Nutrition Unit 0/1
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
Diet
A person’s usual pattern of food choice
Carbohydrates
Major source of energy
Lipids
Major source of energy, absorption of fat soluble vitamins
Proteins
Production of structural components (muscle fibers) and functional components (enzyme), Minor energy source
Vitamins
Regulation of body processes, production and maintance of cells
Minerals
Regulation of body processes (fluid balance and energy metabolism)
Water
Maintenance of fluid balance
Essential Nutrients
Must be supplied by food because the body does not synthesize it or make enough to meet its needs
Water is the most
essential nutrient
Majority of nutrients are
essential
Macronutrients
Carbohydrates, fats, proteins, things that the body need in large amounts
Micronutrients
Vitamins, Minerals, Things that the body needs in small amounts
Phytochemicals
Substances in plants that are not nutrients but have negative/positive benefits
Carotenoids
Lowers risk of cancer/macular degeneration (orange/red/yellow plants)
Phenolics
Lowers risk of cancer, heart disease and is a antioxidant (plants, tea, coffee, choclate)
Organosulfides
Reduces risk of heart disease and improves immune function, is antioxidant (garlic, onions, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, kalte)
Alkaloids
Stimulant effects (coffee, tea, cocoa)
Capsaicinoids
Pain relief (chilli peppers)
calorie
Amount of heat needed to raise the temp of 1 g (1mL) of water 1 degree C
Kilocalorie/Calorie
Amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1000 g ( 1L) of water 1 degree C
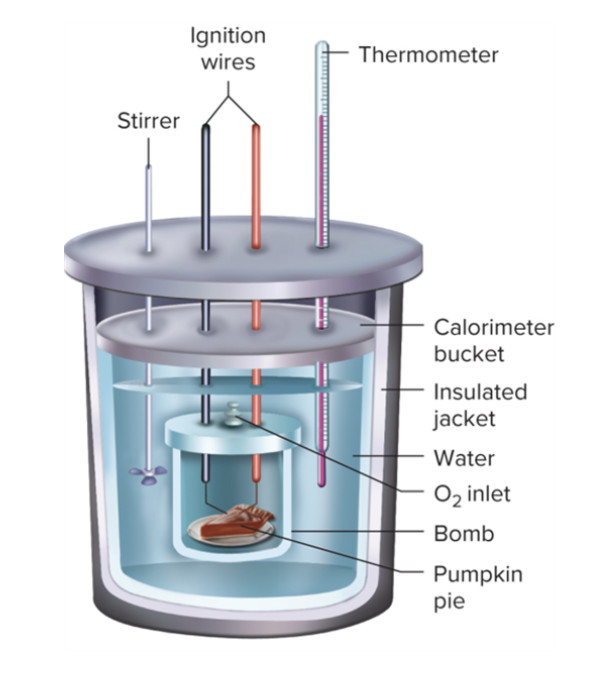
Bomb calorimeter
Device used to measure the calorie content of foods and beverages
Food influences
Taste, smell, stress, culture, religion, cost, availability, attractiveness of food
Dietetics
Application of nutrition and food information to achive/maintain optimal health
Role of a dietetician
Fit your budget, support your health goals, are accessible, taste good
Nutrient dense
Have beneficial nutrients in relation to calories per serving
Energy dense
Have a lot of energy (calories) and few nutrients)
Empty calories
Low sources of nutrients and lots of energy (added fats/sugars/alchols)
Ancedotes
Personal reports concerning the effectiveness of a treatment (Cannot be applied to a group)
In vivo
Describes experiment on living animals (Hard/difficult to be conducted, lots of variables and limitations)
In vitro
Describes experiments on cells or other compoents derived from living organisms (Inexpensive, fast and lots of variable control)
Why are mice used on in vivo experiments?
Adapts to surroundings easily, are small, reproduce quickly, short life span, are cheap, docile, and has behavior that closely resemble those of humans and their symptoms
Epidemiology
Adapts to surroundings easily, are small, reproduce quickly, short life span, are cheap, docile, and has behavior that closely resemble those of humans and their symptoms
Most nutritional research on humans are
observational
Case control studies
Study where individuals with health conditions are matched to people with similar characteristics who don't have that condition.
Advantages/Disadvantages of Case control studies
Can be quick/cheap, are good to use in outbreaks or in studying rare disease. But have a small pool
Cohort studies
Study where various kinds of information about a large group of people over time are collected/analyzed
Advantages/Disadvantages of Cohort studies
Can be retrospective/prospective (Follow over time to see disease development or look at the past to ID the disease) and allows scientists to examin multiple outcomes simultaniously. But requires a large pool, is expensive, and takes a long time
Correlations
Relationships between variables and health outcomes
Direct/positive correlations
When two variables change in the same direction (both increase or decrease)
Inverse/negative correlations
When two variables change in opposite direction (one increases and other decrease)
Epidemiological studies cannot establish
causation (Difficult to prove, can’t control all variables in free living humans)
Causation
A specific practice that is responsible for an effect
Randomized control trials
Study in which only the treatment group receives the intervention with their outcomes being compared to the control group
Pragmatic Trials
Clinical trial that measures the relative effectiveness of treatments in real world conditions
FDA
Regulates nutrition and health related claims on product labels (Cannot prevent spread of misinformation on internet)
FTC
Protects consumers against unfair/deceptive acts or practices by businesses in the U.S.
Nutritional Requirement
Smallest amount needed to maintain a level of nutritional health
Enrichment
Nutrients that are lose during food processing that's been added back
Fortification
Addition of nutrients to any food that were not originally in the food
What is the Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Guideline that promots nutriential need, health and provent chronic diseases