2.2.1 Characteristics of aggregate demand
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
AGGREGATE DEMAND- DEFINITION
the total level of spending in the economy at any given price
COMPONENTS OF AD
AD= C+l+G+(X-M)
made up of consumption (C), investment (I), government spending (G) and net exports (X-M)
CONSUMPTION
consumer spending on g and s
makes up about 60% of AD
INVESTMENT
spending by firms on capital goods (e.g. new equipment)
makes up about 15-20% of AD
most investment is by the private sector (about 75%) but there is also investment by the gov
GOVERNMENT SPENDING
spending by the gov on providing g and s (public and merit goods), wages and salaries of public sector workers and on investment goods like new roads and schools
transfer payments (e.g. pensions and jobseekers' allowances) not included as money is just transferred from one group to another
gov spending is around 18-20% of GDP
NET EXPORTS
exports minus imports
when imports>exports=minus figure as more money leaves the UK than comes in
the UK has a large trade deficit, but this minor figure and is the least significant part of AD at around 5%
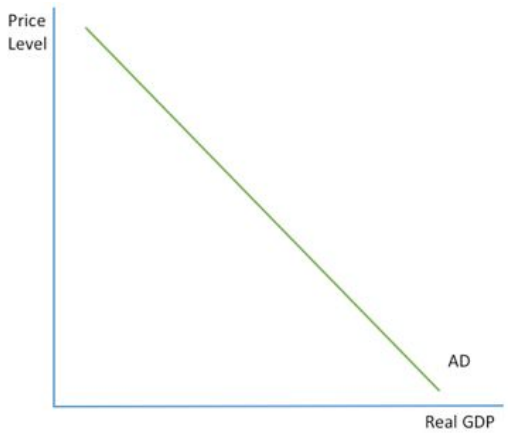
AD CURVE
same as demand curve for an individual market
instead shows the relationship between general price level and real GDP
AD curve is downward sloping as a rise in prices causes a fall in real GDP (inverse relationship)
4 reasons for this:
income effect
substitution effect
real balance effect
interest rate effect
INCOME EFFECT
as a rise in prices is not matched straight away by a rise in income, people have lower real incomes so can afford to buy less, leading to a contraction demand
SUBSTITUTION EFFECT
if prices in the UK rise, less foreigners will buy British exports and more UK residents will buy imported foreign goods bc they’re cheaper
rise in imports and fall of exports will decrease net exports so AD will contract
REAL BALANCE EFFECT
rise in prices means the amount people have saved up will no longer be worth as much and so will offer less security
they will want to save more and so reduce their spending, causing a contraction in AD
INTEREST RATE EFFECT
rising prices mean firms have to pay their workers more and so there is higher demand for money
if supply stays the same, then the 'price of money' i.e. interest rates will rise because of this higher demand
higher interest rates mean that more people will save and less will borrow and will also mean that businesses invest less, so AD will contract
MOVEMENT ALONG AD CURVE
movement along the AD curve is caused by a change in prices, caused by inflation or deflation
SHIFT OF AD CURVE
shift of the AD curve is caused by a change in any other variable
right shift represents increase in AD and left shift represents decrease in AD
absolute change: fall in the amount of consumption reduces AD
rates of change: fall in the rate of rise of consumption means that consumption is still rising so AD will still increase but by not as much