Human Evolution
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What is the classification of apes?
Apes are divided into Lesser Apes (e.g., Gibbons) and Great Apes, which include Orangutans, Gorillas, Chimpanzees, and Bonobos.
What are the shared derived characteristics of apes?
Apes have relatively large brains, no tails, more erect posture, increased flexibility in hips, ankles, wrists, and thumbs, and adaptations in arm and shoulder structure.
What evidence supports the common ancestry between humans and apes?
Morphological evidence (shared derived traits) and molecular analyses provide strong support for the evolutionary relationship.
What is the key evidence for the phylogenetic relationship between humans and great apes?
Cladistic analyses of both morphological and molecular data highlight the close relationship, especially between humans and African great apes.
What are some unique derived morphological traits of humans compared to other apes?
Humans have elongated skulls, enlarged brow ridges, shortened canines, changes in upper jaw, wrist bone fusion, and reduced hairiness.
What is the genetic difference in karyotypes between humans and African great apes?
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, while African great apes have 24 pairs
How genetically similar are humans and chimpanzees?
The average genetic similarity is 98.77% similarity, with 35 million base pair differences and around 5 million insertion/deletion differences.
What genetic changes are associated with human-specific traits like bipedalism and language?
the FOXP2 gene
What is the significance of HAR1 in human evolution?
HAR1 is involved in brain development, particularly in the cerebral cortex, and has evolved rapidly in humans compared to other primates.
What is the estimated time of divergence between humans and chimpanzees?
5.4 million years ago
What are hominids?
Hominids refer to any species more closely related to humans than to chimpanzees.
Have any chimpanzee fossils been found?
No chimpanzee fossils have ever been found.
What is significant about the Sahelanthropus tchadensis fossil?
It is a single fossil skull dating back 6-7 million years, discovered before the divergence of hominids and chimpanzees.
Where and when was Sahelanthropus tchadensis discovered?
Found in the Djurab Desert of Chad in July 2001.
What is notable about the braincase size of Sahelanthropus tchadensis?
It has a small braincase, smaller than any known hominid and comparable to a chimpanzee.
What was initially thought about the facial structure of Sahelanthropus tchadensis?
Initially thought to have a relatively flat face, later found to be distorted during fossilization
What do most scientists currently consider Sahelanthropus tchadensis to be?
An ape, not a hominid, reflecting advancements in human paleoanthropology
What is a common misconception about human evolution?
That humans are descended from apes; in reality, hominids and modern apes share a common ancestor.
What major trend is observed in cranial capacity over time?
There is a clear trend of increasing cranial capacity, indicating larger brain sizes.
What ongoing disagreement exists among scientists regarding hominids?
The number of distinct genera and species of hominids and their relationships to one another due to a sparse fossil record.
What challenges do taxonomists face when classifying hominid fossils?
Limited sample sizes make it difficult to determine whether variations represent different species or just variations within a single species.
Why are analyses of hominid fossils often focused on skull and tooth characters?
They have a more complete fossil record compared to other skeletal parts
What was the objective of Collard and Wood's analysis?
To reconstruct the phylogeny of living apes using cladistic analysis based on skull and tooth characters.
How many hominid species are recognized, and how are they classified?
Approximately 20 hominid species are recognized, classified into six genera, including Homo (modern humans).
Where is the origin of hominids believed to be?
Hominids are widely accepted to have originated in Africa, with recognized fossils found exclusively there.
What is Orrorin tugenensis?
The only species in the genus Orrorin, known from fossils of at least five individuals.
Where were Orrorin fossils discovered and how old are they?
Discovered in the Tugen Hills of Kenya, dated between 6.1 and 5.8 million years ago.
What suggests Orrorin tugenensis may have walked upright?
The structure of its femur bone indicates a probable bipedal habit.
What are the dental characteristics of Orrorin tugenensis?
Small molars with rounded cusps and small canines, typical of hominids.
What type of environment did Orrorin tugenensis inhabit?
A dry evergreen forest environment, contrasting with previous beliefs about bipedalism evolution.
What genus do the next oldest fossil hominids belong to?
Ardipithecus, with two recognized species.
What key fossil was discovered for Ardipithecus ramidus?
A relatively complete fossil nicknamed "Ardi," discovered in Ethiopia.
When did A. ramidus live, and what does it indicate about locomotion?
Lived about 4.4 million years ago; showed facultative bipedalism, walking on the ground and climbing in trees
What dietary implications are suggested by the teeth of A. ramidus?
An omnivorous diet, more generalized than that of modern apes.
What is Australopithecus?
An early hominid genus that appears later in the fossil record and shows advanced characteristics compared to earlier hominids.
How many species of Australopithecus are recognized?
7 species
Where have all recognized Australopithecus species been found?
Exclusively in Africa.
What is the most famous fossil of Australopithecus?
The almost complete skeleton of Australopithecus afarensis, nicknamed Lucy.
What are some primitive traits of Australopithecus afarensis?
Lower facial projection, relatively large canines, long arms compared to legs, and a smaller brain size.
What bipedal adaptations are observed in Australopithecus afarensis?
Pelvis and leg structure indicating bipedal locomotion and curved finger and toe bones for climbing.
What significant evolutionary split occurred after Australopithecus afarensis?
