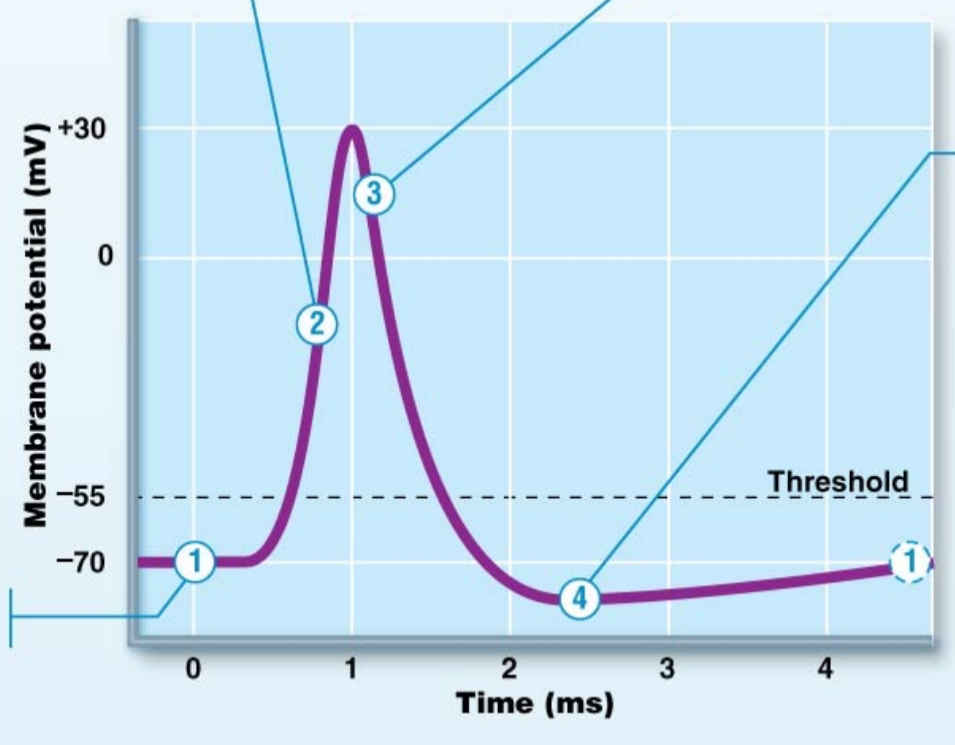
action potential - #4
K+ channels are still open > hyperpolarization
positives still leaving neuron; getting even more negative
once K+ channels close, resting membrane potential is re-established (-70mV)
at resting membrane potential > unequal leakage of Na+/K+ pumps
absolute refractory period
excited neuron cannot generate a second action potential
from -55mV until membrane is back down to -70mV
relative refractory periods
AP can be initiated by a suprathreshold stimulus during period of hyperpolarization
would need an extremely strong stimulus to bring the membrane potential from below -70mV back up to -50mV
how do neurons communicate with their targets?
stimulus > AP initiated at axon hillock > electrical signal across axon > neurotransmitter > effector/target
propagation of an action potential along unmyelinated axons
continuous conduction
wave of depolarization spreads one-way down axon
voltage gated Na+ channels are opened in succession all along the membrane
APs occur all along the axon
have leakage through leak channels
slows down conduction
propagation of an action potential along unmyelinated axons
saltatory conduction
APs only occur at nodes of Ranvier
current passes quickly inside myelinated areas of axon
faster conduction
How are action potentials propagated down the axon?
what events occur when the impulse reaches the axon terminal?
