Micro Exam 1 Study Guide Questions
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
1
New cards
In what ways are microorganisms important to humans?
Negative- Food spoilage and foodborne disease
Positive- Food safety, preservation
Biofuels, Wastewater treatment, bioremediation, biofilms
gut microbiomes
Positive- Food safety, preservation
Biofuels, Wastewater treatment, bioremediation, biofilms
gut microbiomes
2
New cards
What is a bacterial colony and how is on formed?
streak for isolation- A population of cells all formed from one cell
3
New cards
How can you get a pure culture of bacteria and why are pure cultures important?
Streak for isolation- Give you one type of bacteria- Important because there are no other bacteria that could influence results
4
New cards
where do you find microorganisms and do they typically live in a pure culture?
Microorganisms found everywhere and they do not live in a pure culture- There is not usually only one type of bacteria in an area
5
New cards
What cellular structures distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Pro- Cell wall, 70S Ribosomes, No nucleus
Euk- No cell wall, 80S Ribosomes, Mitochondria, ER, Golgi, Nucleus,
Euk- No cell wall, 80S Ribosomes, Mitochondria, ER, Golgi, Nucleus,
6
New cards
What are some differences between a cell wall and a cell membrane?
Cell wall- made of polysaccharides, Rigid
Cell Membrane- made of phospholipids, Flowy, Contains proteins and carbs within the wall, Selectivity permeable
Cell Membrane- made of phospholipids, Flowy, Contains proteins and carbs within the wall, Selectivity permeable
7
New cards
In what types of organisms would you expect to find cell walls and or cell membranes?
All cells have a cell membrane but few have cell wall
Plants, bacteria, and fungi have cell walls
Plants, bacteria, and fungi have cell walls
8
New cards
How has the Earth changed over its history? How have microorganisms contributed to these changes?
First cells- 3.8-4.3 billion years ago, Atmosphere had no oxygen, Only anaerobic
Cyanobacteria- 2.6 billion years ago, started to produce oxygen as a byproduct, Allowed for eukaryotic cells to exist
Cyanobacteria- 2.6 billion years ago, started to produce oxygen as a byproduct, Allowed for eukaryotic cells to exist
9
New cards
Name the three domains of life. Which of these contain eukaryotic life forms? How are they similar and different?
Bacteria- Pro, 0.5-10 micrometers long
Archaea- Pro, extreme environments
Euk- Plants, animals, fungi, protists
Archaea- Pro, extreme environments
Euk- Plants, animals, fungi, protists
10
New cards
Why were cyanobacteria so important in the evolution of life on Earth? What is a genus name of a cyanobacterium and what is unique about these organisms?
produced oxygen and allowed for aerobic life
11
New cards
How do microbes contribute to the nutrition of animals such as humans and cows?
Humans- Found in the gut to help break food and aid digestion, Break down carbs, Synthesize vitamins and nutrients
Cows- Found in the four chambered stomach, Helps break down cellulose for cows to digest grass
Cows- Found in the four chambered stomach, Helps break down cellulose for cows to digest grass
12
New cards
Describe several ways in which microorganisms are important in the food and agricultural industries.
Food- Can cause food spoilage and disease but also helps with preservation, Fermentation
Ag- Soil enrichment, Nitrogen fixing bacteria
Ag- Soil enrichment, Nitrogen fixing bacteria
13
New cards
What is wastewater treatment and why is it important?
Wastewater treatment is the removal of contaminants from waste water- Important because it allows us to recycle water creating an endless resource
14
New cards
What is the difference between magnification and resolution?
Magnification is the ability to enlarge an image, resolution is the ability to tell 2 different object apart
15
New cards
what is the function of staining in light microscopy
Cells are not normally colored(Cells are 70% water so usually transparent), and staining cells allows us to have some contrast between the cell and the background
16
New cards
What color will a gram-negative cell be after Gram staining by the conventional method? Gram positive? Why?
