Microbiology Exam 2
1/261
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
262 Terms
Sepsis
Bacterial contamination
Asepsis
absence of significant contamination
Sterilization
removing and destroying all microbial life using temp and pressure
Commercial Sterilization
killing Clostridium botulinum endospores from canned goods
Disinfection
destroying harmful microorganisms on non-living things
Antisepsis
Destroying harmful microorganisms on living things
Degerming
the mechanical removal of microbes from a limited area
Sanitization
removal of pathogens from objects to meet public health standards
Biocide (Germicide)
Treatment that kills microbes
Bacteriostasis
Inhibiting microbes (not killing)
What does the effectiveness of treatment depend on?
Number of microbes, environment (organic matter, temperature, biofilms), time of exposure, microbial characteristics
Microbial Control Agent Actions
Altercation of membrane permeability; damage to proteins (enzymes); damage to nucleic acids
What are the physical methods of microbial control?
Heat, low temp, desiccation, osmotic pressure, radiation
How does heat control microbial growth?
Denatures enzymes
What is the Thermal death point (TDP)?
lowest temperature at which all cells in a liquid culture are killed in 10 min
What is the Thermal death time (TDT)?
minimal time for all bacteria in a liquid culture to be killed at a particular temperature
What is the Decimal reduction time (DRT)?
Minutes to kill 90% of a specific population of bacteria at a given temperature
Moist Heat Sterilization
Autoclaving; Pasteurization; Boiling
Autoclave
Steam under pressure; 121 degrees C, 15 psi, 15 minutes; kills all organisms and endospores
Pasteurization
reduces spoilage organisms and pathogens
High-temperature short-time (HTST)
most common form of pasteurization; uses metal plates and hot water to raise milk temperatures to at least 72° C for 15 seconds, followed by rapid cooling
Dry Heat Sterilization
kills by oxidation (removal of electrons); flaming; incineration; hot-air sterilization
Filtration Sterilization
a "cold" method of sterilization that removes microbes instead of killing them; used for heat-sensitive materials;
HEPA (high-efficiency particulate air) filter
remove microbes > 0.3μm in diameter
Membrane filters
remove microbes >0.22 μm
How does low temperature control microbial growth?
Refrigeration, deep-freezing, lyophilization (freeze drying)
Desiccation
Absence of water prevents metabolism; drying out an organism
How does osmotic pressure control microbial growth?
uses high concentrations of salts and sugars to create hypertonic environment
Ionizing radiation
Includes X-Rays, gamma rays, electron beams; Ionizes water to create reactive hydroxyl radicals; Damages DNA by causing lethal mutations
Nonionizing radiation
Includes ultraviolet, 260 nm; Damages DNA by creating thymine dimers
Microwaves
kill by heat; not especially antimicrobial
Radiant Energy Spectrum
- Wavelength increases as you go from gamma rays to radio waves
- Energy increases as you go from radio waves to gamma rays
Principles of Effective Disinfection
Concentration of disinfectant; Organic matter; pH; Time
Use-Dilution Tests
-Metal cylinders are dipped in test bacteria and dried
-Cylinders are placed in disinfectant for 10 min at 20°C
-Cylinders are transferred to culture media to determine whether the bacteria survived treatment

Disk-Diffusion Method (Kirby-Bauer test)
-Evaluates efficacy of chemical agents
-Filter paper disks are soaked in a chemical and placed on a culture
-Look for zone of inhibition around disks
If you wanted to disinfect a surface contaminated by vomit and a surface contaminated by a sneeze, why would your choice of disinfectant make a difference?
