Week 12 pt2: Social Cognitive Theory: Schemas, Goals, and Resilience
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What are self-schemas?
Elements of our self-knowledge that help organize our information processing.
How do self-schemas influence our perception of events?
They bias us to pay attention to and remember information that fits our self-schema.
What is confirmation bias?
The tendency to seek information that supports our existing beliefs.
What is blind-spot bias?
The bias of not recognizing our own biases while seeing them in others.
What is the antidote to blind-spot bias according to Kelly?
To test your decisions and beliefs as a scientist would.
What is self-enhancement bias?
The tendency to maintain a positive view of oneself, often leading to inflated self-esteem.
What is grandiosity in clinical narcissism?
An extreme form of self-enhancement bias where individuals see themselves as uniquely special.
What is self-verification bias?
The strong motive to be consistent in self-perception, avoiding change that threatens self-image.
What are learning goals according to Dweck?
Goals focused on learning and growth rather than just achievement.
What are performance goals?
Goals focused on being the best and avoiding mistakes.
How do learning goals affect persistence?
Individuals with learning goals are more persistent and accept setbacks as part of the process.
What is the Actual-Ideal self discrepancy?
The feeling of not living up to one's ideal self, leading to sadness and clinical problems.
What is the Actual-Ought self discrepancy?
The feeling of not living up to perceived societal expectations, leading to anxiety and fear of rejection.
What is imposter syndrome?
The constant comparison to others leading to self-doubt and anxiety about one's abilities.
What is maladaptive behavior in psychopathology?
Behavior resulting from dysfunctional learning and responses to stress.
What is Bandura's Bobo doll experiment an example of?
Maladaptive responses learned from observing others.
What is the 90/10 rule in relation to worry?
Rejecting worry and preparing instead to build resilience.
What are dysfunctional expectancies?
Erroneous beliefs about the outcomes of events that can lead to maladaptive behavior.
What is Ellis' Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT)?
A therapeutic approach that focuses on changing irrational beliefs to alter emotional responses.
What does the ABC model in REBT stand for?
Activating event, Belief, Consequence.
What is an example of irrational thinking in REBT?
Catastrophizing, such as believing one critique defines overall competence.
What is the consequence of irrational beliefs according to REBT?
Negative emotions and behaviors that can lead to avoidance and anxiety.
What is the role of counter-thought in REBT?
To challenge and replace irrational beliefs with realistic, grounding statements.
What is the importance of self-actualization in therapy?
Focusing on personal ideals and values to foster growth and happiness.
How can therapy help with self-verification schemas?
By challenging the logic of these schemas to promote personal growth.
What is the impact of low ability and low self-esteem on performance goals?
It causes greater anxiety and procrastination compared to those with learning goals.
What is the antidote for feeling not good enough due to ideal self discrepancies?
Adopting a growth mindset to focus on self-improvement rather than perfection.
What causes anxiety according to the Self-Efficacy Theory?
Threatening events cause anxiety through perceived inefficacy in coping with the event.
What is a 'fear-of-fear' response?
It is a response seen in panic disorder where the fear of experiencing anxiety itself leads to avoidance behavior.
How can high standards contribute to depression?
Dysfunctionally high standards, such as perfectionism, can lead to perceived self-efficacy failures, resulting in frustration and depression.
What is the vicious cycle related to avoidance and quitting?
Perceived self-inefficacy can lead to avoidance of failure and premature quitting, which reinforces the cognitive pathways for quitting.
What is the antidote to avoidance and quitting?
Self-compassion and the willingness to try again.
What is the goal of modeling and mastery in therapeutic change?
To change a person's self-efficacy by performing the task that causes anxiety.
How is the task broken down in therapeutic modeling?
The overall task is divided into small sub-skills that are practiced progressively.
What are the two ways of coping with stressful situations according to Lazarus?
Problem-focused coping (altering the situation) and emotion-focused coping (improving emotional state).
What does CBT stand for?
Cognitive Behavior Therapy.
What are the core principles of CBT?
Identify and correct distortions in thinking, monitor negative thoughts, and substitute them with reality-oriented interpretations.