Gram negative- Pink/red- Thin PG cell wall
Gram positive- Purple- Thick PG cell wall
Gram positive- Purple- Thick PG cell wall
17
New cards
What are the steps of a gram stain and the function of each reagent?
Crystal violet- Stain all the cell purple
Grams Iodine- mordant- Combines CV and CVI
70% Ethanol- Decolorizer- Removes CVI from the gram negative bacteria
Safranin- Counterstain- Makes G- red/pink
Grams Iodine- mordant- Combines CV and CVI
70% Ethanol- Decolorizer- Removes CVI from the gram negative bacteria
Safranin- Counterstain- Makes G- red/pink
18
New cards
What major advantage does phase-contrast microscopy have over staining?
Don’t have to stain anything, Cells can be live and in their natural form
19
New cards
How can cells be made to fluoresce?
They can be naturally fluorescent or be stain with a fluorescent dye
20
New cards
What type of microscope would be used to view the three-dimensional features of a cell? Of the internal parts of a cell? Why?
Scanning electron microscope- Coat cells in gold- See the outside
Transmission microscope- See the inside of cells
Transmission microscope- See the inside of cells
21
New cards
Explain how Pasteur disproved spontaneous generation.
2 flasks- one with a straight neck one with a curved neck and both with nutrient broth
Boiled both to kill any bacteria
Let them sit
Flask with a straight neck became colored showing bacteria growth
Flask with curved neck stayed sterile
Bacteria fell into the straight neck and bacteria could not climb up curved neck
Disproved theory of spontaneous generation of bacteria- Bacteria has to come from somewhere, cannot just apprear
Boiled both to kill any bacteria
Let them sit
Flask with a straight neck became colored showing bacteria growth
Flask with curved neck stayed sterile
Bacteria fell into the straight neck and bacteria could not climb up curved neck
Disproved theory of spontaneous generation of bacteria- Bacteria has to come from somewhere, cannot just apprear
22
New cards
Explain Koch’s postulates.
There is a cause and effect in infection diseases, Diseases don’t not just appear- Has to come from bacteria
23
New cards
What advantages do solid media offer for the isolation of microorganisms? What is an example of a solid bacteriological medium? Liquid growth medium?
In a solid media- You have colonies that are isolated, but in a liquid growth medium there is no separation
Solid- TSA
Liquid-TSB
Solid- TSA
Liquid-TSB
24
New cards
what is a pure culture?
colony of bacteria only made up of one type of bacteria
25
New cards
Describe Griffith’s transformation experiment.
transformation- DNA can be picked up and incorporated into another genome
Type R does not kill mice, Type S does
Just R= mice live
Type R and Type S= Eventually just type S- Kill Mice
Type R and Heat killed type S= Eventually just type S- Kill mice
Type R and type S DNA= Eventually just type S- Kill Mice
Type R does not kill mice, Type S does
Just R= mice live
Type R and Type S= Eventually just type S- Kill Mice
Type R and Heat killed type S= Eventually just type S- Kill mice
Type R and type S DNA= Eventually just type S- Kill Mice
26
New cards
what is a phylogenetic tree and what does it tell you?
depicts evolutionary history of all cells
27
New cards
What are the contributions to microbiology associated with the following people…Robert Hooke, Antoni van Leeuwenhoek, Louis Pasteur, Robert Koch, Frederick Griffith, Carl Woese
Hooke-First to see microorganism
Leewenhoek- First to see bacteria, made hos own microscope, “wee animulcus”
Pasteur-Disprove theory of spontaneous generation
Koch-Koch postulates- Infectious disease has to come from somewhere
Griffith-Transmission- uptake of free DNA
Woose-RNA could be used to look at evolutionary relationships, Made a new category(Archaea)
Leewenhoek- First to see bacteria, made hos own microscope, “wee animulcus”
Pasteur-Disprove theory of spontaneous generation
Koch-Koch postulates- Infectious disease has to come from somewhere
Griffith-Transmission- uptake of free DNA
Woose-RNA could be used to look at evolutionary relationships, Made a new category(Archaea)
28
New cards
Define sterile in terms of microbiology. Name at least two ways to sterilize microbiological media…
sterile- free from all living organisms and viruses
autoclave and membrane filtration can be used to sterilize
autoclave and membrane filtration can be used to sterilize
29
New cards
Why are *Archaea* more closely related to *Eukarya* than *Bacteria* are to *Eukarya*?
