PMLS1 Chapter 1 (Dates)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
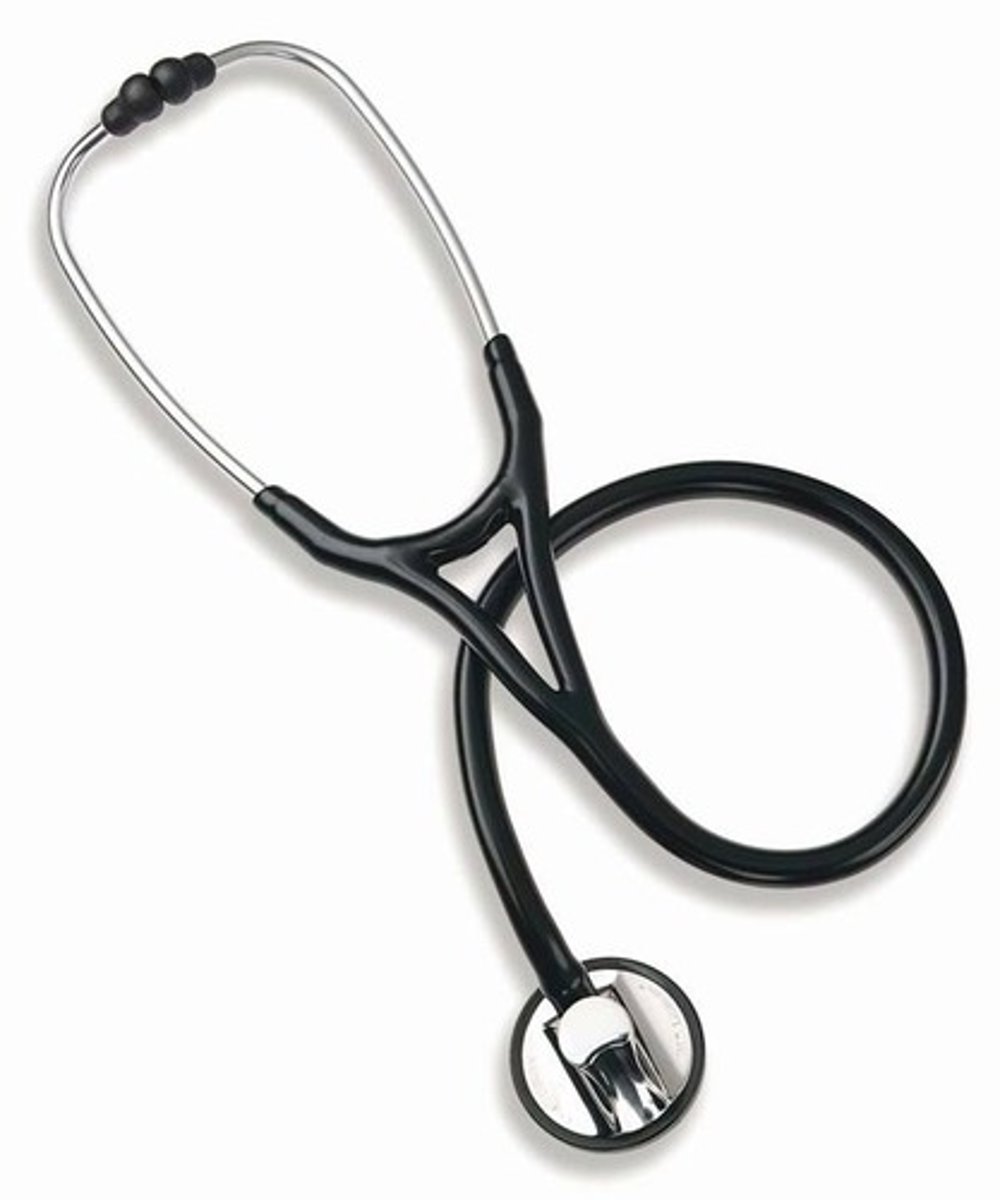
Stethoscope (1816)
First diagnostic medical breakthrough invented by Rene Läennec; used to acquire information about the lungs and heartbeats.