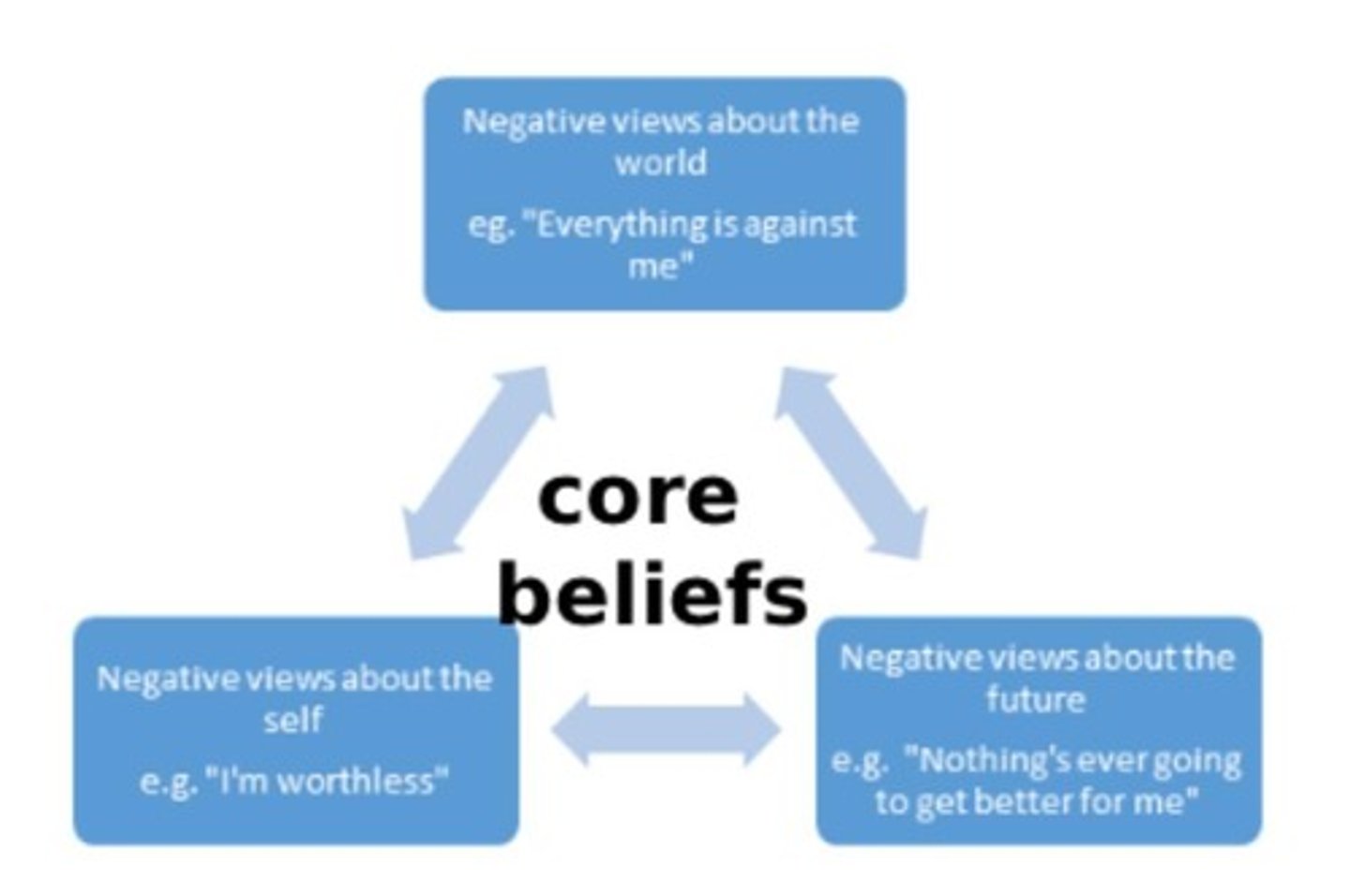
What is the downward arrow technique in CBT?
A method to examine the logic and irrationality in a client's interpretation of their thoughts.
What is a critical evaluation point of social cognitive therapies?
While they have excellent databases, they lack an overarching network of assumptions tying all theoretical elements together.
What is resilience in clinical psychology?
The process and outcome of successfully adapting to difficult life experiences through mental, emotional, and behavioral flexibility.
What are the four core components to improve resilience?
Connection, wellness, healthy thinking, and meaning.
How can one build connections to enhance resilience?
Prioritize supportive relationships, help others, and engage in social activities.
What role does wellness play in resilience?
Taking care of physical and mental health to avoid negative coping strategies.
What is the significance of finding purpose in resilience?
It involves seeking opportunities for self-discovery and proactively moving toward goals.
What are the three types of empathy?
Emotional empathy, cognitive empathy, and empathetic concern.
What is emotional burnout?
The exhaustion that comes from coping with the emotional burden of others.
What are the major contributions of social cognitive therapies?
They are comprehensive, up-to-date, and have shown reliable improvements in therapy outcomes.
What is the most important factor in therapeutic improvement?
The therapeutic alliance between the therapist and the client.
What is the relationship between therapy engagement and improvement?
People who actively engage in therapy typically improve, regardless of the therapy type.
What is the role of cognitive flexibility in resilience?
It allows individuals to adapt their thoughts and behaviors in response to challenges.
How can adverse events contribute to personal growth?
They can empower individuals to grow and improve their lives through the lessons learned.
What is the significance of social resources in resilience?
Quality social connections provide a sense of belonging and purpose, aiding in adaptation to adversity.
What is the impact of negative self-statements in CBT?
They contribute to psychopathologies by reinforcing dysfunctional beliefs.
What is the purpose of behavioral experiments in CBT?
To test maladaptive cognitions and assumptions in real-life situations.