Sneeze is watery and vomit has food so the two are completely different
Phenol (Phenolics)
Injure lipids of plasma membranes, causing leakage
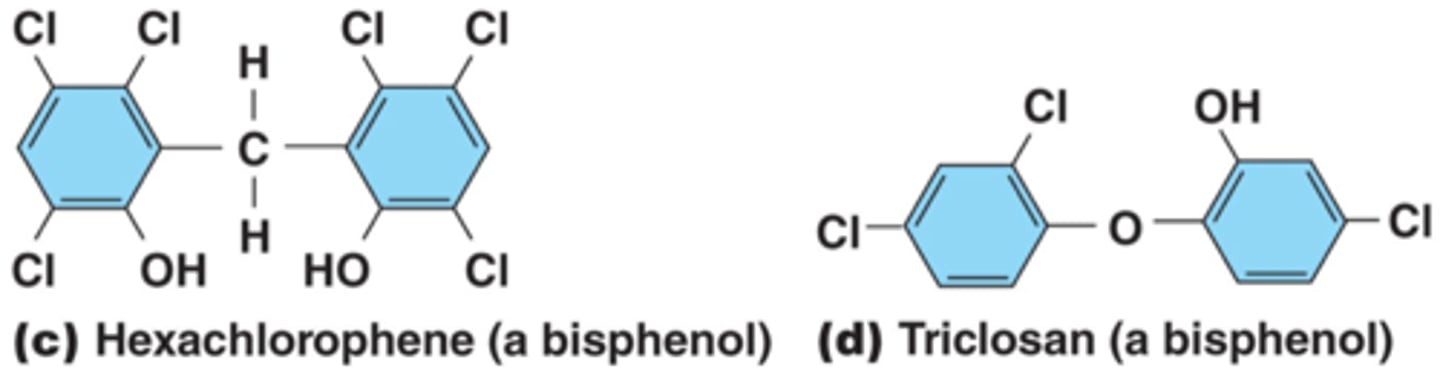
Bisphenols
-Contain two phenol groups connected by a bridge
-Example: Hexachlorophene and triclosan
-Disrupt plasma membranes
Biguanides
- Example: Chlorhexidine
- Used in surgical hand scrubs
- Disrupt plasma membranes
Essential Oils (EOs)
-Mixtures of hydrocarbons extracted from plants
-Examples: Peppermint oil, pine oil, orange oil
-Used for centuries in traditional medicine and for preserving food
-Microbial action primarily due to phenolics and terpenes
-Stronger activity against gram-positive bacteria; effectiveness against viruses not studied to date
Halogens
Iodine and Chlorine
Iodine
-Tincture: solution in aqueous alcohol
-Iodophor: combined with organic molecules
-Impairs protein synthesis and alters membranes
Chlorine
- Oxidizing agents; shut down cellular enzyme systems
- Bleach: hypochlorous acid (HOCl)
- Chloramine: chlorine + ammonia
Alcohols
- Denatures proteins and dissolves lipids
- No effect on endospores and nonenveloped viruses
- Ethanol and isopropanol- Require water
Heavy Metals and their Compounds
-Oligodynamic action: very small amounts exert antimicrobial activity; a biocidal effect of metals, especially heavy metals, that occurs even in low concentrations
-Denature proteins
-Ag, Hg, Cu, Zn
Silver Nitrate
used to prevent ophthalmia neonatorum
Mercuric chloride
prevents mildew in paint
Copper sulfate
algicide
Zinc chloride
found in mouthwash
Surface-Active Agents
soap, acid-anionic sanitizers, quaternary ammonium compounds (quats)
Soap
Degerming; emulsification (breaks down lipids)
acid-anionic sanitizers
Anions react with plasma membrane
quaternary ammonium compounds (quats)
Cations are bactericidal, denatureproteins, disrupt plasma membrane
Chemical Food Preservatives
-Sulfur dioxide prevents wine spoilage
-Organic acids: inhibit metabolism; Sorbic acid, benzoic acid, and calcium propionate prevent molds in acidic foods
-Nitrites and nitrates prevent endospore germination
Bacteriocins
proteins produced by one bacterium that inhibits another
Nisin and natamycin (pimaricin)
prevent spoilage of cheese
Aldehydes
- Inactivate proteins by cross-linking with functional groups (-NH2, OH, -COOH, -SH)
- Used for preserving specimens and in medical equipment (Formaldehyde and ortho-phthalaldehyde) (Glutaraldehyde is one of the few liquid chemical sterilizing agents)
Chemical Sterilization
-Gaseous sterilants cause alkylation—replacing hydrogen atoms of a chemical group with a free radical
-Cross-links nucleic acids and proteins
-Used for heat-sensitive material (Ethylene oxide)
Plasma
- Fourth state of matter, consisting of electrically excited gas
- Free radicals destroy microbes
- Used for tubular instruments
Supercritical Fluids
-CO2 with gaseous and liquid properties
-Used for medical implants
Peroxygens and Other Forms of Oxygen
-Oxidizing agents
-Used for contaminated surfaces and food packaging (O3, H2O2, and peracetic acid)
Is Betadine an antiseptic or a disinfectant when it is used on skin?
antiseptic
What chemical disinfectants can be considered sporicides?
Nitrate and nitrite prevent endospore germination
The presence or absence of endospores has an obvious effect on microbial control, but why are gram-negative bacteria more resistant to chemical biocides than gram-positive bacteria?