archaea have more similar genes and metabolic pathways to eukarya than bacteria does
30
New cards
How do cocci and rods differ in morphology? Give an example of a bacteria with each morphology.
Cocci- Round, sphere- Staphylococcus aureus
Rods- Long, cylindrical- Bacillus cereus
Rods- Long, cylindrical- Bacillus cereus
31
New cards
Using a microscope, could you differentiate a coccus from a spirillum? A pathogen from a nonpathogen?
coccus are spheres, spirillum are spiral shaped
32
New cards
Draw the basic structure of a phospholipid bilayer and label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. Why is the cytoplasmic membrane a good permeability barrier?
Polar, hydophilic heads on the outside of the bilayer(Outside of cell and inside of cell), Hydrophobic tails on the inside of bilayer
Lots of membrane proteins within
Has selective permeability so only certain things can enter
Lots of membrane proteins within
Has selective permeability so only certain things can enter
33
New cards
how are the membrane lipids of bacteria and archaea similar, and how do they differ?
bacteria/eukarya produce membrane lipids with hydrophobic fatty acid tails that are ester bound to glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P)
archaea make membrane lipids with hydrophobic tails that are ether linked to glycerol-1-phosphate (G1P)
archaea make membrane lipids with hydrophobic tails that are ether linked to glycerol-1-phosphate (G1P)
34
New cards
describe the major functions of the cytoplasmic membrane
barrier of outside and inside of cell
allow certain things to pass
allow certain things to pass
35
New cards
Why do bacterial cells need cell walls? Do all bacteria have cell walls?
Allows a higher chance of survival
Maintain shape and pressure
Maintain shape and pressure
36
New cards
Why is peptidoglycan such a strong molecule?
bonds between amino acids
37
New cards
Describe the major differences between the cell walls of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
Gram negative has thin cell wall, outer membrane and gram positive has thick cell wall
38
New cards
Explain whether you expect the enzyme lysozyme to be equally effective against *Bacteria* and *Archaea*
Lysozyme is effective against peptidoglycan as it can cleave the beta 1-4 bonds between the sugars, but archaea does not have peptidoglycan and is not affected by lysozyme.
39
New cards
What do the enzyme lysozyme and the antibiotic penicillin have in common?
They both are effective in destroying the cell wall of bacteria as lysozyme can attack the bonds between sugars and penicillin can attack the bonds between peptides
40
New cards
Describe the major chemical components in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
O-polysaccride, core polysaccharide, lipid A
41
New cards
What is the function of porins and where are they located in a gram-negative cell wall?
transmembrane protein channels for entrance and exit of solutes located in outer membrane
42
New cards
What component of the gram-negative cell has endotoxin properties?
Lipid A, the toxic component of LPS in the outermembrane
43
New cards
What is pseudomurein and where is it found?
the major cell wall component of gram-positive methanogenic archaea, is composed of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (NAG) and N-acetyl-L-talosaminuronic acid (NAT) located in the cell wall
44
New cards
What is the value of a cell having a capsule? What is the capsule composed of and where is it found? Name a bacterium that has a capsule.
Value of a capsule is that it helps the bacteria avoid phagocytosis, assist in attachment to surfaces,
role in development and maintenance of biofilms, contribute to infectivity, prevent dehydration/desiccation. Composed of polysaccharides. Rhodobacter capsulatus
role in development and maintenance of biofilms, contribute to infectivity, prevent dehydration/desiccation. Composed of polysaccharides. Rhodobacter capsulatus
45
New cards
How do fimbriae differ from pili?
