Microbiology: Food Supply Chain (exam 2)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What stresses affect the FSC?
Abiotic factors (storms) and biotic factors (infections, spoilage)
Important of FSC
it is fragile and complex (COVID showed us), the food needs to be consumed and purchased, and agriculture is seasonal and exposed to stresses
More than ½ of the FSC can affect
How can abiotic factors affect the FSC?
a storm disrupts agriculture production, transportation of goods, and no power
What FSC processes were affected by microorganisms during COVID 19?
Labor needs
ecological and climate risks to crops
livestock and poultry disease threats
transportation bottlenecks
What FSc processes were affected by covid but not by microorganisms?
concentration of Agri-Food production, manufacturing and distribution (relying on big companies)
trade disruptions
How do labor needs affect the FSC?
contagious diseases can lead to labor shortages,
lead to the closure of food processing → massive disruptions of the supply chain
higher prices
transportation can be affected by illness
Where can microbes disrupt the supply chain?
Some examples are crop production, animal production, animal feed production, retail stores, consumer storage & preparation
What are some ecological climate risks to crops?
crop diseases caused by microorganisms (most caused by fungi)
wheat rusts
Most common wheat diseases?
leaf rusts, fusarium head blight, triici blotch
How does leaf rust occur?
this is a wheat disease where the fungus has 2 hosts
the first cycle is on wheat and then transfers to meadow rue; it is dependent on the plants being in the vicinity of each other
What are some ways to stop leaf rust?
Crop rotation, breed resistant to fungus wheat plants
How does livestock and poultry affect the FSC?
animal disease (severe and can spread throughout the whole agriculture industry
lead to lower food production
What is an effective method of slowing/ stopping a virus?
create a vaccine against virus or cull any infected herds
not a good answer: treating with antibiotics
What do cells need for growth/ division?
energy, carbon, other nutrients, appropriate environmental conditions
What are examples of energy used for growth?
light, chemicals
What are examples of carbon used for growth?
CO2, CH4, organic chemicals
some source of carbon is needed to make organic carbon and all different cell components
What are examples of other nutrients cells use for growth?
NCHOPS (nitrogen, phosphorus..)
Macronutrients
NCHOPS and are needed in high quantities (depends on organism)
How do cells get carbon?
organic compounds (protein), carbon dioxide, methane
How do cells get nitrogen?
get from amino acids, N2 fixers (nitrates or ammonia), assimilated forms
Micronutrients
needed in tiny amounts (0.01-1%) but ESSENTIAL
magnesium, potassium, iron, calcium, sodium
How do cells transport their micronutrients?
cells have separate transport mechanisms for all of them
Magnesium (micronutrient) function
stabilizes ribosome, needed for ATP dependent reactions
ANYTHING that uses ATP needs magnesium to help it bind to the enzyme
Potassium (micronutrient) function
main cellular cation to balance out charge
Iron (micronutrient) function
needed for many enzymes (metabolism)
Calcium (micronutrient) function
not essential for all cells
Sodium (micronutrient) function
hot essential for all cells
What is the difference between a micronutrient and a trace element?
the concentration: micronutrients don’t need a lot of themselves but still need it or some
Trace elements
needed in small quantities (few molecules per cell) but still very important
OVERALL POINT: microbes will spend a lot of energy to get them into the cell
What are some examples of trace elements?
Boron, chromium, cobalt, copper, zinc, tungsten, nickel, selenium, molybdenum, maganese
specific requirements vary per microorganism
How do trace elements help the cell?
help the active site of enzymes carry out its reaction (in coenzymes and cofactors)
process of iron acquisition (getting into the cell) IN ECOLI
Iron is binded to a siderophore → ,makes its own specific porin to allow iron to pass through the cell membrane → ABC transporter to get inside of the cell (recognition Fep B, transporter Fep D, ATPase Fep C) → cell has iron, reduces it and used it for metabolism
Siderophores
small molecules that bind iron
Growth Factors
not elements they are organic compounds needed by some cells because they can’t make them (get through diet)
How do microbes get food?
absorptive via transport proteins (all microbes)
endocytosis (eukaryotic microbes)
sub categories of endocytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
What is endocytosis?
cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle
the process where something binds the membrane → goes to a clathron coated pit → goes into cell as an endosome PH DROPS on endosome → nutrients are then digested, transported, released into the cell
What is phagocytosis?
engulfs large solid particles
mostly used when talking about the immune system
pinocytosis
a process by which the cell takes in the fluids along with dissolved small molecules.