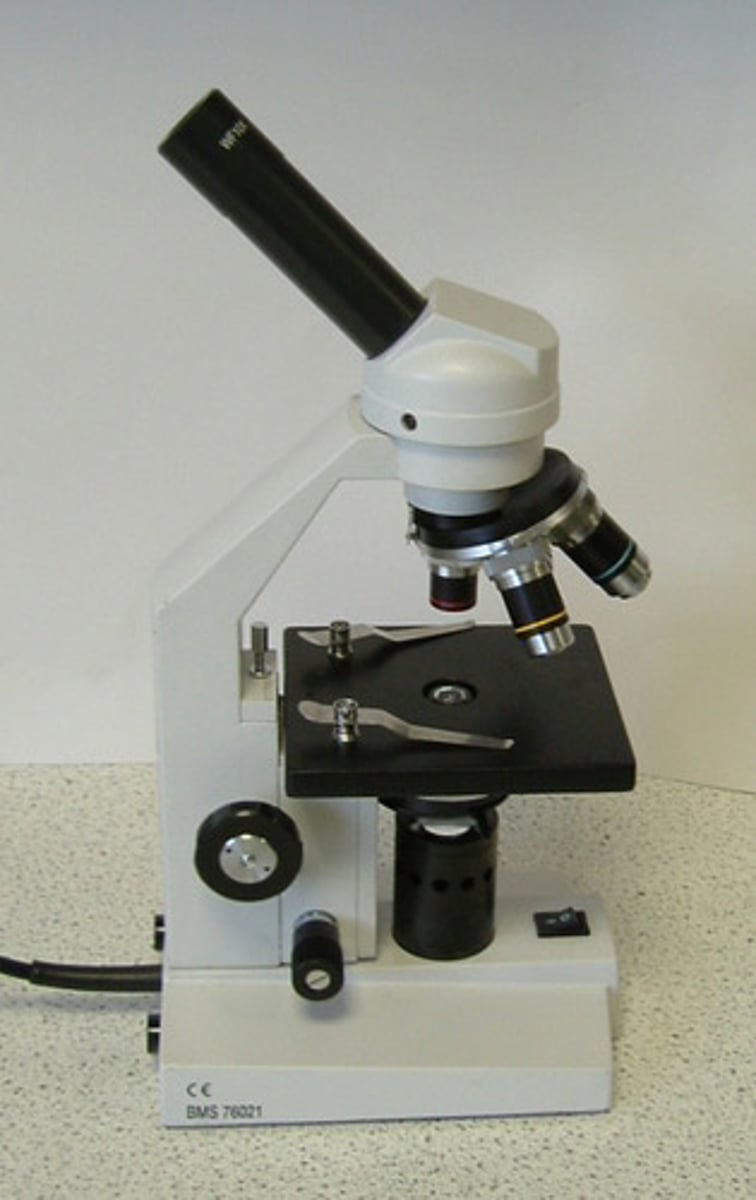
Microscope (1840)
The first practical microscope was devised by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek; developed for medical purposes due to advanced in lenses and lower costs

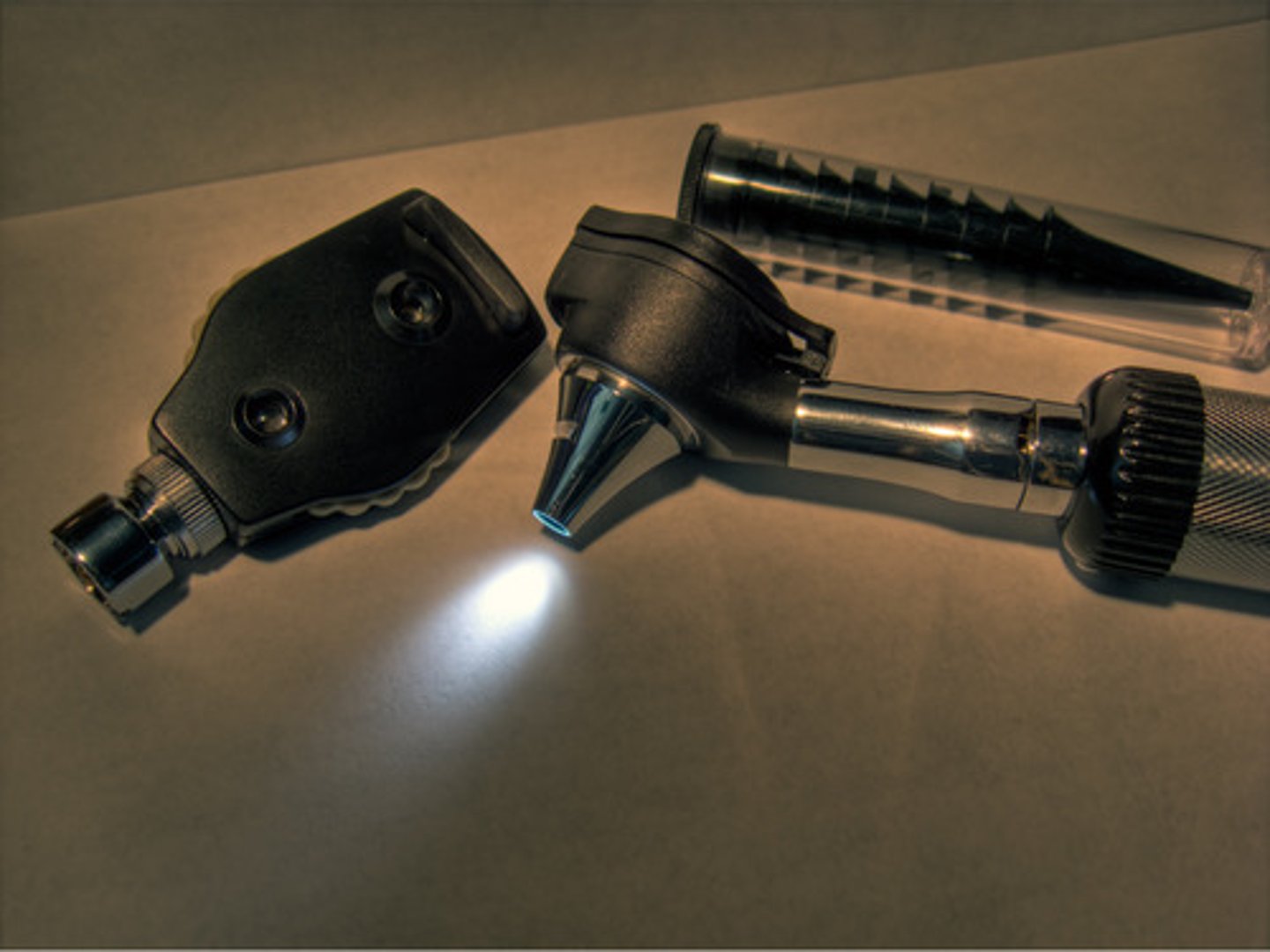
Opthalmoscope (1850)
First visual technology invented by Hermann von Helmholz

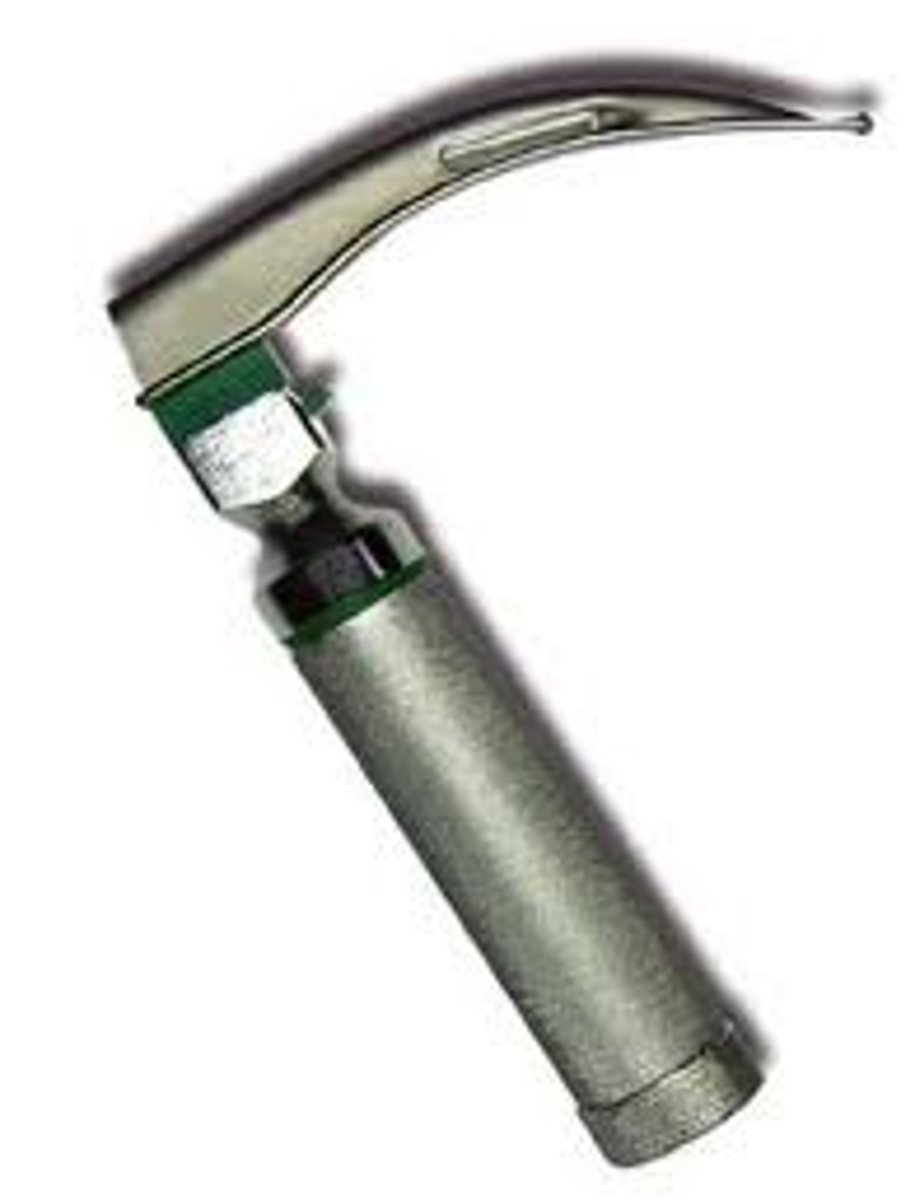
Laryngoscope (1855)
Devised by Manuel Garcia using two mirrors to observe the throat and larynx

X-ray (1859)
Invented by Wilhelm Roentgen when he discovered by accident that radiation could penetrate solid objects of low density; allowed physicians to view the inside of the body without surgery; used to diagnose pneumonia, pleurisy, and tuberculosis since World War II
