3. Visual System
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Retina converts light to neural signals, retinal nerve fibers, optic disc, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract, lateral geniculate body/nucleus, Primary visual cortex (optic radiations), visual cortex
Describe the visual pathway conveying signals from the retina to the thalamus and cortex.
primary visual cortex, secondary visual cortex, other areas that use visual info to adjust movements or visually identify objects, midbrain
Describe the 4 aspects of visual processing
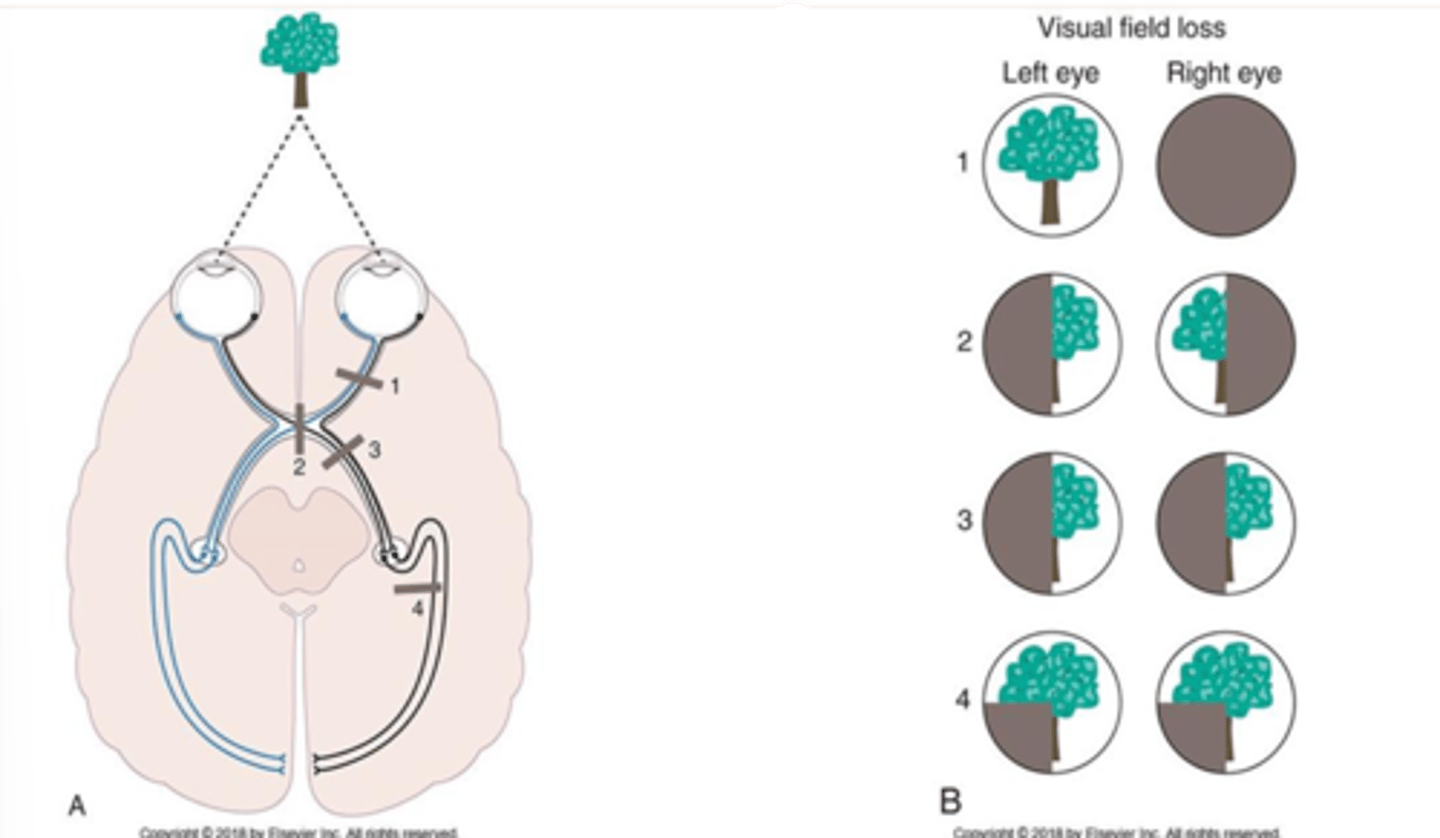
Crosses midline in optic chiasm. Projects to contralateral visual cortex
Explain the nasal half of the retina and the visual fields and the causes and presentations of visual field deficits
Continues ipsilaterally thru optic chiasm. Projects to ipsilateral visual cortex
Explain the temporal half of the retina and the visual fields and the causes and presentations of visual field deficits
sign of nervous system abnormality.
Describe pathologic nystagmus.
normal response elected in an intact nervous system
Describe physiologic nystagmus.
switch vision from one object to another. Voluntarily or elicited by a variety of stimuli
define saccades
used to follow a moving object. image is maintained on the fovea
define smooth pursuit
aims eyes toward the midline. objects fall on core
define convergence.
visual information to stabilize images during slow movements of the head or when visual objects are moving relative to the head. purpose keeps image stable on retina, allows eyes to follow large objects in teh visual field.
Describe the optokinetic nystagmus and their purposes.
action of vestibular information on eye movements during fast movements of the head. purpose to stabilize visual images during head movement. move the eyes in the opposite direction of the head movement to maintain stability of the objects.
