APC EXAM 2- Dr. Z
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the three main aspects of healthcare quality from a medical perspective?
What are the two main aspects of healthcare quality from a patient perspective?
medical:
increase probability of positive outcomes
decrease probability of negative outcomes
correspond with current medical knowledge
patient:
offers the patient what they want
provides the patient with what they need

What is quality by inspection/ quality control?
activities designed to ensure adequate quality by INSPECTION
improvement solely by inspection
focuses on the defect found
What is quality assurance?
ensures standards of quality are being met by INSPECTION
improvement based on performance to meet a specific standard
focuses on dealing with the outlier
Compare quality by inspection and quality assurance:
which is reactive? which is defensive?
do they require inspections?
improvements focus on what?
limitations?
both are:
reactive AND defensive
requires inspection to identify outliers or defects
improvements focus on inspection findings
no process improvement
no variation prevention (aka problems within the system will not be detected… a limitation)

What is continuous quality improvement (CQI)?
definition
what type of shift?
reactive or proactive?
short term or long term?
requires what kind of participation?
focuses on doing what?
promotes a punitive or non-punitive system?
def: continual improvement processes associated with providing a good or service that meets or exceeds customer expectations
paradigmatic shift
proactive
continuous—> never ending
requires organization-wide participation
focuses on preventing and reducing internal sources of variations
promotes a non-punitive system to the individual

Definition of six sigma?
quality management program AND a statistical measure

What does six sigma assume as a quality management model?
What is it used as a statistical measurement?
assumes that defects are responsible for the cost of poor quality
used to compare quality across processes and across organizations

Worldwide standards for quality management and quality assurance = ISO ______.
9000
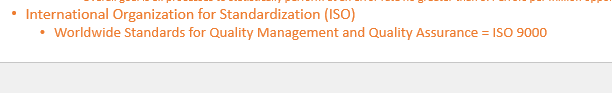
What are the seven steps to the model for improvement? Which are the 3 FUNDAMENTAL STEPS?
forming the team
SETTING AIMS*
ESTABLISHING MEASURES*
SELECTING CHANGES*
testing changes
implementing changes
spreading changes
*= fundamental step
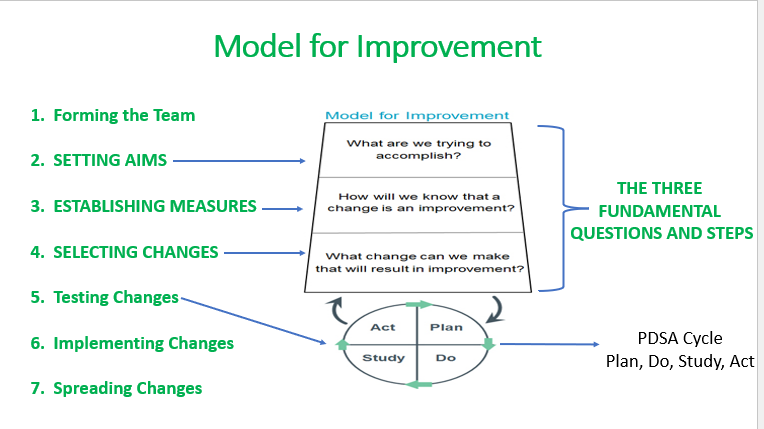
For each of the fundamental steps for the model for improvement, list their “question”.
three fundamental steps with their questions:
SETTING AIMS- “What are we trying to accomplish?”
ESTABLISHING MEASURES- “How will we know that a change is an improvement?”
SELECTING CHANGES- “What change can we make that will result in improvement?”
What are the 6 aims for improvement? describe them.
safe (avoid injuries to pts.)
effective (match care to science)
patient-centered (honor the individual/choice)
timely (reduce wait)
efficient (reduce waste)
equitable (close racial/ethnic gaps in health status)
mnemonics: “SEE PET”

What are the 4 steps in the PDSA Cycle?
Plan
Do
Study
Act

Explain EACH step in the PDSA:
(lowkey i think she’ll just ask about the steps in general and not specifics)
Plan
state the objective of the test
make predictions
develop plan—> who, what, when, where, what data to collect?
Do
do the test on a small scale, do the test frfr
document problems and unexpected observations
begin analysis of data
Study
complete analysis of the data, compare to predictions
summarize/reflect
Act
refine the change, prepare a plan for the next test
determine what modifications should be made

State the conclusion of NPSF’s “Free from Harm: Accelerating Patient Safety Improvement Fifteen Years after To Err is Human” based on the eight recommendations necessary for achieving total systems safety.
conclusion: CALL TO ACTION
safety= top priority and the 8 recommendations give a framework
critical that everyone works together to adopt a systems approach to safety
efforts to create a world free from harm

WHAT are the four foundational and interdependent areas prioritized as essential to create total systems safety in IHI’s “Safer Together: A National Action Plan to Advance Patient Safety”?
culture, leadership, and governance
patient and family caregiver engagement
workforce safety and well-being
learning system