Electrocardiograph (1903)
Developed by William Einthoven to measure electrical changes during the beating of the heart
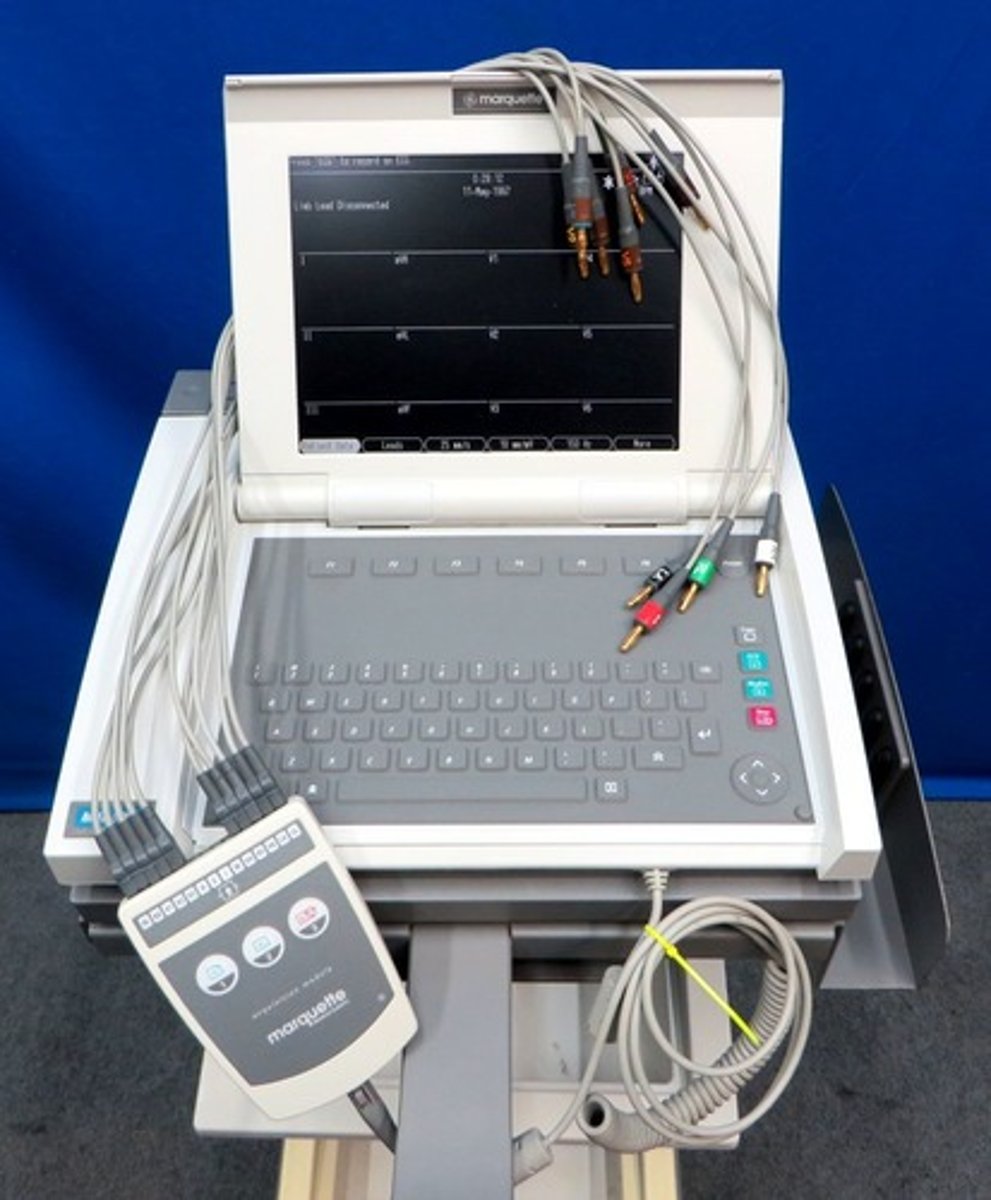

Kenny Method (1910)
Served as the pioneering work for modern physical therapy; devised by Elizabeth Kenny in treatment of polio (then called infantile prompted the invention of a new stretcher (called Sylvia stretcher in 1927) intended for transporting patients in shock.
Drinker Respirator (1927)
Invented by Philip Drinker to help patients with paralytic anterior poliomyelitis recover normal respiration with the assistance of artificial respirator.
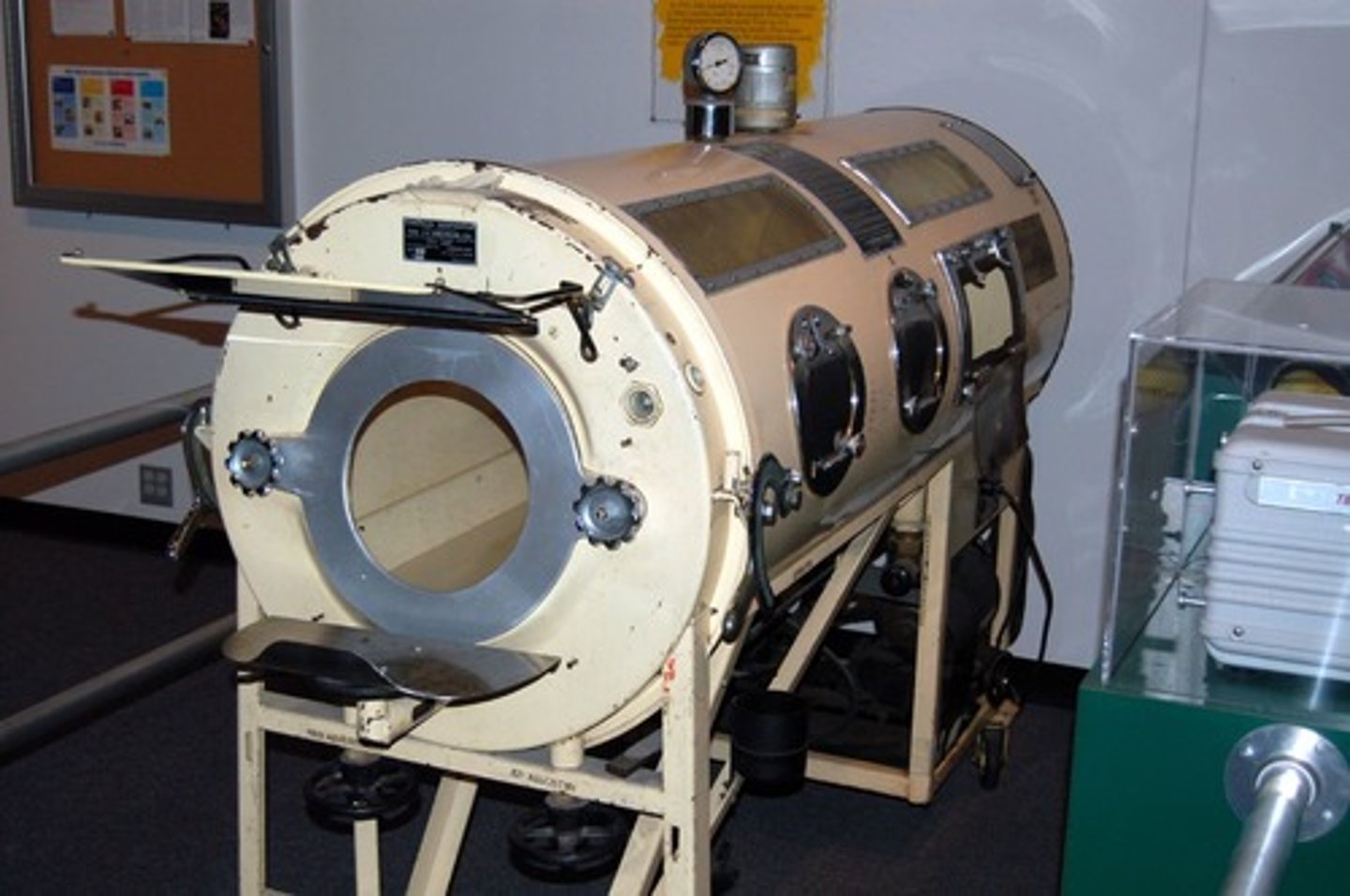

Heart Lung Machine (1939)
