MAMA Sheet (Microbiology Lab Practical II)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Hydrolysis of Starch
Medium: Starch Agar
Substrate: Starch
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Hydrolysis
Enzyme: Amylase
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Indole
End Products: Sugar
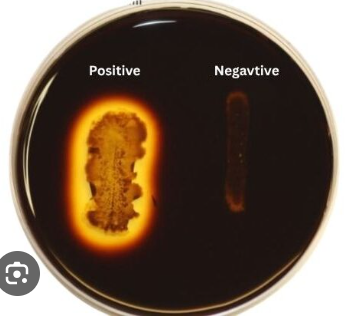
Hydrolysis of Starch Negative Result
Dark (Black/Brown) Area Around Bacteria
*E-coli
Explanation: This bacteria produces amylase to metabolize starch. The clear zone shows that no starch, thus no iodine stain.
Hydrolysis of Starch Positive Result
Light Area/Color (Clear/Golden Zone) Around Bacteria
*B. subtillus
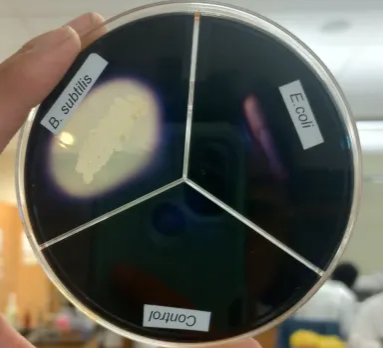
Hydrolysis of Gelatin
Medium: Gelatin (Tall)
Substrate: Gelatin
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Hydrolysis
Enzyme: Gelatinase
pH. Indicator/Reagents: N/A
End Products: Amino Acid
Hyrolysis of Gelatin Negative Result
Solid
Explanation: This bacteria produces gelatinase, which can break down collagen and tissues in a clinical setting.

Hydrolysis of Gelatin Positive Result
Liquid

Fermentation of Carbohydrates
Medium: CHO Broth, 1x Sugar, Phenol Red, Durham Tube, Basal Media
Substrate: 1x Sugar (Glucose, Sucrose, Lactose, or Mannitol)
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Fermentation
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Phenol Red
End Products:
Organic Acids + ATP OR
(Slow) Organic Acids + ATP OR
Organic Acids + ATP + CO2
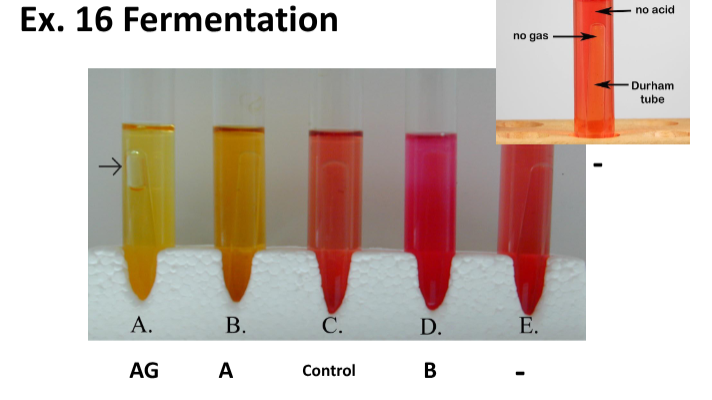
Fermentation of Carbohydrates Negative Result (B)
*B = Basic
pH: Basic
Color: Red/Magenta (emphasis on Magenta)
Explanation: This bacterium ferments carbohydrates and releases organic acids.

Fermentation of Carbohydrates Negative Result (SB)
*SB = Slow Basic
pH: Slow Basic
Color: Patchy Red/Magenta Gradient
Explanation: This bacterium ferments carbohydrates and slowly releases organic acids.

Fermentation of Carbohydrates Positive Result (A)
*A = Acid
pH: Acid
Color: Yellow

Fermentation of Carbohydrates Positive Result (A/g)
*A/g = Acid + Bubble (gas)
pH: Acid
Color: Yellow

Fermentation of Carbohydrates Positive Result (S/A)
*S/A = Slow Acid
pH: Slow Acid
Color: Yellow + Little Orange
Explanation: Yellow with orange layer on top, orange- tinted durham tube.

