unit 2.1 ch.5 metabolism
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
metabolism
all chemical reactions in the body, breakdown and build up of nutrients within a cell
metabolic pathway
determined by enzymes, sequences of enzymatically catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell
anabolism
use energy, endergonic, build up, synthesize
catabolism
exergonic, breaks down, provides energy
enzymes
encoded by genes, biological catalyst act on specific substrate and lowers activation energy, ends with -ase usually, remains unchanged after reaction
factors that influence enzyme activity
high temp, extreme ph denature proteins, high substrate concentration,
activation energy
(collision) energy required for chemical reaction to occur
atp in metabolism
for anabolic rxns it is required for catabolic rxns it is released by oxidation
redox rxns in metabolism
catabolic is oxidation so it loses e- or h atoms, anabolic is reductive gains e- and h atom
electron carriers in metabolism
shuttle electrons between each other to generate atp, cellular respiration, NAD+, NADP, FAD, coenzyme, donates e-
oxidation
+o2, -H, -e
reduction
-o2, +h, +e
redox
oxidation: oxidation agent, +o2, -H, -e, releases energy
reduction: reducing agent, -o2, +h, +e, requires energy
types of phosphorylation
substrate level, oxidative, photophosphorylation
metabolic pathways in cellular respiration generate ATP
breaks down glucose to produce this, 30 to 32 per glucoses (most in etc 28-32)
metabolic pathways in cellular respiration generate NADH
2 in glycolysis, 2 in pyruvate oxidatio,6 in kerbs cycle
metabolic pathways in cellular respiration generate intermediates
pyruvate, acetyl-CoA, and various others
cellular respiration
carb catabolism (glycolysis, Krebs cycle, e-tc oxidation of molecules to operate an electron transport chain), final e- acceptor is from outside cell and is inorganic, aerobic vs anaerobic, atp is generated by oxidative phosphorylation
metabolic pathways in cellular respiration generate co2
(aerobic) Krebs cycle, oxidizes pyretic acid and decarboxylation (loss of co2) occurs, results in acetyl CoA and NADH
aerobic in cellular respiration
uses oxygen as final electron acceptor, presence of O2, oxidizes pyruvic acid to CO2 and H2O
anaerobic cellular respiration
uses a molecule other than oxygen as final electron acceptor, occurs in absence of O2, reduces pyruvic acid to lactic acid
fermentation definition /purpose
releases energy from the oxidation of organic molecules, does not require oxygen, no kerb cycle or etc, uses organic molecule as final e- acceptor, produced small amount of atp
why does cellular respiration produce more atp then fermentation
because it includes the kerbs cycle and the e-tc
foods produced by bacterial fermentation
cheese, yogurt, rye bread, sauerkraut
beverages produced by bacterial fermentation
alcohol (beer &wine),
how fermentation is used in bacteriological identification (MRVP test)
bacteria that catabolize carbohydrate or protein produce acid, causing the pH indicator to change color. below 4.4= red, above 6= yellow
light dependent photosynthesis rxn
light, conversion of light energy into chemical energy, ATP & NADPH
light independent photosynthesis rxn
dark, ATP & NADPH are used to reduce CO2 to sugar (carbon fixation) via the Calvin-Benson Cycle
photosynthesis oxygenic
plants, algae, cyanobacteria, produces O2
CO2 + 12H2O + Light Energy —> C6H12O6 + 6H2O + O2
photosynthesis anoxygenic
purple sulfur/green sulfur bacteria, does not produce O2
6CO2 + 12H2O + Light energy —> C6H12O6 + 6H20 + 12S
amphibole pathways
metabolic pathways that function in both anabolism and catabolism
nutritional patterns of microbes by source of energy and carbon
photoautotroph, photoheterotroph, chemoautotroph, chemohetertroph
substrate
contacts enzymes active site to form complex, transformed and rearranged into products then released from enzyme, has enzymes specific to it
intermediate
chemical substance produced between conversion of substrate/reactant to product
metabolite
carbs, amino acids, proteins, ethanol, substance produced during metabolism
phosphorylation
this happens to adp to become atp, adding a phosphate group/ providing energy
denature
happens to an enzyme/protein at a certain temperature….
