Chi square, significance testing & effect sizes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
null hypothesis
assumes that any kind of difference between the chosen characteristics that you see in your set of data is due to chance
alternative hypothesis
states there is a statistically significant relationship between two variables. what we side with when out p values are small
null hypothesis significance testing
a method of statistical inference that compares an experimental factor to a hypothesis of no effect based on an observation
p-values
the probability under the assumption of no effect (null hypothesis) of obtaining a result equal to or more extreme than was actually observed.
what does a p-value have to be below for your result to be statistically significant
0.05
directional (one-tailed) hypothesis
predicts the direction of a relationship or difference between two variables
non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis
states that there is a relationship between two variables without specifying the direction of that relationship
effect sizes
tells us the magnitude of difference/ similarity/ correlation
what does a Chi-squared test tell you and what is its purpose
used to compare observed results with expected results. Its purpose is the determine if this difference is due to chance or if there is a relationship between them
when is a Chi-squared test used
in nominal or ordinal variables
observed frequencies
number of times an event occurs in a real-world experiment
expected frequencies
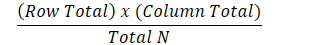
number of times an event is expected to occur based on the probability or theory
what are the chi-squared test assumptions
All frequencies must be unique/independent (so cannot be used for repeated measures/within subject designs)
All expected values should be above 5 (if lots of conditions should be 1 or above)
sample size is important
what test statistic do we report for the Chi-squared

and also degrees of freedom which is (r-1) (c-1)
How to report a Chi-squared test result
X2 (degrees of freedom, N = sample size) = chi-square statistic value, p = p value.