Fimbriae= attachment (shot multiple projections) bristle like short fibers on surface of bacteria. Pili= conjugation, long hair like tubular microfibers found on surface of bacteria.
46
New cards
What is dipicolinic acid and where is it found?
Found in Endospores, enriched in Ca2+, plays a role in the heat resistance of bacterial endospores.
47
New cards
What is formed when an endospore germinates? What causes a cell to make endospores?
Sporulation= vegitative cell(active bacteria cell that undergoes metabolism.) Limiting nutrients trigger endospore formation.
48
New cards
Name two genera that produce endospores and how are the different?
the genus Bacillus (an obligate aerobe often living in the soil) and the genus Clostridium (an obligate anaerobe living in the gastrointestinal tract of animals) produce endospores.
49
New cards
Cells of *Salmonella* are peritrichously flagellated, those of *Pseudomonas* polarly flagellated, and those of *Spirillum* lophotrichously flagellated. Using a sketch, show how each organism would appear in a flagellar stain.
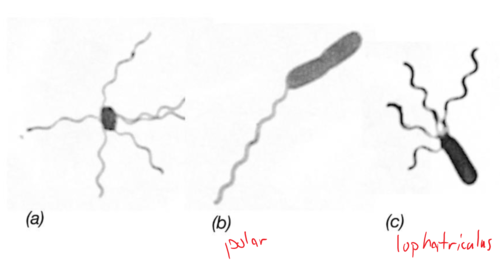
50
New cards
what is archealla and where are they found
structure that assists in swimming in bacteria and archaea, respectively found on surfaces of archaea
51
New cards
What is positive and negative chemotaxis? When would you see each?
Positive chemotaxis= movement towards higher concentration of chemicals
negative chemotaxis- movement of a cell away from chemical or physical gradient
negative chemotaxis- movement of a cell away from chemical or physical gradient
52
New cards
What are the gram reaction, morphology and arrangement of the following bacteria? *E. coli, Bacillus, Staphylococcus, Micrococcus, Streptococcus, Vibrio, Treponema* H
a. E. coli—negative, rod-shaped, single-cell or in clumps
b. Bacillus—rod-shaped, small chains, clumps, or single cell, positive
c. Staphylococcus—cocci in clusters, positive
d. Micrococcus—cocci in tetrads, positive
e. Streptococcus—cocci in chains, positive
f. Vibrio—curved, rod-shaped, negative
g. Treponema—negative, spiral
b. Bacillus—rod-shaped, small chains, clumps, or single cell, positive
c. Staphylococcus—cocci in clusters, positive
d. Micrococcus—cocci in tetrads, positive
e. Streptococcus—cocci in chains, positive
f. Vibrio—curved, rod-shaped, negative
g. Treponema—negative, spiral
53
New cards
How big is *E. coli?* How big is *Staphylococcus?*
E.coli= 1.0-2.0 micrometers long. Staphylococcus= 0.5-1.0 micrometers long
54
New cards
Compare and contrast gram positive and gram-negative cells. Draw a diagram of each and label the structures. What components are unique to each.
Gram-negative peptidoglycan is only a few nanometers thick, representing one to a few layers, Gram-positive peptidoglycan is 30–100 nm thick and contains many layers.
55
New cards
What value do gas vesicles give to bacteria?
provide buoyancy
56
New cards
What is the function of flagella? What are flagella made of?
Flagella help organism in movement and they are made of the protein flagellin
57
New cards
Compare and contrast a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell. Give examples of both. What are the functions of each of the components?
Prokaryotes are always unicellular, while eukaryotes are often multi-celled organisms. Both have plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes. Prokaryote= streptococcus. Eukaryote= yeast
58
New cards
How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ when it comes to reproduction? In general, how do bacteria, fungi (molds and yeast), plants and animals reproduce?