Fermentation
Medium: Litmus Milk
Substrate: Lactose
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Fermentation
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Litmus Dye
End Products:
Organic Acids + ATP OR
Organic Acids + ATP + Hard Curd/Protein OR
Organic Acids + ATP + Hard Curd + CO2
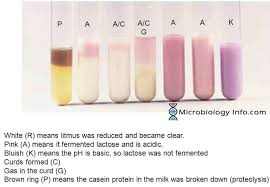
Fermentation Negative Result
Color:
Purple Milk/Control
Blue Milk (Blueberry Blue)
Grape Juice (Diluted Yellow/Clear)

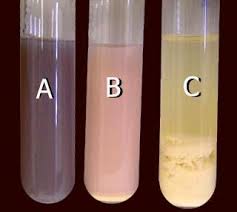
Fermentation Positive Result (A)
*A = Pink
pH: Acid
Color: Pink Milk

Fermentation Positive Result (A/C)
*A = Pink (Acidic), C = Curd (Solid)
pH: Acid
Color: Pastel Pink Milk + Hard Curd (Solid)
Explanation: In overly acidic environments, the milk curdles and coagulases the following milk proteins: casein and lactalbumin.
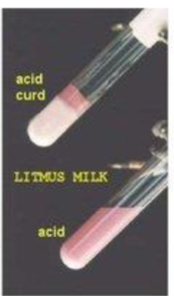
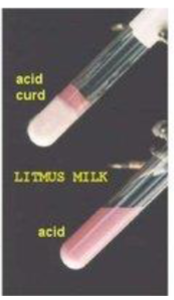
Fermentation Positive Result (A/C/G)
*A = Pink (Acidic), C = Curd (Solid), G = Gas (CO2 gas cracks)
pH: Acid
Color: Pastel Pink Milk + Hard Curd (Solid) + Gas Cracks
Alkalinization
Medium: Litmus Milk
Substrate: Casein (Colloid)
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Alkalinization (partial hydrolysis)
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Litmus Dye
End Products:
Polypetides (Colloids) + Basic Amines
Alkalinization Negative Result (-)
Color:
Pink Milk
Purple Milk (Control)
Grape Juice
Alkalinization Positive Result (B or BR)
*B = Blue, R = Bleached
pH: Basic
Color: (Blueberry) Blue Milk

Peptonization
Medium: Litmus Milk
Substrate: Proteins: Casein & Lactalbumin
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Peptonization (complete hydrolysis)
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Litmus Dye
End Products:
Amino Acids OR
Amino Acids + Rennet Curd

Peptonization Negative Result (-)
Pink Milk
Purple Milk/Control
(Blueberry) Blue Milk

Peptonization Positive Result (P/PR/PRC)
*P = Translucent, R = Bleached, C = Curd
Color:
Translucent/Clearish Liquid OR Translucent + Soft Curd

Reduction
Medium: Litmus Milk
Substrate: Litmus
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Reduction (anaerobic respiration)
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Litmus Dye
End Products:
Leucolitimus (reduced litmus) + ATP
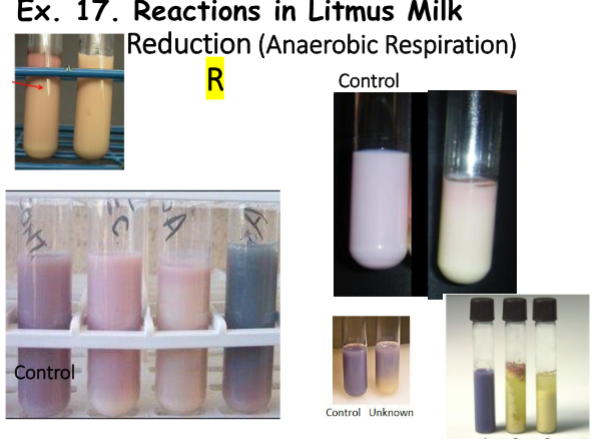
Reduction Negative Result
Color: Litmus Colors (Pink, Purple, Blue) or Partially White Bowl

Reduction Positive Result (R)
Color: Bleached Litmus
*Area of NO pink, purple, or blue.
*Bowl must be completely white.