Describe the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) and their purposes.
loss of information in both temporal visual fields. damage to fibers in the center of the optic chiasm
Describe the deficits and locations of lesions causing bitemporal hemianopia
loss of visual information from the same visual field. complete lesion anywhere posterior to the optic chiasm
Describe the deficits and locations of lesions causing homonymous hemianopia
no awareness of any visual information dur to a lesion in the brain
Describe the deficits and locations of lesions causing cortical blindness.
bitemporal hemianopsia
What is 2
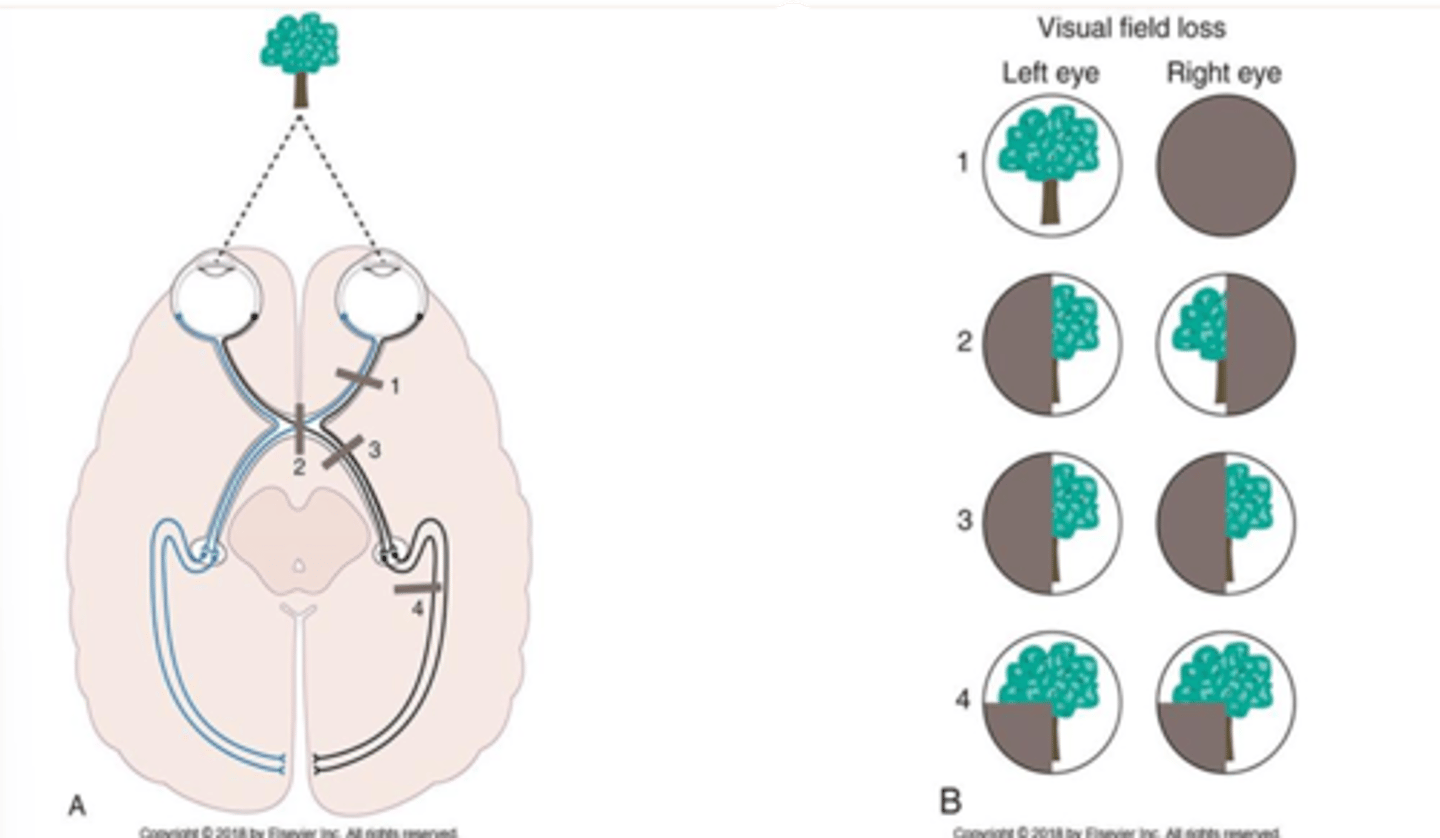
homonymous hemianopsia
What is 3
Contracts when looking at near objects, increasing the curvature of the lens, lens of eye adjusts to focus light on the retina. Afferent limb optic n. Efferent limb oculomotor n.
Describe the stimulus, afferent limb and efferent limb, and response for the accommodation reflex
pupil constricts in eye stimulated by light, pupil of contralateral eye constricts. Afferent limb Optic n. Efferent limb oculomotor n.
Describe the stimulus, afferent limb and efferent limb, and response for the pupillary reflex
3( moves eye up, down and medially raises the upper eyelid), 4 (moves eye down, especially when adducted), 6 (abducts the eye). Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MFL) looking right
List the 3 CN's and MLF and their contributions to normal eye movements.
internuclear ophthalmoplegia. eye ipsilateral to the lesion cannot adduct past midline when contralateral eye moves laterally
Identify the deficits associated with lesions affecting the MLF
Ipsilateral blindness and loss of the direct pupillary light reflex
Identify the deficits associated with lesions affecting CN 2
sever ptosis (drooping of eyelid_, ipsilateral eye is aimed outward and down, diplopia (double vision), deficits in moving ipsilateral eye medially, downward, and upward, loss of direct (ipsilateral) pupillary light reflex, loss of constriction of pupil in response to focusing on a near object
Identify the deficits associated with lesions affecting CN 3
prevents activation of superior oblique muscle
Identify the deficits associated with lesions affecting CN 4
eye deviates inward. Unable to voluntarily abduct the eye will have double vision.
Identify the deficits associated with lesions affecting : CN 6.
eye movement disorders
Lesions affecting the CNs innervate extraocular muscles and result in what?
eye movements will not be coordinated with each other or with movements of the head
Lesions affecting the MLF result in what?