Prokaryote= asexual. Eukaryote= sexual. Bianary fission
59
New cards
explain endosymbiosis
a symbiotic relationship where one organism lives inside the other
60
New cards
do bacteria have cilia
No
61
New cards
How do bacterial endospores differ from fungal spores in function?
Fungal spores are reproductive structures, while bacterial endospores are survival structures.
62
New cards
what is phototaxsis
directional movement along a light vector towards (positive) or away from (negative) a light source
63
New cards
How does a chemoorganotroph differ from a chemolithotroph? A chemotroph from a phototroph? What does troph mean?
Chemoorganotroph- Get energy from organic materials
Chemolithotroph- Get energy froim inorganic coumpounds
Phototrophs- Energy from light
Troph means feeding
Chemolithotroph- Get energy froim inorganic coumpounds
Phototrophs- Energy from light
Troph means feeding
64
New cards
How does an autotroph differ from a heterotroph?
Auto- Obtain carbon from CO2
Hetero-Get carbon from organics
Hetero-Get carbon from organics
65
New cards
What are enzymes made of? Why is that important when it comes to high temperatures?
enzymes are made of proteins (sometimes RNA) and they can denature in high temps
66
New cards
where on the enzyme does the substrate binds?
active site- very specific for substrate
67
New cards
what is energy activation?
the energy required to being a chemical reaction- minimum energy required for molecules to become reactive
68
New cards
How is catabolism different from anabolism?
Catabolism- Breaking down of materials and making ATP--- Break bonds to get ATP
Anabolism- Building up of materials using ATP-----Make bonds
Anabolism- Building up of materials using ATP-----Make bonds
69
New cards
How is respiration different from fermentation?
Respiration is the complete breakdown of glucose into O2 and H20, whereas fermentation is the imcomplete breakdown of substrates------End in acids, alcohols, or Gases
70
New cards
What are some of the endproducts of fermentations?
acids, gases, alcohols
71
New cards
What yeast is commonly used for fermentations?
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
72
New cards
what happens in glycolysis
glucose breaks into 2 Pryuvic Acids (pyruvate)
73
New cards
How does glucose get into a cell?
facilitated diffusion- use of membrane protein
74
New cards
Where is the most ATP produced? Glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle or in the ETC?
electron transport chain
75
New cards
What is the final election acceptor in aerobic respiration and what does it form?
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor and it forms water
76
New cards
What is the final electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration?
Anything other than oxygen- Nitrate, Ferric iron(Fe+3), Sulfate(SO4) CO2
77
New cards
What is the carbon source for autotrophic organism? Energy source?
CO2, glucose
78
New cards
where do bacteria get their nutrients from?
photosynthesis, decomposing dead organisms and wastes, or breaking down chemical compounds
79
New cards
What happens during nitrogen fixation and what types of organisms fix nitrogen?
nitrogen fixation- bacteria in the soil and in roots of some plans convert nitrogen gas in the atmosphere to ammonia
typically bacteria
typically bacteria
80
New cards
Which four chemical elements make up the bulk of a cell’s dry weight?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
81
New cards
Which two classes of macromolecules contain most of a cell’s nitrogen?
DNA/RNA, proteins
82
New cards
Differentiate between trace metals and growth factors. How are these used by the cell?
Trace metals- Not organic
Growth factors- Not found in the environment, have to be made/ synthesized----Organic
Growth factors- Not found in the environment, have to be made/ synthesized----Organic
83
New cards
How is a complex medium different from a defined medium? What type of media is TSA and why?
Complex medium- Do not know the structure of everything within the media- Contain yeast extract and Peptones-small amino acids chains
Defined medium- Know the structure of everything within the media
TSA is complex
Defined medium- Know the structure of everything within the media
TSA is complex
84
New cards
What is meant by the word sterile? Why is aseptic technique necessary for successful maintenance of pure cultures in the laboratory?