Reduction of Nitrates
Medium: Nitrate Broth
Substrate: Nitrates
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Shake tube, pour 1ml, + 3 drops of Sulfanillic Acid, + 2 drops DAN, wait 1-2 mins
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Anaerobic Respiration (ETC)
End Products: Nitrites

Reduction of Nitrates Negative Result
Color:
Pink
Anything Else

Reduction of Nitrates Positive Result
Colors:
Red
Magenta
Orange-Red
Explanation: This bacterium uses nitrate as a final electron acceptor during anaerobic respiration, reducing it to nitrite.

Production of Decarboxylase
Medium: Decarboxylase Broth +Basal Medium + Bromcresol Purple + 1x Amino Acid (aa) + Mineral Oil
Substrate: Amino Acid
Pathway/Enzyme:
Enzyme: Decarboxylase
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Bromcresol Purple
End Products: N/A
Production of Decarboxylase Negative Result
Color:
Yellow
Burgundy
*COVER OIL & HOLD UP TO LIGHT!

Production of Decarboxylase Positive Result
Color: Purple/Violet
pH: Basic
*COVER OIL & HOLD UP TO LIGHT!
Explanation: This bacteria produces decarboxylase to remove carboxyl group from amino acid. Amino acid becomes a basic amine, making the medium basic.

Hydrolysis of Urea
Medium: Urea Broth
Substrate: Urea
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Hydrolysis
Enzyme: Urease
pH. Indicator/Reagents: N/A
End Products: Basic Ammonia + CO2
Hydrolysis of Urea Negative Result
pH: Acidic
Color: Any other color aside from magenta.
Hydrolysis of Urea Positive Result
pH: Basic
Color: Magenta
Explanation: This bacteria produces urease to hydrolyze urea. End product is ammonium, making the broth basic.

Oxygen Requirements - Obligate Aerobe
YES Oxygen
Bacteria grows from the TOP where concentration of oxygen is the highest.
Oxygen Requirements - Obligate Anerobe
NO Oxygen
Bacteria grows at the BOTTOM where concentration of oxygen is the lowest.
Slant: Growth
Tall: Growth on Top
Thiglycollate Broth: No Growth
Oxygen Requirements - Facultative Anaerobe
YES or NO Oxygen (Can grow in the presence or absence of oxygen).
Bacteria grows in the MIDDLE.
Slant: Growth
Tall: Growth
Thiglycollate Broth: Growth.
Oxygen Requirements - Microaerophile
Bacteria can only grow in the presence of a small/limited amount of oxygen; TOO much oxygen is toxic.
Slant: No Growth
Tall: Growth
Thiglycollate Broth: Growth just below the surface.

Oxygen Requirements - Guess the following.
SIM Test - S: Hydrogen Sulfide Production
Medium: SIM
Substrate: CyStine
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Anaerobic Respiration
pH. Indicator/Reagents: N/A
End Products: ATP + H2S

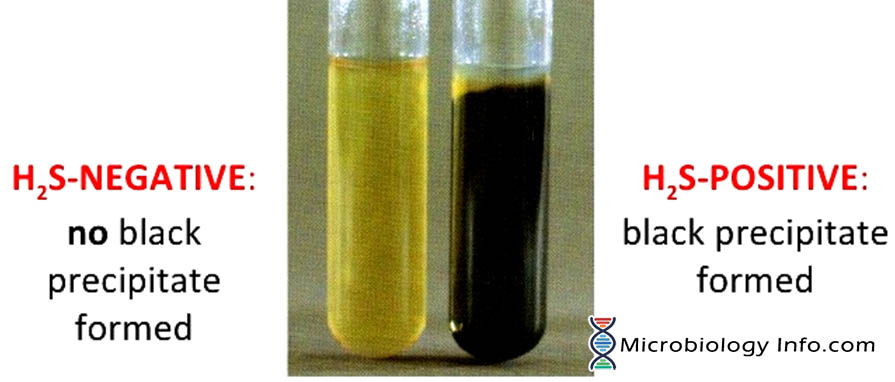
SIM Test - S: Hydrogen Sulfide Production Negative & Positive Results
Negative: No Black Precipitate
Positive: Black Precipiate
Explanation: This bacteria takes sulfur (from R-group of cysteine) and uses sulfate as a final electron acceptor in ETC. Produces hydrogen sulfide.
SIM Test - I: Indole Production
Medium: SIM
Substrate: Trytophan
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Hydrolysis of Trytophan
Enzyme: Trytophanase
pH. Indicator/Reagents: 10 Drops of Kovacs Indicator
End Products: Intermediate Products of Kovacs Indicator (2)
Indole
Pyruvic Acid + Ammonia

SIM Test - I: Indole Production Negative & Positive Results
Negative: Anything Else (surface lacks red layer/ring)
Positive: Red Surface Layer/Ring
Explanation: This bacteria metabolizes tryptophan into indole.