removal of neurotransmitter from cleft
diffusion
enzyme degradation of neurotransmitter
ex: acetylcholinesterase enzyme breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
reuptake into presynaptic neuron
neurotransmitter is actively pumped back into the presynaptic axon terminal that released it
summation
ability of postsynaptic neuron to “add up” EPSPs and IPSPs and generate an appropriate response
if the net summation of EPSP and IPSP brings the membrane to threshold, neuron will fire
brain - cerebrum
divided into right and left cerebral hemispheres
connected via corpus callosum
brain - 5 cerebral hemisphere lobes
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
insula (sensing emotions)
frontal lobe
motor function, conscious, thought; short term memory
parietal lobe
somatosensory (touch, temperature)
temporal lobe
hearing, language
occipital lobe
vision
cerebrum three main regions
cerebral cortex (outer surface)
highly convoluted gray matter
most complex integrating area of the brain
site of conscious mind: awareness, sensory perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, understanding
internal white matter
basal nuclei
gray matter
darker
cell bodies, dendrites, glial cells
integration of sensory input and motor output occurs via synapse
white matter
white
tracts of myelinated and unmyelinated axons
signal transmission between parts of cortex and between cortex and other regions of CNS
cerebral cortex
highly convoluted gray matter
most complex integrating area of the brain
site of conscious mind: awareness, sensory perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, understanding
three types of functional areas
motor areas - controls voluntary movement
sensory areas - conscious awareness of sensation
association areas - integrate diverse information (making sense of stimulus)
language - broca’s area
present in left hemisphere
motor speech areas that directs muscles of speech production
active in planning speech and voluntary motor activities
language - wernicke’s area
left cortex at the juncture of parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes
associated with language comprehension of spoken and written messages
aphasia
language disorder due to damage in cortical areas
expressive aphasia (broca’s aphasia)
“non fluent” aphasia
difficulty producing words, saying the correct words
receptive aphasia (wernicke’s aphasia)
“fluent” aphasia
language comprehension and understanding the meaning of words is impaired but speech production is not impaired
brain stem
consists of midbrain, pons and medulla
contains centers that control cardiovascular and respiratory functions
cerebellum
coordination
smoothing out movement
balance
important in coordinating thought and emotions
thalamus
afferent fibers from all parts of body synapse onto one or more nuclei in thalamus
“grand central station”
“screens out” insignificant signals
cerebrum - basal nuclei
“islands of gray matter” within cerebral white matter
influence muscle movements
select and maintain purposeful motor activity
control voluntary and habitual movements
inhibit antagonistic/unnecessary movement
limbic system
functional brain system
network of neurons that function together
associated with emotions, inborn survival patterns, motivation, learning, memory
include amygdala and hippocampus
amygdala
important in emotions of all types
hippocampus
important in consolidation of memories from short-term to long term
meninges
protect CNS
three connective tissue layers
dura mater - outermost
arachnoid mater - middle
pia mater - innermost
blood-brain barrier
protect CNS
refers to impermeable capillaries in brain
only allow certain substances to cross
limits access of blood-borne materials into brain tissue
O2, CO2, water, lipid-soluble substances can cross via simple diffusion
glucose crosses via facilitated diffusion
maintained by astrocytes
importance of blood, glucose, oxygen to the brain
brain depends on constant blood supply
brain metabolizes exclusively aerobically (required O2)
preferred fuel for brain: glucose
body exhibits “glucose sparing” activities to ensure adequate glucose supply for brain
“glucose sparing” helps the body spare (conserve) glucose for tissues that need it most
stoke (cerebrovascular accicent)
part of the brain deprived of O2 and nutrients
causes of stoke
clot in blood vessels within brain or leading to brain
leads to impaired blood flow to a tissue = ischemia
hemorrhage = blood loss, “brain bleed”
divisions of autonomic nervous system
parasympathetic and sympathetic
parasympathetic division
dominates in quiet and relaxed situations
“rest and digest” division
activities support body functions that conserve energy, restore energy during recovery and/or rest periods
main parasympathetic responses/actions: (3 decreases and 3 Ds)
3 decreases
heat rate
airway diameter
pupil diameter
3 Ds
digestion (increased GI smooth muscle contraction, increased secretory activity in GI tract)
defecation
diuresis (urination - bladder smooth muscle contracts)
sympathetic division
most active in stressful situations
“fight or flight” system
exercise, excitement, emergency, embarrassment
increased heart rate, increased force of heart contraction (contractility)
blood vessels supplying skeletal muscles and heart dilate (vasodilation)
blood vessels supplying GI tract and kidneys constrict (vasoconstriction)
respiratory airways dilate (via relaxation of airway smooth muscle)
smooth muscle of GI tract relaxes (digest activity slows)
bladder smooth muscle relaxes (no urination)
pupils dilate
receptors ACh binds to
cholinergic receptors
types of cholinergic receptors
nicotinic receptors (N1-N2)
found on skeletal muscle and on all postganglionic neurons
muscarinic receptors (M1-M5)
found on all parasympathetic targets
receptors norepi and epi binds to
adrenergic recepetors
types of adrenergic receptors
alpha-1
beta-1
beta-2
(all found on many organs throughout the body)
autonomic nervous system
system of motor neurons that innervates cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands; involuntary
neurotransmitters - acetylcholine (ACh)
neuron that releases ACh = cholinergic neurons
receptors that binds ACh = cholinergic receptors
neurotransmitters - biogenic amines (from amino acids)
serotonin
catecholamines
dopamine
norepinephrine - main NT of sympathetic branch of autonomic NS
epinephrine (adrenaline) - mainly released by adrenal glands
neuron that releases norepi/epi = adrenergic neuron
receptor that binds to norepi/epi = adrenergic receptor
neurotransmitter - amino acids
glutamate - main excitatory NT in CNS
gaba - main inhibitory NT in CNS
aspartate
glycine
CNS and PNS contain?
CNS : contains many types of neurotransmitters
PNS : contains mainly ACh, norepi, epi