What if food is a gas, how can it be concentrated?
Gas is membrane permeable, goes right into cell and floats out
How is oxygen transported?
hemoglobin is in our red blood cells and binds to O2 molecule
Explain how gases are captured (enzymes and cofactors)
When high concentr. of O2 in lungs → hemogl. binds to O2 molecul. → binds to red blood cell (erythrocyte) → rbc goes through body to muscles where there is less O2 and goes into cells → bound by things inside cells like (cytochromes → to mitochondria)
What if food is too large to transport?
bacteria sends enzymes (exoenzymes) to break down the polymers to monomers → brings in monomers
What are common polymers?
cellulose, proteins, lignin chitin
where do microbes get food?
soluble nutrients (saprobes) (take stuff from the environment and bring it in)
other cells (predators and parasites)
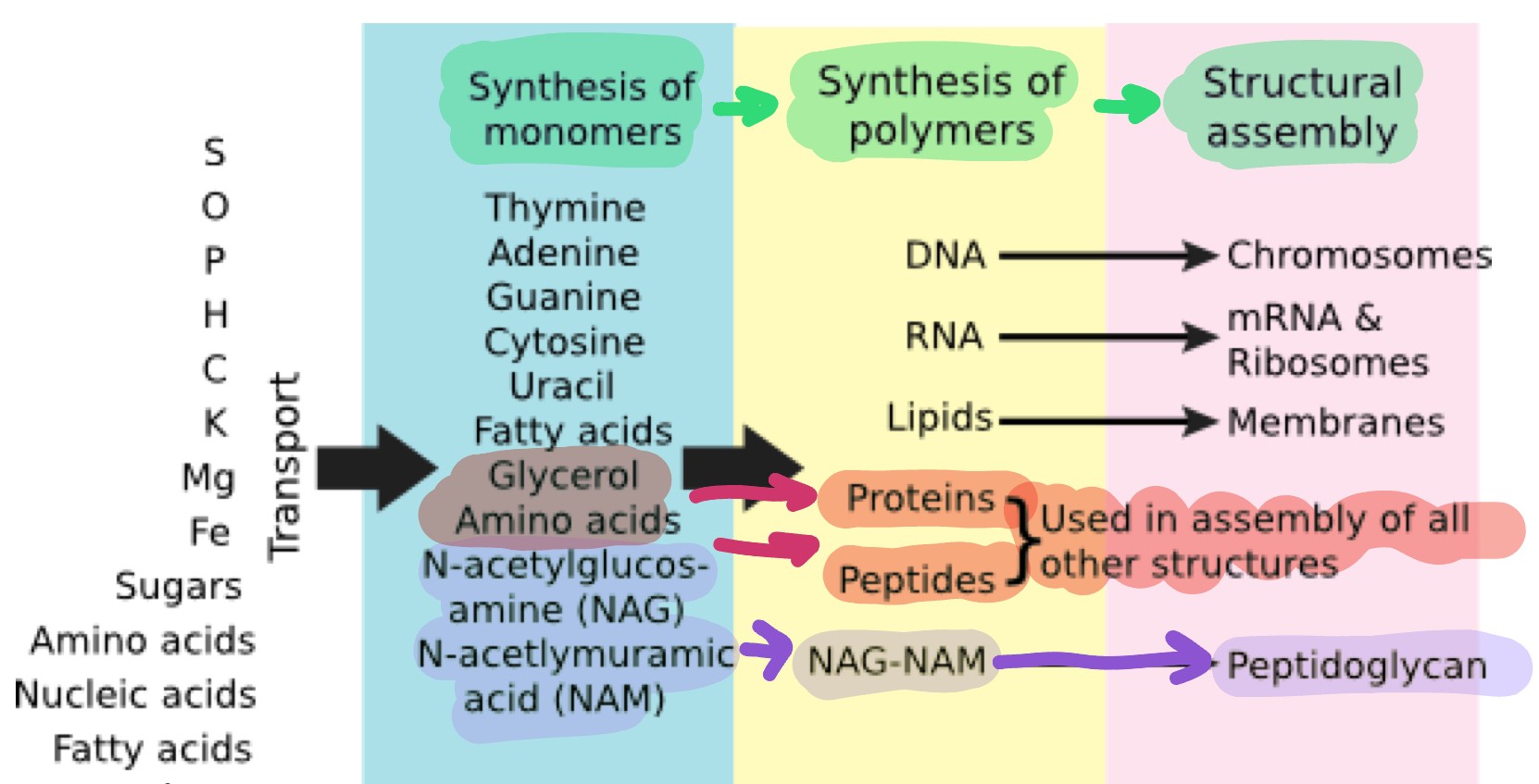
where do the macronutrients go?