Gram-negative has two plasma membranes and a liposaccharide covering and when it's broken down, Lipid A is released which is a toxin
Selective toxicity
selectively finding and destroying pathogens without damaging the host
Chemotherapy
the use of chemicals to treat a disease. Paul Ehrlich coined the term "chemotherapy"
Antibiotic
a substance produced by a microbe that, in small amounts, inhibits another microbe
Antimicrobial drugs
synthetic substances that interfere with the growth of microbes
Who coined the term chemotherapy?
Paul Ehrlich coined the term "chemotherapy"
More than half our antibiotics are produced by a certain genus of bacteria. What is it?
Streptomyces genus
Narrow spectrum of microbial activity
drugs that affect a narrow range of microbial types
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
affect a broad range of gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria
Superinfection
overgrowth of normal microbiota that is resistant to antibiotics
Identify at least one reason why it's so difficult to target a pathogenic virus without damaging the host's cells.
Because the virus lives inside the host cell so it's difficult to get to it and can affect the host cells
Why are antibiotics with a very broad spectrum of activity not as useful as one might first think?
They destroy many normal microbiota of the host
Bactericidal
Kill microbes directly
Bacteriostatic
Prevent microbes from growing
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
1. Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
2. Inhibition of protein synthesis
3. Inhibition of nucleic acid replication and transcription
4. Injury to plasma membrane
5. Inhibition of synthesis of essential metabolites
Inhibiting cell wall synthesis example
Penicillins prevent the synthesis of peptidoglycan
Inhibiting protein synthesis
-Target bacterial 70S ribosomes
-Examples: Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, streptomycin, tetracyclines
Injuring the plasma membrane examples
- Polypeptide antibiotics change membrane permeability.
- Antifungal drugs combine with membrane sterols.
- Ionophores antibiotics allow uncontrolled movement of cations (not for human use)
What cellular function is inhibited by tetracyclines?
Protein Synthesis
Inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis
Interfere with DNA replication and transcription
Inhibiting the synthesis of essential metabolites
- Antimetabolites compete with normal substrates for an enzyme
- Example: Sulfanilamide competes with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), stopping the synthesis of folic acid
Penicillin
- Contain a β-lactam ring: Types are differentiated by the chemical side chains attached to the ring
- Prevent the cross-linking of peptidoglycans, interfering with cell wall construction(especially gram-positives)
Natural penicillins
- Extracted from Penicillium fungi cultures: Penicillin G (injected) and Penicillin V (oral)
- Narrow spectrum of activity
- Susceptible to penicillinases (β-lactamases)
β-lactamases
inactivate beta-lactam antibiotics
Semisynthetic penicillins
- Contain chemically added side chains, making them resistant to penicillinases
- Oxacillin: Narrow spectrum; only gram-positives; resistant to penicillinases
- Ampicillin: Broad spectrum; mostly gram-negatives
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins
Methicillin and oxacillin
Extended-spectrum penicillins
- Effective against gram-negatives as well as gram-positives
- Example: ampicillin, amoxicillin
Penicillins plus β-lactamase inhibitors
Contain clavulanic acid, a noncompetitive inhibitor of penicillinase
Carbapenems
modified to make broad spectrum
Monobactam
- Synthetic; single ring instead of the β-lactam double ring
- Low toxicity; works against only certain gram-negatives
Cephalosporins
- Work similar to penicillins
- β-lactam ring differs from penicillin
- Grouped according to their generation of development
Polypeptide antibiotics
-Bacitracin: Topical application; works against gram-positives
- Vancomycin: Last line against antibiotic-resistant MRSA
- Teixobactin: A new class of antibiotics; worksagainst gram-positives
Antimycobacterial Antibiotics
- Isoniazid (INH): Inhibits the mycolic acid synthesis in mycobacteria
- Ethambutol: Inhibits incorporation of mycolic acid into the cell wall
One of the most successful groups of antibiotics targets the synthesis of bacterial cell walls; why does the antibiotic not affect the mammalian cell?
No cell walls in mammals
What phenomenon prompted the development of the first semisynthetic antibiotics, such as methicillin?
Staphylococcus became resistant to penicillin so methicillin was discovered
What genus of bacteria has mycolic acids in the cell wall?
Microbacteria
Nitrofurantoin
- Converted to intermediates that attack bacterial ribosomal proteins
- Synthesized chemically
- Treatment for urinary bladder infections