SIM Test - M: Motility
Negative: Clean Stab (No Fuzz/Spikes)
Positive: Fuzz/Spikes Around Stab


MR-VP Broth: Methyl Red Test
Medium: MR-VP Broth
Substrate: Glucose
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Fermentation
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Shake Broth, Pour 1ml, + 10 Drops of Methyl Red
End Products:
ATP + Amino Acids
MR-VP Broth: Methyl Red Test Negative & Positive Results
Negative: Red Color
Positive: Yellow Color or Anything Else
Explanation: This bacteria ferments and releases lactic acid (pH <4.4).

MR-VP Broth: Voges-Proskauer Test
Medium: MR-VP Broth
Substrate: Glucose
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Fermentation
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Shake Broth, Pour 1 ml, +10 Drops of Naphthol, +10 Drops Potassium Hyroxide (KOH)
End Products:
Organic Acids + ATP + Acetyl Methyl Carbinol (AMC)
MR-VP Broth: Voges-Proskauer Test Negative & Positive Results
Negative: No Red Ring
Positive: Red Ring
Explanation: The bacterium ferments and releases alcohols.

Utilization of Unusual Nitrogen
Medium: Ammonium Phosphate Broth + Bromcresol Dye
Substrate: Ammonium (NH2)
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Ammonium Phosphate (Unique Nitrogen Source)
pH. Indicator/Reagents: N/A
End Products: Ammonia (NH3) + Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
Utilization of Unusual Nitrogen Negative Results
Colors:
Red
Burgundy
Utilization of Unusual Nitrogen Positive Results (A or S+)
*A = Acidic, S+ = Slow Positive
A = Yellow Color
S+ = Brown Color
Explanation: The bacterium uses ammonium as a nitrogen source, producing phosphoric acid and turning the media acidic.
Utilization of Unusual Carbon
Medium: SMinimal MediaIM
Substrate: Citrate
Pathway/Enzyme:
Enzyme: Citrase (Unique Carbon Source)
pH. Indicator/Reagents: N/A
End Products: Acetate (C2H4O2) + Oxalacetone (C4H4O5)
Utilization of Unusual Carbon Negative Results
No Growth/Clumps/Clear

Utilization of Unusual Carbon Positive Results
Growth
Shingle
Cloudy/Turbid
Specks
Membrane Layer on Top
Explanation: This bacteria produces citritase to break down citrate as a carbon source for growth.

Detection of Catalase
Medium: Nutrient Agar Slant
Substrate: Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)
Pathway/Enzyme:
Enzyme: Catalase
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Hydrogen Peroxide
End Products: Intermediate Products of Kovacs Indicator (2)
Water (H2O)
Oxygen (O2)
Detection of Catalase Negative & Positive Results
Negative Result: No Bubbles
Positive Result: Bubbles
Explanation: The bacteria produces catalase to break down hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water.

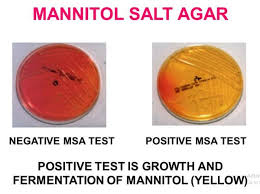
MSA/Staph Test
Medium: Mannitol Salt Agar
*Mannitol Sugar, High Salt (selective), Phenol Red Indicator (differential)
Substrate: Mannitol
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Fermentation
pH. Indicator/Reagents: N/A
End Products: Organic Acids + ATP
MSA/Staph Negative Results
Color: Medium Remains Red/Pink

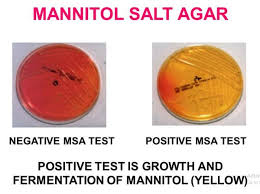
MSA/Staph Positive Results
Color: Yellow Agar
Yellowing of media next to media (indicates fermentation).
Explanation: This bacteria survives high salt environment, breaks down manitol, releases organic acids. If it ferments, pathogenic strain. Preliminary test for staph.