atp
adenosine triphosphate, main source of energy
catalyst
speed up chemical reactions without being altered
glycolysis
breaks down glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvate, 2NADH, 2atp, cytosol
CITRIC CYCLE/ KREBS CYCLE
completes breakdown of glucose, twice for 1 mol. of glucose, 2co2 &6NADH & 2FADH & 2ATP per glucose mol. mitochondrion
oxidative phosphorlation
accounts for most of atp synthesis, etc, chemiosmosis, mitochondrion
3 process of cellular respiration
glycolysis, kerbs cycle, (oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate oxidation= 2 acetyl CoA in mitochondrion) etc
biosynthesis
purine & pyrimidine (glycolysis & Krebs cycle), amino acid (Krebs cycle, transamination), simple lipids (glycolysis, dihydroxyacetone, Krebs cycle), polysaccharides (glycolysis)
electron acceptor
gains e-, ex) O, Fe(III), Mn(IV), SO4
enterobacteriaceae
rod shaped, gram negative, facultative anaerobes, ferment glucose, non spore forming, motile, reduces nitrate, e.coli. foodborne pathogens, UTIs
coliform
gram negative, rod shape, ferment lactose produce acid and gas
cyanobacteria
photoautotroph, oxygenic, oxygen production and nitrogen fixation
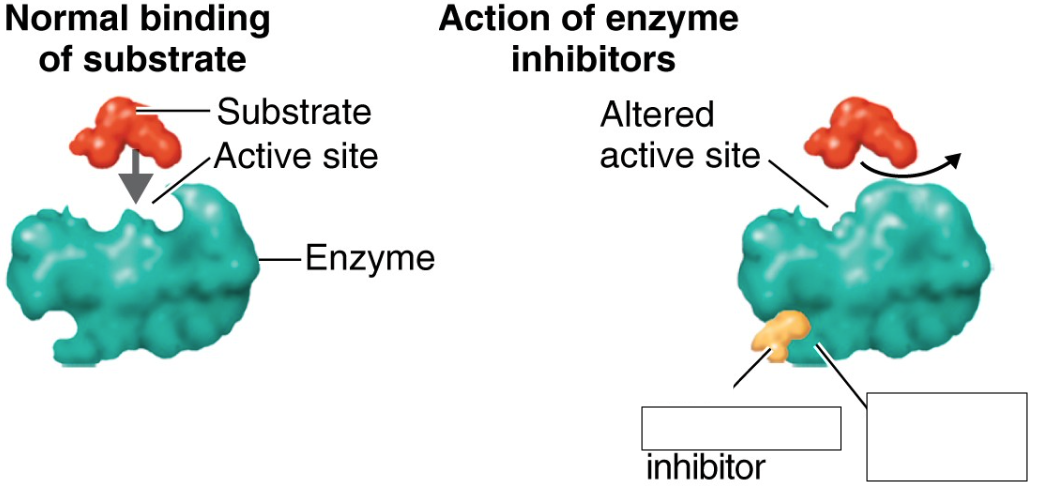
allosteric inhibition
indirectly changes the shape of the active site, rendering the enzyme nonfunctional, can be reversible or irreversible
anabaena
cyanobacterium, nitrogen fixing, aquatic, algae, photoautotroph
rhizobium
entner-doudoroff pathway, bacteria, gram negative, nitrogen fixation, rod shaped
carbon fixation
light independent reactions via calvin-benson cycle
chemiosmosis
process where ATP is generated from ADP using energy derived from the etc, electrons pass down while protons are pumped across membrane , establishes proton gradient (proton motive force) higher proton conc. diffuses to other side through atp synthase, releases energy to synthesize ATP
amphibolic