The split led to two lineages: Slender Australopithecines (leading to modern humans) and Robust Australopithecines (leading to Paranthropus).
Which species are considered intermediates between Australopithecus and Homo?
Homo ergaster, Homo rudolfensis, and Homo habilis.
What are the key anatomical features of early modern humans (Homo sapiens)?
Larger brain size, thinner skull walls, flat forehead, reduced brow ridges, and smaller teeth.
What important behavioral developments occurred in Homo heidelbergensis?
Use of fire, hunting tools, and shelter construction.
When did early modern humans migrate out of Africa?
By 115,000 years ago to South Africa and by 180,000 years ago to Israel.
What significant fossil represents early modern humans?
A 195,000-year-old fossil from Ethiopia showing early changes in skull structure - Omo 1
When did the evolutionary split between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens occur?
Between 400,000 and 500,000 years ago.
What skeletal features are notable in Neanderthals?
They had denser bones, thicker skulls with projecting brow ridges, a distinct bump on the back of the skull, and overall physical similarities to modern humans.
Were Neanderthals and Homo sapiens capable of interbreeding?
Yes, they were anatomically similar enough to interbreed, though it was not frequent.
How long did Homo sapiens coexist with Neanderthals?
For several thousand years in parts of Europe.
When did Neanderthals go extinct?
Approximately 30,000 years ago.
When and where were the fossils of H. floresiensis discovered?
In 2003 in a cave on the island of Flores, Indonesia.
What is unique about the stature of H. floresiensis?
It measured about 3 feet 6 inches in height and had a very small brain, earning it the nickname "the hobbit.
What distinctive physical features set H. floresiensis apart?
A receding forehead, lack of a chin, and distinctive wrist bones.
What is the current understanding of the phylogenetic placement of H. floresiensis?
It remains uncertain, but it may have descended from Homo erectus.
What does local folklore on Flores speak of?
An ancient small human-like creature called Ebu gogo, thought to still exist in the 17th century.
How did brain size evolve in the hominid lineage?
It did not occur uniformly; some periods saw rapid changes in brain size.
What selective pressures may have driven the evolution of bipedalism?
To free the arms for carrying food back to social units, especially to mates and offspring.
How did teeth evolve in response to diet?
Smaller teeth of a more even size evolved due to changes in diet.
What is the Geographic Distribution of Early Hominoids?
All hominoid species up to Homo erectus were primarily restricted to Africa, with diversity centered in the African Rift Valley (Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania).
What were environmental conditions for Early Hominoids?
The African Rift Valley was wetter during the time of early hominoids, likely featuring greater forest cover and diverse habitats.
What is the significance of Homo erectus?
Homo erectus represents a significant evolutionary advancement and was the first Homo species to appear outside Africa.
What is the fossil distribution of Homo erectus?
Oldest Homo erectus fossils found almost simultaneously in Africa, Europe, and Asia, dating to approximately 1.9 to 1.6 million years ago.
What is the evolutionary lineage of Homo erectus to Homo sapiens?
Homo erectus is a direct ancestor of Homo sapiens. Homo heidelbergensis and Homo neanderthalensis may represent stages in this lineage or side branches.
Where was the first Homo sapiens fossils found?
Earliest fossils date back to approximately 130,000 years ago in Africa, with migrations outside Africa evidenced in Israel around 100,000 years ago.
What is controversy in the Origin of Homo sapiens?
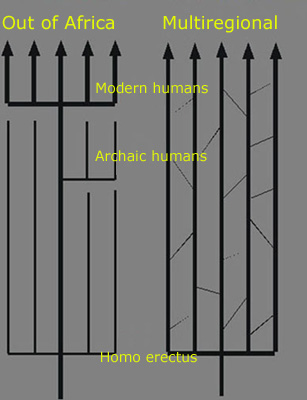
Various hypotheses exist regarding the transition from Homo erectus to Homo sapiens, including the Out of Africa and Multiregional models.
What is the Out of Africa Model?
Proposes anatomically modern humans originated in Africa around 200,000-130,000 years ago, migrating out around 60,000 years ago, replacing other Homo species.
What is the Multiregional Hypothesis?
Suggests Homo sapiens emerged from four lineages of Homo erectus in Africa, Europe, Asia, and Australia, with hybridization maintaining a single species.
What is evidence that supports the African Replacement model?
Current human genetic diversity is greater in Africa, and genetic differences among populations outside Africa suggest colonization by a small number of individuals.
When is the last common ancestor dated?
The last common ancestor of African and non-African populations is dated to approximately 52,000 years ago, supporting the African Replacement Model.
Interbreeding of Homo sapeins and Neandethals caused what genome % to be found in non-Africans?
1-4%
What are some insights into Neanderthal Appearance?
Genomic analysis suggests Neanderthals likely had pale skin and red hair, advantageous for vitamin D synthesis in low sunlight regions.
What were the migration pathways of early humans?
Early humans migrated out of Africa via two main routes; colonization of the Americas occurred from Siberia across the Bering Strait during the last ice age.
What is the molecular evidence that suggests the African Replacement model?
DNA evidence shows that people within Africa have the highest degree of genetic diversity and the farther one travels from the continent, the less genetically diverse the population.