Coagulase Production
Medium: Rabbit Plasma + Anticoagulant (EDTA)
Substrate: Rabbit Plasma
Pathway/Enzyme:
Enzyme: Coagulase
pH. Indicator/Reagents: N/A
End Products: Coagulation/Clotting
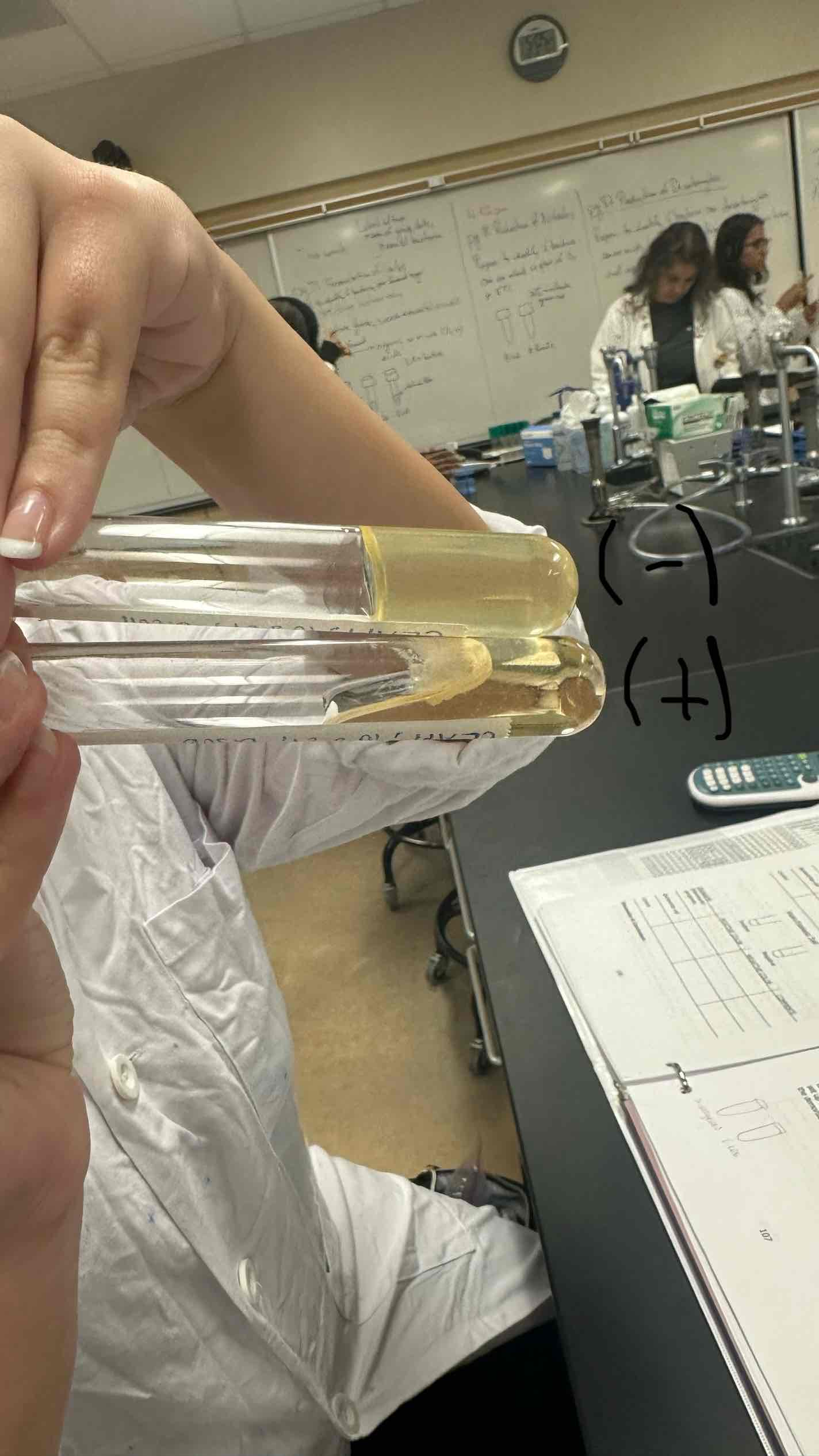
Coagulase Production Negative & Positive Results
Negative Result: Liquid
Positive Result: Solid
Explanation: This bacteria produces coagulace and clots plasma (which is liquid due to anticoagulant). Confirmatory test for staph.
*Tilt when observing tubes.