they are metabolized to make more cellular components
simple elements → structures in cell
food is a…
macronutrient
Nutritional classification
source of energy to fuel cell functions
source of carbon
source of electrons - need high energy e- and energy in the form of ATP and other chemical phosphates
chemotroph
chemical energy
phototroph
light energy
autotroph
CO2 carbon dioxide
heterotroph
organic compounds
lithotroph
inorganic chemicals
organotroph
organic chemicals
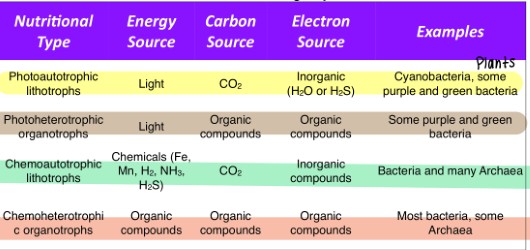
four most common groups in nature
photoautotrophic lithotrophs
photoheterotrophic organotrophs
chemoautotrophic lithotrophs
chemoheterotrophic organotrophs
photoautotrophic lithotrophs
energy source: light
carbon source: CO2
e- source: inorganic (H2O or H2S)
ex: plants, cyanobacteria, some purple / green bacteria
photoheterotrophic organotrophs
energy source: light
carbon source: organic compounds
e- source: organic compounds
ex: some purple / green bacteria
chemoautotrophic lithotrophs
energy source: chemicals (Fe, Mn, H2, NH3, H2S)
carbon source: CO2
e- source: inorganic compounds
ex: bacteria, MANY archaea
chemoheterotrophic organotrophs
energy source: organic compounds
carbon source: organic compounds
e- source: organic compounds
ex: most bacteria, some archaea
what does nutritional classification ignore about bacteria?
ignores that certain bacteria has needs for other nutrients besides electron source and carbon energy
What is the difference between trace elements and growth factors?
growth factors are organic compounds (both of these are required in small amounts)
Isolation techniques
simple plating- plate everything there
enrichment culture
simple plating
selects for fastest growing, best adapted to those conditions
use a medium that you think will support a lot of stuff
enrichment culture
stacking deck in your favor
manipulating the nutrient conditions and stack in your favor
What are pros of simple plating (or tube culture)?
may be able to isolate colonies
What are cons of simple plating?
microbe must grow on medium
competition between microbes
hard to select desired microbe
What is a pro of enrichment culture?
can select for desired metabolic capacity?
What is a con of enrichment culture?
will only get certain types
What are the types of media?
differential and selective
differential media
allows us to identify microbes by a reaction in the medium
everything can grow on the plate but there is a way to detect what you are interested in
selective medium
favors the growth of some microbes (only one can grow)
every medium is selective
syntrophy
cooperation between organisms (dependent on one another)
why cant we isolate some organisms?
when trying to culture them individually they don’t survive because they don’t have partners they depend on
Other growth requirements
presence of other microbes
nutrient concentration
unique microenviornments
growth on surface
Defined media
know everything that goes into it AND you know exact amounts you put in
complex media
know what it is and how much you added but don’t know everything that’s in it