42. Fractures of the pelvis. Diagnosis and therapy.
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is the pelvis?
The bony structure that forms the posterior part of the trunk and connects the spine to the hind limbs

What is the ilium?
Largest & most cranial part of pelvis, extends forward & upward. Forms "wings" of pelvis & articulates with the sacrum at sacroiliac joint
What is the ischium?
Located caudally, forming the lower part of the pelvis. Provides attachment points for several muscles & forms bony prominence known as ischial tuberosity.
What is the pubis?
Smallest of three bones, located ventrally. Pubic bones from both sides meet at pubic symphysis, a fibrous-cartilaginous joint in the midline.
The deep socket formed by the ilium, ischium, and pubis, which articulates with the caput femoris, forming the hip joint
What are the joints associated with the pelvis?
Sacroiliac joint
Hip joint
Supports weight of body during movement & when standing.
Protects organs like bladder, rectum, & reproductive organs.
Provides attachment sites for muscles of hind limbs & trunk.
What is the effect of the many muscles surrounding the pelvis?
Open fractures are less common, as muscle helps stabilise it → heal fast → malunion (common)
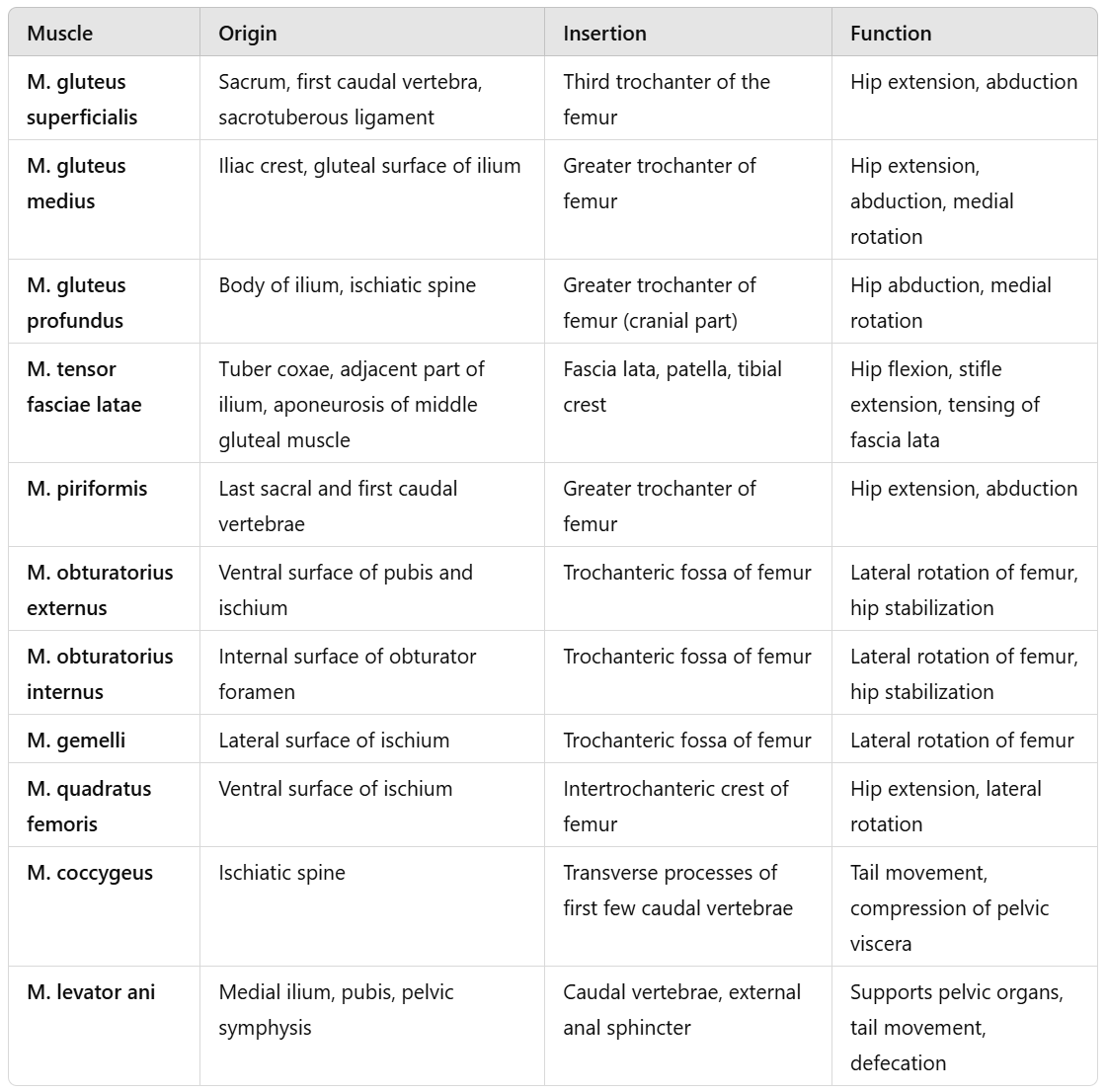
Sacroiliac fracture/luxation: Lux of sacroiliac joint, fracture of sacral wing, partial sacroiliac luxation w/ partial fracture of sacral wing
Iliac wing fracture: Fracture of cranial non-weight bearing & non-articular portion of iliac wing
Ilial body fracture: Ilial fracture between sacroiliac joint & acetabulum
Acetabular fracture: Any fracture involving articular surface, may extend into ilium & ischium
Ischial fracture: Fracture of ischial body or ramus or fracture/avulsion of tuber ischium
Pelvic floor fracture: Fractures of pelvic symphysis, pubic body or ramus, & ischial ramus.