*Top = Negative Result; Bottom = Positive Result

Latex Agglutination Test
Medium: Reaction Card
Substrate: Antigen OR Antibody
Pathway/Enzyme:
Pathway: Antigen-Antibody Complex
pH. Indicator/Reagents: Latex particles/beads coated with antibodies.
End Products: Visible Antigen-Antibody Complexes
Latex Agglutination Test Negative & Positive Results
Negative Results: No Clumping/Smooth Texture (after drying)
Positive Results: Clumping (after drying)
Explanation: This bacteria produces protein A, which is recognized by the latex agglutins. Indicative of staphylococcus.

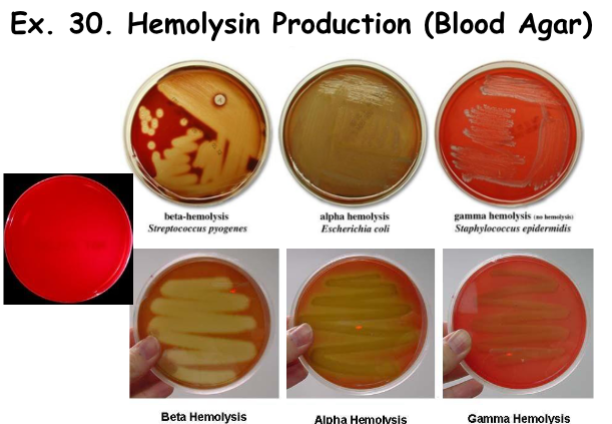
Hemolysin Production: Alpha Hemolysis
Partial Lysis of Hemoglobin
Result: Greenish/Brown/Mettalic Color on Media

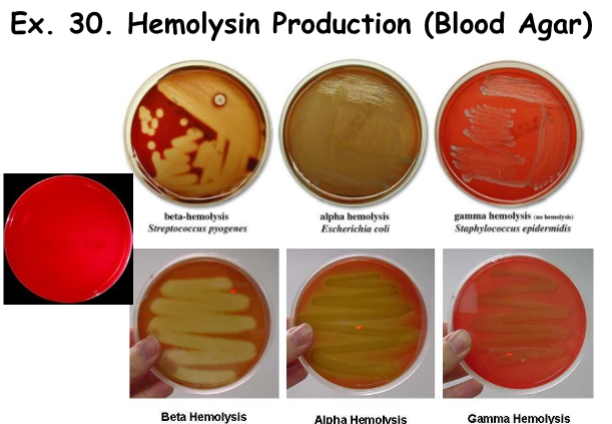
Hemolysin Production: Beta Hemolysis
Complete Lysis of Hemoglobin & RBCs
Result: Clear, Colorless Zone Surrounding Colonies (plate is slightly transparent)

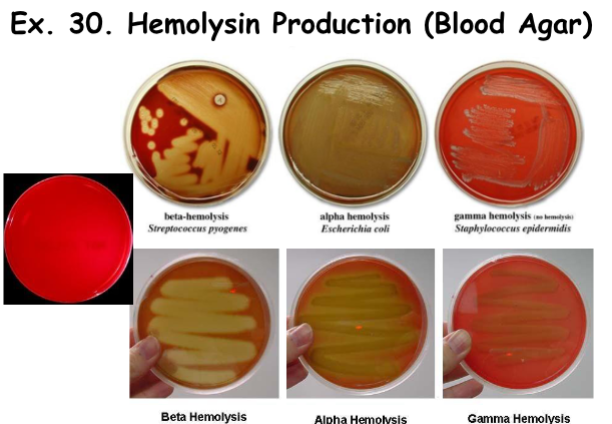
Hemolysin Production: Gamma Hemolysis
Hemoglobin remains unaffected; plasma proteins are used for growth.
Results: Red (no change in media/plate)