metabolic pathways that function in both anabolism and catabolism
entner-doudoroff pathway
produces NADPH & ATP, does not involve glycolysis, operates independently, occurs in pseudomonas, rhizobium, and agrobacterium
pentose phosphate pathway
breaks down 5c sugars and/or glucose produces NADH, operates simultaneously w/ glycolysis, can provide intermediates for synthesis rxns
(1)coenzyme vs (2)cofactor
(1) an organic version of 2, (2) the non protein component of an enzyme and activator
alcohol fermentation
produces ethanol + CO2, glucose is oxidized to pyruvic acid (converted to acetaldehyde and CO2; NADH reduces acetaldehyde to ethanol)
lactic acid
heterlactic (produces lactic acid and other compounds) and homolactic (only produces lactic acid), glucose is oxidized to pyruvic acid, which is then reduced by NADH
heterotroph
obtains energy by consuming other organiusms
noncompetitive inhibitors
interact with another part of the enzyme (allosteric state) rather than the active site, inhibits allosterically
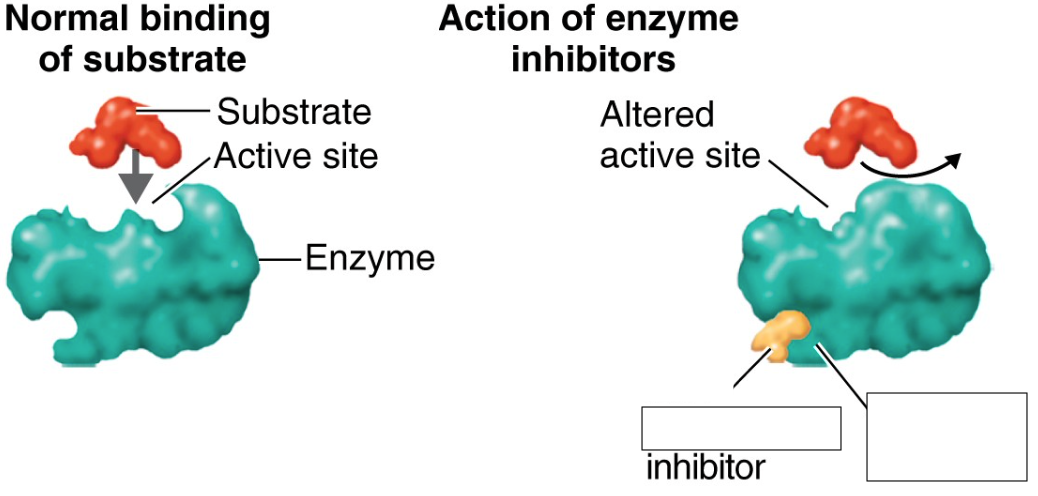
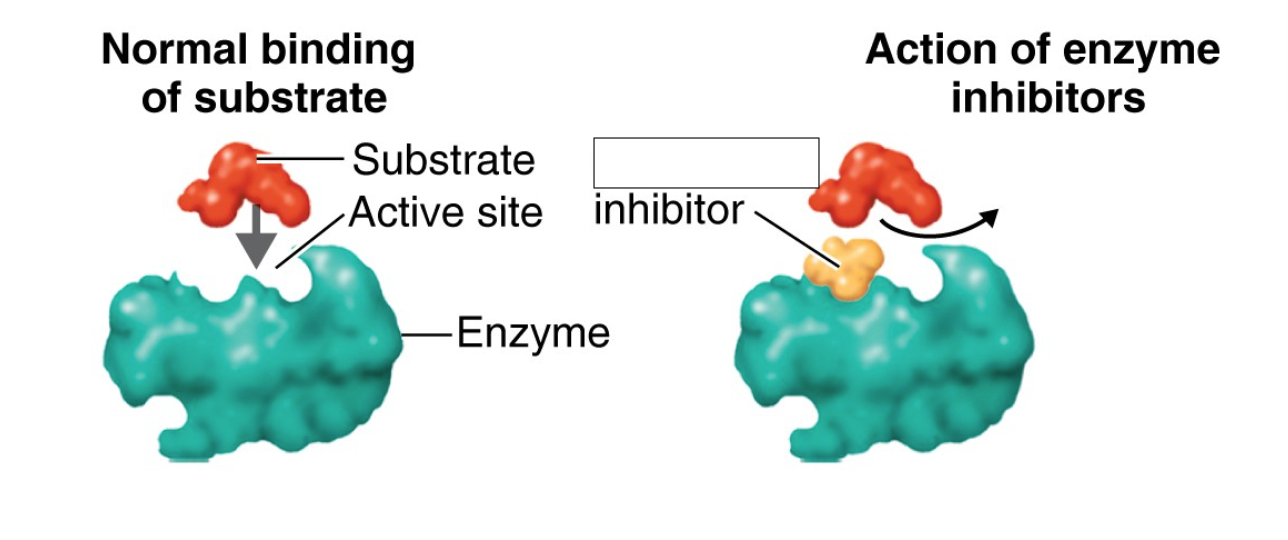
competitive inhibitors
fills active site of an enzyme and competes with the substrate, sulfanilamide
autotroph
produces its own food
phototrophs
uses light energy to drive atp production
photoautotrophs
uses energy obtain initially from light in the calvin benson cycle to fix co2 to sugar, oxygenic or anoxygenic, oxygenic: cyanbacteria, plans and anoxygenic: green bacteria, purple bacteria
photohetertrophs
uses organic compounds as source of carbon, anoxygenic, green bacteria, purple nonsulfur bacteria
chemoautotrophs
obtain energy from inorganic chemicals use CO2 as c source, energy is used in Calvin-benson cycle to fix CO2, iron oxidizing bacteria
chemohetertroph
obtain energy and carbon from organic chemicals, medically and economically important, animals, fungi, protozoa, bactera