Sterile- No living organisms
Need aseptic techniques to transfer organisms without contamination- Airborne contaminants everwhere
Need aseptic techniques to transfer organisms without contamination- Airborne contaminants everwhere
85
New cards
Why is a viable count more sensitive than microscopic count? What major assumption is made in relating plate count results?
in a microscopic count all organisms dead or alive are included. But in viable cell counts the medium used for plating may support only a certain living organism. Viable counts depend on the different nutrient requirements and thus is why its more sensitive.
86
New cards
Describe how you would dilute a bacterial culture to 10-7.
(Take one ml of the orginal solution and put it with 10 ml of broth)X7= 10^-7 dilution
87
New cards
explain the “great plate count anomaly.”
Microscope counts of actual nature will have more organisms than on plates- “Direct microscopic counts of natural samples reveal far more orgalnisms than those recoverable on plates.”
88
New cards
Describe how you could use a turbidity measurement to tell how many colonies you would expect from plating a culture of a given OD.
A certain optical density will match with a certain number of cells- As cells increase so does OD
89
New cards
What is meant by the term generation time? What is the average generation time of *E. coli*?
Time it takes for a population of microbial cells to replicate
90
New cards
How do binary fission and budding cell division differ?
Binary fission- Parent is split into 2 daughter cells(Equal cell division)
Budding- Small organism is attached to the parent cell(Unequal cell division)
Budding- Small organism is attached to the parent cell(Unequal cell division)
91
New cards
in which phase of the growth curve are cells actively growing?
Exponential phase- Preparations to replicate already made in lag phase- Now use resources to replicate
92
New cards
under what conditions would a lag phase not occur
if the actively dividing cells of the exponential phase are transferred to the same medium under the same environmental conditions like temp and aeration
93
New cards
why do cells enter a stationary phase
All of the resources are used and there is no growth
94
New cards
How do microorganisms in a chemostat differ from microorganisms in a batch culture?
Chemostat- Constant nutrients are provided which allows microbial cells to stay in an exponential growth rate(Open system)
Batch culture- closed system of microbial culture
Batch culture- closed system of microbial culture
95
New cards
Explain how to do a plate count? How many bacteria would be in the culture if you had 234 colonies on the 1/1,000,000 plate?
Take one ml of the original solution with the sample to be counted, Put the one ml of orginal solution in 9 ml of nutrient broth, Plate one ml from that mixture ,Repeat but the original solution= previous solution
To find the colonies= Colonies X Reciprocal of dilution= 234 \* 1,000,000= 2.34 X 10^8
To find the colonies= Colonies X Reciprocal of dilution= 234 \* 1,000,000= 2.34 X 10^8
96
New cards
What are the stages and events that occur during biofilm formation?
attachment, colonization, development, dispersal
97
New cards
Why is biofilm formation such a major problem in human medicine?
microorganisms growing as biofilms are significantly less susceptible to antibiotics and host defenses than are planktonic forms of the same microorganisms
98
New cards
How does a hyperthermophile differ from a psychrophile?
Hyperthermophile- Lives in extreme heat- Over 80 degrees C
Psychrophile- Lives in extreme cold- Below 15 degrees C
Psychrophile- Lives in extreme cold- Below 15 degrees C
99
New cards
What are the cardinal temperature for *E. coli*? To what temperature class does it belong?
Cardinal temp-the minimum, maximum, optimal temp of organism
E coli cardianl temp= Optimal=Mesophile(39)
E coli cardianl temp= Optimal=Mesophile(39)
100
New cards
How do psychrotolerant organisms differ from psychrophilic organisms?
Psychrotolerant- Can tolerate the cold, not optimal temp( Can grow in 0 but optimal in 20-40)
Phychrophile- Have to be in cold= optimal below 15)
Phychrophile- Have to be in cold= optimal below 15)