First visual technology invented by Hermann von Helmholz
Cardiac Catheterization and Angiography (1941)
First operated by Forsmann in 1929; developed by Moniz, Reboul, Rousthoi between 1930 and 1940; discovered as safe method in humans by Cournand in 1941; made seeing the heart, lung vessels, and valves possible through inserting a cannula in an arm vein and into the heart with an injection of radiopaque dye for X-ray visualization.
Antoine van Leeuwenhoek (1660)
Father of microbiology known for his work on the improvement of microscope.
Edward Jenner (1796)
Discovered vaccination to establish immunity to small pox; Impact of contribution: Immunology
Marie Francois Xavier Bichat (1880)
Identified organs by their types of tissues; Impact of contribution: Histology
Agostino Bassi (1835)
Produced disease in worms by injection of organic material-the beginning of bacteriology
Louis Pasteur (1857)
Successfully produced immunity to rabies
Gregor Mendel (1866)
Enunciated his law of inherited characteristics from studies on plants
Joseph Lister (1870)
Demonstrated that surgical infections are caused by airborne organisms
Robert Koch (1877)
Presented the first pictures of bacilli (anthrax), and later tubercle bacilli
Elie Metchnikoff (1886)
Described phagocytes in blood and their role in fighting infection
Ernest Von Bergmann (1886)
Introduced steam sterilization in surgery
Karl Landsteiner (1902)
distinguished blood groups through the development of the ABO blood group system
August von Wassermann (1906)
Developed immunologic tests for syphilis
Howard Ricketts (1906)
Discovered microorganisms whose range lies between bacteria & viruses called rickettsae.
Hans Fischer (1929)
Worked out the structure of hemoglobin
Jonas Salk (1954)
Developed poliomyelitis vaccine
James Westgard (1973)
Introduced the Westgard Rules for quality control in the clinical laboratory
Baruch Samuel Blumberg (1980)
Introduced the Hepatitis B vaccine
Kary Mullis (1985)
developed the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Andre van Steirteghem (1992)
Introduced the intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF)
James Thomson (1998)
Derived the first human stem cell line