What are the types of non-stable fractures?
Segmental fractures: body of ilium, pubis & ischium are fractured, or fracture of symphysis & ilio-sacral junction
Acetabular fractures: one or more fracture lines, weight bearing on limb is faulty
What are complications of pelvic fractures?
DJD (acetabular fractures → change articular congruity)
Concurrent injuries to vital organs (should be addressed before definitive fracture management)
Lameness, limb weakness, haematomas, inability to walk/stand.
How are pelvic fractures diagnosed?
Physical exam of entire body
Focus on complicating injuries (traumatic lung injuries, myocarditis, pneumothorax, rupture of bladder or urethra, fractures of femoral head or neck, fracture of spine with neurological deficits)
Palpation of pelvic bones
Neurological exam (test reflexes, proprioception, withdrawal, perineal reflex etc)
Imaging diagnostics: CT, X-ray.
Conservative (75%) or surgical.
What are examples of conservative treatments for pelvic fractures?
Cage rest, limitation of activity (Well-padded kennel to prevent decubital ulcers)
Ensure urination (catheterisation) & defecation
Physical rehabilitation
NSAIDs (meloxicam, carprofen)
Supportive therapy (vitamins, calcium)
What types of surgical methods are used for treatment of pelvic fractures?
Repaired according to location, with use of bone plates, lag screws, & Kirschner wires
