Head, neck, nose, shoulder
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
General health
overall first impression of a person
helps decide what objective data to collect
state of health→ acute or chronically ill, frail, fit, and robust
level of consciousness→ awake, alert, responsive
signs of distress→ pain, anxiety
skin colour and obvious elsiosn
PAMFROSSTI
Past medical history
Allergies
Medications
Family history
Review of systems
Occupation
Social history
Safety
Travel/sick contacts
Immunizations
abdominal assessment sequence
inspection
auscultation
percussion
palpation
auscultate bowel sounds for at least 15 seconds in each quadrant using the diaphragm of the sthethscope
start with the lower right quadrant and move clock-wise
general survey memorization
Behaviour
Anatomy
Movement
Overall impression
Skin
(BAMOS-like bam os…)
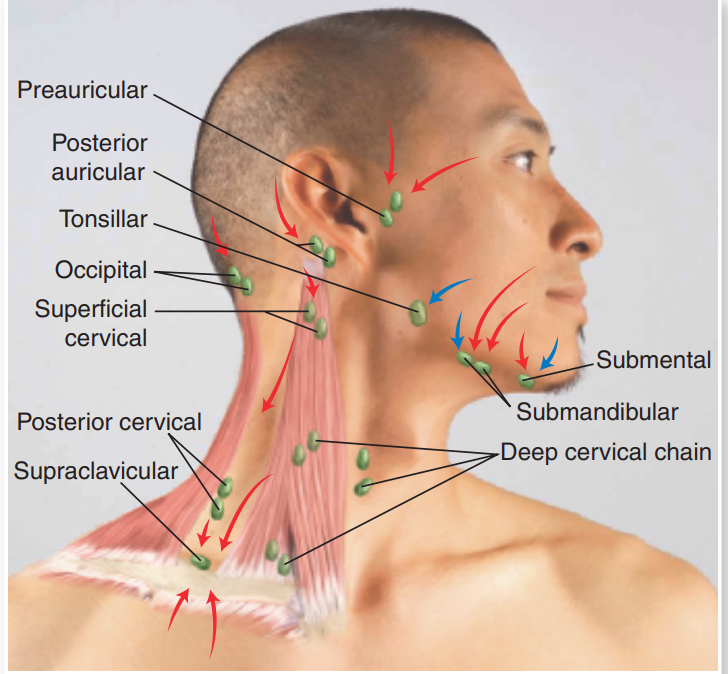
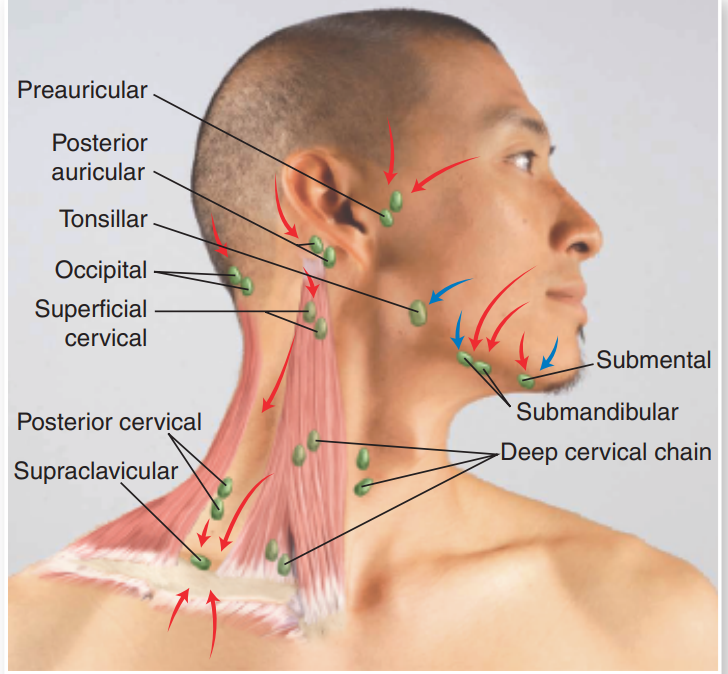
lymph nodes
Small, bean-shaped structures that are part of the lymphatic system
responsible for filtering lymph fluid and housing immune cells that help fight infection
an enlarged lymoh node indicates inflammation that is “upstream from it”
expected findings: non-tender soft mobile
Inspection of head, face, nose
inspect:
hair
lips
frontal and maxillary sinuses
nose→ anterior, inferior and profile views
inspect with speculum(septum, middle and inferior turbinate’s)
palpation head, face, nose
scalp and hair: feel from vertex to occiput including temporal regions→ any tenderness?
palpate hair for characteristics
assess newborns for fontanelles→ posterior closes 1st then anterior
fontanelles should be flat, soft, squishy, not sunken → sunken fontanelle indicates dehydration not full
temporal arteries with finger pads
assess temporomandibular joint
palpate entire length of nose→ including maxillary sinuses and frontal sinuses. Assess for tenderness, crepitus, or deformities.
inspection of neck and throat
entire neck, jugular veins, and carotid arteries
assess jugular venous distension(the visible bulging of the jugular vein, often indicating increased central venous pressure)
thyroid→ look at the position and distension should not be able to see someone’s thyroid
spine and back of the neck
palpation
carotid arteries:
feel separately at the level of the cricoid using thumb or index finger with middle finger
lymph nodes:
move in circular motion with finger pads of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th fingers
thyroid:
palpate each lobe from behind
thyroid should be smooth, rubbery, non-tender, symmetrical and barely palpable
common problems with the head, neck, throat
lymphadenopathy→ swelling of the lymph node, ultrasound the lymph node if swollen
changes in vision, hearing, taste, smell(red flags)
headache→ e.g. icepick headache can be sign of vascular issue
red flags
acute onset of severe headache in patient with no headache history→ except in newly menstruating female
unrelenting headache
headache associated with stiff neck/neck pain and feer
headache associated with trauma, changes to mentation or level of consciousness
persistent headache following trauma to the head
changes in vision, dizziness, vomiting
change in gait, balance, motor function
hyperthyroidism
thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones
leads to symptoms such as increased metabolism, weight loss, and rapid heartbeat
hypothyroidism
too little T3 and T4 is released causing slowed metabolism, leading to fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
Dry skin, hair thinning, and brittle nails due to reduced cell turnover.
Bradycardia (slow heart rate) and low blood pressure from decreased cardiac output.
parotid gland
located in the cheek anterior to the bottom part of the near
near the upper 2nd molars