What are the 6 leadership domains?
(as defined in “Leading a Culture of Safety: A Blueprint for Success”)
establish a compelling VISION for safety
Value TRUST, RESPECT, AND INCLUSION
Select, develop, and ENGAGE YOUR BOARD
Prioritize safety in selection and DEVELOPMENT OF LEADERS
Lead and reward a JUST CULTURE
Establish organizational BEHAVIOR EXPECTATIONS

What is the key concept AND primary goal defined in “Leading a Culture of Safety: A Blueprint for Success”?
key concept: building trust respect, and enthusiasm for improvement through behaviors and principles that focus on bettering systems issues while requiring fair and inclusive practices by all
goal: ZERO HARM to pts., families, and the workforce

What are the 3 common types of safety cultures?
punitive
blame-free
just

For EACH of the common types of safety cultures describe them:
Punitive |
|
Blame-free |
|
Just |
|
Punitive |
|
Blame-free |
|
Just |
|

MUE or medication use evaluations includes all medications and all aspects of medication use including what?
prescribing, dispensing, administering, monitoring, and outcome

What is the definition of an MUE? purpose?
tool used to promote the systematic improvement in medication-related performance in a healthcare setting
purpose: performance improvement method that aims to optimize patient outcomes through evaluation and improvement of medication use

MUEs can be broad or narrow. What does that mean?
narrowly focused—> focusing on a specific drug and or disease state
broadly focused—> designed to cover an entire class or indication of meds

What are the 2 types of outcomes in MUEs?
therapeutic outcomes—> patient-centered outcomes
clinical events, quality of life, outcomes= efficacy, incidence, rates
process outcomes—> processes related to medication use
prescribing, dispensing, admin, monitoring= frequency, cost

PRACTICE:
Evaluating the incidence of major bleeding in pt. treated with thrombolytic therapy is an example of what kind of outcome?
a. process outcome
b. therapeutic outcome
b.
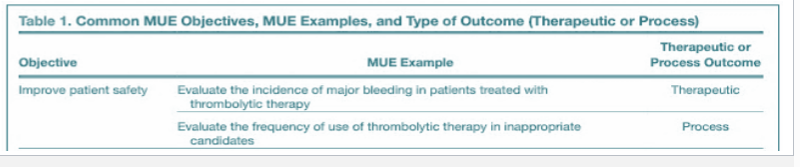
PRACTICE:
Evaluating the frequency of use of thrombolytic therapy in inappropriate candidates is an example of what kind of outcome?
a. process outcome
b. therapeutic outcome
a.
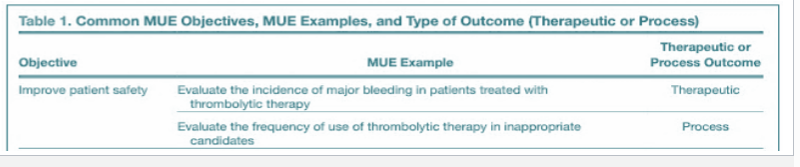
What are common MUE objectives?
improve pt. safety
assess vale of innovative practices
meet quality or regulatory standards
minimize cost

Performance improvement frameworks like FOCUS-PDCA are used by healthcare organization to improve what areas in patient care?
safety
efficacy
quality
efficiency

What do the letters of FOCUS-PDCA stand for?
F- find
O- organize
C- clarify
U- understand
S- select
-
P- plan
D- do
C- check
A- act

What are some criteria for prioritizing and selecting medications or healthcare processes that require evaluation or MUEs? (aka what would make one med chosen over another to be evaluated)
(sorry there’s so many, but it’s a LO)
high risk medications
known/suspected to cause ADRs
used in the tx of higher risk pts. or hasn’t been evaluated in high-risk populations
safety concerns
interacts with other meds, foods, or procedures
subject of FDA recall, safety alert, withdrawal, or not even FDA approved
potentially toxic at normal doses
impact on patient care
affects large # of pts.
crucial component of care for a specific disease
drugs that have (-) or no therapeutic impact
cost/ compliance
under consideration for a formulary change
med or process is expensive
determination if clinicians are complying with formulary
others:
new/ innovative processes
evaluating pharmacist-directed collaborative practices
analytic tools or scoring systems suggest the need for intervention

If MUE outcomes are undesired/negative, what steps should be done next?
understand causes of process variation—> conduct root cause analysis, consider the “5 WHYS”
Develop idea to address the root cause of process variation—> use FACES tool (FACE= feasibility, acceptability, cost/benefit, effectiveness)

What are high reliability organizations?
idk how imp
refer to organizations or systems that operate in hazardous conditions but have fewer than their fair share of adverse events (ex: air traffic controllers)
What is situational awareness?
idk how imp
refers to the degree to which one's perception of a situation matches reality