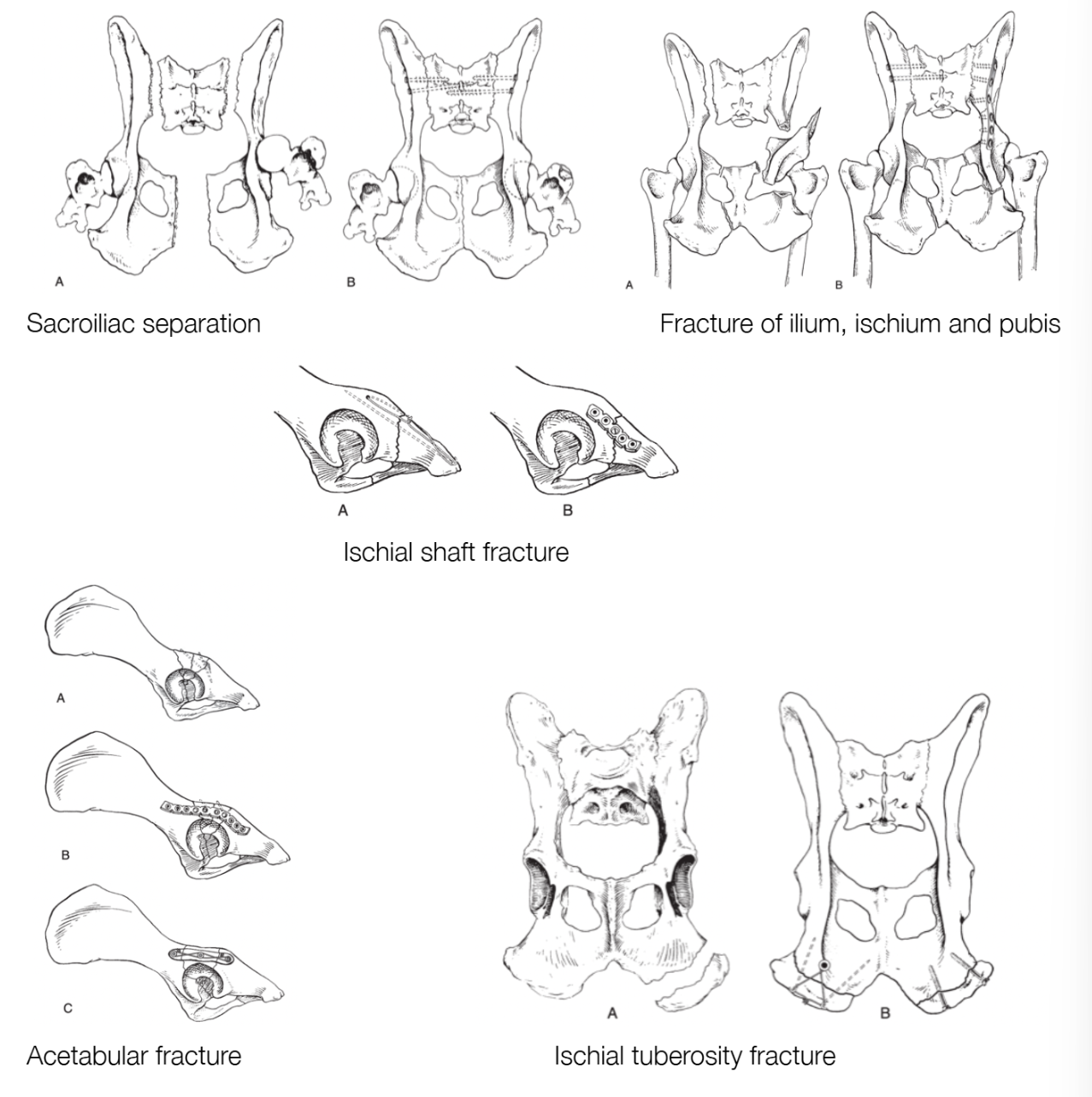
What are the methods of fixation for ilial body fractures?
Lateral bone plate placement
Bone forceps & rotational movement to counteract overlap of oblique fragments
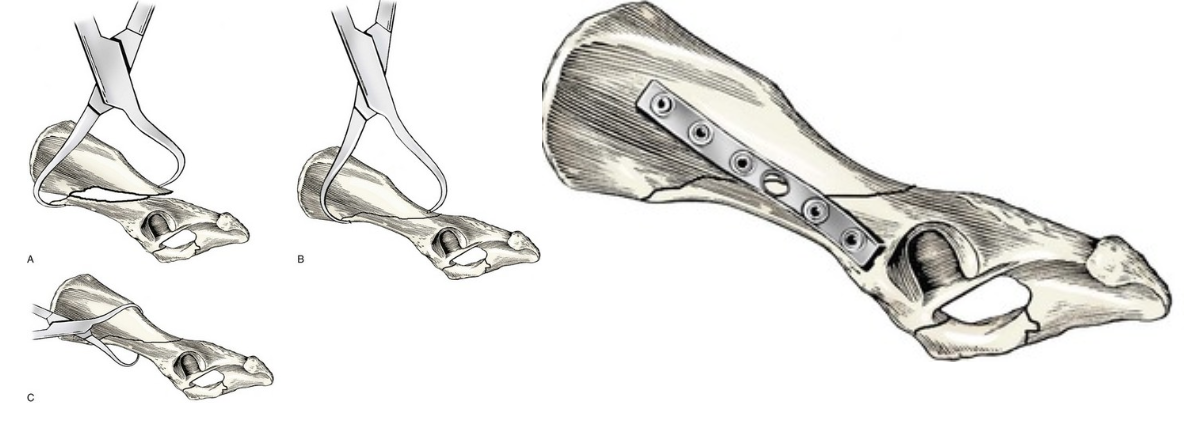
What are some types of acetabular fractures?
Transverse, oblique, comminuted.
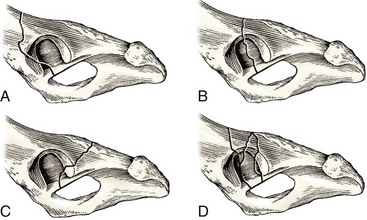
Femoral head and neck excision
Total hip replacement (at later date)
Young animals.
When is only a conservative treatment indicated for treatment, not surgery?
When the fracture is stable and none of the important ligaments are involved and if the animal is young and healthy.
Why is surgical treatment of pelvic fractures generally avoided?
Strong muscles can compensate
What structures are also commonly affected with pelvic fractures?
Bladder.
How is bladder rupture diagnosed?
Cystography with contrast.
What would be used to treat an ileosacral break?
Screws or pins.
What are examples of the main muscles of the pelvis?
Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle (External Pelvic Muscles)
M. gluteus superficialis
M. gluteus medius
M. gluteus profundus
M. tensor fasciae latae
Muscles of the Hip (Lateral Rotators of the Femur)
M. piriformis
M. obturatorius externus
M. obturatorius internus
M. gemelli
M. quadratus femoris
Muscles of the Pelvic Floor (Internal Pelvic Muscles)
M. coccygeus
M. levator ani